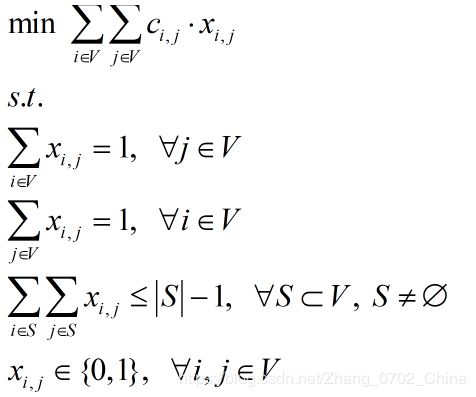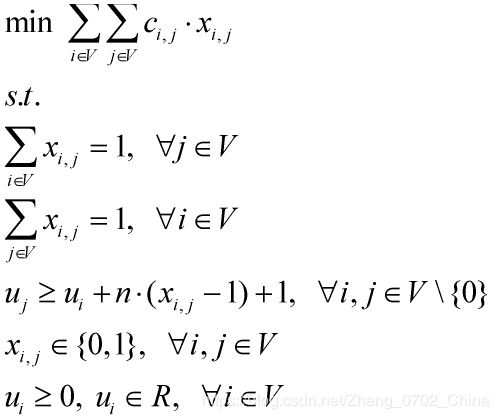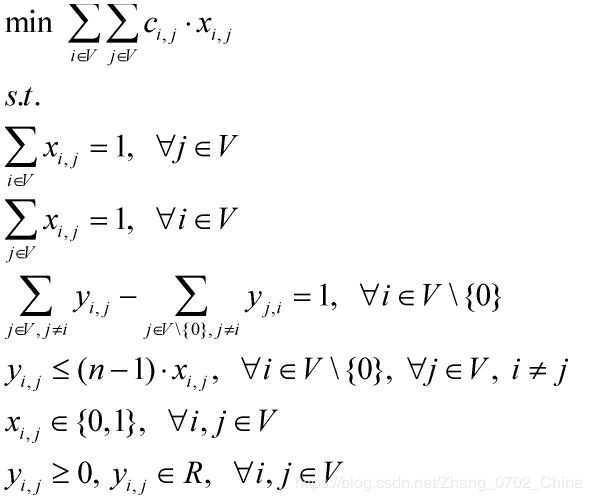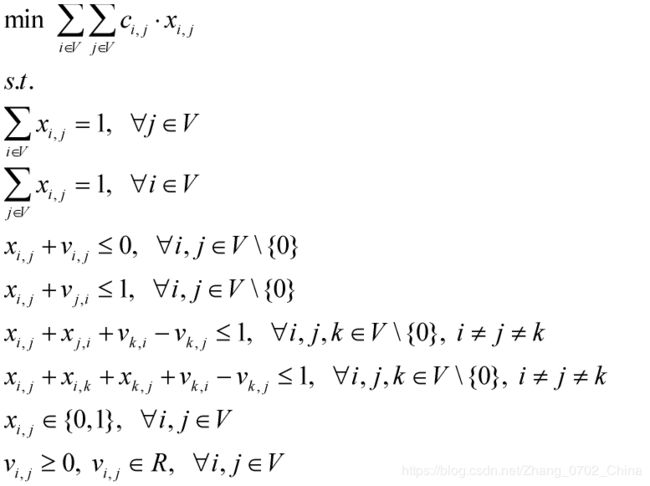【整数规划】TSP问题的几种经典建模方式
关于TSP问题的建模,关键在于子回路的消除,以及模型规模对求解效率的影响。
本文简要介绍几种经典的建模方式。
【1】Dantzig-Fulkerson-Johnson formulation(DFJ)
模型结构:
分析:约束规模过大,无法求解大规模算例
【2】Miller-Tucker-Zemlin formulation(MTZ)
模型结构:
分析:通过增加一组变量,确定点的次序,来消除子回路
【3】Gavish-Graves formulation(GG)
模型结构:
分析:通过增加一组变量,确定每两点间的弧的前序弧数,来消除子回路
【4】Gouveia-Pires L3RMTZ formulation(GP)
模型结构:
分析:
1. L3RMTZ 模型要强于 Gouveia 和 Pires 提出的另外几种模型,但该模型推导的原理较为复杂,本文不予介绍;
2. 该模型理论上更好,但实际求解时间更长。
【算例对比】
Gurobi 服务器上进行算例求解的结果:
| 建模方式 | 点的数量 | 求解总时间 / s | 得到可行解的时间 / s | gap / % |
| MTZ | 30 | 1.331 | 0 | 0 |
| GG | 1.358 | 0 | 0 | |
| GP | 14.572 | 1 | 0 | |
| MTZ | 50 | 82.641 | 2 | 0 |
| GG | 3.515 | 0 | 0 | |
| GP | 472.405 | 7 | 0 | |
| MTZ | 100 | 601.239 | 24 | 4.3572 |
| GG | 101.054 | 12 | 0 | |
| GP | 607.384 | 174 | 33.1285 |
【参考文献】
Dantzig, G., Fulkerson, R., & Johnson, S. (1954). Solution of a large-scale traveling-salesman problem. Journal of the operations research society of America, 2(4), 393-410.
Miller, C. E., Tucker, A. W., & Zemlin, R. A. (1960). Integer programming formulation of traveling salesman problems. Journal of the ACM (JACM), 7(4), 326-329.
Gavish, B., & Graves, S. C. (1978). The travelling salesman problem and related problems.
Gouveia L, Pires J (1999) The asymmetric travelling salesman problem and a reformulation of the Miller–Tucker–Zemlin constraints. Eur J Oper Res 112:134–146.
Roberti, R., & Toth, P. (2012). Models and algorithms for the asymmetric traveling salesman problem: An experimental comparison. EURO Journal on Transportation and Logistics, 1(1-2), 113-133.