Linux下用文件IO的方式操作GPIO(/sys/class/gpio)
英文不错的,可以看看:https://blog.csdn.net/ruanjianruanjianruan/article/details/47734397
先看:
嵌入式linux下操作GPIO
在嵌入式设备中对GPIO的操作是最基本的操作。一般的做法是写一个单独驱动程序,网上大多数的例子都是这样的。其实Linux下面有一个通用的GPIO操作接口,那就是我要介绍的 “/sys/class/gpio” 方式。首先,看看系统中有没有“/sys/class/gpio”这个文件夹。如果没有请在编译内核的时候加入 Device Drivers-> GPIO Support-> /sys/class/gpio/… (sysfs interface)。/sys/class/gpio 的使用说明:
1、gpio_operation 通过/sys/文件接口操作IO端口 GPIO到文件系统的映射,
2、控制GPIO的目录位于/sys/class/gpio
3、/sys/class/gpio/export文件用于通知系统需要导出控制的GPIO引脚编号
4、/sys/class/gpio/unexport 用于通知系统取消导出
5、/sys/class/gpio/gpiochipX目录保存系统中GPIO寄存器的信息,包括每个寄存器控制引脚的起始编号base,寄存器名称,引脚总数 导出一个引脚的操作步骤
6、首先计算此引脚编号,引脚编号 = 控制引脚的寄存器基数 + 控制引脚寄存器位数
7、向/sys/class/gpio/export写入此编号,比如12号引脚,echo 12 > /sys/class/gpio/export,命令成功后生成/sys/class/gpio/gpio12目录,如果没有出现相应的目录,说明此引脚不可导出:
8、direction文件,定义输入输入方向,可以通过下面命令定义为输出,direction接受的参数:in, out, high, low。high/low同时设置方向为输出
9、value文件是端口的数值,为1或0.
下面在2440下进行一下测试:
1.取得GPIO信息,在终端中敲入以下命令:
- $ cd /sys/class/gpio
- $ for i in gpiochip* ; do echo `cat $i/label`: `cat $i/base` ; done
终端中显示如下:
- GPIOA: 0
- GPIOE: 128
- GPIOF: 160
- GPIOG: 192
- GPIOH: 224
- GPIOB: 32
- GPIOC: 64
- GPIOD: 96
这里有可能不同
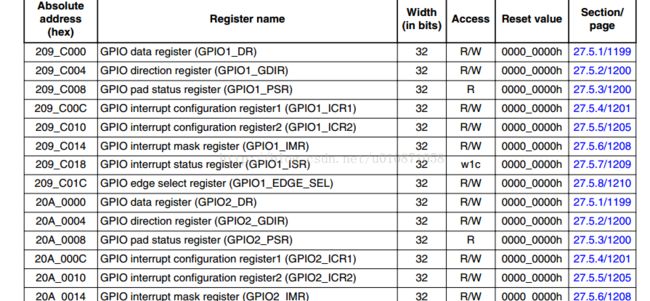
查找数据手册:得到的是地址对应的GPIO号,例如这里的209c000就是对应gpio1
2.计算GPIO号码
例如我们把GPE11用来控制LED。GPE0的头是128,GPE11 就是128+11 = 139.于是我们将139写入export中:
$ echo 139 > /sys/class/gpio/export
ls 一下看看有没有 gpio139这个目录,
3.GPIO控制测试:
- $ echo out > /sys/class/gpio/gpio139/direction
- $ echo 1 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio139/value
- $ echo 0 > /sys/class/gpio/gpio139/value
这时LED灯就会灭或亮
再看:
转自:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_7880d3350102w2um.html
通过sysfs方式控制GPIO,先访问/sys/class/gpio目录,向export文件写入GPIO编号,使得该GPIO的操作接口从内核空间暴露到用户空间,GPIO的操作接口包括direction和value等,direction控制GPIO方向,而value可控制GPIO输出或获得GPIO输入。文件IO方式操作GPIO,使用到了4个函数open、close、read、write。
首先,看看系统中有没有“/sys/class/gpio”这个文件夹。如果没有请在编译内核的时候加入 Device Drivers-> GPIO Support ->/sys/class/gpio/… (sysfs interface)。
/sys/class/gpio 的使用说明:
gpio_operation 通过/sys/文件接口操作IO端口 GPIO到文件系统的映射
◇ 控制GPIO的目录位于/sys/class/gpio
◇ /sys/class/gpio/export文件用于通知系统需要导出控制的GPIO引脚编号
◇ /sys/class/gpio/unexport 用于通知系统取消导出
◇ /sys/class/gpio/gpiochipX目录保存系统中GPIO寄存器的信息,包括每个寄存器控制引脚的起始编号base,寄存器名称,引脚总数 导出一个引脚的操作步骤
◇ 首先计算此引脚编号,引脚编号 = 控制引脚的寄存器基数 + 控制引脚寄存器位数
◇ 向/sys/class/gpio/export写入此编号,比如12号引脚,在shell中可以通过以下命令实现,命令成功后生成/sys/class/gpio/gpio12目录,如果没有出现相应的目录,说明此引脚不可导出
◇ direction文件,定义输入输入方向,可以通过下面命令定义为输出。direction接受的参数:in, out, high, low。high/low同时设置方向为输出,并将value设置为相应的1/0
◇ value文件是端口的数值,为1或0
几个例子:
1. 导出
/sys/class/gpio# echo 44 > export
2. 设置方向
/sys/class/gpio/gpio44# echo out > direction
3. 查看方向
/sys/class/gpio/gpio44# cat direction
4. 设置输出
/sys/class/gpio/gpio44# echo 1 > value
5. 查看输出值
/sys/class/gpio/gpio44# cat value
6. 取消导出
/sys/class/gpio# echo 44 > unexport
文件读写例程:
#include stdlib.h
#include stdio.h
#include string.h
#include unistd.h
#include fcntl.h //define O_WRONLY and O_RDONLY
//芯片复位引脚: P1_16
#define SYSFS_GPIO_EXPORT "/sys/class/gpio/export"
#define SYSFS_GPIO_RST_PIN_VAL "48"
#define SYSFS_GPIO_RST_DIR "/sys/class/gpio/gpio48/direction"
#define SYSFS_GPIO_RST_DIR_VAL "OUT"
#define SYSFS_GPIO_RST_VAL "/sys/class/gpio/gpio48/value"
#define SYSFS_GPIO_RST_VAL_H "1"
#define SYSFS_GPIO_RST_VAL_L "0"
int main()
{
int fd;
//打开端口/sys/class/gpio# echo 48 > export
fd = open(SYSFS_GPIO_EXPORT, O_WRONLY);
if(fd == -1)
{
printf("ERR: Radio hard reset pin open error.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
write(fd, SYSFS_GPIO_RST_PIN_VAL ,sizeof(SYSFS_GPIO_RST_PIN_VAL));
close(fd);
//设置端口方向/sys/class/gpio/gpio48# echo out > direction
fd = open(SYSFS_GPIO_RST_DIR, O_WRONLY);
if(fd == -1)
{
printf("ERR: Radio hard reset pin direction open error.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
write(fd, SYSFS_GPIO_RST_DIR_VAL, sizeof(SYSFS_GPIO_RST_DIR_VAL));
close(fd);
//输出复位信号: 拉高>100ns
fd = open(SYSFS_GPIO_RST_VAL, O_RDWR);
if(fd == -1)
{
printf("ERR: Radio hard reset pin value open error.\n");
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
while(1)
{
write(fd, SYSFS_GPIO_RST_VAL_H, sizeof(SYSFS_GPIO_RST_VAL_H));
usleep(1000000);
write(fd, SYSFS_GPIO_RST_VAL_L, sizeof(SYSFS_GPIO_RST_VAL_L));
usleep(1000000);
}
close(fd);
printf("INFO: Radio hard reset pin value open error.\n");
return 0;
}
另外参考网上一个网友的程序,这里做了验证,并实现中断检测函数。如下:
#include stdlib.h
#include stdio.h
#include string.h
#include unistd.h
#include fcntl.h
#include poll.h
#define MSG(args...) printf(args)
//函数声明
static int gpio_export(int pin);
static int gpio_unexport(int pin);
static int gpio_direction(int pin, int dir);
static int gpio_write(int pin, int value);
static int gpio_read(int pin);
static int gpio_export(int pin)
{
char buffer[64];
int len;
int fd;
fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/export", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
MSG("Failed to open export for writing!\n");
return(-1);
}
len = snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d", pin);
if (write(fd, buffer, len) < 0) {
MSG("Failed to export gpio!");
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
static int gpio_unexport(int pin)
{
char buffer[64];
int len;
int fd;
fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/unexport", O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
MSG("Failed to open unexport for writing!\n");
return -1;
}
len = snprintf(buffer, sizeof(buffer), "%d", pin);
if (write(fd, buffer, len) < 0) {
MSG("Failed to unexport gpio!");
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
//dir: 0-->IN, 1-->OUT
static int gpio_direction(int pin, int dir)
{
static const char dir_str[] = "in\0out";
char path[64];
int fd;
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%d/direction", pin);
fd = open(path, O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
MSG("Failed to open gpio direction for writing!\n");
return -1;
}
if (write(fd, &dir_str[dir == 0 ? 0 : 3], dir == 0 ? 2 : 3) < 0) {
MSG("Failed to set direction!\n");
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
//value: 0-->LOW, 1-->HIGH
static int gpio_write(int pin, int value)
{
static const char values_str[] = "01";
char path[64];
int fd;
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%d/value", pin);
fd = open(path, O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
MSG("Failed to open gpio value for writing!\n");
return -1;
}
if (write(fd, &values_str[value == 0 ? 0 : 1], 1) < 0) {
MSG("Failed to write value!\n");
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
static int gpio_read(int pin)
{
char path[64];
char value_str[3];
int fd;
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%d/value", pin);
fd = open(path, O_RDONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
MSG("Failed to open gpio value for reading!\n");
return -1;
}
if (read(fd, value_str, 3) < 0) {
MSG("Failed to read value!\n");
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return (atoi(value_str));
}
// none表示引脚为输入,不是中断引脚
// rising表示引脚为中断输入,上升沿触发
// falling表示引脚为中断输入,下降沿触发
// both表示引脚为中断输入,边沿触发
// 0-->none, 1-->rising, 2-->falling, 3-->both
static int gpio_edge(int pin, int edge)
{
const char dir_str[] = "none\0rising\0falling\0both";
char ptr;
char path[64];
int fd;
switch(edge){
case 0:
ptr = 0;
break;
case 1:
ptr = 5;
break;
case 2:
ptr = 12;
break;
case 3:
ptr = 20;
break;
default:
ptr = 0;
}
snprintf(path, sizeof(path), "/sys/class/gpio/gpio%d/edge", pin);
fd = open(path, O_WRONLY);
if (fd < 0) {
MSG("Failed to open gpio edge for writing!\n");
return -1;
}
if (write(fd, &dir_str[ptr], strlen(&dir_str[ptr])) < 0) {
MSG("Failed to set edge!\n");
return -1;
}
close(fd);
return 0;
}
//GPIO1_17
int main()
{
int gpio_fd, ret;
struct pollfd fds[1];
char buff[10];
unsigned char cnt = 0;
//LED引脚初始化
gpio_export(115);
gpio_direction(115, 1);
gpio_write(115, 0);
//按键引脚初始化
gpio_export(49);
gpio_direction(49, 0);
gpio_edge(49,1);
gpio_fd = open("/sys/class/gpio/gpio49/value",O_RDONLY);
if(gpio_fd < 0){
MSG("Failed to open value!\n");
return -1;
}
fds[0].fd = gpio_fd;
fds[0].events = POLLPRI;
ret = read(gpio_fd,buff,10);
if( ret == -1 )
MSG("read\n");
while(1){
ret = poll(fds,1,0);
if( ret == -1 )
MSG("poll\n");
if( fds[0].revents & POLLPRI){
ret = lseek(gpio_fd,0,SEEK_SET);
if( ret == -1 )
MSG("lseek\n");
ret = read(gpio_fd,buff,10);
if( ret == -1 )
MSG("read\n");
gpio_write(115, cnt++%2);
}
usleep(100000);
}
return 0;
}
参考文档:
http://blog.csdn.net/xukai871105/article/details/38456079
http://blog.csdn.net/sukhoi27smk/article/details/26447765