Flume使用和特点
Flume使用和特点
1)分布式:可以在多台机器上运行多个flume,日志文件往往分布在不同的机器里面
(2) collecting, aggregating, and moving
收集 聚集 移动
(3)组件agent
source:从数据源读取数据的,将数据转换为数据流,将数据丢给channel
channel:类似于一个队列,临时存储source发送过来的数据
sink:负责从channel中读取数据, 然后发送给目的地
(4)flume的使用很简单,就是一个配置文件,
版本:
flume-ng:(next generation): 目前使用该版本
1.5~1.7
flume-og:(Original generation):以前的版本,淘汰
修改配置
(1)mv flume-env.sh.template flume-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/opt/modules/jdk1.8.0_91
(2)找到HDFS的地址:
(1)声明Hadoop_home为全局环境变量
全局配置
(2)将core-site.xml和hdfs-site.xml放到flume配置文件下(推荐)
cp /opt/cdh5.7.6/hadoop-2.6.0-cdh5.7.6/etc/hadoop/core-site.xml /opt/cdh5.7.6/hadoop-2.6.0-cdh5.7.6/etc/hadoop/hdfs-site.xml ./
(3)直接在使用的时候给HDFS绝对路径
hdfs://hostname:8020/aa/bb
(3)添加HDFS的Jar包lib目录下:在执行的过程中需要使用HDFS api
运行测试
bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f case/1-flume-conf.properties -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
-f 动态查看日志,进行操作时在输出台上可以看到变化。
常用source、channel、sink
案例:读取Hive日志信息到HDFS上
2-file-file-hdfs.properties
a1.sources = s1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
# defined sources
a1.sources.s1.type = exec
a1.sources.s1.command = tail -F /opt/cdh5.7.6/hive-1.1.0-cdh5.7.6/logs/hive.log
a1.sources.s1.shell=/bin/sh -c
# defined channel
a1.channels.c1.type = file
#设置检查点,记录相关传输的信息,比如取了多少event
a1.channels.c1.checkpointDir=/opt/datas/flume/channel/checkpoint
a1.channels.c1.dataDirs=/opt/datas/flume/channel/data
# defined sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
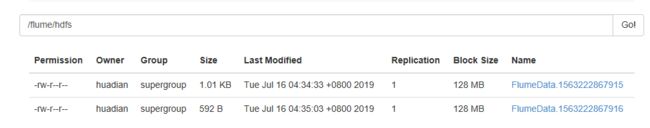
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=/flume/hdfs2/
#设置文件类型和写的格式
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
#bond
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1
案例:存储在HDFS文件大小的问题
fume存储到hdfs的文件默认的大小时1kb,可以根据需求修改大小。
3-file-file-size.properties
a1.sources = s1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
# defined sources
a1.sources.s1.type = exec
a1.sources.s1.command = tail -F /opt/cdh5.7.6/hive-1.1.0-cdh5.7.6/logs/hive.log
a1.sources.s1.shell=/bin/sh -c
# defined channel
a1.channels.c1.type = file
#设置检查点,记录相关传输的信息,比如取了多少event
a1.channels.c1.checkpointDir=/opt/datas/flume/channel/checkpoint
a1.channels.c1.dataDirs=/opt/datas/flume/channel/data
# defined sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
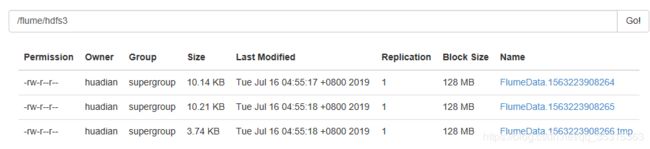
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=/flume/hdfs3/
#设置文件类型和写的格式
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
#设置HDFS文件大小
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize=10240
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount=0
#bond
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1案例:数据指定目录,hive分区
官方文档给的信息:
For all of the time related escape sequences, a header with the key “timestamp” must exist among the headers of the event (unlesshdfs.useLocalTimeStamp is set to true). One way to add this automatically is to use the TimestampInterceptor.
4-file-file-part.properties
a1.sources = s1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
# defined sources
a1.sources.s1.type = exec
a1.sources.s1.command = tail -F /opt/cdh5.7.6/hive-1.1.0-cdh5.7.6/logs/hive.log
a1.sources.s1.shell=/bin/sh -c
# defined channel
a1.channels.c1.type = file
#设置检查点,记录相关传输的信息,比如取了多少event
a1.channels.c1.checkpointDir=/opt/datas/flume/channel/checkpoint
a1.channels.c1.dataDirs=/opt/datas/flume/channel/data
# defined sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=/flume/part/yearst=%Y/monthstr=%m/daystr=%d/minutestr=%M
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
#设置文件类型和写的格式
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
#设置HDFS文件大小
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize=10240
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount=0
#bond
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1案例:hive的sink(企业中不用)
-》要求Hive表中的数据的存储格式必须为ORC
stored as textFile
orc、parquet
-》要求Hive表为桶表
按照每条数据进行分桶(2个表join的时候采用用)
A bulk01 bulk02
1 bulk01
2 bulk02
3 bulk01
4 bulk02
B bulk01 bulk02
2 bulk02
4 bulk02
6 bulk02
7 bulk01
案例:如何动态监听一个目录Spooling Directory Source
a1.sources = s1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
# defined sources
a1.sources.s1.type = spooldir
a1.sources.s1.spoolDir = /opt/datas/flume/spool
# defined channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
#容量
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
#瓶口大小
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
# defined sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=/flume/spooling
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
#设置文件类型和写的格式
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
#设置HDFS文件大小
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize=10240
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount=0
#bond
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1当运行
bin/flume-ng agent -n a1 -c conf -f case/5-spool-file-hdfs.properties -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console后,在flume/spool中放入文件,会被立刻重命名,之后再对文件bian
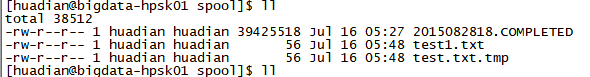
案例:过滤一些文件
6-spool-filter-hdfs.properties
a1.sources = s1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
# defined sources
a1.sources.s1.type = spooldir
a1.sources.s1.spoolDir = /opt/datas/flume/spool
a1.sources.s1.ignorePattern=([^ ]*\.tmp)
# defined channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
#容量
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
#瓶口大小
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
# defined sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=/flume/spooling
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
#设置文件类型和写的格式
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
#设置hdfs文件大小
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize=10240
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount=0
#bind
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
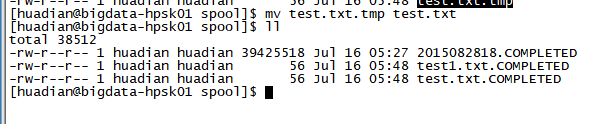
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1过滤.tmp结尾的文件,
运行flume前
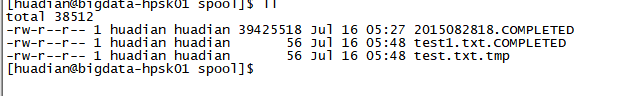
运行后
将test.txt.tmp去除后缀。
案例:动态监听多个文件
多个日志文件
实时采集
exec:动态监听单个文件
spool:动态监听单个文件目录
taildir:动态监听多个文件的动态变化(1.7)
apache 1.7版本之前:需要自己找到源码手动编译
a1.sources = s1
a1.channels = c1
a1.sinks = k1
# defined sources
#如果是自己编译的类,这里写类的全路径
a1.sources.s1.type = TAILDIR
a1.sources.s1.positionFile = /opt/cdh5.7.6/flume-1.6.0-cdh5.7.6-bin/position/taildir_position.json
a1.sources.s1.filegroups=f1 f2
a1.sources.s1.filegroups.f1 = /opt/datas/flume/taildir/hd.txt
a1.sources.s1.headers.f1.age = 17
a1.sources.s1.filegroups.f2 = /opt/datas/flume/taildir/huadian/.*
a1.sources.s1.headers.f2.age = 18
a1.sources.s1.headers.f2.type = aa
# defined channel
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
#容量
a1.channels.c1.capacity=1000
#瓶口大小
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity=100
# defined sink
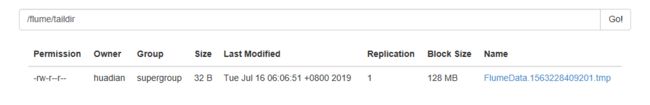
a1.sinks.k1.type = hdfs
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.path=/flume/taildir
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.useLocalTimeStamp=true
#设置文件类型和写的格式
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.fileType=DataStream
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.writeFormat=Text
#设置hdfs文件大小
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollInterval=0
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollSize=10240
a1.sinks.k1.hdfs.rollCount=0
#bind
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sources.s1.channels = c1