Simple Problem with Integers POJ - 3468
Simple Problem with Integers
You have N integers, A1, A2, … , AN. You need to deal with two kinds of operations. One type of operation is to add some given number to each number in a given interval. The other is to ask for the sum of numbers in a given interval.
Input
The first line contains two numbers N and Q. 1 ≤ N,Q ≤ 100000.
The second line contains N numbers, the initial values of A1, A2, … , AN. -1000000000 ≤ Ai ≤ 1000000000.
Each of the next Q lines represents an operation.
“C a b c” means adding c to each of Aa, Aa+1, … , Ab. -10000 ≤ c ≤ 10000.
“Q a b” means querying the sum of Aa, Aa+1, … , Ab.
Output
You need to answer all Q commands in order. One answer in a line.
Sample Input
10 5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Q 4 4
Q 1 10
Q 2 4
C 3 6 3
Q 2 4
Sample Output
4
55
9
15
题目大意就是有n个整数,如果输入 CLR X,就在L-R区间所有元素均加上一个值x,
输入QLR,就是输出L-R区间内的所有元素之和
因为数据范围很大,如果用for循环的话肯定超时,那我们可以用线段树,来维护区间和,和更改区间值,首先看这个图(网上搜的)
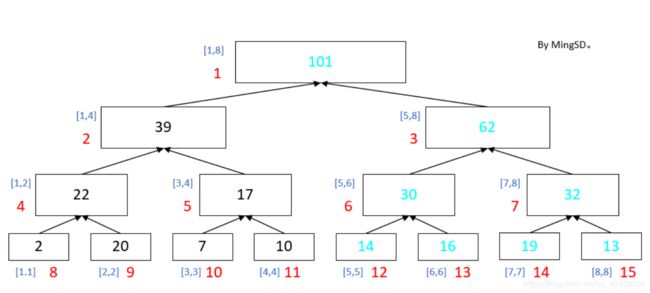
类似一个二叉树,不同的是,每个点都变成了一段区间,最上面的就是一开始的根区间,每次分为下面两个区间左儿子区间和右儿子区间,我们用一个sum数组,记录区间和,那么每个点的值就是最下面的叶区间(L等于R),这就是一个点,我们每次需要做的就是,用给出的范围x和y,在已有范围LR内进行查询,首先你的L-R与X-Y区间有交合,我们才能执行操作,但有可能未必全部包含,所以我们需要递归查询,然后线段树有个神奇的东西就是lazy标记,就是什么呢,每次更新,我们未必在每个元素上都加了X,可能只是在这段区间上加了x*(
R-L+),我们可以用一个lazy记录下,未下传的值,因为我们已经知道了这段区间和,所以不用再继续下传,节省时间,而对于下次查询,当我们要用一个区间时,首先判断一下,这个位置的lazy标记里面是否有值,如果有就下传,这就是pushdown函数,
void pushdown(int o,int l)
{
if(add[o])
{
add[o*2]+=add[o];
add[o*2+1]+=add[o];
sum[o*2]+=add[o]*(l-l/2);
sum[o*2+1]+=add[o]*(l/2);
add[o]=0;
}
}
对于每个区间呢有sum[o]=sum[o2]+sum[o2+1];每个父亲区间等于两个儿子区间和,
递归建树.
void build(int l,int r,int o)
{
if(l==r){scanf("%lld",&sum[o]);return;}
int mid=(l+r)/2;
build(l,mid,o*2);
build(mid+1,r,o*2+1);
sum[o]=sum[o*2]+sum[o*2+1];
}
每次对于区间的维护更新
void update(int l,int r,int x,int y,int c,int o)
{
if(l>=x&&r<=y)
{
sum[o]+=(ll)c*(r-l+1);
add[o]+=c;
return ;
}
int mid=(l+r)/2;
pushdown(o,r-l+1);
if(mid>=x) update(l,mid,x,y,c,o*2);
if(mid当mid>=x说明,该区间左儿子区间有需要更新的元素,当mid
ll query(int l,int r,int x,int y,int o)
{
if(l>=x&&r<=y) return sum[o];
pushdown(o,r-l+1);
int mid=(l+r)/2;
ll sum=0;
if(mid>=x)sum=query(l,mid,x,y,o*2);
if(y>mid) sum+=query(mid+1,r,x,y,o*2+1);
return sum;
}
这只是简单的维护区间和的模板(您可以试着更改sum[o]=sum[o2]+sum[o2+1]变成sum[o]=sum[o*2]sum[o2+1]的公式尝试敲出维护区间乘的代码),还有各种各样的模板,但也仅仅只是模板,把这些理解后,才能真正的开始学线段树(因为再遇见的题,不太可能仅仅只用模板就可以解决,你说对吧,所以路还很长很长,继续加油吧,多说无益,抱歉忍不住废话一波,)
完整代码:
#include
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn=400010;
ll add[maxn],sum[maxn];
void build(int l,int r,int o)
{
if(l==r){scanf("%lld",&sum[o]);return;}
int mid=(l+r)/2;
build(l,mid,o*2);
build(mid+1,r,o*2+1);
sum[o]=sum[o*2]+sum[o*2+1];
}
void pushdown(int o,int l)
{
if(add[o])
{
add[o*2]+=add[o];
add[o*2+1]+=add[o];
sum[o*2]+=add[o]*(l-l/2);
sum[o*2+1]+=add[o]*(l/2);
add[o]=0;
}
}
void update(int l,int r,int x,int y,int c,int o)
{
if(l>=x&&r<=y)
{
sum[o]+=(ll)c*(r-l+1);
add[o]+=c;
return ;
}
int mid=(l+r)/2;
pushdown(o,r-l+1);
if(mid>=x) update(l,mid,x,y,c,o*2);
if(mid=x&&r<=y) return sum[o];
pushdown(o,r-l+1);
int mid=(l+r)/2;
ll sum=0;
if(mid>=x)sum=query(l,mid,x,y,o*2);
if(y>mid) sum+=query(mid+1,r,x,y,o*2+1);
return sum;
}
int main()
{
int q,n,l,r,c;
char x;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
build(1,n,1);
while(q--)
{
scanf(" %c",&x);
if(x=='Q')
{
scanf("%d%d",&l,&r);
printf("%lld\n",query(1,n,l,r,1));
}
else
{
scanf("%d%d%d",&l,&r,&c);
update(1,n,l,r,c,1);
}
}
}