SystemUI 7.0学习总结一-SystemUI的启动
最近在学习并接触SystemUI模块的工作,Keyguard做为引入库也纳入了SystemUI的大家庭,所以整体感觉SystemUI模块还是挺大的,为了日后的查阅还是要写一下笔记。笔记记录过程中参考了许多网友的文章,在本文最后的文章参考会一一罗列,在此非常感谢他们的分享。
SystemUI概览
SystemUI属于系统级的apk,位置在frameworks\base\packages\SystemUI,主要功能有:
- 状态栏信息显示,比如电池,wifi信号,3G/4G等icon显示
- 通知面板,比如系统消息,第三方应用消息
- 近期任务栏显示面板,比如长按近期任务快捷键,显示近期使用的应用
- 截图服务
- 壁纸服务
- ……
SystemUI的启动流程
SystemServer启动后,会在Main Thread启动ActivityManagerService,当ActivityManagerService systemReady后,会去启动SystemUIService。
SystemServer路径:/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
......
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER, "StartSystemUI");
try {
startSystemUi(context);
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("starting System UI", e);
}
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
......
}
});在这个方法里启动一个SystemUIService服务,
static final void startSystemUi(Context context) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName("com.android.systemui",
"com.android.systemui.SystemUIService"));
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING);
//Slog.d(TAG, "Starting service: " + intent);
context.startServiceAsUser(intent, UserHandle.SYSTEM);
}通过startServiceAsUser,SystemUIService就启动了,即SystemUI进程开机启动。
public class SystemUIService extends Service {
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
((SystemUIApplication) getApplication()).startServicesIfNeeded();
}
......在SystemUIService的onCreate方法中会调用SystemUIApplication的startServicesIfNeeded方法,这个方法会调用 startServicesIfNeeded(SERVICES)方法启动一系列服务(并不是真正的service,都继承自SystemUI)。
public class SystemUIApplication extends Application {
......
/**
* The classes of the stuff to start.
*/
private final Class[] SERVICES = new Class[] {
com.android.systemui.tuner.TunerService.class,
com.android.systemui.keyguard.KeyguardViewMediator.class,
com.android.systemui.recents.Recents.class,
com.android.systemui.volume.VolumeUI.class,
Divider.class,
com.android.systemui.statusbar.SystemBars.class,
com.android.systemui.usb.StorageNotification.class,
com.android.systemui.power.PowerUI.class,
com.android.systemui.media.RingtonePlayer.class,
com.android.systemui.keyboard.KeyboardUI.class,
com.android.systemui.tv.pip.PipUI.class,
com.android.systemui.shortcut.ShortcutKeyDispatcher.class,
com.android.systemui.VendorServices.class
};
......
public void startServicesIfNeeded() {
startServicesIfNeeded(SERVICES);
}
}startServicesIfNeeded方法会遍历SERVICES 这个数组,依次调用service的start方法启动服务。
private void startServicesIfNeeded(Class[] services) {
if (mServicesStarted) {
return;
}
if (!mBootCompleted) {
// check to see if maybe it was already completed long before we began
// see ActivityManagerService.finishBooting()
if ("1".equals(SystemProperties.get("sys.boot_completed"))) {
mBootCompleted = true;
if (DEBUG) Log.v(TAG, "BOOT_COMPLETED was already sent");
}
}
Log.v(TAG, "Starting SystemUI services for user " +
Process.myUserHandle().getIdentifier() + ".");
final int N = services.length;
for (int i=0; i cl = services[i];
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "loading: " + cl);
try {
Object newService = SystemUIFactory.getInstance().createInstance(cl);
mServices[i] = (SystemUI) ((newService == null) ? cl.newInstance() : newService);
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InstantiationException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
mServices[i].mContext = this;
mServices[i].mComponents = mComponents;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "running: " + mServices[i]);
mServices[i].start();
if (mBootCompleted) {
mServices[i].onBootCompleted();
}
}
mServicesStarted = true;
} 看到这里,这么多文字可能不够直观,那就看看图吧,非常感谢参考文章中的分享。
这里以SERVICES 中com.android.systemui.keyguard.KeyguardViewMediator.class为例,
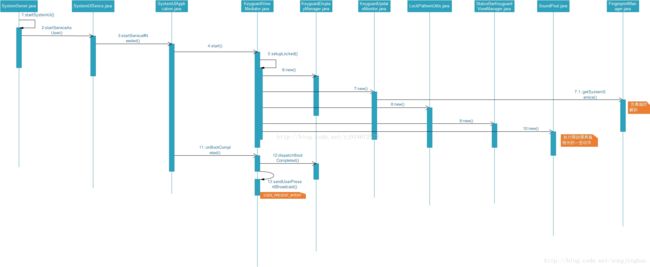
SystemUI Services启动后,根据各Services的功能,SystemUI的各个模块就开始正常工作起来了。
参考文章
- http://blog.csdn.net/qq_31530015/article/details/53507968
- http://blog.csdn.net/zhudaozhuan/article/details/50817180
- http://blog.csdn.net/yj934672573/article/details/54571704
- http://blog.csdn.net/Picasso_L/article/details/69388919
- … …