Android 9.0 A/B升级原理分析
概述:
A/B 系统更新,也称为无缝更新,用于确保可运行的启动系统在无线 (OTA) 更新期间能够保留在磁盘上。这样可以降低更新之后设备无法启动的可能性,也就是说,用户需要将设备送到维修/保修中心进行更换和刷机的情况将有所减少。
用户在 OTA 期间可以继续使用设备。在更新过程中,仅当设备重新启动到更新后的磁盘分区时,会发生一次宕机情况。即使 OTA 失败,设备也仍然可以使用,因为它会启动到 OTA 之前的磁盘分区。您可以再次尝试下载 OTA。建议仅针对新设备通过 OTA 实现 A/B 系统更新。
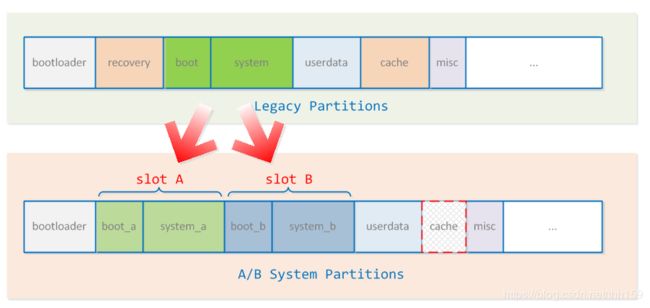
A/B 系统更新使用称为 update_engine 的后台守护进程以及两组分区。这两组分区称为插槽,通常为插槽 A 和插槽 B。系统从其中一个插槽(“当前插槽”)运行,但运行的系统不会访问“未使用的”插槽中的分区(用于正常操作)。
传统升级方式与ab升级方式采用的设备分区如下:
ab升级方式中boot和system均保留了两份,所以对设备的存储容量要求会比传统升级方式要大的多。
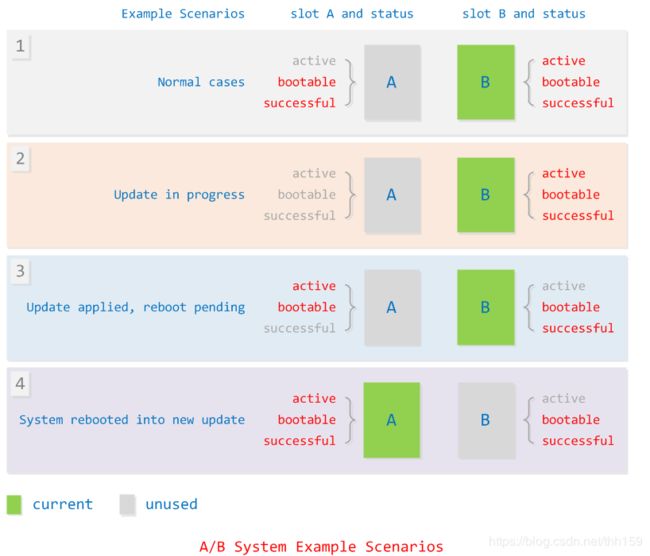
典型应用场景如下,假定当前从slot B中启动
- 正常情况:系统正在从其当前插槽(插槽 B)运行。目前为止尚未应用任何更新。系统的当前插槽是可启动、成功且活动的插槽。
- 正在更新:系统正在从插槽 B 运行,因此,插槽 B 是可启动、成功且活动的插槽。由于插槽 A 中的内容正在更新,但是尚未完成,因此插槽 A 标记为不可启动。在此状态下,应继续从插槽 B 重新启动。
- 已应用更新,正在等待重新启动:系统正在从插槽 B 运行,插槽 B 的状态为可启动且成功,但是插槽 A 过去标记为活动(因此现在标记为可启动)。插槽 A 尚未被标记为成功,引导加载程序应该尝试从插槽 A 启动几次。
- 系统重新启动到新的更新:系统首次从插槽 A 运行,插槽 B 的状态仍为可启动且成功,而插槽 A 仅可启动,且仍然处于活动但不成功的状态。在进行几次检查之后,用户空间守护进程应将插槽 A 标记为成功。
update升级包分析
一、目录结构
update.zip包的目录结构,如下图所示:
二、目录结构分析
下面分析以全量包升级为准。
1、META文件夹
bootargs.txt bootargs启动参数
filesystem_config.txt system目录文件权限
recovery.fstab 分区表
2、META-INF目录
目录结构如下:|---META-INF/
`|CERT.RSA
`|CERT.SF
`|MANIFEST.MF
`|----com/
`|----android/
`|----metadata
`|----google/
`|----android/
`|----update-binary
`|----updater-script
CERT.RSA:与签名文件相关联的签名程序块文件,它存储了用于签名JAR文件的公共签名。
CERT.SF:这是JAR文件的签名文件,其中前缀CERT代表签名者。
MANIFEST.MF:这个manifest文件定义了与包的组成结构相关的数据。类似Android应用的mainfest.xml文件。
metadata文件:是描述设备信息及环境变量的元数据。主要包括一些编译选项,签名公钥,时间戳以及设备型号等。
updater-script:此文件是一个脚本文件,具体描述了更新过程。我们可以根据具体情况编写该脚本来适应我们的具体需求。
update-binary:是一个二进制文件,相当于一个脚本解释器,能够识别updater-script中描述的操作。
文件怎么来的:
1、CERT.RSA、CERT.SF、MANIFEST.MF、metadata文件是自动生成的(怎么生成详见下文签名部分)
2、update-binary一般是系统编译过程中自动生成的升级脚本,但是这部分是可以通过手动编辑(详见后文update-binary脚本语言详解)
3、update-binary在sdk中哪个部分
./device/hisilicon/bigfish/build/emmc.mk
cp -a $(PRODUCT_OUT)/system/bin/updater $(EMMC_PRODUCT_OUT)/update/file/META-INF/com/google/android/update-binary
又上面脚本部分可知update-binary其实就是updater,updater部分是通过源码编译生成的,源码路径在:
bootable/recovery/updater/
3、system目录
system/目录的内容在升级后会放在系统的system分区。主要用来更新系统的一些应用或则应用会用到的一些库等等。
有的时候会以打包的形式(system.img)存在。
4、userdata目录
userdata目录,用来更新系统中的用户数据部分。这部分内容在更新后会存放在系统的/data目录下。
有的时候会以打包的形式(userdata.img)存在。
5、其他文件
*.img是更新各个分区分区所需要的文件。
三、如何制作一个update升级包
update升级包一般有两种方式得到:
一种是通过编译系统得到update.zip包(make ota-package)
另一种是通过自己手动创建的方式得到update升级包
updater-script语法详解
update升级包主要的启动入口为updater-script,因此先介绍一下updater-script的基础语法。
1、mount
语法:
mount(type, location, mount_point);
说明:
type="MTD" location="
type="vfat" location="/dev/block/
例如:
mount("MTD", "system", "/system");
挂载system分区,设置返回指针"/system”
mount("vfat", "/dev/block/mmcblk1p2", "/system");
挂载/dev/block/mmcblk1p2,返回指针"/system”
2、Unmount
语法:
unmount(mount_point);
说明:
mount_point是mount所设置产生的指针。其作用与挂载相对应,卸载分区或设备。此函数与mount配套使用。
例如:
unmount("/system");
卸载/system分区
3、Format
语法:
format(type, location);
说明:
type="MTD" location=partition(分区),格式化location参数所代表的分区。
例如:
format("MTD", "system");
格式化system分区
4、Delete
语法:
delete(
说明:
删除文件
例如:
delete("/data/zipalign.log");
删除文件/data/zipalign.log
5、delete_recursive
语法:
delete_recursive(
说明:
删除文件夹
例如:
delete_recursive("/data/dalvik-cache");
删除文件夹/data/dalvik-cache
6、show_progress
语法:
show_progress(
说明:
为下面进行的程序操作显示进度条,进度条会根据
例如:
show_progress(0.1, 10);
show_progress下面的操作可能进行10s,完成后进度条前进0.1(也就是10%)
7、package_extract_dir
语法:
package_extract_dir(package_path, destination_path);
说明:
释放文件夹package_path至destination_path
例如:
package_extract_dir("system", "/system");
释放ROM包里system文件夹下所有文件和子文件夹至/system
8、package_extract_file
语法:
package_extract_file(package_path, destination_path);
说明:
解压package_path文件至destination_path
例如:
package_extract_dir("my.zip", "/system");
解压ROM包里的my.zip文件至/system
9、Symlink
语法:
symlink(
说明:
建立指向target符号链接src1,src2,……
例如:
symlink("toolbox", "/system/bin/ps");
建立指向toolbox的符号链接/system/bin/ps
10、set_perm
语法:
set_perm(
说明:
设置
例如:
set_perm(1002, 1002, 0440, "/system/etc/dbus.conf");
设置文件/system/etc/dbus.conf的所有者为1002,所属用户组为1002,权限为:所有者有读权限,所属用户组有读权限,其他无任何权限。
11、set_perm_recursive
语法:
set_perm_recursive(
说明:
设置文件夹和文件夹内文件的权限
例如:
set_perm_recursive(1000, 1000, 0771, 0644, "/data/app");
设置/data/app的所有者和所属用户组为1000,app文件夹的权限是:所有者和所属组拥有全部权限,其他有执行权限;app文件夹下的文件权限是:所有者有读写权限,所属组有读权限,其他有读权限。
12、ui_print
语法:
ui_print("str");
说明:
屏幕打印输出"str"
例如:
ui_print("It's ready!");
屏幕打印It’s ready!
13、run_program
语法:
run_program(
说明:
运行
例如:
run_program("/system/xbin/installbusybox.sh");
运行installbusybox.sh脚本文件
14、write_raw_image
语法:
write_raw_image(
说明:
写入
例如:
write_raw_image("/tmp/boot.img", "boot")
将yaffs2格式的boot包直接写入boot分区
15、assert
语法:
assert(
说明:
如果执行sub1不返回错误则执行sub2,如果sub2不返回错误则执行sub3一次类推。
例如:
assert(package_extract_file("boot.img", "/tmp/boot.img"),
write_raw_image("/tmp/boot.img", "boot"),
delete("/tmp/boot.img"));
执行package_extract_file,如果不返回错误则执行write_raw_image,如果write_raw_image不出错则执行delete
16、getprop
语法:
getprop("key")
说明:
通过指定key的值来获取对应的属性信息。
例如:
getprop(“ro.product.device”)
获取ro.product.device的属性值。
17、ifelse
语法:
ifelse(condition, truecondition, falsecondition)
说明:
condition----------------要运算的表达式
Truecondition-----------当值为True时执行的 Edify脚本块
Falsecodnition-----------当值为False时执行的 Edify脚本块
列如:
ifelse(isuserversion(),
ui_print(" ----user version----- "),
ui_print(" --------- ");
set_perm(0, 2000, 04750, "/system/xbin/su");
);
根据isuserversion()返回值判断,如果true,打印" ----user version----- ";如果false,打印" --------- ",并获取su权限。
注意:值得注意的是false分支,执行了两个语句,只需通过‘;’来分割开就可以了。
18、其他
向上一个例子中isuserversion()不是常见的函数,这个是什么呢,怎么识别,这就需要特有的update-binary。
update-binary相当于一个脚本解释器,能够识别updater-script中描述的操作。
ota_from_target_files
OTA包的制作是通过执行ota_from_target_files来实现的。ota_from_target_files文件内容较多,下面分析一下几个主要的方法:
看下参数简介:
Given a target-files zipfile, produces an OTA package that installs that build. An incremental OTA is produced if -i is given, otherwise a full OTA is produced.
Usage: ota_from_target_files [flags] input_target_files output_ota_package
-k (--package_key):指定OTA包的签名
-i (--incremental_from)
--full_radio:包含全射频img的包,只对增量包使用,因为全包一定会包含。
--full_bootloader:和--full_radio功能类似
--verify:对system和vendor分区文件进行校验,只对非A/B升级的增量包使用
--wipe_user_data:对data分区数据进行擦除
--downgrade:指定降级增量包(如从P降级到O版本),该命令会强制执行data数据擦除的操作
--override_timestamp:比较时间戳的反向升级,不会擦除data的操作,该命令并不是真的后向升级,而是一般用于两个不同分支的升级或者是从A->C->B的升级方式。原文如下:
--override_timestamp
Intentionally generate an incremental OTA that updates from a newer build
to an older one (based on timestamp comparison), by setting the downgrade
flag in the package metadata. This differs from --downgrade flag, as we
don't enforce a data wipe with this flag. Because we know for sure this is
NOT an actual downgrade case, but two builds happen to be cut in a reverse
order (e.g. from two branches). A legit use case is that we cut a new
build C (after having A and B), but want to enfore an update path of A ->
C -> B. Specifying --downgrade may not help since that would enforce a
data wipe for C -> B update.
We used to set a fake timestamp in the package metadata for this flow. But
now we consolidate the two cases (i.e. an actual downgrade, or a downgrade
based on timestamp) with the same "ota-downgrade=yes" flag, with the
difference being whether "ota-wipe=yes" is set.该脚本文件的main方法如下:
if __name__ == '__main__':
try:
common.CloseInheritedPipes()
main(sys.argv[1:])
except common.ExternalError as e:
print("\n ERROR: %s\n" % (e,))
sys.exit(1)
finally:
common.Cleanup()
def main(argv):
def option_handler(o, a):
if o in ("-k", "--package_key"):
OPTIONS.package_key = a
elif o in ("-i", "--incremental_from"):
OPTIONS.incremental_source = a
elif o == "--full_radio":
OPTIONS.full_radio = True
elif o == "--full_bootloader":
OPTIONS.full_bootloader = True
elif o == "--wipe_user_data":
OPTIONS.wipe_user_data = True
elif o == "--downgrade":
OPTIONS.downgrade = True
OPTIONS.wipe_user_data = True
elif o == "--override_timestamp":
OPTIONS.downgrade = True
elif o in ("-o", "--oem_settings"):
OPTIONS.oem_source = a.split(',')
elif o == "--oem_no_mount":
OPTIONS.oem_no_mount = True
elif o in ("-e", "--extra_script"):
OPTIONS.extra_script = a
elif o in ("-t", "--worker_threads"):
if a.isdigit():
OPTIONS.worker_threads = int(a)
else:
raise ValueError("Cannot parse value %r for option %r - only "
"integers are allowed." % (a, o))
elif o in ("-2", "--two_step"):
OPTIONS.two_step = True
elif o == "--include_secondary":
OPTIONS.include_secondary = True
elif o == "--no_signing":
OPTIONS.no_signing = True
elif o == "--verify":
OPTIONS.verify = True
elif o == "--block":
OPTIONS.block_based = True
elif o in ("-b", "--binary"):
OPTIONS.updater_binary = a
elif o == "--stash_threshold":
try:
OPTIONS.stash_threshold = float(a)
except ValueError:
raise ValueError("Cannot parse value %r for option %r - expecting "
"a float" % (a, o))
elif o == "--log_diff":
OPTIONS.log_diff = a
elif o == "--payload_signer":
OPTIONS.payload_signer = a
elif o == "--payload_signer_args":
OPTIONS.payload_signer_args = shlex.split(a)
elif o == "--extracted_input_target_files":
OPTIONS.extracted_input = a
elif o == "--skip_postinstall":
OPTIONS.skip_postinstall = True
else:
return False
return True
args = common.ParseOptions(argv, __doc__,
extra_opts="b:k:i:d:e:t:2o:",
extra_long_opts=[
"package_key=",
"incremental_from=",
"full_radio",
"full_bootloader",
"wipe_user_data",
"downgrade",
"override_timestamp",
"extra_script=",
"worker_threads=",
"two_step",
"include_secondary",
"no_signing",
"block",
"binary=",
"oem_settings=",
"oem_no_mount",
"verify",
"stash_threshold=",
"log_diff=",
"payload_signer=",
"payload_signer_args=",
"extracted_input_target_files=",
"skip_postinstall",
], extra_option_handler=option_handler)
if len(args) != 2:
common.Usage(__doc__)
sys.exit(1)
if OPTIONS.downgrade:
# We should only allow downgrading incrementals (as opposed to full).
# Otherwise the device may go back from arbitrary build with this full
# OTA package.
if OPTIONS.incremental_source is None:
raise ValueError("Cannot generate downgradable full OTAs")
# Load the build info dicts from the zip directly or the extracted input
# directory. We don't need to unzip the entire target-files zips, because they
# won't be needed for A/B OTAs (brillo_update_payload does that on its own).
# When loading the info dicts, we don't need to provide the second parameter
# to common.LoadInfoDict(). Specifying the second parameter allows replacing
# some properties with their actual paths, such as 'selinux_fc',
# 'ramdisk_dir', which won't be used during OTA generation.
if OPTIONS.extracted_input is not None:
OPTIONS.info_dict = common.LoadInfoDict(OPTIONS.extracted_input)
else:
with zipfile.ZipFile(args[0], 'r') as input_zip:
OPTIONS.info_dict = common.LoadInfoDict(input_zip)
if OPTIONS.verbose:
print("--- target info ---")
common.DumpInfoDict(OPTIONS.info_dict)
# Load the source build dict if applicable.
if OPTIONS.incremental_source is not None:
OPTIONS.target_info_dict = OPTIONS.info_dict
with zipfile.ZipFile(OPTIONS.incremental_source, 'r') as source_zip:
OPTIONS.source_info_dict = common.LoadInfoDict(source_zip)
if OPTIONS.verbose:
print("--- source info ---")
common.DumpInfoDict(OPTIONS.source_info_dict)
# Load OEM dicts if provided.
OPTIONS.oem_dicts = _LoadOemDicts(OPTIONS.oem_source)
ab_update = OPTIONS.info_dict.get("ab_update") == "true"
# Use the default key to sign the package if not specified with package_key.
# package_keys are needed on ab_updates, so always define them if an
# ab_update is getting created.
if not OPTIONS.no_signing or ab_update:
if OPTIONS.package_key is None:
OPTIONS.package_key = OPTIONS.info_dict.get(
"default_system_dev_certificate",
"build/target/product/security/testkey")
# Get signing keys
OPTIONS.key_passwords = common.GetKeyPasswords([OPTIONS.package_key])
if ab_update:
WriteABOTAPackageWithBrilloScript(
target_file=args[0],
output_file=args[1],
source_file=OPTIONS.incremental_source)
print("done.")
return
# Sanity check the loaded info dicts first.
if OPTIONS.info_dict.get("no_recovery") == "true":
raise common.ExternalError(
"--- target build has specified no recovery ---")
# Non-A/B OTAs rely on /cache partition to store temporary files.
cache_size = OPTIONS.info_dict.get("cache_size")
if cache_size is None:
print("--- can't determine the cache partition size ---")
OPTIONS.cache_size = cache_size
if OPTIONS.extra_script is not None:
OPTIONS.extra_script = open(OPTIONS.extra_script).read()
if OPTIONS.extracted_input is not None:
OPTIONS.input_tmp = OPTIONS.extracted_input
else:
print("unzipping target target-files...")
OPTIONS.input_tmp = common.UnzipTemp(args[0], UNZIP_PATTERN)
OPTIONS.target_tmp = OPTIONS.input_tmp
# If the caller explicitly specified the device-specific extensions path via
# -s / --device_specific, use that. Otherwise, use META/releasetools.py if it
# is present in the target target_files. Otherwise, take the path of the file
# from 'tool_extensions' in the info dict and look for that in the local
# filesystem, relative to the current directory.
if OPTIONS.device_specific is None:
from_input = os.path.join(OPTIONS.input_tmp, "META", "releasetools.py")
if os.path.exists(from_input):
print("(using device-specific extensions from target_files)")
OPTIONS.device_specific = from_input
else:
OPTIONS.device_specific = OPTIONS.info_dict.get("tool_extensions")
if OPTIONS.device_specific is not None:
OPTIONS.device_specific = os.path.abspath(OPTIONS.device_specific)
# Generate a full OTA.
if OPTIONS.incremental_source is None:
with zipfile.ZipFile(args[0], 'r') as input_zip:
WriteFullOTAPackage(
input_zip,
output_file=args[1])
# Generate an incremental OTA.
else:
print("unzipping source target-files...")
OPTIONS.source_tmp = common.UnzipTemp(
OPTIONS.incremental_source, UNZIP_PATTERN)
with zipfile.ZipFile(args[0], 'r') as input_zip, \
zipfile.ZipFile(OPTIONS.incremental_source, 'r') as source_zip:
WriteBlockIncrementalOTAPackage(
input_zip,
source_zip,
output_file=args[1])
if OPTIONS.log_diff:
with open(OPTIONS.log_diff, 'w') as out_file:
import target_files_diff
target_files_diff.recursiveDiff(
'', OPTIONS.source_tmp, OPTIONS.input_tmp, out_file)
print("done.")主要功能函数生成全OTA包方法:def WriteFullOTAPackage(input_zip, output_file):
def WriteFullOTAPackage(input_zip, output_file):
target_info = BuildInfo(OPTIONS.info_dict, OPTIONS.oem_dicts)
# We don't know what version it will be installed on top of. We expect the API
# just won't change very often. Similarly for fstab, it might have changed in
# the target build.
target_api_version = target_info["recovery_api_version"]
script = edify_generator.EdifyGenerator(target_api_version, target_info)
if target_info.oem_props and not OPTIONS.oem_no_mount:
target_info.WriteMountOemScript(script)
metadata = GetPackageMetadata(target_info)
if not OPTIONS.no_signing:
staging_file = common.MakeTempFile(suffix='.zip')
else:
staging_file = output_file
output_zip = zipfile.ZipFile(
staging_file, "w", compression=zipfile.ZIP_DEFLATED)
device_specific = common.DeviceSpecificParams(
input_zip=input_zip,
input_version=target_api_version,
output_zip=output_zip,
script=script,
input_tmp=OPTIONS.input_tmp,
metadata=metadata,
info_dict=OPTIONS.info_dict)
assert HasRecoveryPatch(input_zip)
# Assertions (e.g. downgrade check, device properties check).
ts = target_info.GetBuildProp("ro.build.date.utc")
ts_text = target_info.GetBuildProp("ro.build.date")
script.AssertOlderBuild(ts, ts_text)
target_info.WriteDeviceAssertions(script, OPTIONS.oem_no_mount)
device_specific.FullOTA_Assertions()
# Two-step package strategy (in chronological order, which is *not*
# the order in which the generated script has things):
#
# if stage is not "2/3" or "3/3":
# write recovery image to boot partition
# set stage to "2/3"
# reboot to boot partition and restart recovery
# else if stage is "2/3":
# write recovery image to recovery partition
# set stage to "3/3"
# reboot to recovery partition and restart recovery
# else:
# (stage must be "3/3")
# set stage to ""
# do normal full package installation:
# wipe and install system, boot image, etc.
# set up system to update recovery partition on first boot
# complete script normally
# (allow recovery to mark itself finished and reboot)
recovery_img = common.GetBootableImage("recovery.img", "recovery.img",
OPTIONS.input_tmp, "RECOVERY")
if OPTIONS.two_step:
if not target_info.get("multistage_support"):
assert False, "two-step packages not supported by this build"
fs = target_info["fstab"]["/misc"]
assert fs.fs_type.upper() == "EMMC", \
"two-step packages only supported on devices with EMMC /misc partitions"
bcb_dev = {"bcb_dev": fs.device}
common.ZipWriteStr(output_zip, "recovery.img", recovery_img.data)
script.AppendExtra("""
if get_stage("%(bcb_dev)s") == "2/3" then
""" % bcb_dev)
# Stage 2/3: Write recovery image to /recovery (currently running /boot).
script.Comment("Stage 2/3")
script.WriteRawImage("/recovery", "recovery.img")
script.AppendExtra("""
set_stage("%(bcb_dev)s", "3/3");
reboot_now("%(bcb_dev)s", "recovery");
else if get_stage("%(bcb_dev)s") == "3/3" then
""" % bcb_dev)
# Stage 3/3: Make changes.
script.Comment("Stage 3/3")
# Dump fingerprints
script.Print("Target: {}".format(target_info.fingerprint))
device_specific.FullOTA_InstallBegin()
system_progress = 0.75
if OPTIONS.wipe_user_data:
system_progress -= 0.1
if HasVendorPartition(input_zip):
system_progress -= 0.1
script.ShowProgress(system_progress, 0)
# See the notes in WriteBlockIncrementalOTAPackage().
allow_shared_blocks = target_info.get('ext4_share_dup_blocks') == "true"
# Full OTA is done as an "incremental" against an empty source image. This
# has the effect of writing new data from the package to the entire
# partition, but lets us reuse the updater code that writes incrementals to
# do it.
system_tgt = common.GetSparseImage("system", OPTIONS.input_tmp, input_zip,
allow_shared_blocks)
system_tgt.ResetFileMap()
system_diff = common.BlockDifference("system", system_tgt, src=None)
system_diff.WriteScript(script, output_zip)
boot_img = common.GetBootableImage(
"boot.img", "boot.img", OPTIONS.input_tmp, "BOOT")
if HasVendorPartition(input_zip):
script.ShowProgress(0.1, 0)
vendor_tgt = common.GetSparseImage("vendor", OPTIONS.input_tmp, input_zip,
allow_shared_blocks)
vendor_tgt.ResetFileMap()
vendor_diff = common.BlockDifference("vendor", vendor_tgt)
vendor_diff.WriteScript(script, output_zip)
AddCompatibilityArchiveIfTrebleEnabled(input_zip, output_zip, target_info)
common.CheckSize(boot_img.data, "boot.img", target_info)
common.ZipWriteStr(output_zip, "boot.img", boot_img.data)
script.ShowProgress(0.05, 5)
script.WriteRawImage("/boot", "boot.img")
script.ShowProgress(0.2, 10)
device_specific.FullOTA_InstallEnd()
if OPTIONS.extra_script is not None:
script.AppendExtra(OPTIONS.extra_script)
script.UnmountAll()
if OPTIONS.wipe_user_data:
script.ShowProgress(0.1, 10)
script.FormatPartition("/data")
if OPTIONS.two_step:
script.AppendExtra("""
set_stage("%(bcb_dev)s", "");
""" % bcb_dev)
script.AppendExtra("else\n")
# Stage 1/3: Nothing to verify for full OTA. Write recovery image to /boot.
script.Comment("Stage 1/3")
_WriteRecoveryImageToBoot(script, output_zip)
script.AppendExtra("""
set_stage("%(bcb_dev)s", "2/3");
reboot_now("%(bcb_dev)s", "");
endif;
endif;
""" % bcb_dev)
script.SetProgress(1)
script.AddToZip(input_zip, output_zip, input_path=OPTIONS.updater_binary)
metadata["ota-required-cache"] = str(script.required_cache)
# We haven't written the metadata entry, which will be done in
# FinalizeMetadata.
common.ZipClose(output_zip)
needed_property_files = (
NonAbOtaPropertyFiles(),
)
FinalizeMetadata(metadata, staging_file, output_file, needed_property_files)
JAVA层调用相关:
涉及文件主要有:frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\UpdateEngine.java
frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\UpdateEngineCallback.java
frameworks\base\core\java\android\os\SystemUpdateManager.java
UpdateEngine是UpdateEngineService服务提供的jave层调用接口,包含了各个状态值,和错误码,错误码:
public static final class ErrorCodeConstants {
public static final int SUCCESS = 0;
public static final int ERROR = 1;
public static final int FILESYSTEM_COPIER_ERROR = 4;
public static final int POST_INSTALL_RUNNER_ERROR = 5;
public static final int PAYLOAD_MISMATCHED_TYPE_ERROR = 6;
public static final int INSTALL_DEVICE_OPEN_ERROR = 7;
public static final int KERNEL_DEVICE_OPEN_ERROR = 8;
public static final int DOWNLOAD_TRANSFER_ERROR = 9;
public static final int PAYLOAD_HASH_MISMATCH_ERROR = 10;
public static final int PAYLOAD_SIZE_MISMATCH_ERROR = 11;
public static final int DOWNLOAD_PAYLOAD_VERIFICATION_ERROR = 12;
public static final int UPDATED_BUT_NOT_ACTIVE = 52;
}
updateEngineService服务返回的状态值:
public static final class UpdateStatusConstants {
public static final int IDLE = 0;
public static final int CHECKING_FOR_UPDATE = 1;
public static final int UPDATE_AVAILABLE = 2;
public static final int DOWNLOADING = 3;
public static final int VERIFYING = 4;
public static final int FINALIZING = 5;
public static final int UPDATED_NEED_REBOOT = 6;
public static final int REPORTING_ERROR_EVENT = 7;
public static final int ATTEMPTING_ROLLBACK = 8;
public static final int DISABLED = 9;
}
主要方法如下:
接收服务返回的错误码已经当前运行的状态值给用户,方便客户端进程更新ui显示。
@SystemApi
public boolean bind(final UpdateEngineCallback callback, final Handler handler) {
synchronized (mUpdateEngineCallbackLock) {
mUpdateEngineCallback = new IUpdateEngineCallback.Stub() {
@Override
public void onStatusUpdate(final int status, final float percent) {
if (handler != null) {
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callback.onStatusUpdate(status, percent);
}
});
} else {
callback.onStatusUpdate(status, percent);
}
}
@Override
public void onPayloadApplicationComplete(final int errorCode) {
if (handler != null) {
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
callback.onPayloadApplicationComplete(errorCode);
}
});
} else {
callback.onPayloadApplicationComplete(errorCode);
}
}
};
try {
return mUpdateEngine.bind(mUpdateEngineCallback);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
开始升级:url可以试下载链接,或者本地文件,如果是本地文件,以file://格式表示
@SystemApi
public void applyPayload(String url, long offset, long size, String[] headerKeyValuePairs)
{
try {
mUpdateEngine.applyPayload(url, offset, size, headerKeyValuePairs);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
除此之外还有取消升级、暂停升级、恢复升级、重置状态、解除绑定,校验升级包。
NATIVE层相关:
来自谷歌官网有如下描述:
想要实现 A/B 系统更新的原始设备制造商 (OEM) 和 SoC 供应商必须确保其引导加载程序实现 boot_control HAL,并将正确的参数传递到内核。
支持 A/B 更新的引导加载程序必须在hardware/libhardware/include/hardware/boot_control.h 中实现 boot_control HAL。您可以使用 system/extras/bootctl 实用工具和 system/extras/tests/bootloader/ 来测试此类实现。
\hardware\libhardware\include\hardware\boot_control.h中定义了boot_control_module结构体:
typedef struct boot_control_module {
struct hw_module_t common;
/*
* (*init)() perform any initialization tasks needed for the HAL.
* This is called only once.
*/
void (*init)(struct boot_control_module *module);
/*
* (*getNumberSlots)() returns the number of available slots.
* For instance, a system with a single set of partitions would return
* 1, a system with A/B would return 2, A/B/C -> 3...
*/
unsigned (*getNumberSlots)(struct boot_control_module *module);
/*
* (*getCurrentSlot)() returns the value letting the system know
* whether the current slot is A or B. The meaning of A and B is
* left up to the implementer. It is assumed that if the current slot
* is A, then the block devices underlying B can be accessed directly
* without any risk of corruption.
* The returned value is always guaranteed to be strictly less than the
* value returned by getNumberSlots. Slots start at 0 and
* finish at getNumberSlots() - 1
*/
unsigned (*getCurrentSlot)(struct boot_control_module *module);
/*
* (*markBootSuccessful)() marks the current slot
* as having booted successfully
*
* Returns 0 on success, -errno on error.
*/
int (*markBootSuccessful)(struct boot_control_module *module);
/*
* (*setActiveBootSlot)() marks the slot passed in parameter as
* the active boot slot (see getCurrentSlot for an explanation
* of the "slot" parameter). This overrides any previous call to
* setSlotAsUnbootable.
* Returns 0 on success, -errno on error.
*/
int (*setActiveBootSlot)(struct boot_control_module *module, unsigned slot);
/*
* (*setSlotAsUnbootable)() marks the slot passed in parameter as
* an unbootable. This can be used while updating the contents of the slot's
* partitions, so that the system will not attempt to boot a known bad set up.
* Returns 0 on success, -errno on error.
*/
int (*setSlotAsUnbootable)(struct boot_control_module *module, unsigned slot);
/*
* (*isSlotBootable)() returns if the slot passed in parameter is
* bootable. Note that slots can be made unbootable by both the
* bootloader and by the OS using setSlotAsUnbootable.
* Returns 1 if the slot is bootable, 0 if it's not, and -errno on
* error.
*/
int (*isSlotBootable)(struct boot_control_module *module, unsigned slot);
/*
* (*getSuffix)() returns the string suffix used by partitions that
* correspond to the slot number passed in parameter. The returned string
* is expected to be statically allocated and not need to be freed.
* Returns NULL if slot does not match an existing slot.
*/
const char* (*getSuffix)(struct boot_control_module *module, unsigned slot);
/*
* (*isSlotMarkedSucessful)() returns if the slot passed in parameter has
* been marked as successful using markBootSuccessful.
* Returns 1 if the slot has been marked as successful, 0 if it's
* not the case, and -errno on error.
*/
int (*isSlotMarkedSuccessful)(struct boot_control_module *module, unsigned slot);
void* reserved[31];
} boot_control_module_t;
实现boot_control接口需要厂商自己实现用于读取和设置启动槽位信息,在system/updateEngine中有如下类:
\system\update_engine\boot_control_android.h
\system\update_engine\boot_control_recovery.h
#include
#include "update_engine/common/boot_control.h"
namespace chromeos_update_engine {
// The Android implementation of the BootControlInterface. This implementation
// uses the libhardware's boot_control HAL to access the bootloader.
class BootControlAndroid : public BootControlInterface {
public:
BootControlAndroid() = default;
~BootControlAndroid() = default;
// Load boot_control HAL implementation using libhardware and
// initializes it. Returns false if an error occurred.
bool Init();
// BootControlInterface overrides.
unsigned int GetNumSlots() const override;
BootControlInterface::Slot GetCurrentSlot() const override;
bool GetPartitionDevice(const std::string& partition_name,
BootControlInterface::Slot slot,
std::string* device) const override;
bool IsSlotBootable(BootControlInterface::Slot slot) const override;
bool MarkSlotUnbootable(BootControlInterface::Slot slot) override;
bool SetActiveBootSlot(BootControlInterface::Slot slot) override;
bool MarkBootSuccessfulAsync(base::Callback
private:
::android::sp<::android::hardware::boot::V1_0::IBootControl> module_;
DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(BootControlAndroid);
};
} // namespace chromeos_update_engine
#endif // UPDATE_ENGINE_BOOT_CONTROL_ANDROID_H_
#include
#include
#include
#include "update_engine/common/boot_control.h"
namespace chromeos_update_engine {
// The Android recovery implementation of the BootControlInterface. This
// implementation uses the legacy libhardware's boot_control HAL to access the
// bootloader by linking against it statically. This should only be used in
// recovery.
class BootControlRecovery : public BootControlInterface {
public:
BootControlRecovery() = default;
~BootControlRecovery() = default;
// Load boot_control HAL implementation using libhardware and
// initializes it. Returns false if an error occurred.
bool Init();
// BootControlInterface overrides.
unsigned int GetNumSlots() const override;
BootControlInterface::Slot GetCurrentSlot() const override;
bool GetPartitionDevice(const std::string& partition_name,
BootControlInterface::Slot slot,
std::string* device) const override;
bool IsSlotBootable(BootControlInterface::Slot slot) const override;
bool MarkSlotUnbootable(BootControlInterface::Slot slot) override;
bool SetActiveBootSlot(BootControlInterface::Slot slot) override;
bool MarkBootSuccessfulAsync(base::Callback
private:
// NOTE: There is no way to release/unload HAL implementations so
// this is essentially leaked on object destruction.
boot_control_module_t* module_;
DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(BootControlRecovery);
};
} // namespace chromeos_update_engine
#endif // UPDATE_ENGINE_BOOT_CONTROL_RECOVERY_H_
\system\update_engine\common\boot_control.h定义了获取得到boot_control接口实体的方法:
namespace chromeos_update_engine {
namespace boot_control {
// The real BootControlInterface is platform-specific. This factory function
// creates a new BootControlInterface instance for the current platform. If
// this fails nullptr is returned.
std::unique_ptr
} // namespace boot_control
} // namespace chromeos_update_engine
两个实现如下:
boot_control_android.cc
// Factory defined in boot_control.h.
std::unique_ptr
std::unique_ptr
if (!boot_control->Init()) {
return nullptr;
}
return std::move(boot_control);
}
boot_control_recovery.cc
// Factory defined in boot_control.h.
std::unique_ptr
std::unique_ptr
if (!boot_control->Init()) {
return nullptr;
}
return std::move(boot_control);
}
update_engine进程分析:
从system/update_engine根目录下的android.mk中
部分截取如下:
include $(CLEAR_VARS)
LOCAL_MODULE := update_engine
LOCAL_MODULE_CLASS := EXECUTABLES
LOCAL_SRC_FILES := \
main.cc
ifeq ($(local_use_omaha),1)
LOCAL_C_INCLUDES += \
$(ue_libupdate_engine_exported_c_includes)
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES += \
libupdate_engine \
$(ue_libupdate_engine_exported_static_libraries:-host=)
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES += \
$(ue_libupdate_engine_exported_shared_libraries:-host=)
else # local_use_omaha == 1
LOCAL_STATIC_LIBRARIES += \
libupdate_engine_android \
$(ue_libupdate_engine_android_exported_static_libraries:-host=)
LOCAL_SHARED_LIBRARIES += \
$(ue_libupdate_engine_android_exported_shared_libraries:-host=)
endif # local_use_omaha == 1
可知:update_engine进程的入口是main.cc类,该进程有两个重要依赖库:libupdate_engine和libupdate_engine_android。
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
省略部分初始化日志设置
得到update_engine_daemon后调用其run方法
chromeos_update_engine::UpdateEngineDaemon update_engine_daemon;
int exit_code = update_engine_daemon.Run();
LOG(INFO) << "Chrome OS Update Engine terminating with exit code "
<< exit_code;
return exit_code;
}
chromeos_update_engine命名空间下的UpdateEngineDaemon类如下所示:
system\update_engine\daemon.h
namespace chromeos_update_engine {
class UpdateEngineDaemon : public brillo::Daemon {
brillo::Daemon如下:
\external\libbrillo\brillo\daemons\daemon.h
Daemon是一个简单的基础系统守护进程,提供了许多有用的功能,比如消息循环,信号处理,信号挂起等,您可以直接使用此类来实现您的守护程序,或者您可以通过创建自己的类并从brillo :: Daemon派生它来专门化它。 覆盖一些提供的虚拟方法,以微调其行为以满足您的守护程序的需要。
class BRILLO_EXPORT Daemon : public AsynchronousSignalHandlerInterface {
public:
Daemon();
virtual ~Daemon();
// Performs proper initialization of the daemon and runs the message loop.
// Blocks until the daemon is finished. The return value is the error
// code that should be returned from daemon's main(). Returns EX_OK (0) on
// success.
virtual int Run();
// Can be used by call-backs to trigger shut-down of a running message loop.
// Calls QuiteWithExitCode(EX_OK);
// WARNING: This method (as well as QuitWithExitCode) can only be called when
// the message loop is running (that is, during Daemon::Run() call). Calling
// these methods before (e.g. during OnInit()) or after (e.g in OnShutdown())
// will lead to abnormal process termination.
void Quit();
// |exit_code| is the status code to be returned when the daemon process
// quits. See the warning for Quit() above regarding the allowed scope for
// this method.
void QuitWithExitCode(int exit_code);
// AsynchronousSignalHandlerInterface overrides.
// Register/unregister custom signal handlers for the daemon. The semantics
// are identical to AsynchronousSignalHandler::RegisterHandler and
// AsynchronousSignalHandler::UnregisterHandler, except that handlers for
// SIGTERM, SIGINT, and SIGHUP cannot be modified.
void RegisterHandler(
int signal, const
AsynchronousSignalHandlerInterface::SignalHandler& callback) override;
void UnregisterHandler(int signal) override;
protected:
// Overload to provide your own initialization code that should happen just
// before running the message loop. Return EX_OK (0) on success or any other
// non-zero error codes. If an error is returned, the message loop execution
// is aborted and Daemon::Run() exits early.
// When overloading, make sure you call the base implementation of OnInit().
virtual int OnInit();
// Called when the message loops exits and before Daemon::Run() returns.
// Overload to clean up the data that was set up during OnInit().
// |return_code| contains the current error code that will be returned from
// Run(). You can override this value with your own error code if needed.
// When overloading, make sure you call the base implementation of
// OnShutdown().
virtual void OnShutdown(int* exit_code);
// Called when the SIGHUP signal is received. In response to this call, your
// daemon could reset/reload the configuration and re-initialize its state
// as if the process has been reloaded.
// Return true if the signal was processed successfully and the daemon
// reset its configuration. Returning false will force the daemon to
// quit (and subsequently relaunched by an upstart job, if one is configured).
// The default implementation just returns false (unhandled), which terminates
// the daemon, so do not call the base implementation of OnRestart() from
// your overload.
virtual bool OnRestart();
// Returns a delegate to Quit() method in the base::RunLoop instance.
base::Closure QuitClosure() const {
return message_loop_.QuitClosure();
}
private:
// Called when SIGTERM/SIGINT signals are received.
bool Shutdown(const signalfd_siginfo& info);
// Called when SIGHUP signal is received.
bool Restart(const signalfd_siginfo& info);
// |at_exit_manager_| must be first to make sure it is initialized before
// other members, especially the |message_loop_|.
base::AtExitManager at_exit_manager_;
// The brillo wrapper for the base message loop.
BaseMessageLoop message_loop_;
// A helper to dispatch signal handlers asynchronously, so that the main
// system signal handler returns as soon as possible.
AsynchronousSignalHandler async_signal_handler_;
// Process exit code specified in QuitWithExitCode() method call.
int exit_code_;
DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(Daemon);
};
} // namespace brillo
run方法如下:进入了循环消息读取中。
int Daemon::Run() {
int exit_code = OnInit();
if (exit_code != EX_OK)
return exit_code;
message_loop_.Run();
OnShutdown(&exit_code_);
// base::RunLoop::QuitClosure() causes the message loop to quit
// immediately, even if pending tasks are still queued.
// Run a secondary loop to make sure all those are processed.
// This becomes important when working with D-Bus since dbus::Bus does
// a bunch of clean-up tasks asynchronously when shutting down.
while (message_loop_.RunOnce(false /* may_block */)) {}
return exit_code_;
}
在run之前调用了OnInit,在子类\system\update_engine\daemon.cc中的OnInit中,主要操作有:
初始化全局update engine状态:
DaemonStateAndroid* daemon_state_android = new DaemonStateAndroid();
daemon_state_.reset(daemon_state_android);
生成bindservice
binder_service_ = new BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService{
daemon_state_android->service_delegate()};
将该binderservice加入到bind服务管理中
auto binder_wrapper = android::BinderWrapper::Get();
if (!binder_wrapper->RegisterService(binder_service_->ServiceName(),
binder_service_)) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to register binder service.";
}
daemon_state_->AddObserver(binder_service_.get());
开始升级:
daemon_state_->StartUpdater();
\system\update_engine\daemon_state_interface.h如下:
namespace chromeos_update_engine {
class DaemonStateInterface {
public:
virtual ~DaemonStateInterface() = default;
// Start the daemon loop. Should be called only once to start the daemon's
// main functionality.
virtual bool StartUpdater() = 0;
// Add and remove an observer. All the registered observers will be called
// whenever there's a new status to update.
virtual void AddObserver(ServiceObserverInterface* observer) = 0;
virtual void RemoveObserver(ServiceObserverInterface* observer) = 0;
// Return the set of current observers.
virtual const std::set
protected:
DaemonStateInterface() = default;
};
} // namespace chromeos_update_engine
DaemonStateAndroid继承自DaemonStateInterface,部分定义如下,升级相关的主要操作都已经包含在内了。
bool StartUpdater() override;
ServiceDelegateAndroidInterface* service_delegate();
std::set
std::unique_ptr
std::unique_ptr
std::unique_ptr
std::unique_ptr
OpenSSLWrapper openssl_wrapper_;
std::unique_ptr
\system\update_engine\update_attempter_android.h
UpdateAttempterAndroid类包含了升级相关的所有方法,升级操作最终通过UpdateAttempterAndroid该类来实现。
java层调用updateEngine的apply后,通过binder调用到BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService类的apply中,升级的具体开始没有在该方法中实现,而是调用了ServiceDelegateAndroidInterface的ApplyPayload方法,UpdateAttempterAndroid继承自ServiceDelegateAndroidInterface,所以最终升级是在\system\update_engine\update_attempter_android.cc中实现。
\system\update_engine\binder_service_android.h如下:
ServiceDelegateAndroidInterface* service_delegate_;
Status BinderUpdateEngineAndroidService::applyPayload(
const android::String16& url,
int64_t payload_offset,
int64_t payload_size,
const std::vector
const std::string payload_url{android::String8{url}.string()};
std::vector
str_headers.reserve(header_kv_pairs.size());
for (const auto& header : header_kv_pairs) {
str_headers.emplace_back(android::String8{header}.string());
}
brillo::ErrorPtr error;
if (!service_delegate_->ApplyPayload(
payload_url, payload_offset, payload_size, str_headers, &error)) {
return ErrorPtrToStatus(error);
}
return Status::ok();
}
system\core\libbinderwrapper\binder_wrapper.cc中
BinderWrapper* BinderWrapper::Get() {
CHECK(instance_) << "Not initialized; missing call to Create()?";
return instance_;
}
void BinderWrapper::Create() {
CHECK(!instance_) << "Already initialized; missing call to Destroy()?";
instance_ = new RealBinderWrapper();
}
E:\source\AndroidP_r3\system\core\libbinderwrapper\real_binder_wrapper.cc中通过RegisterService方法将该服务加入到service_manager中。
bool RealBinderWrapper::RegisterService(const std::string& service_name,
const sp
sp
if (!service_manager.get()) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Unable to get service manager";
return false;
}
status_t status = defaultServiceManager()->addService(
String16(service_name.c_str()), binder);
if (status != OK) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Failed to register \"" << service_name << "\" with service "
<< "manager";
return false;
}
return true;
参考链接:
https://blog.csdn.net/hhp5127447/article/details/78349825
https://blog.csdn.net/thh159/article/details/88377184
https://blog.csdn.net/twk121109281/article/details/90693512
https://blog.csdn.net/twk121109281/article/details/90697586