android自定义view实现流式布局(FlowLayout)和热门标签
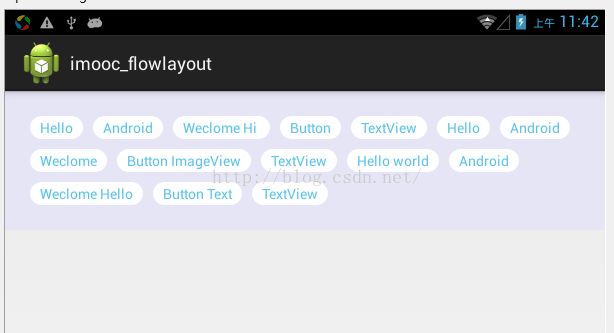
流式布局的效果图如图所示:应用场景诸如在搜索框的关键词显示等等。自定义view的流式布局(这里定义为FlowLayout)其实它就是一个Viewgroup,而后重写了它的几个方法,
代码如下:
package com.imooc.view;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* 流式布局
*
* @author 黄海
*
*/
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int sizeWidth = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int modeWidth = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int sizeHeight = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int modeHeight = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
// wrap_content
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
// 记录每一行的宽度与高度
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
// 得到内部元素的个数
int cCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 测量子View的宽和高
measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 得到LayoutParams
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
// 子View占据的宽度
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
// 子View占据的高度
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight() + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
// 换行
if (lineWidth + childWidth > sizeWidth - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight()) {
// 对比得到最大的宽度
width = Math.max(width, lineWidth);
// 重置lineWidth
lineWidth = childWidth;
// 记录行高
height += lineHeight;
lineHeight = childHeight;
} else
// 未换行
{
// 叠加行宽
lineWidth += childWidth;
// 得到当前行最大的高度
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight);
}
// 最后一个控件
if (i == cCount - 1) {
width = Math.max(lineWidth, width);
height += lineHeight;
}
}
Log.e("TAG", "sizeWidth = " + sizeWidth + "|sizeHeight = " + sizeHeight);
Log.e("TAG", "width = " + width);
setMeasuredDimension(
//
modeWidth == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeWidth : width + getPaddingLeft()
+ getPaddingRight(), modeHeight == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY ? sizeHeight
: height + getPaddingTop() + getPaddingBottom()//
);
}
/**
* 存储所有的View
*/
private List> mAllViews = new ArrayList>();
/**
* 每一行的高度
*/
private List mLineHeight = new ArrayList();
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
Log.e("TAG", "onLayout");
mAllViews.clear();
mLineHeight.clear();
// 当前ViewGroup的宽度
int width = getWidth();
int lineWidth = 0;
int lineHeight = 0;
List lineViews = new ArrayList();
int cCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < cCount; i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 如果需要换行
if (childWidth + lineWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin > width - getPaddingLeft()
- getPaddingRight()) {
// 记录LineHeight
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
// 记录当前行的Views
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
// 重置我们的行宽和行高
lineWidth = 0;
lineHeight = childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin;
// 重置我们的View集合
lineViews = new ArrayList();
}
lineWidth += childWidth + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight, childHeight + lp.topMargin + lp.bottomMargin);
lineViews.add(child);
}// for end
// 处理最后一行
mLineHeight.add(lineHeight);
mAllViews.add(lineViews);
// 设置子View的位置
int left = getPaddingLeft();
int top = getPaddingTop();
// 行数
int lineNum = mAllViews.size();
for (int i = 0; i < lineNum; i++) {
// 当前行的所有的View
lineViews = mAllViews.get(i);
lineHeight = mLineHeight.get(i);
for (int j = 0; j < lineViews.size(); j++) {
View child = lineViews.get(j);
// 判断child的状态
if (child.getVisibility() == View.GONE) {
continue;
}
MarginLayoutParams lp = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams();
int lc = left + lp.leftMargin;
int tc = top + lp.topMargin;
int rc = lc + child.getMeasuredWidth();
int bc = tc + child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 为子View进行布局
child.layout(lc, tc, rc, bc);
left += child.getMeasuredWidth() + lp.leftMargin + lp.rightMargin;
}
left = getPaddingLeft();
top += lineHeight;
}
}
/**
* 与当前ViewGroup对应的LayoutParams
*/
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
}
package com.imooc.flowlayout;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.Window;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.imooc.view.FlowLayout;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private String[] mVals = new String[] { "Hello", "Android", "Weclome Hi ", "Button",
"TextView", "Hello", "Android", "Weclome", "Button ImageView", "TextView",
"Hello world", "Android", "Weclome Hello", "Button Text", "TextView" };
private FlowLayout mFlowLayout;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
// requestWindowFeature(Window.FEATURE_NO_TITLE);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
mFlowLayout = (FlowLayout) findViewById(R.id.id_flowlayout);
initData();
}
public void initData() {
// for (int i = 0; i < mVals.length; i++)
// {
// Button btn = new Button(this);
//
// MarginLayoutParams lp = new MarginLayoutParams(
// MarginLayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT,
// MarginLayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
//
// btn.setText(mVals[i]);
// mFlowLayout.addView(btn, lp);
// }
LayoutInflater mInflater = LayoutInflater.from(this);
for (int i = 0; i < mVals.length; i++) {
TextView tv = (TextView) mInflater.inflate(R.layout.tv, mFlowLayout, false);
tv.setText(mVals[i]);
mFlowLayout.addView(tv);
}
}
@Override
protected void onResume() {
Log.e("TAG","onResume");
super.onResume();
}
}
tv.xml布局文件
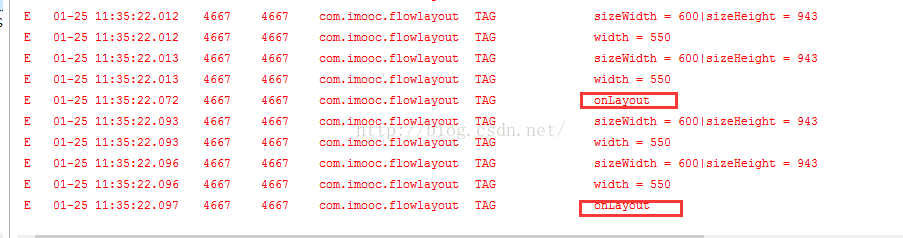
这里我打了几个log,发现FlowLayout的 onMeasure方法会执行4次,onLayout方法会执行两次,请问有知道为什么的吗?
说明:此代码是我看到网上的,觉得这东西不错然后自己写下来做个记录,以便以后学习使用。原作者链接http://www.imooc.com/learn/237,大家有兴趣的可以看下。
源码地址:http://download.csdn.net/detail/u014763302/9416943