关联查询sql编写的思路,1,先确定所连接的表,2,再确定所要查询的字段,3,确定连接条件以及连接方式
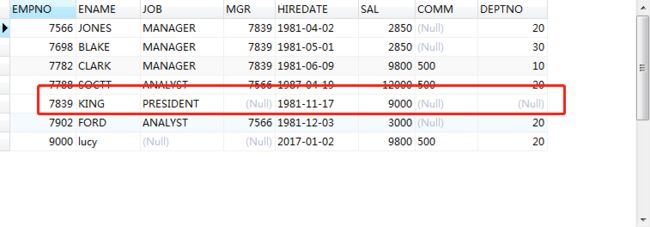
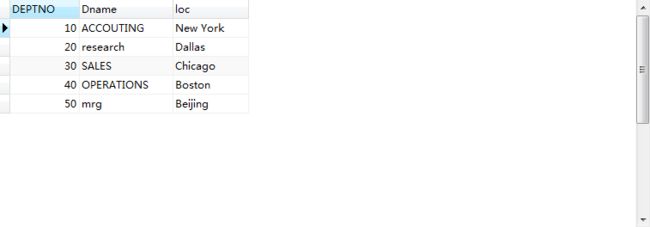
两个表的创建与数据:
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_emptest`; CREATE TABLE `t_emptest` ( `EMPNO` int(10) DEFAULT NULL, `ENAME` varchar(10) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL, `JOB` varchar(10) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL, `MGR` decimal(10,0) DEFAULT NULL, `HIREDATE` date DEFAULT NULL, `SAL` decimal(10,2) DEFAULT NULL, `COMM` varchar(10) COLLATE utf8_bin DEFAULT NULL, `DEPTNO` int(10) DEFAULT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of t_emptest -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `t_emptest` VALUES ('7566', 'JONES', 'MANAGER', '7839', '1981-04-02', '2850.00', null, '20'); INSERT INTO `t_emptest` VALUES ('7698', 'BLAKE', 'MANAGER', '7839', '1981-05-01', '2850.00', null, '30'); INSERT INTO `t_emptest` VALUES ('7782', 'CLARK', 'MANAGER', '7839', '1981-06-09', '9800.00', '500', '10'); INSERT INTO `t_emptest` VALUES ('7788', 'SOCTT', 'ANALYST', '7566', '1987-04-19', '12000.00', '500', '20'); INSERT INTO `t_emptest` VALUES ('7839', 'KING', 'PRESIDENT', null, '1981-11-17', '9000.00', null, null); INSERT INTO `t_emptest` VALUES ('7902', 'FORD', 'ANALYST', '7566', '1981-12-03', '3000.00', null, '20'); INSERT INTO `t_emptest` VALUES ('9000', 'lucy', null, null, '2017-01-02', '9800.00', '500', '20');
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `t_depttest`; CREATE TABLE `t_depttest` ( `DEPTNO` int(11) NOT NULL, `Dname` varchar(20) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL, `loc` varchar(10) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin; -- ---------------------------- -- Records of t_depttest -- ---------------------------- INSERT INTO `t_depttest` VALUES ('10', 'ACCOUTING', 'New York'); INSERT INTO `t_depttest` VALUES ('20', 'research', 'Dallas'); INSERT INTO `t_depttest` VALUES ('30', 'SALES', 'Chicago'); INSERT INTO `t_depttest` VALUES ('40', 'OPERATIONS', 'Boston'); INSERT INTO `t_depttest` VALUES ('50', 'mrg', 'Beijing');
高级查询:
内连接
外连接:左外连接,右外连接,完全外连接
自然(自我)连接
多表查询--注意点:where一个,多条件时and连接,多表查询先得有连接条件,另外一个条件and连接,,多个地点时用in 而不是or,用or查询结果会有问题
-- 查询部门在NewYork 和芝加哥的员工编号和员工名称
SELECT empno ,ename
-- 多张表
FROM t_emptest,t_depttest
-- 连接条件
WHERE t_emptest.DEPTNO=t_depttest.DEPTNO
-- and 其他条件 尽量用in
AND t_depttest.loc in ('New York' , 'Chicago');
内连接
连接的多表必须有公共列(相等连接)
通过INNER JOIN语法实现
内连接语法:
SELECT tab1.col_name, tab2.col_name….
FROM tab1 (INNER) JOIN tabe2
ON tab.col = tab2.col
其中col是两表的公共列
-- 查询部门在NewYork 和芝加哥的员工编号和员工名称
SELECT EMPNO,ENAME,JOB,SAL,t_depttest.Dname,t_emptest.DEPTNO FROM t_emptest
-- inner join连接
INNER JOIN t_depttest
-- 连接条件
ON t_depttest.DEPTNO = t_emptest.DEPTNO
-- 其他筛选条件
WHERE t_depttest.loc in ('New York' , 'Chicago');
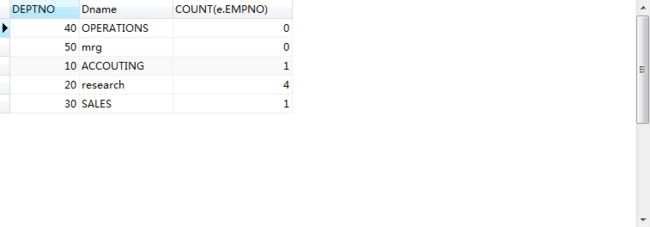
-- 外连接
-- 查询部门编号,部门名称,部门员工人数
SELECT d.DEPTNO,d.Dname,COUNT(e.EMPNO) FROM t_emptest e LEFT JOIN t_depttest d ON e.DEPTNO=d.DEPTNO GROUP BY e.DEPTNO,d.Dname; SELECT d.DEPTNO,d.Dname,COUNT(e.EMPNO) FROM t_emptest e RIGHT JOIN t_depttest d ON e.DEPTNO=d.DEPTNO GROUP BY e.DEPTNO,d.Dname;
左外连接和右外连接结果区别:---结果对比两表格的数据
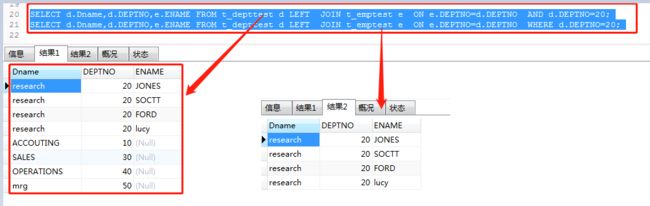
连接where和and的区别
SELECT d.Dname,d.DEPTNO,e.ENAME FROM t_depttest d
LEFT JOIN t_emptest e
ON e.DEPTNO=d.DEPTNO
-- 区别,显示部门编号不为20的数据
AND d.DEPTNO=20;
SELECT d.Dname,d.DEPTNO,e.ENAME FROM t_depttest d
LEFT JOIN t_emptest e
ON e.DEPTNO=d.DEPTNO
-- 仅显示部门数据为20的数据
WHERE d.DEPTNO=20;
自我连接 有上下级关系
自我连接-and 和where结果一致
-- 4.1 找到雇员名称为blake的雇员名称和经理 SELECT e.ENAME,mgr.Ename FROM t_emptest e JOIN t_emptest mgr ON e.MGR=mgr.EMPNO WHERE e.ENAME='BLAKE'; SELECT e.ENAME,mgr.Ename FROM t_emptest e JOIN t_emptest mgr ON e.MGR=mgr.EMPNO AND e.ENAME='BLAKE';
-- 查询部门经理,经理编号,以及他下面的人数
SELECT mgr.EMPNO,mgr.ENAME,COUNT(mgr.EMPNO) FROM t_emptest mgr
JOIN t_emptest e
-- 连接条件
ON e.MGR=mgr.EMPNO
-- 统计人数
GROUP BY mgr.MGR ;
-- 查询员工编号,员工名,上级编号,上级名称,所在部门 SELECT e.EMPNO eEMPNO,e.ENAME eENAME, mgr.EMPNO mgrEMPNO,mgr.ENAME mgrENAME ,d.Dname FROM t_emptest e
INNER JOIN t_emptest mgr
ON e.MGR=mgr.EMPNO
INNER JOIN t_depttest d
ON d.DEPTNO=e.DEPTNO ;