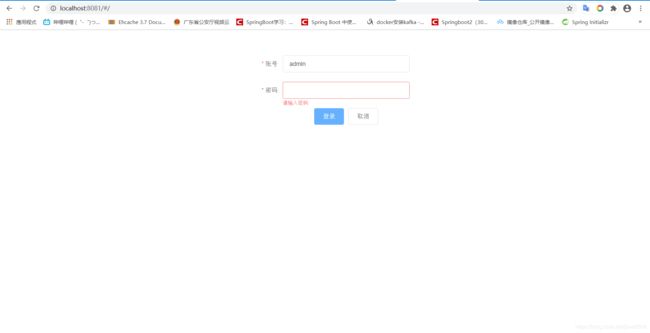
Vue框架新手教程,一步步搭建即开即用Vue项目:Vue集成axios,Vuex,route和element.js
1 背景
平时比较闲的时候呢,喜欢帮别人写写毕业设计,做做课设题目.但本人是正经的Java开发,前端那东西每次呢都是从其他开源项目扒下来修修补补.这两天比较闲,想着自己搭一个即开即用的Vue项目,日后就在element上面找找组件修改修改就可用那种.
搜了搜博客发现.写Vue框架的不少,但是集成度比较高的几乎没有.像axios和springboot微服务搭配肯定会遇到跨域问题和请求头信息携带的问题,直接调用在实际项目实在是不科学.但是在以往的vue项目搭建博客中,我却没有看见这一点.
心想,既然自己要做,那么顺便也记录一下搭建过程,给后来者提供一个思路,于是便有了这篇博客
2 项目准备
2.1 下载安装node.js
Vue项目依赖于node.js,所以首先应该安装node.js.进入node.js官网,然后下载LTS版本.下载完毕一路直点下一步,基本和安装qq微信什么的没什么区别.
安装完成后,输入npm -v出现版本号,可以认为已经安装结束
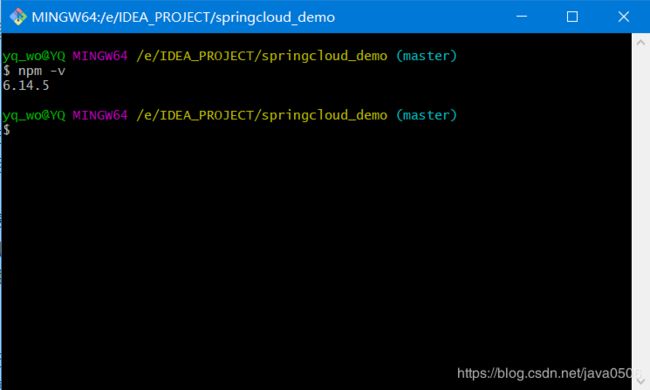
2.2 安装Vue客户端工具Vue Cli并创建一个项目
这一部分内容参见官网Vue Cli,主要就是执行两条命令npm install -g @vue/cli以及vue create vue-demo
- 执行
npm install -g @vue/cli,查看版本号成功则安装成功

- 初始化项目:
vue create vue-demo然后回车选择default就可以了
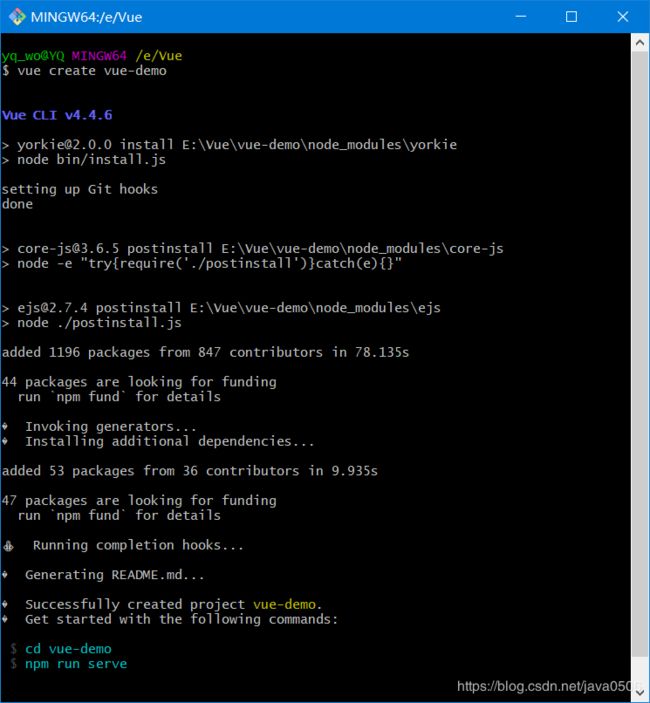
- 接下的操作正如vue cli所给的提示:进入项目目录,然后执行
npm run serve

- 进入图片所提示的local地址,我这里是http://localhost:8081/,如果出现如下界面,那么恭喜你,项目初始化完毕
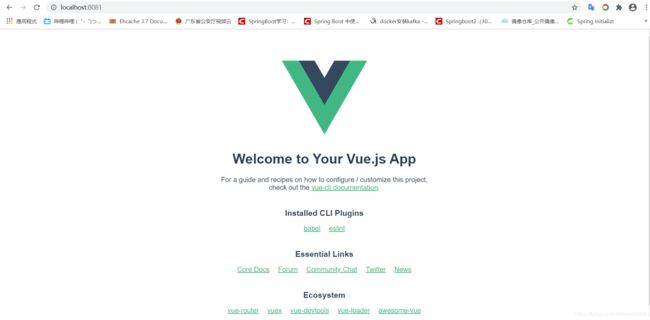
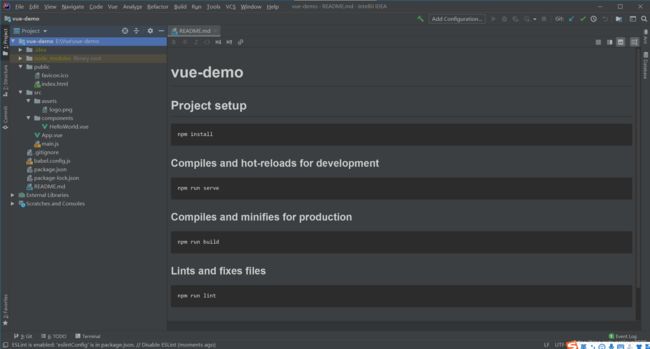
2.3 认识目录结构
前端工具有很多,我这里依然使用Java巨无霸IDE的IDEA(安装一个vue.js就可以无缝使用).目录结构如下图所示
新手可能会好奇,上上张图片显示的那张V的界面是怎么出来的.我这里简单介绍一下它的渲染流程
- index.html里面有个id为app的div,事实上App.vue这个根实例所生成的内容就挂在这个div上面
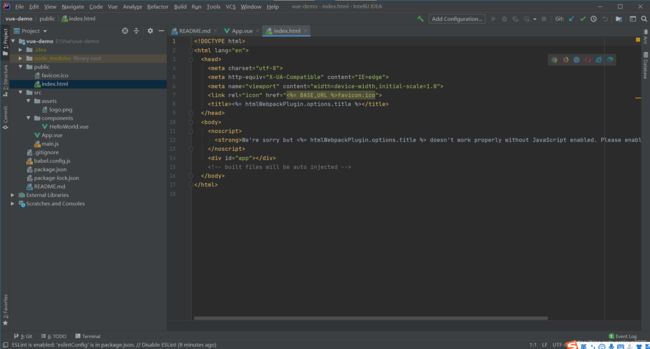
上图可以看到这个app的div,这个就是Vue实例挂载的dom节点

而app.vue里面可以清楚的看到,里面又引入了一个Helloworld.vue的单文件 - 显然,初始化的页面应该是由Helloworld.vue来生成,这里我来验证一下:把helloworld里面的内容改为helloworld

这里我把里面那些乱七八糟的链接全部删除了,改成了Hello world!!

可以看到页面也随之改动,可见页面内容的确是Helloworld这个单文件所渲染出来的,当然v这个图片是App.vue渲染的,仔细看看app.vue就可以知道了
3 框架改造
经过以上步骤,我们已经初始化了一个基础的vue项目.但是显然,这个原始框架还不怎么好用:不支持页面跳转,也不支持后端交互,跟咸鱼没什么区别.
奇怪的很多vue项目初始化博客就停在了上面的步骤,我就想问,搭成这种程度对新手也太不友好了.我相信绝大部分新手做到这里之后,完全不知道下面要干嘛.
为了对新手更友好一点,就由我做一个简单的演示 :一个简单的登录界面,登录成功之后(涉及ajax请求,axios),进行页面跳转(涉及route),并携带app信息(Vuex,全局变量管理).
3.1 页面跳转(route的使用)
- 准备2个Vue文件(login.vue和home.vue),并将app.vue指向的单文件由Helloworld改为Login.此步骤完成的效果为:项目主页面是一个home的按钮(app.vue的指向更改成功),单击触发弹窗消息(按钮单击可以触发事件)




- 接下来就要进行route的引入:安装vue-router组件,并修改两个js文件:index.js和main.js,以及app.vue文件
App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App'
}
</script>
<style>
#app {
font-family: Avenir, Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;
-webkit-font-smoothing: antialiased;
-moz-osx-font-smoothing: grayscale;
text-align: center;
color: #2c3e50;
margin-top: 60px;
}
</style>
index.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import VueRouter from 'vue-router';
Vue.use(VueRouter)
import Home from '../views/home.vue'
import Login from '../views/login.vue'
export default new VueRouter({
routes: [{
path: '/', //登录页面的路由要定义为/,这样在项目运行时就可以直接加载
name: 'login',
component: Login
},
{
path: '/home',
name: 'home',
component: Home
}
]
})
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './route/index.js'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
login.vue
<template>
<div class="login">
<button v-on:click="to_home">home</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'Login',
methods:{
to_home(){
alert("THIS IS LOGIN");
this.$router.replace("/home")
}
}
};
</script>
3.2 Element的引入
以上步骤,我们已经可以从一个页面跳转到另外一个页面.接下来我们对页面进行简单的美化工作,也就是引入element组件
3.2.1 引入Element组件
老规矩,首先进入Element的官网调研一波,点此进入Element官网.由官网可知,要在项目中引入element,大致分为两步:
- 安装组件:
npm i element-ui -S - main.js中引入element
至此main.js应该是下面这样的:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './route/index.js'
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css';
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.use(ElementUI);
new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
3.2.2 Element实战使用Element的button组件替换原生button
简单来说,就是查看Element官网的组件介绍,然后直接复制组件的代码到项目文件中即可,比如button的使用
<template>
<div class="login">
<!-- <button v-on:click="to_home">home</button>-->
<el-button type="primary" icon="el-icon-share" v-on:click="to_home">home</el-button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name:'Login',
methods:{
to_home(){
alert("THIS IS LOGIN");
this.$router.replace("/home")
}
}
};
</script>
效果如下
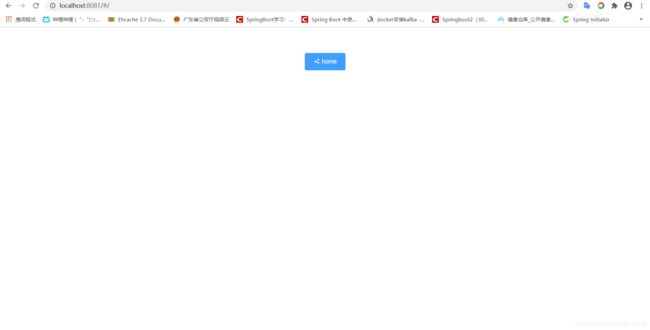
至此,我们已经掌握element组件引入的方法:查看官网的组件介绍,复制组件代码并根据自己的需要做成一定更改
3.2.3 实战:利用改造login和home => login改为表单形式,而home改为表格形式
<template>
<div class="login">
<!-- <button v-on:click="to_home">home</button>-->
<!-- <el-button type="primary" icon="el-icon-share" v-on:click="to_home">home</el-button>-->
<el-form :model="ruleForm" :rules="rules" ref="ruleForm" label-width="100px" class="demo-ruleForm">
<el-form-item label="账号" prop="name">
<el-input v-model="ruleForm.name"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="密码" prop="password">
<el-input v-model="ruleForm.password"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="onSubmit('ruleForm')">登录</el-button>
<el-button>取消</el-button>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Login',
data() {
return {
ruleForm: {
name: '',
password: ''
},
rules: {
name: [
{required: true, message: '请输入账号', trigger: 'blur'},
],
password: [
{required: true, message: '请输入密码', trigger: 'blur'}
],
}
}
},
methods: {
// to_home() {
// alert("THIS IS LOGIN");
// this.$router.replace("/home")
// },
onSubmit(formName) {
this.$refs[formName].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
alert('submit!');
this.$router.replace("/home")
} else {
console.log('error submit!!');
return false;
}
})
}
}
};
</script>
<style scoped="scoped">
.login {
width: 400px;
margin: auto;
}
</style>
3.3 axios组件的使用和封装
- 引入axios和qs组件
- 修改ajax.js和main.js
ajax.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import ajax from 'axios';
const service = ajax.create({
baseURL:'http://localhost:8094',
timeout: 1000 * 30,
withCredentials: false // 允许跨域带token
})
service.interceptors.request.use(config => {
if (config.method === "post") {
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(config.data) === '[object Object]') {
config.data = Vue.prototype.$qs.stringify({...config.data })
}
}
return config
}, error => {
return Promise.reject(error)
})
Vue.prototype.$http = service;
main.js
尤其要注意:import "./common/utils/ajax.js";,如果没有这一句,那么会报$http不是方法
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './route/index.js'
import ElementUI from 'element-ui';
import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css';
import qs from 'qs'
import "./common/utils/ajax.js";
Vue.config.productionTip = false
Vue.use(ElementUI);
Vue.prototype.$qs=qs
new Vue({
router,
render: h => h(App),
}).$mount('#app')
- login中使用ajax完成登录功能
<template>
<div class="login">
<!-- <button v-on:click="to_home">home</button>-->
<!-- <el-button type="primary" icon="el-icon-share" v-on:click="to_home">home</el-button>-->
<el-form :model="ruleForm" :rules="rules" ref="ruleForm" label-width="100px" class="demo-ruleForm">
<el-form-item label="账号" prop="name">
<el-input v-model="ruleForm.name"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item label="密码" prop="password">
<el-input v-model="ruleForm.password"></el-input>
</el-form-item>
<el-form-item>
<el-button type="primary" @click="onSubmit('ruleForm')">登录</el-button>
<el-button>取消</el-button>
</el-form-item>
</el-form>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'Login',
data() {
return {
ruleForm: {
name: '',
password: ''
},
rules: {
name: [
{required: true, message: '请输入账号', trigger: 'blur'},
],
password: [
{required: true, message: '请输入密码', trigger: 'blur'}
],
}
}
},
methods: {
// to_home() {
// alert("THIS IS LOGIN");
// this.$router.replace("/home")
// },
onSubmit(formName) {
this.$refs[formName].validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
alert('submit!');
this.checkLogin();
} else {
console.log('error submit!!');
return false;
}
})
},
checkLogin(){
this.$http({
url:'http://localhost:8094/user/login',
method:'post',
data:this.$qs.stringify({
username:this.ruleForm.name,
password:this.ruleForm.password
})
}).then(res=>{
let data=res.data;
if(data.code===0){
alert("登录成功");
this.$router.replace("/home")
}else {
alert("登录失败,原因为:"+data.msg)
}
})
}
}
};
</script>
<style scoped="scoped">
.login {
width: 400px;
margin: auto;
}
</style>
@SuperBuilder
@AllArgsConstructor
@Setter
@Getter
public class UserVO implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -442947605606160969L;
@NotNull(message = "账号不允许为空")
private String username;
@NotNull(message = "密码不允许为空")
@Length(min = 4,max = 12,message = "密码长度不低于4位,不高于12位")
private String password;
}
UserController
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@PostMapping("login")
@ResponseBody
public Object login(@Validated UserVO user) {
if ("admin".equals(user.getUsername()) && "admin".equals(user.getPassword()))
return ReturnDTO.success();
else
return ReturnDTO.fail("账号或密码错误");
}
}
全局异常处理:
@ControllerAdvice
public class GlobalException {
@ExceptionHandler(value={BindException.class})
@ResponseBody
public Object exception(BindException e){
String defaultMessage = e.getAllErrors().get(0).getDefaultMessage();
return ReturnDTO.fail(defaultMessage);
}
@ExceptionHandler(value={Exception.class})
@ResponseBody
public Object exception(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
return ReturnDTO.fail("系统错误,原因为:"+e.getMessage());
}
}
跨域配置:
@Configuration
public class CorsConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* 页面跨域访问Controller过滤
*/
@Override
public void addCorsMappings(CorsRegistry registry) {
WebMvcConfigurer.super.addCorsMappings(registry);
registry.addMapping("/**")
.allowedHeaders("*")
.allowedMethods("POST","GET")
.allowedOrigins("*");
}
}