Android之AIDL实现两个app的调用以及双进程app的进程通信
1.AIDL是一个缩写,全称是Android Interface Definition Language,也就是Android接口定义语言。是 Android 提供的一种进程间通信 (IPC) 机制。我们可以利用它定义客户端与服务使用进程间通信 (IPC) 进行相互通信时都认可的编程接口。
在 Android 上,一个进程通常无法访问另一个进程的内存。 尽管如此,进程需要将其对象分解成操作系统能够识别的原语,并将对象编组成跨越边界的对象。编写执行这一编组操作的代码是一项繁琐的工作,因此 Android 会使用 AIDL 来处理。通过这种机制,我们只需要写好 aidl 接口文件,编译时系统会帮我们生成 Binder 接口。
2.AIDL支持的数据类型:
Java的基本数据类型;List和Map,元素必须是 AIDL 支持的数据类型,Server 端具体的类里则必须是 ArrayList 或者 HashMap;其他生成的接口;实现 Parcelable 的实体。
3.如何编写AIDL
(1)创建AIDL文件
创建要操作的实体类,实现 Parcelable 接口;
新建 aidl 文件夹;
第一种:一个bean对象,实现parcelable接口
// Cat.aidl
//第一类AIDL文件的例子
//这个文件的作用是引入了一个序列化对象 Cat 供其他的AIDL文件使用
//注意:Cat.aidl与Cat.java的包名应当是一样的
package com.ysl.myandroidbase.bean;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
//注意parcelable是小写
parcelable Cat;
第二种:
// ICatService.aidl
//第二类AIDL文件的例子
package com.ysl.myandroidbase;
// Declare any non-default types here with import statements
//导入所需要使用的非默认支持数据类型的包
import com.ysl.myandroidbase.bean.Cat;
interface ICatService {
//所有的返回值前都不需要加任何东西,不管是什么数据类型
Cat getCat();
int getCatCount();
//传参时除了Java基本类型以及String,CharSequence之外的类型
//都需要在前面加上定向tag,具体加什么量需而定
void setCatPrice(in Cat cat , int price);
void setCatName(in Cat cat , String name);
void addCatIn(in Cat cat);
void addCatOut(out Cat cat);
void addCatInout(inout Cat cat);
}
具体的看代码中的注释。
编译工程。
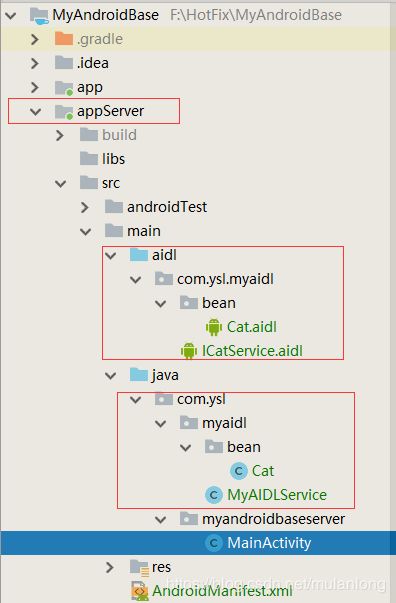
(2)两个app的工程目录
服务端指的是服务端app。这样可以和客户端区分为两个app,自然而然是两个不同的进程了。
大家可以对比一下这两个app的目录结构。其中aidl的文件夹下面完全一样的。
bean对象cat以及service所在的包名都要和aidl文件的包名一致。
(3)服务端app的service
package com.ysl.myaidl;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import com.ysl.myaidl.bean.Cat;
public class MyAIDLService extends Service {
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return myBinder;
}
private IBinder myBinder = new ICatService.Stub(){
@Override
public Cat getCat() throws RemoteException {
return new Cat("tom", 100);
}
@Override
public int getCatCount() throws RemoteException {
return 100;
}
@Override
public void setCatPrice(Cat cat, int price) throws RemoteException {
}
@Override
public void setCatName(Cat cat, String name) throws RemoteException {
}
@Override
public void addCatIn(Cat cat) throws RemoteException {
}
@Override
public void addCatOut(Cat cat) throws RemoteException {
}
@Override
public void addCatInout(Cat cat) throws RemoteException {
}
};
}
在onbind方法中返回aidl接口的sub即可。
manifest文件中:
要给service定义一个特有的action。这样在客户端中就可以使用隐式的方式来绑定此服务了。
(4)客户端app
package com.ysl.myandroidbase;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.ComponentName;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.content.ServiceConnection;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.os.RemoteException;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.ysl.myaidl.ICatService;
import com.ysl.myaidl.bean.Cat;
public class Main2Activity extends AppCompatActivity {
private ICatService iCatService;
private TextView tv;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2);
tv = findViewById(R.id.tv);
findViewById(R.id.bind).setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.ysl.myandroidbase.MyAIDLService");
intent.setPackage("com.ysl.myandroidbaseserver");
bindService(intent, serviceConnection, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);
}
});
}
private void setTv() {
try {
Cat cat = iCatService.getCat();
int catCount = iCatService.getCatCount();
tv.setText(cat.name+"_"+cat.price+"/n"+catCount);
iCatService.setCatName(new Cat(), "abcdef");
} catch (RemoteException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private ServiceConnection serviceConnection = new ServiceConnection() {
@Override
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
iCatService = ICatService.Stub.asInterface(service);
setTv();
}
@Override
public void onServiceDisconnected(ComponentName name) {
}
};
}
这里就是绑定一下服务端app的service。
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction("com.ysl.myandroidbase.MyAIDLService");
intent.setPackage("com.ysl.myandroidbaseserver");
bindService(intent, serviceConnection, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);要显式的设置service的action(服务端manifest中定义的),设置包名(服务端app的包名)。
绑定的服务启动并连接成功后,在onServiceConnected中使用
iCatService = ICatService.Stub.asInterface(service);就可以获取到接口服务了,然后就可以调用里面定义的一些方法来传递数据了。
4.如果在同一个app中使用。
在activity中调用的地方可以直接显式调用:
Intent intent = new Intent(Main2Activity.this, MyAIDLService.class);
bindService(intent, serviceConnection, Service.BIND_AUTO_CREATE);在manifest文件中可以把此服务放在另一个进程中:
这样同一个app就可以使用两个进程,然后进行数据传递。一般可以把请求数据放到此服务中,让服务进程去专心处理数据。然后再把数据传到主进程中去。
此外,双进程的app,也可以做进程保活,只要其中一个被杀死了,另一个要立马把它拉起来。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/luoyanglizi/article/details/51980630
https://blog.csdn.net/u011240877/article/details/72765136
关于in , out , inout 是三个定向tag:https://blog.csdn.net/luoyanglizi/article/details/51958091
结论:AIDL中的定向 tag 表示了在跨进程通信中数据的流向,其中 in 表示数据只能由客户端流向服务端, out 表示数据只能由服务端流向客户端,而 inout 则表示数据可在服务端与客户端之间双向流通。其中,数据流向是针对在客户端中的那个传入方法的对象而言的。in 为定向 tag 的话表现为服务端将会接收到一个那个对象的完整数据,但是客户端的那个对象不会因为服务端对传参的修改而发生变动;out 的话表现为服务端将会接收到那个对象的参数为空的对象,但是在服务端对接收到的空对象有任何修改之后客户端将会同步变动;inout 为定向 tag 的情况下,服务端将会接收到客户端传来对象的完整信息,并且客户端将会同步服务端对该对象的任何变动。