Android中Adapter接口及其实现类详解
一、Adapter简单介绍:
(1)Android官方文档这样介绍:
An Adapter object acts as a bridge between an AdapterView and the underlying data for that view. The Adapter provides access to the data items. The Adapter is also responsible for making a View for each item in the data set.
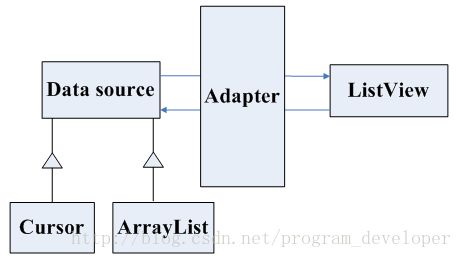
我的翻译:一个Adapter充当着AdapterView视图与数据之间的桥梁。Adapter提供对数据项的访问,并且Adapter也负责为数据集中每一项数据产生对应的view。其作用如图所示:
(2)Adapter接口及实现类
先来一张图,了解一下Adapter实现类的继承关系:
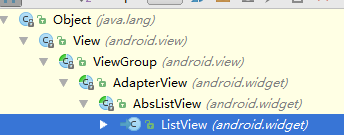
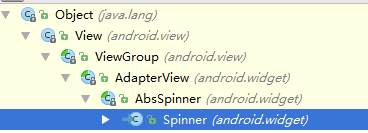
Adapter本身只是一个接口,它派生了SpinnerAdapter和ListAdapter两个子接口,其中ListAdapter为AbsListView提供列表项,而SpinnerAdapter为AbsSpinner提供列表项。由于ListView和GridView两个控件都继承AbsListView,所以ListAdapter其实是为ListView和GridView提供列表项。当然,Spinner和Gallery两个控件都继承AbsSpinner,所以SpinnerAdapter其实是为Spinner和Gallery提供列表项。控件的继承关系如下图:
BaseAdapter同时实现了SpinnerAdapter和ListAdapter两个接口。几乎所有Adapter都继承了BaseAdapter,因此,BaseAdapter及其子类可以同时为AbsListView、AbsSpinner提供列表项。
二、Adapter常用的实现类如下:
1. BaseAdapter:是一个抽象类,继承它需要实现较多的方法,所以灵活性和扩展性比较好。
class MyAdapter extends BaseAdapter{
private List> mList = null;//要显示的数据
/**
* 得到数据集合中数据项数
* @return 集合中数据的项数
*/
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mList.size();
}
/**
* 返回指定位置的数据项
* @param i 指定的位置
* @return
*/
@Override
public Object getItem(int i) {
return mList.get(i);
}
/**
* 返回指定位置数据项的ID
* @param i
* @return
*/
@Override
public long getItemId(int i) {
return i;
}
//为每一个数据项产生相应的视图
@Override
public View getView(int i, View view, ViewGroup viewGroup) {
return null;
}
//----以上方法是必须实现的,下面两个方法是非必须实现的。
//当一个ListView的列表项有多种布局的情况下,需要实现这两个方法。
//根据数据源的position返回需要显示的布局的类型
@Override
public int getItemViewType(int position) {
return super.getItemViewType(position);
}
//返回所有布局的数量
@Override
public int getViewTypeCount() {
return super.getViewTypeCount();
}
}
(1)数据是数组的情况:
ListView ls= (ListView) this.findViewById(R.id.listView);
//列表项的数据
String[] strs={"JAVA","C#","JAVA Web","Android"};
//适配器
ArrayAdapter adapter=new ArrayAdapter(this,R.layout.support_simple_spinner_dropdown_item,strs);
//把数据填充到ListView中
ls.setAdapter(adapter);
(2)数据是List集合的情况:
ListView ls= (ListView) this.findViewById(R.id.listView);
//列表项的数据
List list=new ArrayList();
list.add("JAVA");
list.add("C#");
list.add("JAVA Web");
list.add("Android");
//适配器
ArrayAdapter adapter=new ArrayAdapter(this,R.layout.support_simple_spinner_dropdown_item,list);
//把数据填充到ListView中
ls.setAdapter(adapter); /**
* Constructor
*
* @param context The context where the View associated with this SimpleAdapter is running
* @param data A List of Maps. Each entry in the List corresponds to one row in the list. The
* Maps contain the data for each row, and should include all the entries specified in
* "from"
* @param resource Resource identifier of a view layout that defines the views for this list
* item. The layout file should include at least those named views defined in "to"
* @param from A list of column names that will be added to the Map associated with each
* item.
* @param to The views that should display column in the "from" parameter. These should all be
* TextViews. The first N views in this list are given the values of the first N columns
* in the from parameter.
*/
public SimpleAdapter(Context context, List> data,
@LayoutRes int resource, String[] from, @IdRes int[] to) {
mData = data;
mResource = mDropDownResource = resource;
mFrom = from;
mTo = to;
mInflater = (LayoutInflater) context.getSystemService(Context.LAYOUT_INFLATER_SERVICE);
}
(1)Context :上下文,表示访问整个Android应用程序的接口。一般表示控件所在的当前Activity。
(2)包含Map类型的List集合。该集合中每个Map对象生成一个列表项。
(3)指定一个界面布局的ID。
(4)该参数应该是一个String[]类型的参数,该参数决定提取Map对象中哪些key对应的value来生成列表项。
(5)该参数应该是一个int[]类型的参数,该参数决定填充哪些控件。需要注意的是:Map对象中key对应的值依次填充组件,是有对应关系的。
demo:
activity_main.xml文件内容:
package com.example.adapter;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
String[] name = {"小强", "小红", "小芳"};
String[] motto = {"好记性不如烂笔头", "好好学习,天天向上", "一寸光阴一寸金"};
int[] imageId = new int[]{R.drawable.e, R.drawable.g, R.drawable.l};
//创建一个List集合,List集合的元素是Map
List> list = new ArrayList>();
for (int i = 0; i < name.length; i++) {
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("header", imageId[i]);
map.put("name", name[i]);
map.put("motto", motto[i]);
list.add(map);
}
//在布局文件中找到ListView
ListView ls = (ListView) this.findViewById(R.id.listView);
//创建适配器Adapter
SimpleAdapter simpleAdapter = new SimpleAdapter(this, list, R.layout.simple_item,
new String[]{"header", "name", "motto"}, new int[]{R.id.head, R.id.name, R.id.motto});
//为ListView设置Adapter
ls.setAdapter(simpleAdapter);
}
}
4.SimpleCursorAdapter:这个Adapter是Android专门为了连接数据库与视图而产生的。先看一下Android源码中SimpleCursorAdapter的构造函数:
/**
* Standard constructor.
*
* @param context The context where the ListView associated with this
* SimpleListItemFactory is running
* @param layout resource identifier of a layout file that defines the views
* for this list item. The layout file should include at least
* those named views defined in "to"
* @param c The database cursor. Can be null if the cursor is not available yet.
* @param from A list of column names representing the data to bind to the UI. Can be null
* if the cursor is not available yet.
* @param to The views that should display column in the "from" parameter.
* These should all be TextViews. The first N views in this list
* are given the values of the first N columns in the from
* parameter. Can be null if the cursor is not available yet.
* @param flags Flags used to determine the behavior of the adapter,
* as per {@link CursorAdapter#CursorAdapter(Context, Cursor, int)}.
*/
public SimpleCursorAdapter(Context context, int layout, Cursor c, String[] from,
int[] to, int flags) {
super(context, layout, c, flags);
mTo = to;
mOriginalFrom = from;
findColumns(c, from);
}
(2)ListView控件中每一列表项的布局资源文件。
(3)数据库的游标。
(4)数据库中每一列字段的名字。
(5)上面的数据库中字段所对应的显示在哪个控件上。
(6)参数flags是一个标识,用于决定适配器的行为。一般情况flag永远传0就可以啦!
实现这个适配器也很简单,和上边几个Adapter大同小异,请读者自己实现。