自定义View常用细节性集合
简述:
在自定义View的过程中我们经常会用到一些相同的但是又是必须要主要的细节,今天分享一些细节行东西。
1、字体属性及宽高测量
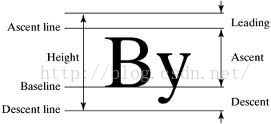
我们先来了解一下FontMetrics这个类:
这是Paint的内部类我直接Copy过来看一下,接下来再通过一张图具体描述一下其各个参数的意义:
/**
* Class that describes the various metrics for a font at a given text size.
* Remember, Y values increase going down, so those values will be positive,
* and values that measure distances going up will be negative. This class
* is returned by getFontMetrics().
*/
public static class FontMetrics {
/**
* The maximum distance above the baseline for the tallest glyph in
* the font at a given text size.
*/
public float top;
/**
* The recommended distance above the baseline for singled spaced text.
*/
public float ascent;
/**
* The recommended distance below the baseline for singled spaced text.
*/
public float descent;
/**
* The maximum distance below the baseline for the lowest glyph in
* the font at a given text size.
*/
public float bottom;
/**
* The recommended additional space to add between lines of text.
*/
public float leading;
}然后字体的高度就是descent-ascent,我们直接代码实现如下:
/**
* 方法描述:获取文本字符的高度
*
* @param mPaint 画文本字符的画笔
* @return 文本字符的高度
*/
private double getTxtHeight(Paint mPaint) {
Paint.FontMetrics fm = mPaint.getFontMetrics();
return Math.ceil(fm.descent - fm.ascent);
} /**
* 方法描述:获取文本的宽度
*/
private float getTxtWidth(Paint paint, String txt) {
return paint.measureText(txt);
}2、重置图片的宽高
对于2.2以后版本可以直接调用下面的函数:
/**
* Creates a centered bitmap of the desired size.
*
* @param source original bitmap source
* @param width targeted width
* @param height targeted height
*/
ThumbnailUtils.extractThumbnail(Bitmap source, int width, int height)/**
* 方法描述:重置图片的宽高
*/
private Bitmap zoomImg(Bitmap bm, int width, int height) {
int originWidth = bm.getWidth();
int originHeight = bm.getHeight();
float scaleWidth = ((float) width) / originWidth;
float scaleHeight = ((float) height) / originHeight;
Matrix matrix = new Matrix();
matrix.postScale(scaleWidth, scaleHeight);
return Bitmap.createBitmap(bm, 0, 0, originWidth, originHeight, matrix, true);
}3、判断触摸事件是否在View内
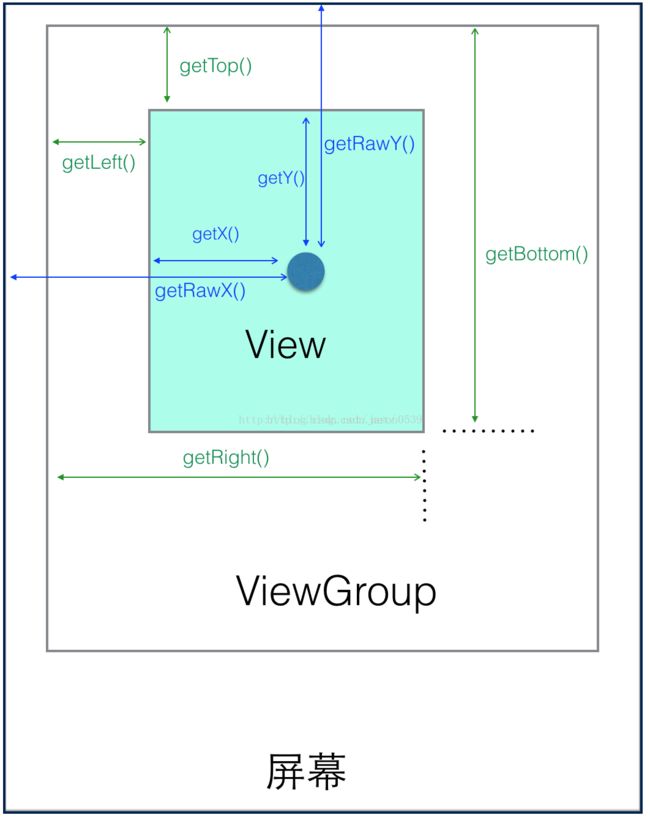
弄明白这个事情之前我们先来学习一下View坐标系,先来卡一张图(图片来源于网络):
所以我们要想判断我们的触摸事件是否在View内只需要判断当前点坐标(getRawX(),getRawY())是否在View这个矩形区域内就OK啦,那现在缕清了思路接下来代码实现:
① 首先我们先确定我们的View所处的矩形区域的获取:
/**
* 方法描述:计算指定的 View 在屏幕中的坐标(矩形区域)
*/
private RectF calcViewScreenLocation(View view) {
int[] location = new int[2];
view.getLocationOnScreen(location);
return new RectF(location[0], location[1], location[0] + view.getWidth(),
location[1] + view.getHeight());
}(event.getRawX(), event.getRawY()) RectF rectF = calcViewScreenLocation(this);
boolean contains = rectF.contains(event.getRawX(), event.getRawY());