简述RecyclerView的fling过程
我们以RecyclerView为例,研究一下ListView是怎么滑动并且更新view的。
首先可以肯定的是以Choreographer为基础实现的。
一、fling过程研究
fling动作是由input事件触发的。
1.1 RecyclerView.onTouchEvent
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent e) {
if (mLayoutFrozen || mIgnoreMotionEventTillDown) {
return false;
}
// 给子view一个拦截处理input事件的机会
if (dispatchOnItemTouch(e)) {
cancelTouch();
return true;
}
if (mLayout == null) {
return false;
}
final boolean canScrollHorizontally = mLayout.canScrollHorizontally();
final boolean canScrollVertically = mLayout.canScrollVertically();
if (mVelocityTracker == null) {
mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain();
}
boolean eventAddedToVelocityTracker = false;
final MotionEvent vtev = MotionEvent.obtain(e);
final int action = e.getActionMasked();
final int actionIndex = e.getActionIndex();
if (action == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
mNestedOffsets[0] = mNestedOffsets[1] = 0;
}
vtev.offsetLocation(mNestedOffsets[0], mNestedOffsets[1]);
switch (action) {
......
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: {
// 计算速度
mVelocityTracker.addMovement(vtev);
eventAddedToVelocityTracker = true;
mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000, mMaxFlingVelocity);
final float xvel = canScrollHorizontally
? -mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity(mScrollPointerId) : 0;
final float yvel = canScrollVertically
? -mVelocityTracker.getYVelocity(mScrollPointerId) : 0;
// 速度大于0,就可以执行fling了
if (!((xvel != 0 || yvel != 0) && fling((int) xvel, (int) yvel))) {
setScrollState(SCROLL_STATE_IDLE);
}
resetTouch();
} break;
......
}
......
return true;
}
1.2 RecyclerView.fling
public boolean fling(int velocityX, int velocityY) {
if (mLayout == null) {
Log.e(TAG, "Cannot fling without a LayoutManager set. "
+ "Call setLayoutManager with a non-null argument.");
return false;
}
if (mLayoutFrozen) {
return false;
}
final boolean canScrollHorizontal = mLayout.canScrollHorizontally();
final boolean canScrollVertical = mLayout.canScrollVertically();
if (!canScrollHorizontal || Math.abs(velocityX) < mMinFlingVelocity) {
velocityX = 0;
}
if (!canScrollVertical || Math.abs(velocityY) < mMinFlingVelocity) {
velocityY = 0;
}
if (velocityX == 0 && velocityY == 0) {
// If we don't have any velocity, return false
return false;
}
// 先将这个fling事件分发给嵌套的滚动父视图
if (!dispatchNestedPreFling(velocityX, velocityY)) {
final boolean canScroll = canScrollHorizontal || canScrollVertical;
dispatchNestedFling(velocityX, velocityY, canScroll);
if (mOnFlingListener != null && mOnFlingListener.onFling(velocityX, velocityY)) {
return true;
}
if (canScroll) {
velocityX = Math.max(-mMaxFlingVelocity, Math.min(velocityX, mMaxFlingVelocity));
velocityY = Math.max(-mMaxFlingVelocity, Math.min(velocityY, mMaxFlingVelocity));
// 如果条件都符合,开始fling
mViewFlinger.fling(velocityX, velocityY);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
1.3 RecyclerView.ViewFlinger.fling
public void fling(int velocityX, int velocityY) {
setScrollState(SCROLL_STATE_SETTLING);
mLastFlingX = mLastFlingY = 0;
// 1.4 使用OverScroller处理每一帧的速度和下一帧的距离
mScroller.fling(0, 0, velocityX, velocityY,
Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE, Integer.MIN_VALUE, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
// 1.5 通过Choreographer实现动画
postOnAnimation();
}
说明一下,ViewFlinger是一个实现Runnable的类.
1.4 OverScroller.fling
public void fling(int startX, int startY, int velocityX, int velocityY,
int minX, int maxX, int minY, int maxY) {
fling(startX, startY, velocityX, velocityY, minX, maxX, minY, maxY, 0, 0);
}
public void fling(int startX, int startY, int velocityX, int velocityY,
int minX, int maxX, int minY, int maxY, int overX, int overY) {
// Continue a scroll or fling in progress
if (mFlywheel && !isFinished()) {
float oldVelocityX = mScrollerX.mCurrVelocity;
float oldVelocityY = mScrollerY.mCurrVelocity;
if (Math.signum(velocityX) == Math.signum(oldVelocityX) &&
Math.signum(velocityY) == Math.signum(oldVelocityY)) {
velocityX += oldVelocityX;
velocityY += oldVelocityY;
}
}
// 设置模式为FLING_MODE
mMode = FLING_MODE;
// 分别对X轴和Y轴做fling, mScrollerX和mScrollerY都是SplineOverScroller类型
// 当然常见的是以Y轴的滚动。这里我们看Y轴的处理
mScrollerX.fling(startX, velocityX, minX, maxX, overX);
mScrollerY.fling(startY, velocityY, minY, maxY, overY);
}
1.4.1 SplineOverScroller.fling
void fling(int start, int velocity, int min, int max, int over) {
mOver = over;
mFinished = false;
mCurrVelocity = mVelocity = velocity;
mDuration = mSplineDuration = 0;
mStartTime = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis();
mCurrentPosition = mStart = start;
if (start > max || start < min) {
startAfterEdge(start, min, max, velocity);
return;
}
// 注意这里将状态设置为SPLINE,表示是样条插值
mState = SPLINE;
double totalDistance = 0.0;
// 根据初速度计算fling的时长和距离
if (velocity != 0) {
mDuration = mSplineDuration = getSplineFlingDuration(velocity);
totalDistance = getSplineFlingDistance(velocity);
}
mSplineDistance = (int) (totalDistance * Math.signum(velocity));
mFinal = start + mSplineDistance;
// 越界处理
if (mFinal < min) {
adjustDuration(mStart, mFinal, min);
mFinal = min;
}
if (mFinal > max) {
adjustDuration(mStart, mFinal, max);
mFinal = max;
}
}
1.5 RecyclerView.ViewFlinger.postOnAnimation
void postOnAnimation() {
if (mEatRunOnAnimationRequest) {
mReSchedulePostAnimationCallback = true;
} else {
// this就是指ViewFlinger
removeCallbacks(this);
// 最终就是调用父类View的方法
RecyclerView.this.postOnAnimation(this);
}
}
1.5.1 View.postOnAnimation
public void postOnAnimation(Runnable action) {
final AttachInfo attachInfo = mAttachInfo;
if (attachInfo != null) {
// 这里就是使用Choreographer实现回调的,也就是下一帧
// 会回调ViewFlinger中的run方法,而且这里回调也是Animation类型
attachInfo.mViewRootImpl.mChoreographer.postCallback(
Choreographer.CALLBACK_ANIMATION, action, null);
} else {
// Postpone the runnable until we know
// on which thread it needs to run.
getRunQueue().post(action);
}
}
接下来,看下一帧的处理
1.6 ViewFlinger.run
@Override
public void run() {
if (mLayout == null) {
stop();
return; // no layout, cannot scroll.
}
disableRunOnAnimationRequests();
consumePendingUpdateOperations();
// keep a local reference so that if it is changed during onAnimation method, it won't
// cause unexpected behaviors
final OverScroller scroller = mScroller;
final SmoothScroller smoothScroller = mLayout.mSmoothScroller;
// 1.6.1 计算OverScroller的滚动,滚动结束返回false
if (scroller.computeScrollOffset()) {
// 根据滚动距离计算应该显示的item
final int x = scroller.getCurrX();
final int y = scroller.getCurrY();
final int dx = x - mLastFlingX;
final int dy = y - mLastFlingY;
int hresult = 0;
int vresult = 0;
mLastFlingX = x;
mLastFlingY = y;
int overscrollX = 0, overscrollY = 0;
if (mAdapter != null) {
eatRequestLayout();
onEnterLayoutOrScroll();
Trace.beginSection(TRACE_SCROLL_TAG);
if (dx != 0) {
hresult = mLayout.scrollHorizontallyBy(dx, mRecycler, mState);
overscrollX = dx - hresult;
}
if (dy != 0) {
vresult = mLayout.scrollVerticallyBy(dy, mRecycler, mState);
overscrollY = dy - vresult;
}
Trace.endSection();
repositionShadowingViews();
onExitLayoutOrScroll();
resumeRequestLayout(false);
if (smoothScroller != null && !smoothScroller.isPendingInitialRun()
&& smoothScroller.isRunning()) {
final int adapterSize = mState.getItemCount();
if (adapterSize == 0) {
smoothScroller.stop();
} else if (smoothScroller.getTargetPosition() >= adapterSize) {
smoothScroller.setTargetPosition(adapterSize - 1);
smoothScroller.onAnimation(dx - overscrollX, dy - overscrollY);
} else {
smoothScroller.onAnimation(dx - overscrollX, dy - overscrollY);
}
}
}
if (!mItemDecorations.isEmpty()) {
// 有内容则请求绘制
invalidate();
}
if (getOverScrollMode() != View.OVER_SCROLL_NEVER) {
considerReleasingGlowsOnScroll(dx, dy);
}
if (overscrollX != 0 || overscrollY != 0) {
final int vel = (int) scroller.getCurrVelocity();
int velX = 0;
if (overscrollX != x) {
velX = overscrollX < 0 ? -vel : overscrollX > 0 ? vel : 0;
}
int velY = 0;
if (overscrollY != y) {
velY = overscrollY < 0 ? -vel : overscrollY > 0 ? vel : 0;
}
if (getOverScrollMode() != View.OVER_SCROLL_NEVER) {
absorbGlows(velX, velY);
}
if ((velX != 0 || overscrollX == x || scroller.getFinalX() == 0)
&& (velY != 0 || overscrollY == y || scroller.getFinalY() == 0)) {
scroller.abortAnimation();
}
}
if (hresult != 0 || vresult != 0) {
// 分发滚动事件
dispatchOnScrolled(hresult, vresult);
}
// 这个是绘制ScollBar,也就是滚动条
if (!awakenScrollBars()) {
invalidate();
}
final boolean fullyConsumedVertical = dy != 0 && mLayout.canScrollVertically()
&& vresult == dy;
final boolean fullyConsumedHorizontal = dx != 0 && mLayout.canScrollHorizontally()
&& hresult == dx;
final boolean fullyConsumedAny = (dx == 0 && dy == 0) || fullyConsumedHorizontal
|| fullyConsumedVertical;
// 判断滚动是否结束
if (scroller.isFinished() || !fullyConsumedAny) {
setScrollState(SCROLL_STATE_IDLE); // setting state to idle will stop this.
if (ALLOW_THREAD_GAP_WORK) {
mPrefetchRegistry.clearPrefetchPositions();
}
} else {
// 未结束,发送回调,在下一个Vsync时再来一轮,直到滚动结束
postOnAnimation();
if (mGapWorker != null) {
mGapWorker.postFromTraversal(RecyclerView.this, dx, dy);
}
}
}
// call this after the onAnimation is complete not to have inconsistent callbacks etc.
if (smoothScroller != null) {
if (smoothScroller.isPendingInitialRun()) {
smoothScroller.onAnimation(0, 0);
}
if (!mReSchedulePostAnimationCallback) {
smoothScroller.stop(); //stop if it does not trigger any scroll
}
}
enableRunOnAnimationRequests();
}
1.6.1 OverScroller.computeScrollOffset
public boolean computeScrollOffset() {
if (isFinished()) {
return false;
}
// 我们在#1.4 OverScroller.fling中知道,此时是FLING_MODE中
switch (mMode) {
......
case FLING_MODE:
if (!mScrollerX.mFinished) {
if (!mScrollerX.update()) {
if (!mScrollerX.continueWhenFinished()) {
mScrollerX.finish();
}
}
}
// 判断是否已经结束
if (!mScrollerY.mFinished) {
// #1.6.1.1 处理更新,返回值表明fling是否已结束, false为已结束
// 一般正在fling中是返回true的
if (!mScrollerY.update()) {
// #1.6.1.2 处理fling的结束,结束返回false
if (!mScrollerY.continueWhenFinished()) {
// 结束fling,就是标记当前位置为mFinal,且将mFinished标记为true
mScrollerY.finish();
}
}
}
break;
}
return true;
}
1.6.1.1 SplineOverScroller.update
boolean update() {
final long time = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis();
final long currentTime = time - mStartTime;
if (currentTime == 0) {
// Skip work but report that we're still going if we have a nonzero duration.
return mDuration > 0;
}
if (currentTime > mDuration) {
return false;
}
double distance = 0.0;
switch (mState) {
case SPLINE: {
// 重点看这里的算法,不过在看这个算法之前,我们先看看
// 这个所谓的样条曲线是什么样的,以及SPLINE_POSITION数组
// 是如何生成的。见 #2.1 SplineOverScroller的初始化
final float t = (float) currentTime / mSplineDuration;
final int index = (int) (NB_SAMPLES * t);
float distanceCoef = 1.f;
float velocityCoef = 0.f;
if (index < NB_SAMPLES) {
final float t_inf = (float) index / NB_SAMPLES;
final float t_sup = (float) (index + 1) / NB_SAMPLES;
final float d_inf = SPLINE_POSITION[index];
final float d_sup = SPLINE_POSITION[index + 1];
velocityCoef = (d_sup - d_inf) / (t_sup - t_inf);
distanceCoef = d_inf + (t - t_inf) * velocityCoef;
}
distance = distanceCoef * mSplineDistance;
mCurrVelocity = velocityCoef * mSplineDistance / mSplineDuration * 1000.0f;
break;
}
......
}
mCurrentPosition = mStart + (int) Math.round(distance);
return true;
}
这里我们暂时不看算法内容,在第二节中详细研究。
只要知道这里根据样条插值更新了当前时间对应的距离位置即可。
1.6.1.2 SplineOverScroller.continueWhenFinished
boolean continueWhenFinished() {
switch (mState) {
case SPLINE:
// 正常来讲,mDuration 是等于 mSplineDuration 的
// 如果小于,则说明达到ListView的边界了,需要调整各个参数
if (mDuration < mSplineDuration) {
// If the animation was clamped, we reached the edge
mCurrentPosition = mStart = mFinal;
// TODO Better compute speed when edge was reached
mVelocity = (int) mCurrVelocity;
mDeceleration = getDeceleration(mVelocity);
mStartTime += mDuration;
onEdgeReached();
} else {
// 正常结束
return false;
}
break;
......
}
update();
return true;
}
至此,ListView的滚动流程已经结束。总而言之,就是利用Choreographer的animation回调进行逐帧处理。
接下来,我们研究下传说中的滑动曲线。
二. 样条曲线的核心算法
我们知道,Android中ListView的滑动曲线是一条平滑的曲线,使用的是样条插值方式实现。
样条值是存贮在SplineOverScroller中的, 这个类是一个静态类。
2.1 SplineOverScoller的初始化
在静态区有如下的初始化代码块,就是用来初始化样条曲线的插值的
static {
float x_min = 0.0f;
float y_min = 0.0f;
for (int i = 0; i < NB_SAMPLES; i++) {
final float alpha = (float) i / NB_SAMPLES;
float x_max = 1.0f;
float x, tx, coef;
while (true) {
x = x_min + (x_max - x_min) / 2.0f;
coef = 3.0f * x * (1.0f - x);
tx = coef * ((1.0f - x) * P1 + x * P2) + x * x * x;
if (Math.abs(tx - alpha) < 1E-5) break;
if (tx > alpha) x_max = x;
else x_min = x;
}
SPLINE_POSITION[i] = coef * ((1.0f - x) * START_TENSION + x) + x * x * x;
float y_max = 1.0f;
float y, dy;
while (true) {
y = y_min + (y_max - y_min) / 2.0f;
coef = 3.0f * y * (1.0f - y);
dy = coef * ((1.0f - y) * START_TENSION + y) + y * y * y;
if (Math.abs(dy - alpha) < 1E-5) break;
if (dy > alpha) y_max = y;
else y_min = y;
}
SPLINE_TIME[i] = coef * ((1.0f - y) * P1 + y * P2) + y * y * y;
}
SPLINE_POSITION[NB_SAMPLES] = SPLINE_TIME[NB_SAMPLES] = 1.0f;
}
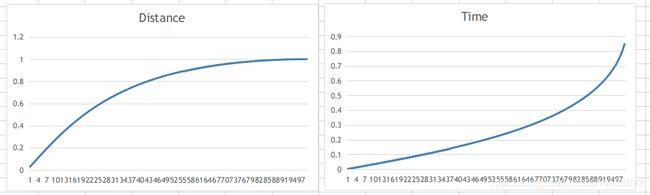
算法的具体实现就不分析,我们看看最终的曲线呈现:
这里就有个疑问了,这里的样条插值只有NB_SAMPLES(100)个。那么这里是如何实现对不同的时长的
滑动也能使用同一条滑动曲线呢?我们回到计算当前帧下的滑动位置方法里,也就是SplineOverScroller.update中。
2.2 SplineOverScroller.update
boolean update() {
// 获取当前时间戳,计算已经滑动的时长
final long time = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis();
final long currentTime = time - mStartTime;
......
double distance = 0.0;
switch (mState) {
case SPLINE: {
// 这个t就是当前滑动的时长所占总滑动时长的百分比
final float t = (float) currentTime / mSplineDuration;
// 注意这里的是int,也就是向下取整
final int index = (int) (NB_SAMPLES * t);
float distanceCoef = 1.f;
float velocityCoef = 0.f;
// 防止越界
if (index < NB_SAMPLES) {
// 计算当前时间对应的前后插值的index
final float t_inf = (float) index / NB_SAMPLES;
final float t_sup = (float) (index + 1) / NB_SAMPLES;
// 拿到最近的前后插值
final float d_inf = SPLINE_POSITION[index];
final float d_sup = SPLINE_POSITION[index + 1];
// 根据比例算的当前时间对应的速度,然后算得当前的滑动距离
velocityCoef = (d_sup - d_inf) / (t_sup - t_inf);
distanceCoef = d_inf + (t - t_inf) * velocityCoef;
}
distance = distanceCoef * mSplineDistance;
mCurrVelocity = velocityCoef * mSplineDistance / mSplineDuration * 1000.0f;
break;
}
......
}
// 更新当前位置
mCurrentPosition = mStart + (int) Math.round(distance);
return true;
}
哦吼,原来滑动曲线并不是真正的曲线,而是由99条线段组成的。
但是由于用户实际滑动的时间一般在1s~5s之间,在60Hz下并不影响体验效果。
如果是高帧率的情况,应该还是有调优的空间的。