SpringMVC源码分析--整体结构和容器组件的初始化(一)
整体结构如图:
一、解析aware和capable
1. XXXAware 在Spring里表示对XXX可以感知,通俗点解释就是,如果某个类里面想要使用spring的一些东西,就可以通过实现XXXAware接口告诉spring,spring看到后就给你送过来,而接受的方式就是通过实现接口唯一的方法setXXX。
例如:有一个类想要使用ApplicationContext接口,然后实现ApplicationContextAware接口,并set,spring就会把applicationContext传给我们。
2. XXXCapable,表示有什么的能力,这里的EnvironmentCapable唯一的方法是getEnvironment,当spring需要的时候,直接提供给spring
二、Environment
在HttpServletBean中的Environment使用的是StandardServletEnvironment,这里封装了ServletContext,ServletConfig,JndiProperty,系统环境变量和系统属性。可以通过一个Controller类实现implements EnvironmentWare接口(记得set这个接口),debug调试查看:如下
@Controller
public class HelloController implements EnvironmentAware {
private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(HelloController.class);
private Environment environment;
@RequestMapping("/")
public String Head(){
return "index.html";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/index.action",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String index(Model model){
logger.info("====正在运行index页面===="); //设置断点
model.addAttribute("msg","欢迎使用Springmvc");
return "go.jsp";
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment=environment;
}
}debug后,查看environment的值,在propertySources可以看到有
1> ServerCofigPropertySource -包含StandardWrapperFacade,封装的是ServletConfig,web.xml定义的contextConfigLocation可以在config下看到,还有相关的参数
2> ServerContextPropertySource --保存的是ServletContext
3>JndiPropertySource --保存的是Jndi
4> MapPropertySource --存放的是我们使用的虚拟机属性,如java的版本,操作系统,用户主目录,临时目录,Catalina的目录等内容
5>SystemEnvironmentPropertySource --存放的是环境变量,比如我们设置的JAVA_HOME,Path等属性
三、HttpServletBean类
它的init方法源码如下,这个类主要是获取配置信息,并设置到DispatcherServlet中,并提供模板方法initServletBean供子类复写。
BeanWrapper使用方式:
这个类是Spring提供的一个用来操作JavaBean属性的工具,使用它可以直接修改一个对象的属性。例如新建的User实体类,
User user = new User()
BeanWrapper bw = PropertyAccessorFactory.forBeanPropertyAccess(user)
bw.setPropertyValue("userName",“visonws”);
System.out.println(user.getUserName()) ; //输出visonws比如下面这段配置,传递了contextConfigLocation参数,之后构造BeanWrapper,这里使用BeanWrapper,有2个理由:1. contextConfigLocation属性在FrameworkServlet中定义,HttpServletBean中未定义 2. 利用Spring的注入特性,只需要调用setPropertyValues方法就可将contextConfigLocation属性设置到对应实例中,也就是以依赖注入的方式初始化属性。
然后设置DispatcherServlet中的contextConfigLocation属性(FrameworkServlet中定义)为web.xml中读取的contextConfigLocation参数,该参数用于构造SpringMVC容器上下文,这里只需要spring-mvc.xml就够了。
dispatcher
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
1
contextConfigLocation
classpath:spring/spring-mvc.xml
dispatcher
/
四、FramewordServlet类
这个类继承HttpServletBean,所以他的入口方法是是复写父类的initServletBean方法,代码如下;
1. 核心代码是this.webApplicationContext = this.initWebApplicationContext();和
this.initFrameworkServlet();
1> initFramwordServlet方法是模板,子类可以覆盖做一些初始化方法
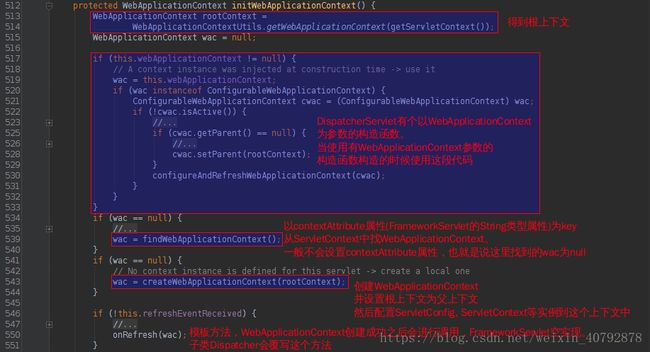
2> initWebApplicationContext方法源代码如下,一般都是第三种方式createWebApplicationContext(rootContext)创建上下文:
1.2 intiWebApplicationContext方法主要做了三件事:
1>:获取spring的根容器rootContext.
2>:设置webApplicationContext并根据情况调用onRefresh方法
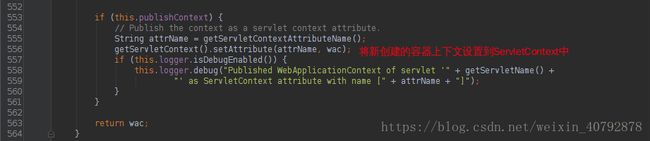
3>:将webApplicationContext通过键值对的形式设置到ServletContext中,设置的key是
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE = WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT";这里的根上下文是web.xml中配置的ContextLoaderListener监听器中根据contextConfigLocation路径生成的上下文。这里的配置属于全局的配置,包含DAO,Service等其他实体的配置信息,属于全局的。
contextConfigLocation
classpath:spring/bean-*.xml
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
总体的上下文环境关系图 可以看下面:
spring上下文容器配置后,初始化了什么?
既然,ServletContext是由Servlet容器初始化的,那spring的ContextLoaderListener又做了什么初始化呢?
1、servlet容器启动,为应用创建一个“全局上下文环境”:ServletContext
2、容器调用web.xml中配置的contextLoaderListener,初始化WebApplicationContext上下文环境(即IOC容器),加载context-param指定的配置文件信息到IOC容器中。WebApplicationContext在ServletContext中以键值对的形式保存
3、容器初始化web.xml中配置的servlet,为其初始化自己的上下文信息servletContext,并加载其设置的配置信息到该上下文中。将WebApplicationContext设置为它的父容器。
4、此后的所有servlet的初始化都按照3步中方式创建,初始化自己的上下文环境,将WebApplicationContext设置为自己的父上下文环境。
对于作用范围而言,在DispatcherServlet中可以引用由ContextLoaderListener所创建的ApplicationContext中的内容,而反过来不行。
当Spring在执行ApplicationContext的getBean时,如果在自己context中找不到对应的bean,则会在父ApplicationContext中去找。这也解释了为什么我们可以在DispatcherServlet中获取到由ContextLoaderListener对应的ApplicationContext中的bean。
五、DispatchServlet 类
他的创建过程主要是对九大组件的初始化。
在FrameworkServlet类中initWebApplicationContext调用了onRefresh 方法,Dispatcher类继承FrameworkServlet类,在DispatcherServlet类中的onRefresh方法中调用了 this.initStrategies(context);这个方法代码如下:
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initStrategies(context);
}
protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {
this.initMultipartResolver(context); //这个没有默认实现方法
this.initLocaleResolver(context);
this.initThemeResolver(context);
this.initHandlerMappings(context);
this.initHandlerAdapters(context);
this.initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);
this.initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);
this.initViewResolvers(context);
this.initFlashMapManager(context);
}从上面的初始化策略可以看到,这里初始化了九个组件,通过初始化方法层层查询,例如:initLocaleResoler(context),这里的context是WebApplicationContext,代码:
private void initLocaleResolver(ApplicationContext context) {
try {
this.localeResolver = (LocaleResolver)context.getBean("localeResolver", LocaleResolver.class);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Using LocaleResolver [" + this.localeResolver + "]");
}
} catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException var3) {
this.localeResolver = (LocaleResolver)this.getDefaultStrategy(context, LocaleResolver.class);
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Unable to locate LocaleResolver with name 'localeResolver': using default [" + this.localeResolver + "]");
}
}
}先通过localeResolver从容器里面找,如果没有找到,则采用默认的localResolver.,方法是getDefaultStrategy,通过层层查询,最后调用的是在DispatcherServlet同一个目录下的一个DispatchServlet.properties文件,如下所示:
# Default implementation classes for DispatcherServlet's strategy interfaces.
# Used as fallback when no matching beans are found in the DispatcherServlet context.
# Not meant to be customized by application developers.//这里是定制开发,不可对外更改的
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolver
// 带"/"的是多个默认配置Handler类
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter
org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslator
//这个也可以有多个,这里默认只配置了一个而已
org.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver
org.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager这里定义了八个默认组件,不包含MultipartResolver文件上传组件。有些还配置了多个,注意的是:这里的默认配置并不是最优配置,只是在没有配置的时候,可以有一个默认值。
总结:HttpServletBean直接继承HttpServlet,作用是将Servlet的配置的设置到相应的属性,FrameworkServlet初始化WebApplicationContext,DispatcherServlet初始化自身的9个组件。参考:
http://www.cnblogs.com/fangjian0423/p/springMVC-dispatcherServlet.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/brolanda/p/4265597.html