- 机器学习与深度学习间关系与区别
ℒℴѵℯ心·动ꦿ໊ོ꫞
人工智能学习深度学习python
一、机器学习概述定义机器学习(MachineLearning,ML)是一种通过数据驱动的方法,利用统计学和计算算法来训练模型,使计算机能够从数据中学习并自动进行预测或决策。机器学习通过分析大量数据样本,识别其中的模式和规律,从而对新的数据进行判断。其核心在于通过训练过程,让模型不断优化和提升其预测准确性。主要类型1.监督学习(SupervisedLearning)监督学习是指在训练数据集中包含输入
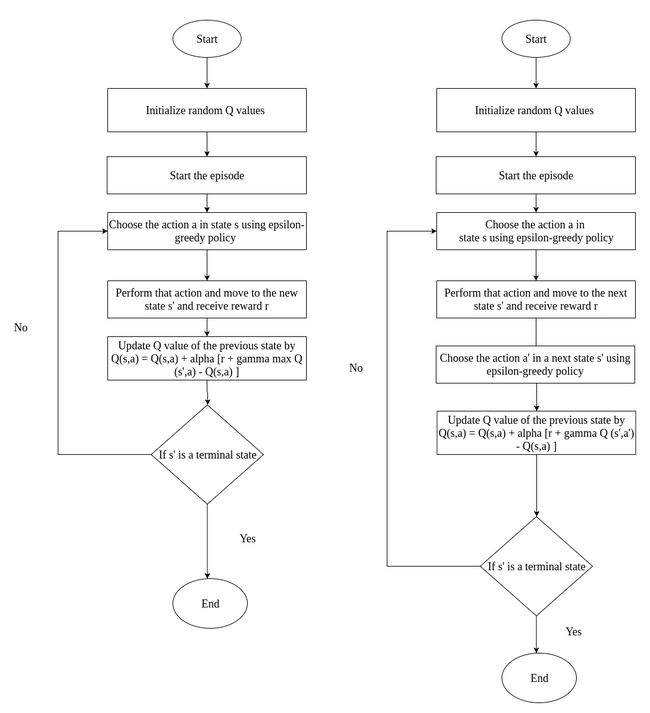
- 深度 Qlearning:在直播推荐系统中的应用
AGI通用人工智能之禅
程序员提升自我硅基计算碳基计算认知计算生物计算深度学习神经网络大数据AIGCAGILLMJavaPython架构设计Agent程序员实现财富自由
深度Q-learning:在直播推荐系统中的应用关键词:深度Q-learning,强化学习,直播推荐系统,个性化推荐1.背景介绍1.1问题的由来随着互联网技术的飞速发展,直播平台如雨后春笋般涌现。面对海量的直播内容,用户很难快速找到自己感兴趣的内容。因此,个性化推荐系统在直播平台中扮演着越来越重要的角色。1.2研究现状目前,主流的个性化推荐算法包括协同过滤、基于内容的推荐等。这些方法在一定程度上缓
- 云服务业界动态简报-20180128
Captain7
一、青云青云QingCloud推出深度学习平台DeepLearningonQingCloud,包含了主流的深度学习框架及数据科学工具包,通过QingCloudAppCenter一键部署交付,可以让算法工程师和数据科学家快速构建深度学习开发环境,将更多的精力放在模型和算法调优。二、腾讯云1.腾讯云正式发布腾讯专有云TCE(TencentCloudEnterprise)矩阵,涵盖企业版、大数据版、AI
- 机器学习VS深度学习
nfgo
机器学习
机器学习(MachineLearning,ML)和深度学习(DeepLearning,DL)是人工智能(AI)的两个子领域,它们有许多相似之处,但在技术实现和应用范围上也有显著区别。下面从几个方面对两者进行区分:1.概念层面机器学习:是让计算机通过算法从数据中自动学习和改进的技术。它依赖于手动设计的特征和数学模型来进行学习,常用的模型有决策树、支持向量机、线性回归等。深度学习:是机器学习的一个子领
- ResNet的半监督和半弱监督模型
Valar_Morghulis
Billion-scalesemi-supervisedlearningforimageclassificationhttps://arxiv.org/pdf/1905.00546.pdfhttps://github.com/facebookresearch/semi-supervised-ImageNet1K-models/权重在timm中也有:https://hub.fastgit.org/r
- 联邦学习 Federated learning Google I/O‘19 笔记
努力搬砖的星期五
笔记联邦学习机器学习机器学习tensorflow
FederatedLearning:MachineLearningonDecentralizeddatahttps://www.youtube.com/watch?v=89BGjQYA0uE文章目录FederatedLearning:MachineLearningonDecentralizeddata1.DecentralizeddataEdgedevicesGboard:mobilekeyboa
- PCL 怎样可视化深度图像
LeonDL168
PCL计算机视觉人工智能视觉检测图像处理算法
本小节讲解如何可视化深度图像的两种方法,在3D视窗中以点云形式进行可视化(深度图像来源于点云),另一种是,将深度值映射为颜色,从而以彩色图像方式可视化深度图像。代码首先,在PCL(PointCloudLearning)中国协助发行的书提供光盘的第7章例2文件夹中,打开名为range_image_visualization.cpp的代码文件,同文件夹下可以找到相关的测试点云文件room_scan1.
- Awesome TensorFlow
weixin_30594001
人工智能移动开发大数据
AwesomeTensorFlowAcuratedlistofawesomeTensorFlowexperiments,libraries,andprojects.Inspiredbyawesome-machine-learning.WhatisTensorFlow?TensorFlowisanopensourcesoftwarelibraryfornumericalcomputationusin
- 【ShuQiHere】探索人工智能核心:机器学习的奥秘
ShuQiHere
人工智能机器学习
【ShuQiHere】什么是机器学习?机器学习(MachineLearning,ML)是人工智能(ArtificialIntelligence,AI)中最关键的组成部分之一。它使得计算机不仅能够处理数据,还能从数据中学习,从而做出预测和决策。无论是语音识别、自动驾驶还是推荐系统,背后都依赖于机器学习模型。机器学习与传统的编程不同,它不再依赖于人类编写的固定规则,而是通过数据自我改进模型,从而更灵活
- 综述论文“A Survey of Zero-Shot Learning: Settings, Methods, and Applications”
硅谷秋水
机器学习机器学习神经网络深度学习
该零样本学习综述,发表于ACMTrans.Intell.Syst.Technol.10,2,Article13(January2019)摘要:大多数机器学习方法着重于对已经在训练中看到其类别的实例进行分类。实际上,许多应用程序需要对实例进行分类,而这些实例的类以前没有见过。零样本学习(Zero-ShotLearning)是一种强大而有前途的学习范例,其中训练实例涵盖的类别与想分类的类别是不相交的。
- 机器学习 VS 表示学习 VS 深度学习
Efred.D
人工智能机器学习深度学习人工智能
文章目录前言一、机器学习是什么?二、表示学习三、深度学习总结前言本文主要阐述机器学习,表示学习和深度学习的原理和区别.一、机器学习是什么?机器学习(machinelearning),是从有限的数据集中学习到一定的规律,再把学到的规律应用到一些相似的样本集中做预测.机器学习的历史可以追溯到20世纪40年代McCulloch提出的人工神经元网络,目前学界大致把机器学习分为传统机器学习和机器学习两个类别
- 端到端的自动驾驶论文与代码整理
大别山伧父
自动驾驶
LearningbyCheatinggithubcodearxivpaperconferenceonrobotlearning最新进展(May2021)Checkoutourlatestfollow-upwork:WorldonRails(2020)Checkoutoursubmissiontothe2020CARLAChallenge!pass
- Lt-8 Multithreading
yanlingyun0210
java
IntendedLearningOutcomesTounderstandtheconceptofconcurrency.Tounderstandthedifferenceofaprocessandathread.TodefineathreadusingtheThreadclassandRunnableinterface.TocontrolthreadswithvariousThreadmethod
- 如何使用Pytorch-Metric-Learning?
鱼儿也有烦恼
PyTorchpytorch
文章目录如何使用Pytorch-Metric-Learning?1.Pytorch-Metric-Learning库9个模块的功能1.1Sampler模块1.2Miner模块1.3Loss模块1.4Reducer模块1.5Distance模块1.6Regularizer模块1.7Trainer模块1.8Tester模块1.9Utils模块2.如何使用PyTorchMetricLearning库中的
- 推荐开源项目:PyTorch-Metric-Learning
潘惟妍
推荐开源项目:PyTorch-Metric-Learningpytorch-metric-learningTheeasiestwaytousedeepmetriclearninginyourapplication.Modular,flexible,andextensible.WritteninPyTorch.项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/py/pytorc
- 推荐:FastAPI驱动的稳定扩散LLMs演示项目
褚知茉Jade
推荐:FastAPI驱动的稳定扩散LLMs演示项目FastAPI-for-Machine-Learning-Live-DemoThisrepositorycontainsthefilestobuildyourveryownAIimagegenerationwebapplication!OutlinedarethecorecomponentsoftheFastAPIwebframework,anda
- 【python】【Ray的概述】
资源存储库
python开发语言
Overview概述Rayisanopen-sourceunifiedframeworkforscalingAIandPythonapplicationslikemachinelearning.Itprovidesthecomputelayerforparallelprocessingsothatyoudon’tneedtobeadistributedsystemsexpert.Rayminimi
- 什么是监督学习(Supervised Learning)
救救孩子把
AIAI学习
一、监督学习概述监督学习(SupervisedLearning)是一种极具威力的机器学习方法,能够训练算法以识别数据中的模式,并据此进行精准的预测或分类。借助已有的标记数据,监督学习模型学会了从输入到输出的映射关系,进而在各类实际问题中实现自动化决策。无论是医疗诊断、金融市场分析、客户行为预测,还是提升生产效率以及个性化推荐系统等领域,监督学习都彰显出巨大的潜力与价值。随着技术的持续进步,监督学习
- 使用3DUNet训练自己的数据集(pytorch)— 医疗影像分割
编程日记✧
智能医疗pytorch人工智能python计算机视觉图像处理深度学习健康医疗
代码:lee-zq/3DUNet-Pytorch:3DUNetimplementedwithpytorch(github.com)文章<cicek16miccai.pdf(uni-freiburg.de)3DU-Net:LearningDenseVolumetricSegmentation
- 探索任务的隐秘世界:推荐Task2Vec
邓越浪Henry
探索任务的隐秘世界:推荐Task2Vecaws-cv-task2vecOfficialcodeforthepaper"Task2Vec:TaskEmbeddingforMeta-Learning"(https://arxiv.org/abs/1902.03545,ICCV2019)项目地址:https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/aw/aws-cv-task2vec在机器学习
- 论文阅读笔记: DINOv2: Learning Robust Visual Features without Supervision
小夏refresh
论文计算机视觉深度学习论文阅读笔记深度学习计算机视觉人工智能
DINOv2:LearningRobustVisualFeatureswithoutSupervision论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2304.07193代码地址:https://github.com/facebookresearch/dinov2摘要大量数据上的预训练模型在NLP方面取得突破,为计算机视觉中的类似基础模型开辟了道路。这些模型可以通过生成通用视觉特征(即无
- linux查看jupyter运行,在Linux服务器上运行Jupyter notebook server教程
天启大烁哥
在Linux服务器上运行Jupyternotebookserver教程很多deeplearning教程都推荐在jupyternotebook运行python代码,方便及时交互。但只在本地运行没有GPU环境,虽然googlecolab是个好办法,但发现保存模型后在云端找不到模型文件,且需要合理上网才能访问。于是想给实验室的服务器配置jupyternotebook,供本机远程访问。踩了不少坑,码一下教
- 如何在DPDK中实现协议解析?
编码小哥
dpdk架构
在DPDK中实现协议解析涉及几个步骤,包括初始化环境、配置网卡、接收数据包、解析数据包并处理数据包。下面将详细介绍这些步骤以及如何在DPDK中实现基本的协议解析。初始化DPDK环境首先,你需要初始化DPDK环境,加载EAL(EthernetAddressLearning)库,并设置好内存池、环形缓冲区等。#include#include#includeintmain(intargc,char**a
- Deep learning for Computer Vision with Python(1)从零开始入门计算机视觉
Hazelyu27
计算机视觉大数据计算机视觉深度学习
本书的内容分成三个部分:1.初始阶段初始阶段学习:机器学习、神经网络、卷积神经网络、建立数据集。2.实践阶段实践阶段:深入学习深度学习,理解先进技术,发现最佳实践方式。3.图像网络阶段完成计算机视觉领域的经验积累。使用大规模数据集和真实图片案例作为数据集,包括年龄和性别预测,交通工具模型识别。本书提供了对应网站:http://pyimg.co/fnkxk本文介绍前两章内容:基本介绍和深度学习简介。
- 使用matlab的热门问题
七十二五
值得关注matlab开发语言青少年编程算法经验分享
MATLAB广泛应用于科学计算、数据分析、信号处理、图像处理、机器学习等多个领域,因此热门问题也涵盖了这些方面。以下是一些可能被认为当前最热门的MATLAB问题:深度学习与神经网络:如何使用MATLAB的深度学习工具箱(DeepLearningToolbox)来构建和训练神经网络?如何利用MATLAB进行图像识别、语音识别或自然语言处理等深度学习应用?数据分析与可视化:如何使用MATLAB进行大数
- COI实验室技能:图像到图像的深度学习开发框架(pytorch版)
山颠海涯
深度学习pytorch人工智能
Basicdeeplearningframeworkforimage-to-image这个开发框架旨在帮助科研人员快速地实现图像到图像之间的模型开发。github连接:https://github.com/SituLab/Basic-deep-learning-framework-for-image-to-image目录1模型开发1-1克隆项目到本地1-2深度学习开发2环境配置2-1安装conda
- 2021-03-31 每日打卡
来多喜
昨日完成情况:1.6k散步,❌帕梅拉(我好懒)2.思维导图,statistical和machinelearning,先快速看一遍中文版,然后细看英文版.太多了,感觉在面试前看不完。决定集中精力讲清楚简历的内容。3.工作kki+myhabeats+handover。kki可以制作dataflow了,有了ga和publihser数据。myhabeatsremarketingaudience遇到困难。感
- 强化学习分类
0penuel0
Model-free:Qlearning,Sarsa,PolicyGradientsModel-based:能通过想象来预判断接下来将要发生的所有情况.然后选择这些想象情况中最好的那种基于概率:PolicyGradients基于价值:Qlearning,Sarsa两者融合:Actor-Critic回合更新:Monte-carlolearning,基础版的policygradients单步更新:Ql
- 机器学习100天-Day2503 Tensorboard 训练数据可视化(线性回归)
我的昵称违规了
首页.jpg源代码来自莫烦python(https://morvanzhou.github.io/tutorials/machine-learning/tensorflow/4-1-tensorboard1/)今日重点读懂教程中代码,手动重写一遍,在浏览器中获取到训练数据Tensorboard是一个神经网络可视化工具,通过使用本地服务器在浏览器上查看神经网络训练日志,生成相应的可是画图,帮助炼丹师
- 元学习(meta learning)(一)
前行居士
学习人工智能神经网络深度学习机器学习元学习
元学习从字面的意思就是“学习”的“学习”,也就是学习如何学习。大部分的深度学习就是在不断的调整超参数,或者在决定网络架构,改变学习率等等。实际上没有什么好方法来调这些超参,今天工业界最常拿来解决调整超参数的方法是买很多张GPU,然后一次训练多个模型,有的训练不起来、训练效果比较差的话就输入掉,最后只看那些可以训练的比较好的模型会得到什么样的性能。所以在业界做实验的时候往往就是一次开几张GPU,这些
- SAX解析xml文件
小猪猪08
xml
1.创建SAXParserFactory实例
2.通过SAXParserFactory对象获取SAXParser实例
3.创建一个类SAXParserHander继续DefaultHandler,并且实例化这个类
4.SAXParser实例的parse来获取文件
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
- 为什么mysql里的ibdata1文件不断的增长?
brotherlamp
linuxlinux运维linux资料linux视频linux运维自学
我们在 Percona 支持栏目经常收到关于 MySQL 的 ibdata1 文件的这个问题。
当监控服务器发送一个关于 MySQL 服务器存储的报警时,恐慌就开始了 —— 就是说磁盘快要满了。
一番调查后你意识到大多数地盘空间被 InnoDB 的共享表空间 ibdata1 使用。而你已经启用了 innodbfileper_table,所以问题是:
ibdata1存了什么?
当你启用了 i
- Quartz-quartz.properties配置
eksliang
quartz
其实Quartz JAR文件的org.quartz包下就包含了一个quartz.properties属性配置文件并提供了默认设置。如果需要调整默认配置,可以在类路径下建立一个新的quartz.properties,它将自动被Quartz加载并覆盖默认的设置。
下面是这些默认值的解释
#-----集群的配置
org.quartz.scheduler.instanceName =
- informatica session的使用
18289753290
workflowsessionlogInformatica
如果希望workflow存储最近20次的log,在session里的Config Object设置,log options做配置,save session log :sessions run ;savesessio log for these runs:20
session下面的source 里面有个tracing
- Scrapy抓取网页时出现CRC check failed 0x471e6e9a != 0x7c07b839L的错误
酷的飞上天空
scrapy
Scrapy版本0.14.4
出现问题现象:
ERROR: Error downloading <GET http://xxxxx CRC check failed
解决方法
1.设置网络请求时的header中的属性'Accept-Encoding': '*;q=0'
明确表示不支持任何形式的压缩格式,避免程序的解压
- java Swing小集锦
永夜-极光
java swing
1.关闭窗体弹出确认对话框
1.1 this.setDefaultCloseOperation (JFrame.DO_NOTHING_ON_CLOSE);
1.2
this.addWindowListener (
new WindowAdapter () {
public void windo
- 强制删除.svn文件夹
随便小屋
java
在windows上,从别处复制的项目中可能带有.svn文件夹,手动删除太麻烦,并且每个文件夹下都有。所以写了个程序进行删除。因为.svn文件夹在windows上是只读的,所以用File中的delete()和deleteOnExist()方法都不能将其删除,所以只能采用windows命令方式进行删除
- GET和POST有什么区别?及为什么网上的多数答案都是错的。
aijuans
get post
如果有人问你,GET和POST,有什么区别?你会如何回答? 我的经历
前几天有人问我这个问题。我说GET是用于获取数据的,POST,一般用于将数据发给服务器之用。
这个答案好像并不是他想要的。于是他继续追问有没有别的区别?我说这就是个名字而已,如果服务器支持,他完全可以把G
- 谈谈新浪微博背后的那些算法
aoyouzi
谈谈新浪微博背后的那些算法
本文对微博中常见的问题的对应算法进行了简单的介绍,在实际应用中的算法比介绍的要复杂的多。当然,本文覆盖的主题并不全,比如好友推荐、热点跟踪等就没有涉及到。但古人云“窥一斑而见全豹”,希望本文的介绍能帮助大家更好的理解微博这样的社交网络应用。
微博是一个很多人都在用的社交应用。天天刷微博的人每天都会进行着这样几个操作:原创、转发、回复、阅读、关注、@等。其中,前四个是针对短博文,最后的关注和@则针
- Connection reset 连接被重置的解决方法
百合不是茶
java字符流连接被重置
流是java的核心部分,,昨天在做android服务器连接服务器的时候出了问题,就将代码放到java中执行,结果还是一样连接被重置
被重置的代码如下;
客户端代码;
package 通信软件服务器;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.O
- web.xml配置详解之filter
bijian1013
javaweb.xmlfilter
一.定义
<filter>
<filter-name>encodingfilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>com.my.app.EncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding<
- Heritrix
Bill_chen
多线程xml算法制造配置管理
作为纯Java语言开发的、功能强大的网络爬虫Heritrix,其功能极其强大,且扩展性良好,深受热爱搜索技术的盆友们的喜爱,但它配置较为复杂,且源码不好理解,最近又使劲看了下,结合自己的学习和理解,跟大家分享Heritrix的点点滴滴。
Heritrix的下载(http://sourceforge.net/projects/archive-crawler/)安装、配置,就不罗嗦了,可以自己找找资
- 【Zookeeper】FAQ
bit1129
zookeeper
1.脱离IDE,运行简单的Java客户端程序
#ZkClient是简单的Zookeeper~$ java -cp "./:zookeeper-3.4.6.jar:./lib/*" ZKClient
1. Zookeeper是的Watcher回调是同步操作,需要添加异步处理的代码
2. 如果Zookeeper集群跨越多个机房,那么Leader/
- The user specified as a definer ('aaa'@'localhost') does not exist
白糖_
localhost
今天遇到一个客户BUG,当前的jdbc连接用户是root,然后部分删除操作都会报下面这个错误:The user specified as a definer ('aaa'@'localhost') does not exist
最后找原因发现删除操作做了触发器,而触发器里面有这样一句
/*!50017 DEFINER = ''aaa@'localhost' */
原来最初
- javascript中showModelDialog刷新父页面
bozch
JavaScript刷新父页面showModalDialog
在页面中使用showModalDialog打开模式子页面窗口的时候,如果想在子页面中操作父页面中的某个节点,可以通过如下的进行:
window.showModalDialog('url',self,‘status...’); // 首先中间参数使用self
在子页面使用w
- 编程之美-买书折扣
bylijinnan
编程之美
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BookDiscount {
/**编程之美 买书折扣
书上的贪心算法的分析很有意思,我看了半天看不懂,结果作者说,贪心算法在这个问题上是不适用的。。
下面用动态规划实现。
哈利波特这本书一共有五卷,每卷都是8欧元,如果读者一次购买不同的两卷可扣除5%的折扣,三卷10%,四卷20%,五卷
- 关于struts2.3.4项目跨站执行脚本以及远程执行漏洞修复概要
chenbowen00
strutsWEB安全
因为近期负责的几个银行系统软件,需要交付客户,因此客户专门请了安全公司对系统进行了安全评测,结果发现了诸如跨站执行脚本,远程执行漏洞以及弱口令等问题。
下面记录下本次解决的过程以便后续
1、首先从最简单的开始处理,服务器的弱口令问题,首先根据安全工具提供的测试描述中发现应用服务器中存在一个匿名用户,默认是不需要密码的,经过分析发现服务器使用了FTP协议,
而使用ftp协议默认会产生一个匿名用
- [电力与暖气]煤炭燃烧与电力加温
comsci
在宇宙中,用贝塔射线观测地球某个部分,看上去,好像一个个马蜂窝,又像珊瑚礁一样,原来是某个国家的采煤区.....
不过,这个采煤区的煤炭看来是要用完了.....那么依赖将起燃烧并取暖的城市,在极度严寒的季节中...该怎么办呢?
&nbs
- oracle O7_DICTIONARY_ACCESSIBILITY参数
daizj
oracle
O7_DICTIONARY_ACCESSIBILITY参数控制对数据字典的访问.设置为true,如果用户被授予了如select any table等any table权限,用户即使不是dba或sysdba用户也可以访问数据字典.在9i及以上版本默认为false,8i及以前版本默认为true.如果设置为true就可能会带来安全上的一些问题.这也就为什么O7_DICTIONARY_ACCESSIBIL
- 比较全面的MySQL优化参考
dengkane
mysql
本文整理了一些MySQL的通用优化方法,做个简单的总结分享,旨在帮助那些没有专职MySQL DBA的企业做好基本的优化工作,至于具体的SQL优化,大部分通过加适当的索引即可达到效果,更复杂的就需要具体分析了,可以参考本站的一些优化案例或者联系我,下方有我的联系方式。这是上篇。
1、硬件层相关优化
1.1、CPU相关
在服务器的BIOS设置中,可
- C语言homework2,有一个逆序打印数字的小算法
dcj3sjt126com
c
#h1#
0、完成课堂例子
1、将一个四位数逆序打印
1234 ==> 4321
实现方法一:
# include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int i = 1234;
int one = i%10;
int two = i / 10 % 10;
int three = i / 100 % 10;
- apacheBench对网站进行压力测试
dcj3sjt126com
apachebench
ab 的全称是 ApacheBench , 是 Apache 附带的一个小工具 , 专门用于 HTTP Server 的 benchmark testing , 可以同时模拟多个并发请求。前段时间看到公司的开发人员也在用它作一些测试,看起来也不错,很简单,也很容易使用,所以今天花一点时间看了一下。
通过下面的一个简单的例子和注释,相信大家可以更容易理解这个工具的使用。
- 2种办法让HashMap线程安全
flyfoxs
javajdkjni
多线程之--2种办法让HashMap线程安全
多线程之--synchronized 和reentrantlock的优缺点
多线程之--2种JAVA乐观锁的比较( NonfairSync VS. FairSync)
HashMap不是线程安全的,往往在写程序时需要通过一些方法来回避.其实JDK原生的提供了2种方法让HashMap支持线程安全.
- Spring Security(04)——认证简介
234390216
Spring Security认证过程
认证简介
目录
1.1 认证过程
1.2 Web应用的认证过程
1.2.1 ExceptionTranslationFilter
1.2.2 在request之间共享SecurityContext
1
- Java 位运算
Javahuhui
java位运算
// 左移( << ) 低位补0
// 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0110 然后左移2位后,低位补0:
// 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0001 1000
System.out.println(6 << 2);// 运行结果是24
// 右移( >> ) 高位补"
- mysql免安装版配置
ldzyz007
mysql
1、my-small.ini是为了小型数据库而设计的。不应该把这个模型用于含有一些常用项目的数据库。
2、my-medium.ini是为中等规模的数据库而设计的。如果你正在企业中使用RHEL,可能会比这个操作系统的最小RAM需求(256MB)明显多得多的物理内存。由此可见,如果有那么多RAM内存可以使用,自然可以在同一台机器上运行其它服务。
3、my-large.ini是为专用于一个SQL数据
- MFC和ado数据库使用时遇到的问题
你不认识的休道人
sqlC++mfc
===================================================================
第一个
===================================================================
try{
CString sql;
sql.Format("select * from p
- 表单重复提交Double Submits
rensanning
double
可能发生的场景:
*多次点击提交按钮
*刷新页面
*点击浏览器回退按钮
*直接访问收藏夹中的地址
*重复发送HTTP请求(Ajax)
(1)点击按钮后disable该按钮一会儿,这样能避免急躁的用户频繁点击按钮。
这种方法确实有些粗暴,友好一点的可以把按钮的文字变一下做个提示,比如Bootstrap的做法:
http://getbootstrap.co
- Java String 十大常见问题
tomcat_oracle
java正则表达式
1.字符串比较,使用“==”还是equals()? "=="判断两个引用的是不是同一个内存地址(同一个物理对象)。 equals()判断两个字符串的值是否相等。 除非你想判断两个string引用是否同一个对象,否则应该总是使用equals()方法。 如果你了解字符串的驻留(String Interning)则会更好地理解这个问题。
- SpringMVC 登陆拦截器实现登陆控制
xp9802
springMVC
思路,先登陆后,将登陆信息存储在session中,然后通过拦截器,对系统中的页面和资源进行访问拦截,同时对于登陆本身相关的页面和资源不拦截。
实现方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23