View之Layout过程
1.作用
计算视图(View)的位置
即计算
View的四个顶点位置:Left、Top、Right、Bottom
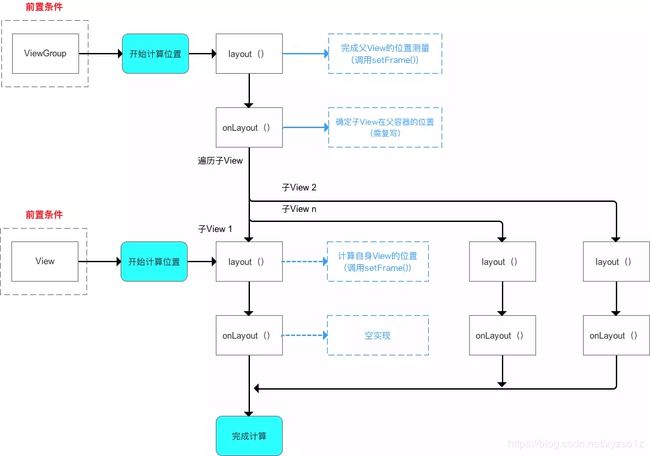
2.layout过程详解
类似measure过程,layout过程根据View的类型分为2种情况:

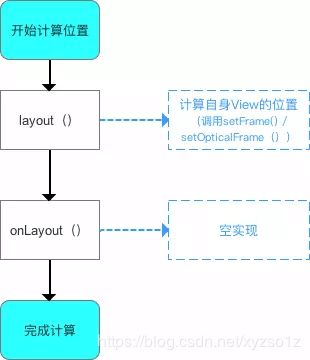
3.1单一View的layout过程
- 应用场景:在无现成的控件
View满足需求、需要自己实现时,则使用自定义单一View - 具体使用:继承自
View、SurfaceView、或其他View;不包含子View - 具体流程
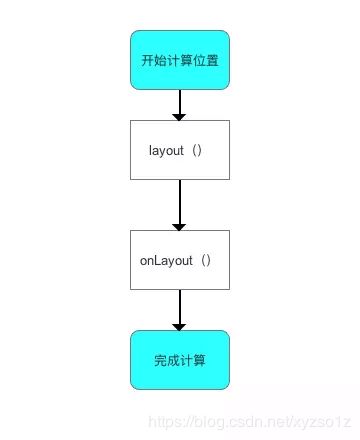
- 源码分析
layout过程的入口=layout(),具体如下:
/**
* 源码分析:layout()
* 作用:确定View本身的位置,即设置View本身的四个顶点位置
*/
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 当前视图的四个顶点
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
// 1. 确定View的位置:setFrame() / setOpticalFrame()
// 即初始化四个顶点的值、判断当前View大小和位置是否发生了变化 & 返回
// ->>分析1、分析2
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
// 2. 若视图的大小 & 位置发生变化
// 会重新确定该View所有的子View在父容器的位置:onLayout()
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
// 对于单一View的laytou过程:由于单一View是没有子View的,故onLayout()是一个空实现->>分析3
// 对于ViewGroup的laytou过程:由于确定位置与具体布局有关,所以onLayout()在ViewGroup为1个抽象方法,需重写实现(后面会详细说)
...
}
/**
* 分析1:setFrame()
* 作用:根据传入的4个位置值,设置View本身的四个顶点位置
* 即:最终确定View本身的位置
*/
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
...
// 通过以下赋值语句记录下了视图的位置信息,即确定View的四个顶点
// 从而确定了视图的位置
mLeft = left;
mTop = top;
mRight = right;
mBottom = bottom;
mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom);
}
/**
* 分析2:setOpticalFrame()
* 作用:根据传入的4个位置值,设置View本身的四个顶点位置
* 即:最终确定View本身的位置
*/
private boolean setOpticalFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
Insets parentInsets = mParent instanceof View ?
((View) mParent).getOpticalInsets() : Insets.NONE;
Insets childInsets = getOpticalInsets();
// 内部实际上是调用setFrame()
return setFrame(
left + parentInsets.left - childInsets.left,
top + parentInsets.top - childInsets.top,
right + parentInsets.left + childInsets.right,
bottom + parentInsets.top + childInsets.bottom);
}
// 回到调用原处
/**
* 分析3:onLayout()
* 注:对于单一View的laytou过程
* a. 由于单一View是没有子View的,故onLayout()是一个空实现
* b. 由于在layout()中已经对自身View进行了位置计算,所以单一View的layout过程在layout()后就已完成了
*/
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
// 参数说明
// changed 当前View的大小和位置改变了
// left 左部位置
// top 顶部位置
// right 右部位置
// bottom 底部位置
}
至此,单一View的layout过程已分析完毕。
-
3.2 ViewGroup的layout过程
-
应用场景
利用现有的组件根据特定的布局方式来组成新的组件 -
具体使用
继承自ViewGroup或各种Layout;含有子View -
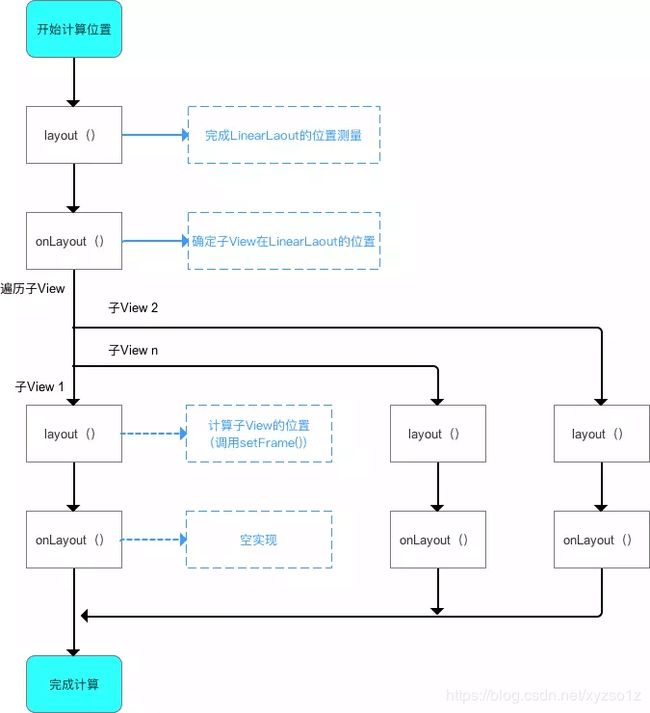
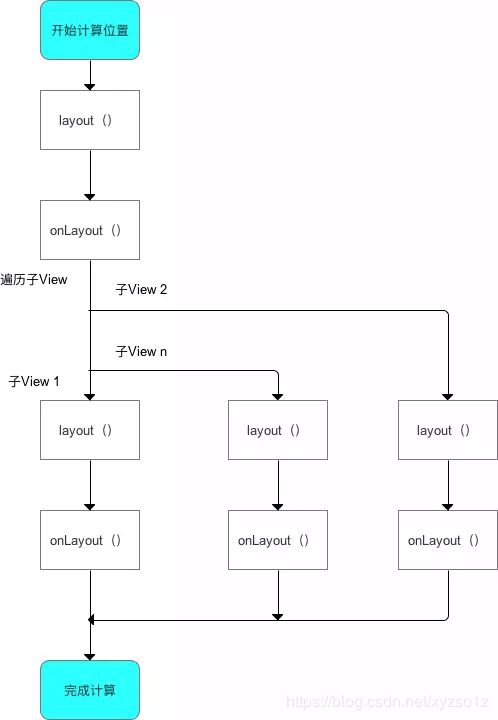
原理(步骤)
- 计算自身
ViewGroup的位置:layout() - 遍历子
View&确定自身子View在ViewGroup的位置(调用子View的layout()):onLayout()
a. 步骤 2 类似于 单一
View的layout过程
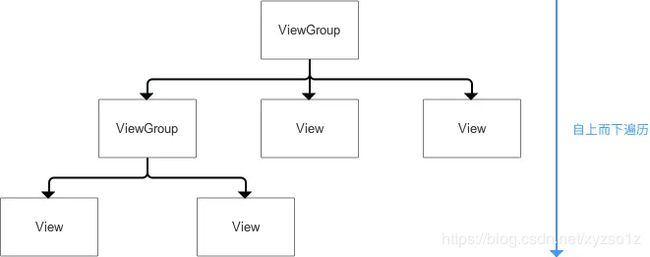
b. 自上而下、一层层地传递下去,直到完成整个View树的layout()过程
- 流程
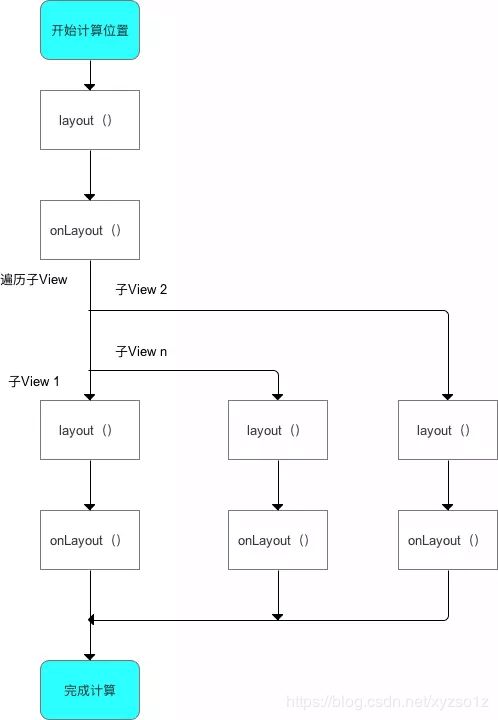
此处需注意:
ViewGroup和View同样拥有layout()和onLayout(),但二者不同的: - 一开始计算
ViewGroup位置时,调用的是ViewGroup的layout()和onLayout(); - 当开始遍历子
View&计算子View位置时,调用的是子View的layout()和onLayout()
类似于单一
View的layout过程
- 下面进行详细分析,
layout过程入口为layout()
/**
* 源码分析:layout()
* 作用:确定View本身的位置,即设置View本身的四个顶点位置
* 注:与单一View的layout()源码一致
*/
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 当前视图的四个顶点
int oldL = mLeft;
int oldT = mTop;
int oldB = mBottom;
int oldR = mRight;
// 1. 确定View的位置:setFrame() / setOpticalFrame()
// 即初始化四个顶点的值、判断当前View大小和位置是否发生了变化 & 返回
// ->>分析1、分析2
boolean changed = isLayoutModeOptical(mParent) ?
setOpticalFrame(l, t, r, b) : setFrame(l, t, r, b);
// 2. 若视图的大小 & 位置发生变化
// 会重新确定该View所有的子View在父容器的位置:onLayout()
if (changed || (mPrivateFlags & PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) == PFLAG_LAYOUT_REQUIRED) {
onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b);
// 对于单一View的laytou过程:由于单一View是没有子View的,故onLayout()是一个空实现(上面已分析完毕)
// 对于ViewGroup的laytou过程:由于确定位置与具体布局有关,所以onLayout()在ViewGroup为1个抽象方法,需重写实现 ->>分析3
...
}
/**
* 分析1:setFrame()
* 作用:确定View本身的位置,即设置View本身的四个顶点位置
*/
protected boolean setFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
...
// 通过以下赋值语句记录下了视图的位置信息,即确定View的四个顶点
// 从而确定了视图的位置
mLeft = left;
mTop = top;
mRight = right;
mBottom = bottom;
mRenderNode.setLeftTopRightBottom(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom);
}
/**
* 分析2:setOpticalFrame()
* 作用:确定View本身的位置,即设置View本身的四个顶点位置
*/
private boolean setOpticalFrame(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
Insets parentInsets = mParent instanceof View ?
((View) mParent).getOpticalInsets() : Insets.NONE;
Insets childInsets = getOpticalInsets();
// 内部实际上是调用setFrame()
return setFrame(
left + parentInsets.left - childInsets.left,
top + parentInsets.top - childInsets.top,
right + parentInsets.left + childInsets.right,
bottom + parentInsets.top + childInsets.bottom);
}
// 回到调用原处
/**
* 分析3:onLayout()
* 作用:计算该ViewGroup包含所有的子View在父容器的位置()
* 注:
* a. 定义为抽象方法,需重写,因:子View的确定位置与具体布局有关,所以onLayout()在ViewGroup没有实现
* b. 在自定义ViewGroup时必须复写onLayout()!!!!!
* c. 复写原理:遍历子View 、计算当前子View的四个位置值 & 确定自身子View的位置(调用子View layout())
*/
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
// 参数说明
// changed 当前View的大小和位置改变了
// left 左部位置
// top 顶部位置
// right 右部位置
// bottom 底部位置
// 1. 遍历子View:循环所有子View
for (int i=0; i<getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 2. 计算当前子View的四个位置值
// 2.1 位置的计算逻辑
...// 需自己实现,也是自定义View的关键
// 2.2 对计算后的位置值进行赋值
int mLeft = Left
int mTop = Top
int mRight = Right
int mBottom = Bottom
// 3. 根据上述4个位置的计算值,设置子View的4个顶点:调用子view的layout() & 传递计算过的参数
// 即确定了子View在父容器的位置
child.layout(mLeft, mTop, mRight, mBottom);
// 该过程类似于单一View的layout过程中的layout()和onLayout(),此处不作过多描述
}
}
}
4. 实例讲解
- 为了更好理解
ViewGroup的layout过程(特别是复写onLayout()) - 下面,我将用2个实例来加深对
ViewGroup layout过程的理解
- 系统提供的
ViewGroup的子类:LinearLayout - 自定义
View(继承了ViewGroup)
4.1 实例解析1(LinearLayout)
4.1.1原理
- 计算出LinearLayout本身在父布局的位置
- 计算出LinearLayout中所有子View在容器中的位置
- 在上述流程中,对于
LinearLayout的layout()的实现与上面所说是一样的,此处不做过多阐述 - 故直接进入
LinearLayout复写的onLayout()分析
/**
* 源码分析:LinearLayout复写的onLayout()
* 注:复写的逻辑 和 LinearLayout measure过程的 onMeasure()类似
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 根据自身方向属性,而选择不同的处理方式
if (mOrientation == VERTICAL) {
layoutVertical(l, t, r, b);
} else {
layoutHorizontal(l, t, r, b);
}
}
// 由于垂直 / 水平方向类似,所以此处仅分析垂直方向(Vertical)的处理过程 ->>分析1
/**
* 分析1:layoutVertical(l, t, r, b)
*/
void layoutVertical(int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
// 子View的数量
final int count = getVirtualChildCount();
// 1. 遍历子View
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getVirtualChildAt(i);
if (child == null) {
childTop += measureNullChild(i);
} else if (child.getVisibility() != GONE) {
// 2. 计算子View的测量宽 / 高值
final int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth();
final int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 3. 确定自身子View的位置
// 即:递归调用子View的setChildFrame(),实际上是调用了子View的layout() ->>分析2
setChildFrame(child, childLeft, childTop + getLocationOffset(child),
childWidth, childHeight);
// childTop逐渐增大,即后面的子元素会被放置在靠下的位置
// 这符合垂直方向的LinearLayout的特性
childTop += childHeight + lp.bottomMargin + getNextLocationOffset(child);
i += getChildrenSkipCount(child, i);
}
}
}
/**
* 分析2:setChildFrame()
*/
private void setChildFrame( View child, int left, int top, int width, int height){
// setChildFrame()仅仅只是调用了子View的layout()而已
child.layout(left, top, left ++ width, top + height);
}
// 在子View的layout()又通过调用setFrame()确定View的四个顶点
// 即确定了子View的位置
// 如此不断循环确定所有子View的位置,最终确定ViewGroup的位置
4.2 实例解析2:自定义View
- 上面讲的例子是系统提供的、已经封装好的
ViewGroup子类:LinearLayout - 但是,一般来说我们使用的都是自定义
View; - 接下来,我用一个简单的例子讲解下自定义
View的layout()过程
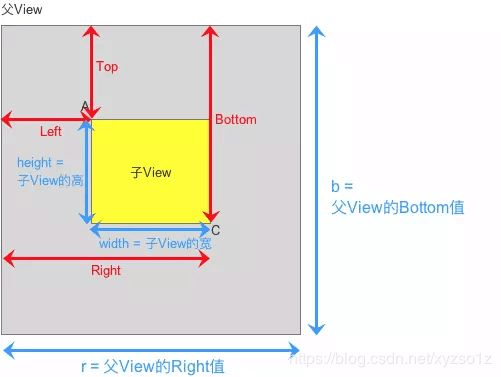
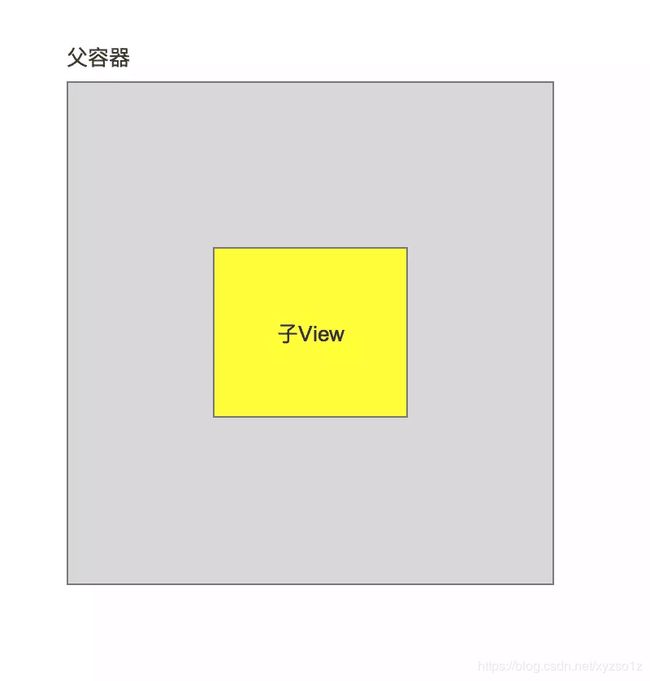
实例视图说明
实例视图=1个ViewGroup(灰色视图),包含1个黄色的子View,如下图:
4.2.2 原理
r = Left + width + Left;// 因左右间距一样
b = Top + height + Top;// 因上下间距一样
Left = (r - width) / 2;
Top = (b - height) / 2;
Right = width + Left;
Bottom = height + Top;
4.2.3代码分析
因为其余方法同上,这里不做过多描述,这里只分析复写onLayout()
/**
* 源码分析:LinearLayout复写的onLayout()
* 注:复写的逻辑 和 LinearLayout measure过程的 onMeasure()类似
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
// 参数说明
// changed 当前View的大小和位置改变了
// left 左部位置
// top 顶部位置
// right 右部位置
// bottom 底部位置
// 1. 遍历子View:循环所有子View
// 注:本例中其实只有一个
for (int i=0; i<getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = getChildAt(i);
// 取出当前子View宽 / 高
int width = child.getMeasuredWidth();
int height = child.getMeasuredHeight();
// 2. 计算当前子View的四个位置值
// 2.1 位置的计算逻辑
int mLeft = (r - width) / 2;
int mTop = (b - height) / 2;
int mRight = mLeft + width;
int mBottom = mTop + height;
// 3. 根据上述4个位置的计算值,设置子View的4个顶点
// 即确定了子View在父容器的位置
child.layout(mLeft, mTop, mRight,mBottom);
}
}
}
布局文件如下:
<scut.Demo_ViewGroup xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:background="#eee998"
tools:context="scut.carson_ho.layout_demo.MainActivity">
<Button
android:text="ChildView"
android:layout_width="200dip"
android:layout_height="200dip"
android:background="#333444"
android:id="@+id/ChildView" />
scut.Demo_ViewGroup >
5.细节:getWidth()(getHeight())与getMeasuredWidth()(getMeasuredHeight())获取的宽(高)有什么区别?
首先明确定义:
getWidth()/getHeight():获得View最终的宽/高getMeasuredWidth()/getMeasuredHeight():获得View测量的宽/高
先看下各自得源码:
// 获得View测量的宽 / 高
public final int getMeasuredWidth() {
return mMeasuredWidth & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
// measure过程中返回的mMeasuredWidth
}
public final int getMeasuredHeight() {
return mMeasuredHeight & MEASURED_SIZE_MASK;
// measure过程中返回的mMeasuredHeight
}
// 获得View最终的宽 / 高
public final int getWidth() {
return mRight - mLeft;
// View最终的宽 = 子View的右边界 - 子view的左边界。
}
public final int getHeight() {
return mBottom - mTop;
// View最终的高 = 子View的下边界 - 子view的上边界。
}
二者的区别:

上面标红:一般情况下,二者获取的宽高是相等的。那么,"非一般"情况是什么?
答:认为设置:通过重写View的layout()强行设置
@Override
public void layout( int l , int t, int r , int b){
// 改变传入的顶点位置参数
super.layout(l,t,r+100,b+100);
// 如此一来,在任何情况下,getWidth() / getHeight()获得的宽/高 总比 getMeasuredWidth() / getMeasuredHeight()获取的宽/高大100px
// 即:View的最终宽/高 总比 测量宽/高 大100px
}
虽然这样的人为设置无实际意义,但证明了View的最终宽高与测量宽高是可以不一样的。
6. 总结