【中文分词】亲手开发一款中文分词器——原理
前文已经谈到几种分词方法的手段和困难,本文将从最基本原理开始,一步一步分析我自己的分词器是如何开发的。文章分为两部分,第一部分谈论了我的一个有趣的尝试,这个尝试是对于最终分词程序没有直接帮助的,所以可以选择性跳过。第二部分谈论HMM模型在程序中的应用,是实现分词器的基本原理。
一、有趣的尝试
从最初出发点开始,我们需要确定那些字的组合是词语。每两个字能否组合成词语,其实取决于两个字同时以相同顺序出现在文章中的次数有关,次数越高,代表他们越有可能组合成词。假设一个字A出现在一篇文章中的概率为P(A),另一个字B出现在文中的概率为P(B),那么AB同时出现在文章中的概率为P(A)·P(B)。此时如果根据统计,发现P(AB)与P(A)·P(B)相近,我们就可以认为AB是一个词语。毫无疑问,如果语料库足够全面,统计学习能够从一定规模的语料库中发现最可能的词语组合。
最初我做了一个尝试,从百度百科中下载了各种内容的文章,覆盖了科学,教育,动物,人文,体育,健康,网络,社会等大约二十多个词条的文章。内容如下:
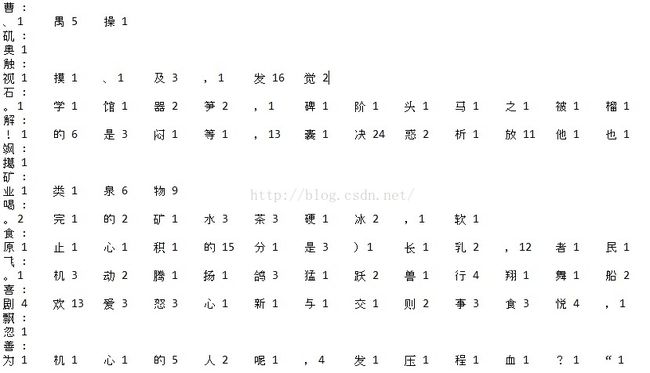
然后用JAVA写了一个程序来统计所有相邻两个字的组合和出现次数并输出。得到了一个大小为365K的txt文件。展示如下:
其中冒号左边的字代表前一个字,后边罗列的是所有在这个字后边出现过的字和对应的次数。其中可以发现在“规”字后边出现较多的字有“律”、“模”、“定”、“划”。在“观”字后边有“的”、“赏”、“看”。“矛”与“盾”的组合也较多。
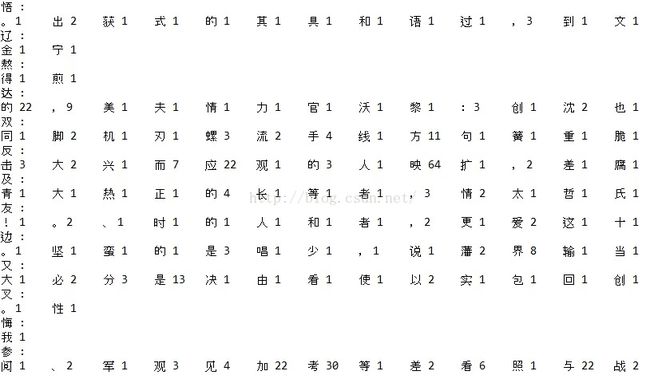
如下再罗列一些结果的截图供参考:
由于屏幕大小原因,无法截取所有的搭配,但是通过一些初略的观察可以发现,除了一些常见的,如 “的”、“,” 等与任何词语都高频出现外,其他大部分高频字都与前一个字构成一个合法的词汇。我仅仅通过二十篇文章初略统计就有一个比较明显的效果,所以如果语料库足够大,内容足够丰富,相信是能够通过统计的方式来确定合法词语的搭配的。
这是我最初对统计方法确定合法词汇搭配的尝试,虽然对后来的开发并没有直接帮助,但确实让我对语言中,字与字的相互关系有了一个直观的感受,这对于后续的学习和开发极为重要。
二、基于HMM开发分词器
2.1 隐马尔科夫原理
通过上一部分的可以发现,虽然我们有很多方法可以确定词语的合法组合,但是字与字在依据话中如何划分其实与上下文是密不可分的。就像第一篇文章中谈及的“人才”两字,并不是任何时候都会放在一起。简单的字典分词,有点类似于脱离意思的机械分词,处理歧义和未登录词时,会有一定的困难。
既然前边说到,字与字的组合与上下文密切相关,那我们将一个字对应某一个词语中的位置作为这个词当前的状态,将状态分为四种情况:词头B,词中M,词尾E和单子成词S,用X表示状态,则Xset = {B, M, E, S}。现在我们就可以试图寻找一个类似的数学模型来描述这种状态出现的概率,从而判断分词的结果。
我们知道,字在一个句子中的出现是一个随机的过程,并且它的出现并不是独立事件。根据我们的语言习惯,字的出现其实与前边是什么字有着密切的联系。这种当前随机状态受之前n-1个状态影响的随机过程有一个很好的数学模型——马尔科夫随机过程。
希望详细了解马尔科夫随机过程,可以参考博文《隐马尔科夫模型详解》。
简而言之,对于一个观察序列O = {O0, O1, ... , On} 如果第n个对象On对应的状态表示为Xn,则其独立观察概率是 P(Xn) 。若之前的 n - 1 个状态表示为 Yi, 其中i = 1, ... , n - 1,则第n的观察对象On对应一个状态的概率就为:
P(On) = P(Xn)·P(Xn | Yn - 1, Y n - 2, ... Y 1)。
其中P(X)是独立观察概率,P(X | Y)是状态转移概率,即前n-1个状态为前提时,当前状态X的出现概率。这个状态转移概率是隐含在马尔科夫过程中的一个因素,因此整个模型称之为隐马尔科夫模型。
所以对于任意的观察序列O = {O0, O1, O2, ... , On}出现的概率可以表示为:
P(O) = Sum(P(Xn)·P(Xn | Yn - 1, Y n - 2, ... Y 1)), n = 1, 2, ... 。 (1)
但是困难的问题来了,每当我们计算第n个状态的概率时,我们需要得到之前n-1个概率的情况,如果有X有m种状态,我们需要进行2n*m^n次乘法。但是细心回过头来分析,我们发现,中文汉字的词语,以两字词语居多。根据黄昌宁博士的论文表述,对Bakeoff-2003和Bakeoff-2005的全部8个训练语料库词长的频率统计,1~2字词占了90%的比例,3字或者3字以下词占了95%,5字和5字一下次更是占据了99%的比例。所以考虑一个字的出现概率,其实无需考虑前边n-1种状态,只需要考虑前边1~2个状态就可以覆盖绝大部分中文词汇了。
其实这样的词语窗口大小在开发中也有规范,只考虑当前字的概率称之为unigram,考虑前一个字的概率称之为bigram,考虑前两个字的概率情况称之为trigram。为了简单起见,我采用了bigram模型。也就是考虑前一个字的情况下来判断当前字的概率。则上式(1)表示为:
P(O) = Sum(P(Xn) · P(Xn | Yn-1)) (2)
这样一来,问题就简单多了。对于一个句子,其中的字的序列组成了观察序列O,统计学习的结果就是确定了各个观察序列中元素标记各种位置的独立概率和状态转移概率。此时使用动态规划,找出使整个句子概率P(O)最大的标记方式作为分词结果即可。
2.2 统计学习
现在我们只需要根据式(2)的定义,来对一个完整的中文语料库进行统计学习就可以训练一个中文分词器了。我使用了微软亚洲研究院提供的中文语料库(本系列前言中附有下载链接)。
微软语料库内容如下:
其内容是人工手动处理的分词结果,词语与词语间由空格分开。所以进行统计学习,我们需要先为这些词打上位置标记来标记它的状态。如下是我的JAVA代码:
// 预处理中文语料库
protected void processTrainingMaterial() {
File f = new File(this.TrainingMaterialPath);
if (!f.exists()) {
System.err.println("未找到中文语料库文件: "
+ this.TrainingMaterialPath);
} else {
try {
if (!f.exists()) {
f.createNewFile();
}
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
InputStreamReader re = new InputStreamReader(fis,
this.DefaultFileFormat);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(re);
String temp;
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(
this.TaggedTrainingMaterialPath, this.DefaultFileFormat);
System.out.println(new Date().toString() + " 开始预处理中文语料库。");
while ((temp = reader.readLine()) != null) {
char[] chararr = temp.toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
int i = 0;
if (chararr[i] == 65279)
i = 1;
int j = i;
while (j <= chararr.length - 1) {
while (j < chararr.length - 1 && chararr[j] == ' ')
j++;
i = j;
while (j < chararr.length - 1 && chararr[j] != 32)
j++;
if (j - i == 1) {
sb.append(chararr[i] + "S");
} else if (j - i == 2) {
sb.append(chararr[i] + "B");
sb.append(chararr[j - 1] + "E");
} else if (j - i > 2) {
sb.append(chararr[i++] + "B");
while (i != j - 1) {
sb.append(chararr[i++] + "M");
}
sb.append(chararr[i] + "E");
}
if (j >= chararr.length - 1)
break;
}
writer.println(sb.toString());
}
System.out.println(new Date().toString() + " 完成中文语料库预处理。");
writer.close();
fis.close();
re.close();
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err
.println("Error in method processTrainingMaterial() : "
+ e.getMessage());
}
}
}每个一个字符后边都紧跟这个字符的位置标记。然后需要做的就是遍历这个文件,统计一下独立概率P(Xn)和状态转移概率P(Xn | Yn-1)。JAVA代码如下:
// 统计学习
protected void statisticTaggedTrainingMaterial() {
this.learningSingleTag(); //状态独立概率P(x)
this.learningRelationTag(); //状态转移概率P(X | Y)
}其中进行了两项统计,统计某一个字与某一位置匹配的次数,以及前后两个字与各种符号匹配在一起的次数。
代码别分如下:
// 学习状态独立概率
protected void learningSingleTag() {
File f = new File(this.TaggedTrainingMaterialPath);
if (!f.exists()) {
System.err.println("未找到训练语料文件"
+ this.TaggedTrainingMaterialPath);
} else {
try {
this._charHash = new HashMap<>();
// 学习独立概率
Double total = 0.0;
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
InputStreamReader re = new InputStreamReader(fis,
this.DefaultFileFormat);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(re);
String temp = null;
System.out.println(new Date().toString() + " 开始学习独立概率。");
while ((temp = reader.readLine()) != null) {
char[] chararr = temp.toCharArray();
if (chararr.length == 0)
continue;
int i = 0;
if ((int) chararr[i] == 65279)
i++;
while (i < chararr.length) {
StringBuilder charsb = new StringBuilder();
charsb.append(chararr[i]);
charsb.append(chararr[i + 1]);
if (this._charHash.containsKey(charsb.toString())) {
Double _t = this._charHash.get(charsb.toString());
_t = _t + 1.0;
this._charHash.put(charsb.toString(), _t);
} else
this._charHash.put(charsb.toString(), 1.0);
total += 1.0;
i += 2;
}
}
File _f = new File(this.FinalTagFilePathForSingle);
if (!_f.exists())
_f.createNewFile();
PrintWriter writer_char = new PrintWriter(
this.FinalTagFilePathForSingle, this.DefaultFileFormat);
for (String key : this._charHash.keySet()) {
writer_char.print(key);
writer_char.println(this._charHash.get(key) / total);
}
System.out
.println(new Date().toString() + " 完成独立概率学习。");
writer_char.close();
fis.close();
re.close();
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Error in method learningSingleTag()");
}
}
}// 学习状态转移概率
protected void learningRelationTag() {
File f = new File(this.TaggedTrainingMaterialPath);
if (!f.exists()) {
System.err.println("未找到训练语料库"
+ this.TaggedTrainingMaterialPath);
} else {
try {
// HMM学习
this._thash = new THash();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
InputStreamReader re = new InputStreamReader(fis,
this.DefaultFileFormat);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(re);
String temp = null;
System.out.println(new Date().toString()
+ " 开始学习状态转移概率。");
while ((temp = reader.readLine()) != null) {
char[] chararr = temp.toCharArray();
int i = 0;
while (i < chararr.length) {
if (i == 0)
this._thash.PutValue('~', '~', chararr[i],
chararr[i + 1]);
else
this._thash.PutValue(chararr[i - 2],
chararr[i - 1], chararr[i], chararr[i + 1]);
i += 2;
}
}
fis.close();
re.close();
reader.close();
this._thash.calculatePossibilityForAllCombinations(
this.FinalTagFilePathForRelation,
this.DefaultFileFormat);
System.out.println(new Date().toString()
+ " 完成状态转移概率学习。");
System.out.println(new Date().toString() + " 训练语料库学习完毕。");
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Error in method learningRelationTag()");
}
}
}private HashMap>>> _myHashMap; 可以记录:前一个字符->前一个字符的位置状态->当前字符->当前字符的位置状态->次数。
其中还封装了插入字符和统计概率的操作。外部程序只需要提供相邻字符和位置标记,THash就能自动插入到对应位置,具体代码如下:
public class THash {
private HashMap>>> _myHashMap;
private static Double INITIAL_VALUE = 1.0;
private static Double POSSIBILITY_INTERPOLATE_VALUE = 1.02;
public THash() {
this._myHashMap = new HashMap<>();
}
public void PutValue(char pri_key, char pri_tag, char sec_key, char sec_tag) {
if (!this._myHashMap.containsKey(pri_key)) {
this._myHashMap.put(pri_key, new HashMap>>());
}
HashMap>> prihash = this._myHashMap
.get(pri_key);
if (!prihash.containsKey(pri_tag)) {
prihash.put(pri_tag,
new HashMap>());
}
HashMap> seccharhash = prihash
.get(pri_tag);
if (!seccharhash.containsKey(sec_key)) {
seccharhash.put(sec_key, new HashMap());
}
HashMap sectaghash = seccharhash.get(sec_key);
if (!sectaghash.containsKey(sec_tag)) {
sectaghash.put(sec_tag, THash.INITIAL_VALUE);
} else {
Double _temp = sectaghash.get(sec_tag);
_temp++;
}
}
public void calculatePossibilityForAllCombinations(String path, String format) {
File f = new File(path);
try {
if (!f.exists())
f.createNewFile();
PrintWriter writer = new PrintWriter(path, format);
for(Character pri_key : this._myHashMap.keySet()){
HashMap>>
_pritaghash = this._myHashMap.get(pri_key);
for(Character pri_tag : _pritaghash.keySet()){
HashMap>
_sechash = _pritaghash.get(pri_tag);
for(Character sec_key : _sechash.keySet()){
HashMap _sectaghash = _sechash.get(sec_key);
Double total = 0.0;
for(Character sec_tag : _sectaghash.keySet()){
total += _sectaghash.get(sec_tag);
}
total *= THash.POSSIBILITY_INTERPOLATE_VALUE;
for(Character sec_tag : _sectaghash.keySet()){
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(pri_key);
sb.append(pri_tag);
sb.append(sec_key);
sb.append(sec_tag);
sb.append(_sectaghash.get(sec_tag) / total);
writer.println(sb.toString());
}
}
}
}
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err
.println("Error in method calculatePossibilityForAllCombinations()");
}
}
} 独立概率文件:
其次是状态转移概率文件:
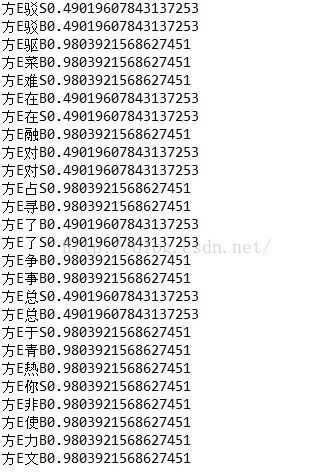
其中记录了前一个字符的位置和对应后一个字符的位置以及概率值。
2.3 分词操作
有了统计学习的结果之后,无需每次载入分词对象都进行一次学习。所以编写一个初始化方法来初始化两种概率结果并保存在两个相应的哈希表中就拥有了一个分词标注器了。载入过程是一个文本处理的过程,这里不赘述。构建独立概率标注器时,使用一个一层嵌套的哈希表存储字符->位置->概率的数据。构建一个状态转移概率标注器时,使用一个类似于THash对象结构的哈希表即可,但是此时字符与其位置标记可以合并为一个字符作为Key,结构也就简单了不少,同时也不再需要计算概率和输出的方法。如下是我的JAVA代码:
// 初始化标注器表
protected void initialiseTagHashMap() {
File f = new File(this.FinalTagFilePathForRelation);
if (!f.exists()) {
System.out.println("未找到标注器初始化文件"
+ this.FinalTagFilePathForRelation);
} else {
try {
this._tagHashForRelation = new HashMap<>();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
InputStreamReader re = new InputStreamReader(fis,
this.DefaultFileFormat);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(re);
String temp = null;
while ((temp = reader.readLine()) != null) {
char[] chararr = temp.toCharArray();
StringBuilder pri_key_sb = new StringBuilder();
StringBuilder sec_key_sb = new StringBuilder();
pri_key_sb.append(chararr[0]);
pri_key_sb.append(chararr[1]);
sec_key_sb.append(chararr[2]);
sec_key_sb.append(chararr[3]);
int j = 6;
char[] pos_chararr = new char[7];
for (int n = 0; n < 7; n++, j++) {
pos_chararr[n] = chararr[j];
}
Double pos = 0.1 * this.convertStringtoDouble(pos_chararr,
0);
HashMap _hash;
if (this._tagHashForRelation.containsKey(pri_key_sb
.toString())) {
_hash = this._tagHashForRelation.get(pri_key_sb
.toString());
_hash.put(sec_key_sb.toString(), pos);
} else {
_hash = new HashMap<>();
_hash.put(sec_key_sb.toString(), pos);
this._tagHashForRelation.put(pri_key_sb.toString(),
_hash);
}
}
fis.close();
re.close();
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("Error in method initialise -> relation");
}
}
f = new File(this.FinalTagFilePathForSingle);
if (!f.exists()) {
System.out.println("为找到标注器初始化文件"
+ this.FinalTagFilePathForSingle);
} else {
try {
this._tagHashForSingle = new HashMap<>();
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(f);
InputStreamReader re = new InputStreamReader(fis,
this.DefaultFileFormat);
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(re);
String temp = null;
while ((temp = reader.readLine()) != null) {
char[] chararr = temp.toCharArray();
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(chararr[0]);
sb.append(chararr[1]);
char[] pos_chararr = new char[5];
for (int j = 0, i = 4; j < 5; j++, i++) {
pos_chararr[j] = chararr[i];
}
Double pos = 0.1 * this.convertStringtoDouble(pos_chararr,
0);
pos = pos + chararr[2] - 48;
if (chararr[chararr.length - 2] == '-') {
int n = chararr[chararr.length - 1] - 48;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
pos *= 0.1;
}
}
this._tagHashForSingle.put(sb.toString(), pos);
}
fis.close();
re.close();
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.err.println("Error in method initialise -> single");
}
}
} // 拆分句子,分离标点,符号,数字和英文字符等
protected List segmentSentence(char[] sentence) {
int i = 0;
int j = i;
try {
while (j < sentence.length) {
if (sentence[j] == '。' || sentence[j] == ','
|| sentence[j] == '?' || sentence[j] == ':'
|| sentence[j] == '!' || sentence[j] == ' '
|| sentence[j] == '(' || sentence[j] == ')') {
if (i < j)
this.segmentWords(sentence, i, j - 1);
i = ++j;
continue;
}
if ((sentence[j] >= 65 && sentence[j] <= 90)
|| (sentence[j] >= 97 && sentence[j] <= 122)) {
if (i != j)
this.segmentWords(sentence, i, j - 1);
i = j;
while (j < sentence.length
&& ((sentence[j] >= 65 && sentence[j] <= 90) || (sentence[j] >= 97 && sentence[j] <= 122))) {
j++;
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (i < j) {
sb.append(sentence[i]);
i++;
}
this.resultlist.add(sb.toString());
i = j;
continue;
}
if (sentence[j] < 127) {
if (i < j) {
segmentWords(sentence, i, j - 1);
i = j;
}
while (j < sentence.length && sentence[j] < 127) {
j++;
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
while (i < j) {
sb.append(sentence[i]);
i++;
}
this.resultlist.add(sb.toString());
i = j;
continue;
}
j++;
}
if (i < j)
this.segmentWords(sentence, i, j - 1);
return resultlist;
} catch (OutOfMemoryError | ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println(sentence.length);
System.out.println(sentence[i]);
System.out.println(sentence[j]);
return this.resultlist;
}
} 分词过程是一个动态规划寻找最优解的过程。首先构建一个二维矩阵,假设文本长度为n,则矩阵为n*4的二维矩阵。其中行索引代表文本中字符的索引,列代表当前字符的四个状态,一次为B, M, E, S。每个元素是一个自定义的对象GNode,其中记录当前位置标记,当前最大概率和得到最大概率的上一级标注。GNode定义如下:
public class GNode {
public Double MaxPos;
public char CurTag;
public char PreTag;
public GNode(){
this.MaxPos = 0.0;
}
}计算概率的算法描述如下:
1. 遍历当前行的每一个GNode对象G2,根据行列索引,求得当前字符与位置标记,记为Sec_Key。
2. 遍历前一行的每一个GNode对象G1,得到对应的前一个字符为其位置标记,记为Pri_Key。
3. 查询从Pri_Key到Sec_Key的状态转移概率并诚意Sec_Key的独立概率,记为Cur_Pos。
4. if Cur_Pos >= G2.MaxPos {
G2.MaxPos = Cur_Pos; //记录单签最大概率
G2.PreTag = Pri_Key.Tag; //记录下获得当前最大概率的前一个标记
} else continue;
其中有两个地方值得注意:
1. 在查询状态转移概率时,只处理合理搭配,比如B接M,B接E等的情况,对于S接E或者M接S等不合法搭配,直接跳过,可以减少一半的查询计算操作。
2. 对于无法查询到的状态转移概率或独立概率的情况,也就是这样的(Pri_Key, Sec_Key)的组合或者Sec_Key在语料库中未出现,即可能是未登录词,比如人名,地名等,也可能是语料库为包含的合法生僻词语,我在程序中为其添加了一个默认概率值。究其原因,一方面如果这样的概率值赋位0,则整个观察序列的概率就为0了,没有任何意义,另一方面我们承认未登录词的存在的。这样一个值需要反复调试程序来确定,不能太小也不能太大。太小了分词结果更倾向于将未登录次拆解成单字,太大了就影响到了很多从语料库中统计出来的正确词语的组合概率。
动态规划算法实现如下:
// 分词操作
protected void segmentWords(char[] sentence, int start, int end) {
int length = end - start + 1;
GNode[][] graph = new GNode[length][4];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
graph[i][j] = new GNode();
}
}
// 初始化状态矩阵
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
graph[0][j].CurTag = getTag(j);
if (j == 0 || j == 3) {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append(sentence[start]);
sb.append(graph[0][j].CurTag);
graph[0][j].MaxPos = this.getPossiblity("~~", sb.toString());
} else
graph[0][j].MaxPos = 0.0;
}
// 动态规划过程
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
graph[i][j].CurTag = this.getTag(j);
StringBuilder sec_key_sb = new StringBuilder();
sec_key_sb.append(sentence[i + start]);
sec_key_sb.append(graph[i][j].CurTag);
for (int n = 0; n < 4; n++) {
if (!this.checkLogicalCombination(graph[i - 1][n].CurTag,
graph[i][j].CurTag))
continue;
StringBuilder pri_key_sb = new StringBuilder();
pri_key_sb.append(sentence[i + start - 1]);
pri_key_sb.append(graph[i - 1][n].CurTag);
Double _pos = this.getPossiblity(pri_key_sb.toString(),
sec_key_sb.toString());
if (this._tagHashForSingle.containsKey(pri_key_sb
.toString()))
_pos *= this._tagHashForSingle.get(pri_key_sb
.toString());
else
_pos *= this.StrangeSingleDefaultPossibility;
_pos *= graph[i - 1][n].MaxPos;
if (_pos >= graph[i][j].MaxPos) {
graph[i][j].MaxPos = _pos;
graph[i][j].PreTag = graph[i - 1][n].CurTag;
}
}
}
}
// 筛选最优解
int m = 0;
Double _maxpos = 0.0;
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
if (graph[length - 1][j].MaxPos >= _maxpos) {
_maxpos = graph[length - 1][j].MaxPos;
m = j;
}
}
char[] chararr = new char[length * 2];
for (int i = end - start, j = chararr.length - 1, n = end; i >= 0
&& j > 0; i--, j -= 2, n--) {
chararr[j] = graph[i][m].CurTag;
chararr[j - 1] = sentence[n];
m = this.getInt(graph[i][m].PreTag);
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < chararr.length; i += 2) {
sb.append(chararr[i]);
if (chararr[i + 1] == 'E' || chararr[i + 1] == 'S') {
this.resultlist.add(sb.toString());
sb = new StringBuilder();
} else if (i == chararr.length - 2)
this.resultlist.add(sb.toString());
}
}如希望直接尝试这个分词器,请访问我的网站:http://august-charter-92912.appspot.com/nlp,再次声明,这是谷歌服务器,需要访问要发功。
另外希望看到分词器完整源代码,可以参考博文《【中文分词】亲手开发一款中文分词器——源代码 》。
我会在晚些时候尝试使用专业工具测试一下这个分词气的精度,召回率和F率,但是这里不报太高期望。
我是应届毕业生,所以知识结构不完整,文章问题较多, 欢迎指正。