ActivityManagerService启动之旅(一)
一、AMS的简介
- ActivityManagerService,简称AMS。如果没有学习它的话,你可能会对他感觉到神秘而复杂。如果你学习了解之后就会觉得它并不那么神秘但是确实很复杂。AMS的主要工作就是:Activity的管理,service的管理,brocastreceiver的管理,进程管理和APP Crash的管理,其实APP crash涉及到的知识主要还是Activity的管理和进程管理这两部分知识。AMS还管控其他事情,比如,app的耗电量,性能,近期列表等,有些朋友可能会说近期列表是SystemUI显示与管理的。这个也没错,但是SystemUI里面获取的近期任务栈的数据是从AMS获取的,而AMS把近期任务栈的管控交给了RecentTasks这个类来处理。
总的来说AMS确实非常庞大,就ActivityManagerService.java这个类就有2.5W行代码,如果再包括与他相关的类,知识体系那就更大得多。所以一个个看是不现实的,因此我们抓住主要的来研究,今后几章会围绕:AMS的启动流程,Activity的启动流程,进程管理,以及APP Crash的管理,四个方向来研究。
本文很多代码引用于邓凡平的深入理解系列,大家可以去查看他的相关文章。他写的文章是目前我看过有关于framework最有深度的文章之一。邓凡平深入理解系列
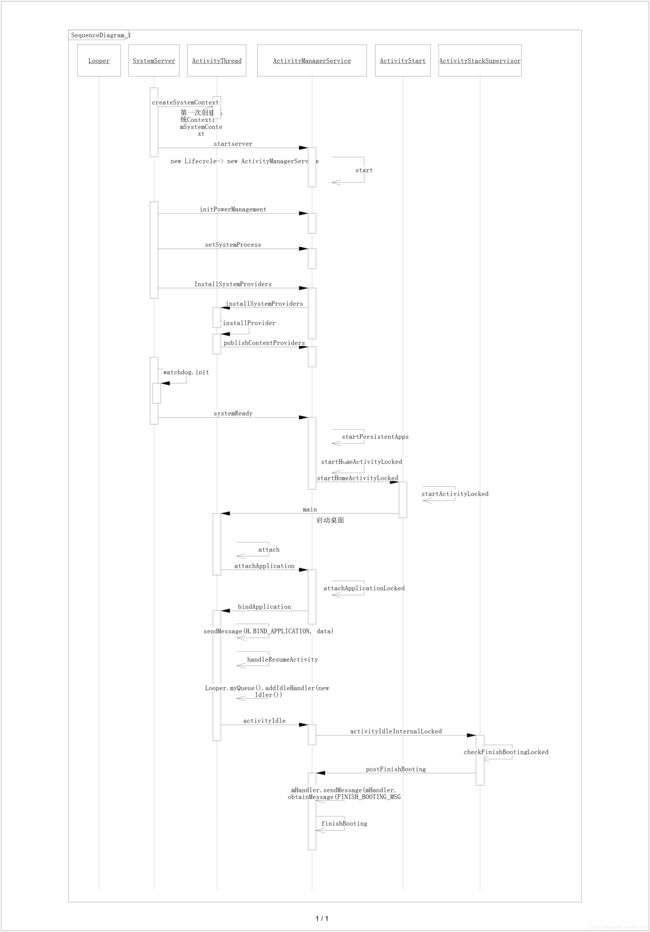
2.AMS的启动流程图如下:如果图片不够清晰可以查看:https://download.csdn.net/download/Bill_xiao/12546960
这上面的流程覆盖了AMS的启动到系统发送开机广播,可能很多朋友不清楚开机广播(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED)是什么时候发送的。大家可能会觉得就是系统启动完成的时候发送。这样理解没错,那又有个问题是:那系统什么时候算启动完成?
答:系统第一个具有Activity界面的并且此Activity显示在用户面前可操作的app进程,比如我们常说的Launcher3或者开机向导就具有此功能。一旦我们Launcher3启动完成或者开机向导启动完成,系统就会发送一个开机广播。其实这样设计的逻辑思维也可以理解,就是android系统是否启动完成不应该是由自己本身来判断,而是应该依据能否正常启动一个app进程。因为android系统所做的所有工作就是为了app提供合适的运行环境,如果app启动有问题,那说明android系统就有问题,也就不能算完全启动。后面我就来研究一下AMS的整个启动流程包括开机广播(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED)的发送。
二、AMS的启动探究之旅
1
AMS的启动我个人把它分为两个阶段:1.为进程提供一些运行环境,context的初始化,context的初始化主要是加载framework-res.apk 的资源文件,还有就是系统启动的各种数据库的加载,ContentProvider,目前来看主要是加载SettingsProvider这个apk。2.启动一些系统服务和系统app,最后发送开机广播。
2 第一阶段:运行环境的启动
2.2.1 AMS由SystemServer启动
mActivityManagerService = mSystemServiceManager.startService(
ActivityManagerService.Lifecycle.class).getService();
mActivityManagerService.setSystemServiceManager(mSystemServiceManager);
mActivityManagerService.setInstaller(installer);在上面的代码中AMS的启动跟网上很多博文的不同,这是android O版本之后的写法,点击Lifecycle类发现所做的事情还是一样,就是换汤不换药。
2.2.2 Lifecycle:就是创建AMS实例,并且在系统调用onStart的方法的时候调用AMS的start方法。
public static final class Lifecycle extends SystemService {
private final ActivityManagerService mService;
public Lifecycle(Context context) {
super(context);
mService = new ActivityManagerService(context);
}
@Override
public void onStart() {
mService.start();
}
@Override
public void onCleanupUser(int userId) {
mService.mBatteryStatsService.onCleanupUser(userId);
}
public ActivityManagerService getService() {
return mService;
}
}
2.2.3 ActivityManagerService构造函数:
1.获取context,学android的都是context的重要性,哪这个systemContext是哪里来的呢?是SystemServer创建的后面会贴出代码块。
2.创建一个前台线程和进程死亡线程,前台线程顾名思义主要是处理一些前台UI的handle消息。进程死亡线程处理KILL_PROCESS_GROUP_MSG这个消息。
3.前台广播列队(mFgBroadcastQueue)和后台广播列队(mBgBroadcastQueue)的初始化,后续我们发送的广播都由这两个类来安排发送。
4.mBatteryStatsService,mProcessStats,mAppOpsService,mUserController这几个关键服务类的创建。
5.mStackSupervisor,mActivityStarter,mRecentTasks 这三个类是关于Activity的管理,任务栈的管理。比较关键,后续会介绍。
6.把AMS添加到看门狗,还有MTK的aee log的监听
public ActivityManagerService(Context systemContext) {
//LockGuard 是一个锁机制,实现了一个类一个锁的方案 ArrayMap sKnown = new ArrayMap<>(0, true)
LockGuard.installLock(this, LockGuard.INDEX_ACTIVITY);
mInjector = new Injector();//测试用的
//systemServer.createSystemContext
mContext = systemContext;
mFactoryTest = FactoryTest.getMode();
//ActivityThread里面的sCurrentActivityThread是当执行了systemServer 的createSystemContext方法,
//ActivityThread.systemMain()的thread.attach(true);方法创建的。
//app进程创建完成也会创建一个ActivityThread,创建的入口是ActivityThread.main。其中执行thread.attach(false)
mSystemThread = ActivityThread.currentActivityThread();
mUiContext = mSystemThread.getSystemUiContext();
Slog.i(TAG, "Memory class: " + ActivityManager.staticGetMemoryClass());
/// M: CTA requirement - permission control
mPermissionReviewRequired = CtaManagerFactory.getInstance().makeCtaManager()
.isCtaSupported() ? true :
mContext.getResources().getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.bool.config_permissionReviewRequired);
///@}
//创建一个前台线程,主要处理一些前台有关的handle
mHandlerThread = new ServiceThread(TAG,
THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND, false /*allowIo*/);
mHandlerThread.start();
mHandler = new MainHandler(mHandlerThread.getLooper());
mUiHandler = mInjector.getUiHandler(this);
//创建Constants管理类ActivityManagerConstants
mConstants = new ActivityManagerConstants(this, mHandler);
/* static; one-time init here */
//创建死亡服务线程,主要是处理一杀死进程KILL_PROCESS_GROUP_MSG的MSG。
if (sKillHandler == null) {
sKillThread = new ServiceThread(TAG + ":kill",
THREAD_PRIORITY_BACKGROUND, true /* allowIo */);
sKillThread.start();
sKillHandler = new KillHandler(sKillThread.getLooper());
}
//前台广播 ,后台广播列队管理类
mFgBroadcastQueue = new BroadcastQueue(this, mHandler,
"foreground", BROADCAST_FG_TIMEOUT, false);
mBgBroadcastQueue = new BroadcastQueue(this, mHandler,
"background", BROADCAST_BG_TIMEOUT, true);
mBroadcastQueues[0] = mFgBroadcastQueue;
mBroadcastQueues[1] = mBgBroadcastQueue;
mServices = new ActiveServices(this);//servcie管理类
mProviderMap = new ProviderMap(this);//ContentProvider 管理类
mAppErrors = new AppErrors(mUiContext, this);//app错误管理类
// TODO: Move creation of battery stats service outside of activity manager service.
File dataDir = Environment.getDataDirectory();//指向/data/目录
File systemDir = new File(dataDir, "system");//指向/data/system/目录
systemDir.mkdirs();
//提供App各部件執行時間的服务类
mBatteryStatsService = new BatteryStatsService(systemContext, systemDir, mHandler);
mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics().readLocked();
mBatteryStatsService.scheduleWriteToDisk();
mOnBattery = DEBUG_POWER ? true
: mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics().getIsOnBattery();
mBatteryStatsService.getActiveStatistics().setCallback(this);
//mProcessStats为IProcessStats类型,用于统计CPU、内存等信息。其内部工作原理就是
//读取并解析/proc/stat文件的内容。该文件由内核生成,用于记录kernel及system
//一些运行时的统计信息。可在Linux系统上通过man proc命令查询详细信息
mProcessStats = new ProcessStatsService(this, new File(systemDir, "procstats"));
//运行权限检查服务
mAppOpsService = mInjector.getAppOpsService(new File(systemDir, "appops.xml"), mHandler);
mAppOpsService.startWatchingMode(AppOpsManager.OP_RUN_IN_BACKGROUND, null,
new IAppOpsCallback.Stub() {
@Override public void opChanged(int op, int uid, String packageName) {
if (op == AppOpsManager.OP_RUN_IN_BACKGROUND && packageName != null) {
if (mAppOpsService.checkOperation(op, uid, packageName)
!= AppOpsManager.MODE_ALLOWED) {
runInBackgroundDisabled(uid);
}
}
}
});
mGrantFile = new AtomicFile(new File(systemDir, "urigrants.xml"));//授权的xml文件
mUserController = new UserController(this);//用户相关控制类
mVrController = new VrController(this);//vr相关
//获取OpenGl版本
GL_ES_VERSION = SystemProperties.getInt("ro.opengles.version",
ConfigurationInfo.GL_ES_VERSION_UNDEFINED);
if (SystemProperties.getInt("sys.use_fifo_ui", 0) != 0) {
mUseFifoUiScheduling = true;
}
mTrackingAssociations = "1".equals(SystemProperties.get("debug.track-associations"));
mTempConfig.setToDefaults();
mTempConfig.setLocales(LocaleList.getDefault());
mConfigurationSeq = mTempConfig.seq = 1;
//Activity栈的管理类,其中有许多不同类型的list用来存放ActivityRecord。
mStackSupervisor = createStackSupervisor();
mStackSupervisor.onConfigurationChanged(mTempConfig);
mKeyguardController = mStackSupervisor.mKeyguardController;
//解析/data/system/packages-compat.xml文件,该文件用于存储那些需要考虑屏幕尺寸
//的APK的一些信息。可参考AndroidManifest.xml中compatible-screens相关说明。
//当APK所运行的设备不满足要求时,AMS会根据设置的参数以采用屏幕兼容的方式去运行它
mCompatModePackages = new CompatModePackages(this, systemDir, mHandler);
mIntentFirewall = new IntentFirewall(new IntentFirewallInterface(), mHandler);
mTaskChangeNotificationController =
new TaskChangeNotificationController(this, mStackSupervisor, mHandler);
//Activity 的启动类
mActivityStarter = new ActivityStarter(this, mStackSupervisor);
//近期任务列表
mRecentTasks = new RecentTasks(this, mStackSupervisor);
//主要是用于cpu的信息记录线程
mProcessCpuThread = new Thread("CpuTracker") {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (mProcessCpuTracker) {
mProcessCpuInitLatch.countDown();
mProcessCpuTracker.init();
}
while (true) {
try {
try {
synchronized(this) {
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
long nextCpuDelay = (mLastCpuTime.get()+MONITOR_CPU_MAX_TIME)-now;
long nextWriteDelay = (mLastWriteTime+BATTERY_STATS_TIME)-now;
//Slog.i(TAG, "Cpu delay=" + nextCpuDelay
// + ", write delay=" + nextWriteDelay);
if (nextWriteDelay < nextCpuDelay) {
nextCpuDelay = nextWriteDelay;
}
if (nextCpuDelay > 0) {
mProcessCpuMutexFree.set(true);
this.wait(nextCpuDelay);
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
}
updateCpuStatsNow();
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Unexpected exception collecting process stats", e);
}
}
}
};
Watchdog.getInstance().addMonitor(this);//把AMS添加到看门狗
Watchdog.getInstance().addThread(mHandler);
/// M: AEE exception log @{
if (SystemProperties.get("ro.have_aee_feature").equals("1")) {
exceptionLog = new ExceptionLog();//抓取aee
}
/// M: AEE exception log @}
} 2.2.4 创建systemcontext,这是第一次创建。
private void createSystemContext() {
ActivityThread activityThread = ActivityThread.systemMain();
mSystemContext = activityThread.getSystemContext();
mSystemContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
final Context systemUiContext = activityThread.getSystemUiContext();
systemUiContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
}
2.2.5 start()
private void start() {
removeAllProcessGroups();//移除所有的 process groups
mProcessCpuThread.start();//在AMS构造函数创建,计算每个进程cpu使用情况,再依据cpu的使用情况计算电池使用情况
mBatteryStatsService.publish();
mAppOpsService.publish(mContext);
Slog.d("AppOps", "AppOpsService published");
LocalServices.addService(ActivityManagerInternal.class, new LocalService());
// Wait for the synchronized block started in mProcessCpuThread,
// so that any other acccess to mProcessCpuTracker from main thread
// will be blocked during mProcessCpuTracker initialization.
/// M: ANR Debug Mechanism
mAnrManager.startAnrManagerService(MY_PID);//启动anr服务,服务的具体实现是vendor下面mtk写的。
/// M: Duraspeed
mAmsExt.startDuraSpeedService(mContext);//启动Duraspeed服务,这个是MTK添加的
try {
mProcessCpuInitLatch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Interrupted wait during start", e);
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new IllegalStateException("Interrupted wait during start");
}
}2.2.6 initPowerManagement:主要是有关电源服务相关的初始化。
public void initPowerManagement() {
mStackSupervisor.initPowerManagement();
mBatteryStatsService.initPowerManagement();
mLocalPowerManager = LocalServices.getService(PowerManagerInternal.class);
PowerManager pm = (PowerManager)mContext.getSystemService(Context.POWER_SERVICE);
mVoiceWakeLock = pm.newWakeLock(PowerManager.PARTIAL_WAKE_LOCK, "*voice*");
mVoiceWakeLock.setReferenceCounted(false);
}
2.2.7 setSystemProcess
1.把一些服务添加到ServiceManager,比如meminfo cpuinfo。比如cupinfo服务可以用adb shell dumpsys cpuinfo 来查询
2.为system进程提供运行环境之资源环境,绑定frameworks-res.apk,把frameworks-res.apk添加到mSystemContext和mSystemUiContext的运行环境。并且把system进程添加到AMS来管理。
public void setSystemProcess() {
try {
ServiceManager.addService(Context.ACTIVITY_SERVICE, this, true);//把自己添加到ServiceManager
ServiceManager.addService(ProcessStats.SERVICE_NAME, mProcessStats);//在AMS构造函数创建
ServiceManager.addService("meminfo", new MemBinder(this));
ServiceManager.addService("gfxinfo", new GraphicsBinder(this));
ServiceManager.addService("dbinfo", new DbBinder(this));
if (MONITOR_CPU_USAGE) {
ServiceManager.addService("cpuinfo", new CpuBinder(this));
}
ServiceManager.addService("permission", new PermissionController(this));//跟动态运行权限
ServiceManager.addService("processinfo", new ProcessInfoService(this));
/// M: ANR Debug Mechanism
mAnrManager.AddAnrManagerService();//添加ANR服务
/// M: DuraSpeed
mAmsExt.addDuraSpeedService();
//获取的info是包名为android的信息,而包名android的是framework-res.apk,
ApplicationInfo info = mContext.getPackageManager().getApplicationInfo(
"android", STOCK_PM_FLAGS | MATCH_SYSTEM_ONLY);
//systemServer.createSystemContext 第一次创建mSystemContext,只是创建了一个Android运行环境
//这一次绑定frameworks-res.apk,把frameworks-res.apk添加到mSystemContext和mSystemUiContext的运行环境。
//这样在activity中引用context就能
mSystemThread.installSystemApplicationInfo(info, getClass().getClassLoader());
synchronized (this) {
ProcessRecord app = newProcessRecordLocked(info, info.processName, false, 0);
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "setSystemProcess processName:"+info.processName+",pid:"+app.pid);
app.persistent = true;
app.pid = MY_PID;
app.maxAdj = ProcessList.SYSTEM_ADJ;
app.makeActive(mSystemThread.getApplicationThread(), mProcessStats);
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
mPidsSelfLocked.put(app.pid, app);
}
updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
updateOomAdjLocked();//根据系统当前状态,调整进程的调度优先级和OOM_Adj
}
/// M: Dynamically enable AMS logs @{
mAmsExt.enableAmsLog(mLruProcesses);
/// @}
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to find android system package", e);
}
}2.2.8 InstallSystemProviders
安装SettingsProvider为system进程提供数据库
public final void installSystemProviders() {
List providers;
ProcessRecord app;
synchronized (this) {
/*
从mProcessNames找到进程名为“system”且uid为SYSTEM_UID的ProcessRecord,
就是前面newProcessRecordLocked
*/
app = mProcessNames.get("system", SYSTEM_UID);
providers = generateApplicationProvidersLocked(app);
if (providers != null) {
for (int i=providers.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProviderInfo pi = (ProviderInfo)providers.get(i);
//将非系统APK(即未设ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM标志)提供的Provider从providers列表中去掉
//其实也就是找到SettingsProvider这个apk
if ((pi.applicationInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) == 0) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Not installing system proc provider " + pi.name
+ ": not system .apk");
providers.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
//com.android.providers.settings.SettingsProvider和com.android.server.am.DumpHeapProvider
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "installSystemProviders ProcessRecord:"+app.processName +",providers:"+providers);
if (providers != null) {
mSystemThread.installSystemProviders(providers);//为SystemServer进程安装Provider
}
//监视 contants的数据库变化
mConstants.start(mContext.getContentResolver());
//监视Settings数据库中Secure表的变化,LONG_PRESS_TIMEOU,MULTI_PRESS_TIMEOUT,TIME_12_24,DEBUG_VIEW_ATTRIBUTES
mCoreSettingsObserver = new CoreSettingsObserver(this);
//监视Settings数据库中Secure表的变化,字体和缩放
mFontScaleSettingObserver = new FontScaleSettingObserver();
// Now that the settings provider is published we can consider sending
// in a rescue party.
RescueParty.onSettingsProviderPublished(mContext);
//mUsageStatsService.monitorPackages();
}
private void startPersistentApps(int matchFlags) {
if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) return;
synchronized (this) {
try {
final List apps = AppGlobals.getPackageManager()
.getPersistentApplications(STOCK_PM_FLAGS | matchFlags).getList();
for (ApplicationInfo app : apps) {
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "startPersistentApps app packageName:"+app.packageName);
if (!"android".equals(app.packageName)) {
addAppLocked(app, null, false, null /* ABI override */);
}
}
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
}
}
}
/**
* When a user is unlocked, we need to install encryption-unaware providers
* belonging to any running apps.
*/
private void installEncryptionUnawareProviders(int userId) {
// We're only interested in providers that are encryption unaware, and
// we don't care about uninstalled apps, since there's no way they're
// running at this point.
final int matchFlags = GET_PROVIDERS | MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_UNAWARE;
synchronized (this) {
final int NP = mProcessNames.getMap().size();
for (int ip = 0; ip < NP; ip++) {
final SparseArray apps = mProcessNames.getMap().valueAt(ip);
final int NA = apps.size();
for (int ia = 0; ia < NA; ia++) {
final ProcessRecord app = apps.valueAt(ia);
if (app.userId != userId || app.thread == null || app.unlocked) continue;
final int NG = app.pkgList.size();
for (int ig = 0; ig < NG; ig++) {
try {
final String pkgName = app.pkgList.keyAt(ig);
final PackageInfo pkgInfo = AppGlobals.getPackageManager()
.getPackageInfo(pkgName, matchFlags, userId);
if (pkgInfo != null && !ArrayUtils.isEmpty(pkgInfo.providers)) {
for (ProviderInfo pi : pkgInfo.providers) {
// TODO: keep in sync with generateApplicationProvidersLocked
final boolean processMatch = Objects.equals(pi.processName,
app.processName) || pi.multiprocess;
final boolean userMatch = isSingleton(pi.processName,
pi.applicationInfo, pi.name, pi.flags)
? (app.userId == UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM) : true;
if (processMatch && userMatch) {
Log.v(TAG, "Installing " + pi);
app.thread.scheduleInstallProvider(pi);
} else {
Log.v(TAG, "Skipping " + pi);
}
}
}
} catch (RemoteException ignored) {
}
}
}
}
}
} 2.2.9 ActivityThread installSystemProviders
public final void installSystemProviders(List providers) {
if (providers != null) {
installContentProviders(mInitialApplication, providers);
}
} 2.3.0 ActivityThread installContentProviders
private void installContentProviders(
Context context, List providers) {
final ArrayList results = new ArrayList<>();
for (ProviderInfo cpi : providers) {
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) {
StringBuilder buf = new StringBuilder(128);
buf.append("Pub ");
buf.append(cpi.authority);
buf.append(": ");
buf.append(cpi.name);
Log.i(TAG, buf.toString());
}
//创建ContentProvider
ContentProviderHolder cph = installProvider(context, null, cpi,
false /*noisy*/, true /*noReleaseNeeded*/, true /*stable*/);
if (cph != null) {
cph.noReleaseNeeded = true;
results.add(cph);//将返回的cp保存到results数组中
}
}
try {
//②调用AMS的publishContentProviders注册这些ContentProvider,第一个参数为ApplicationThread
ActivityManager.getService().publishContentProviders(
getApplicationThread(), results);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} 2.3.1 ActivityThread installProvider
private ContentProviderHolder installProvider(Context context,
ContentProviderHolder holder, ProviderInfo info,
boolean noisy, boolean noReleaseNeeded, boolean stable) {
ContentProvider localProvider = null;
IContentProvider provider;
if (holder == null || holder.provider == null) {
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER || noisy) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Loading provider " + info.authority + ": "
+ info.name);
}
Context c = null;
/*
下面这个if判断的作用就是为该ContentProvider找到对应的Application。
在AndroidManifest.xml中,ContentProvider是Application的子标签,所以
ContentProvider和Application有一种对应关系
其实是mInitialApplication)代表的是framework-res.apk,而Provider代表的
是SettingsProvider。而SettingsProvider.apk所对应的Application还未创建,
所以下面的判断语句最终会进入最后的else分支
*/
ApplicationInfo ai = info.applicationInfo;
if (context.getPackageName().equals(ai.packageName)) {
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityThread installProvider packageName1"+ai.packageName);
c = context;
} else if (mInitialApplication != null &&
mInitialApplication.getPackageName().equals(ai.packageName)) {
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityThread installProvider packageName2"+ai.packageName);
c = mInitialApplication;
} else {
try {
//ai.packageName应该是SettingsProvider.apk的Package,
//名为“com.android.providers.settings”
//下面将创建一个Context,指向该APK
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityThread installProvider packageName3"+ai.packageName);
c = context.createPackageContext(ai.packageName,
Context.CONTEXT_INCLUDE_CODE);
} catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
if (c == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to get context for package " +
ai.packageName +
" while loading content provider " +
info.name);
return null;
}
if (info.splitName != null) {
try {
c = c.createContextForSplit(info.splitName);
} catch (NameNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
try {
/*
为什么一定要找到对应的Context呢?除了ContentProvider和Application的
对应关系外,还有一个决定性原因:即只有对应的Context才能加载对应APK的Java字节码,
从而可通过反射机制生成ContentProvider实例
*/
final java.lang.ClassLoader cl = c.getClassLoader();
//通过Java反射机制得到真正的ContentProvider,
//此处将得到一个SettingsProvider对象
localProvider = (ContentProvider)cl.
loadClass(info.name).newInstance();
provider = localProvider.getIContentProvider();
if (provider == null) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Failed to instantiate class " +
info.name + " from sourceDir " +
info.applicationInfo.sourceDir);
return null;
}
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.v(
TAG, "Instantiating local provider " + info.name);
// XXX Need to create the correct context for this provider.
//初始化该ContentProvider,内部会调用其onCreate函数
localProvider.attachInfo(c, info);
} catch (java.lang.Exception e) {
if (!mInstrumentation.onException(null, e)) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to get provider " + info.name
+ ": " + e.toString(), e);
}
return null;
}
} else {
provider = holder.provider;
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.v(TAG, "Installing external provider " + info.authority + ": "
+ info.name);
}
ContentProviderHolder retHolder;
//contentprovider的保存
synchronized (mProviderMap) {
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) Slog.v(TAG, "Checking to add " + provider
+ " / " + info.name);
IBinder jBinder = provider.asBinder();
if (localProvider != null) {
ComponentName cname = new ComponentName(info.packageName, info.name);
ProviderClientRecord pr = mLocalProvidersByName.get(cname);
if (pr != null) {
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) {
Slog.v(TAG, "installProvider: lost the race, "
+ "using existing local provider");
}
provider = pr.mProvider;
} else {
holder = new ContentProviderHolder(info);
holder.provider = provider;
holder.noReleaseNeeded = true;
pr = installProviderAuthoritiesLocked(provider, localProvider, holder);
mLocalProviders.put(jBinder, pr);
mLocalProvidersByName.put(cname, pr);
}
retHolder = pr.mHolder;
} else {
ProviderRefCount prc = mProviderRefCountMap.get(jBinder);
if (prc != null) {
if (DEBUG_PROVIDER) {
Slog.v(TAG, "installProvider: lost the race, updating ref count");
}
// We need to transfer our new reference to the existing
// ref count, releasing the old one... but only if
// release is needed (that is, it is not running in the
// system process).
if (!noReleaseNeeded) {
incProviderRefLocked(prc, stable);
try {
ActivityManager.getService().removeContentProvider(
holder.connection, stable);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
//do nothing content provider object is dead any way
}
}
} else {
ProviderClientRecord client = installProviderAuthoritiesLocked(
provider, localProvider, holder);
if (noReleaseNeeded) {
prc = new ProviderRefCount(holder, client, 1000, 1000);
} else {
prc = stable
? new ProviderRefCount(holder, client, 1, 0)
: new ProviderRefCount(holder, client, 0, 1);
}
mProviderRefCountMap.put(jBinder, prc);
}
retHolder = prc.holder;
}
}
return retHolder;
}2.3.2 ActivityThread attachInfo
contextProvider 调用自身onCreate方法创建contextprovider
private void attachInfo(Context context, ProviderInfo info, boolean testing) {
mNoPerms = testing;
/*
* Only allow it to be set once, so after the content service gives
* this to us clients can't change it.
*/
if (mContext == null) {
mContext = context;
if (context != null && mTransport != null) {
mTransport.mAppOpsManager = (AppOpsManager) context.getSystemService(
Context.APP_OPS_SERVICE);
}
mMyUid = Process.myUid();
if (info != null) {
setReadPermission(info.readPermission);
setWritePermission(info.writePermission);
setPathPermissions(info.pathPermissions);
mExported = info.exported;
mSingleUser = (info.flags & ProviderInfo.FLAG_SINGLE_USER) != 0;
setAuthorities(info.authority);
}
ContentProvider.this.onCreate();//创建ContentProvider
}
}2.3.3 AMS publishContentProviders
到现在为止系统需要的资源环境和数据库环境已经启动完成,可以开始启动app进程。
public final void publishContentProviders(IApplicationThread caller,
List providers) {
if (providers == null) {
return;
}
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "publishContentProviders providers:"+providers +",caller:"+caller);
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("publishContentProviders");
synchronized (this) {
//找到调用者所在的ProcessRecord对象
final ProcessRecord r = getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
/// M: Fix NullPointerException @{
if (DEBUG_MU && r != null) {
Slog.v(TAG_MU, "ProcessRecord uid = " + r.uid);
}
/// M: Fix NullPointerException @}
if (r == null) {
throw new SecurityException(
"Unable to find app for caller " + caller
+ " (pid=" + Binder.getCallingPid()
+ ") when publishing content providers");
}
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
final int N = providers.size();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
ContentProviderHolder src = providers.get(i);
if (src == null || src.info == null || src.provider == null) {
continue;
}
//①注意:先从该ProcessRecord中找对应的ContentProviderRecord
ContentProviderRecord dst = r.pubProviders.get(src.info.name);
/// M: Fix NullPointerException @{
if (DEBUG_MU && dst != null) {
Slog.v(TAG_MU, "ContentProviderRecord uid = " + dst.uid);
}
/// M: Fix NullPointerException @}
if (dst != null) {
//以ComponentName为key,保存到mProvidersByClass中
ComponentName comp = new ComponentName(dst.info.packageName, dst.info.name);
mProviderMap.putProviderByClass(comp, dst);
String names[] = dst.info.authority.split(";");
for (int j = 0; j < names.length; j++) {
mProviderMap.putProviderByName(names[j], dst);
}
//mLaunchingProviders用于保存处于启动状态的Provider
int launchingCount = mLaunchingProviders.size();
int j;
boolean wasInLaunchingProviders = false;
for (j = 0; j < launchingCount; j++) {
if (mLaunchingProviders.get(j) == dst) {
mLaunchingProviders.remove(j);
wasInLaunchingProviders = true;
j--;
launchingCount--;
}
}
if (wasInLaunchingProviders) {
mHandler.removeMessages(CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
}
synchronized (dst) {
dst.provider = src.provider;
dst.proc = r;
dst.notifyAll();
}
updateOomAdjLocked(r, true);//每发布一个Provider,需要调整对应进程的oom_adj
maybeUpdateProviderUsageStatsLocked(r, src.info.packageName,
src.info.authority);
}
}
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}
} 3 第一阶段:系统准备完成,启动桌面Home
3.3.1 systemReady:
1.设置一些系统启动标识符mSystemReady 和mProcessesReady为true。
2.对进程管控,启动persistent app进程和一些系统服务,比如systemui。什么样的进程才能算是persistentapp,需要满足两点: priv-app下面的apk,2.在AndroidManifest里面声明android:persistent="true"。
3.启动桌面,这个桌面需要区分情况,如果有包含谷歌包的,就是开机向导app,如果没有的话,就是Launcher。那有朋友问开机向导启动完成后我们Launcher是谁启动的。从代码来看是开机向导来启动Launcher。对于MTK方案来说,startHomeActivityLocked启动的第一Activity并不是开机向导的或者Launcher的。而是Settings的CryptKeeper类,
CryptKeeper的intent-filter如下:
android:priority=10也就意味着此activity的 intent信息是最优先获取的,也就意味它被最先启动。至于为什么 第一眼看到的画面不是这个Activity呢?具体的可以 大家可以看CryptKeeper代码实现。
public void systemReady(final Runnable goingCallback, TimingsTraceLog traceLog) {
/// M: Boot time profiling @{
sMtkSystemServerIns.addBootEvent("AMS:systemReady");
/// M: @}
traceLog.traceBegin("PhaseActivityManagerReady");
/// M: onSystemReady @{
// phase 0: On start of AMS systemReady
mAmsExt.onSystemReady(mContext);
/// M: onSystemReady @}
synchronized(this) {
if (mSystemReady) {
// If we're done calling all the receivers, run the next "boot phase" passed in
// by the SystemServer
if (goingCallback != null) {
goingCallback.run();
}
return;
}
mLocalDeviceIdleController
= LocalServices.getService(DeviceIdleController.LocalService.class);
mAssistUtils = new AssistUtils(mContext);
mVrController.onSystemReady();
// Make sure we have the current profile info, since it is needed for security checks.
//一些app开始准备工作。
mUserController.onSystemReady();
mRecentTasks.onSystemReadyLocked();
mAppOpsService.systemReady();
mSystemReady = true;//系统准备完毕
}
try {
sTheRealBuildSerial = IDeviceIdentifiersPolicyService.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(Context.DEVICE_IDENTIFIERS_SERVICE))
.getSerial();
} catch (RemoteException e) {}
ArrayList procsToKill = null;
//正常情况下,mPidsSelfLocked 里面只有system进程
synchronized(mPidsSelfLocked) {
for (int i=mPidsSelfLocked.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProcessRecord proc = mPidsSelfLocked.valueAt(i);
if (!isAllowedWhileBooting(proc.info)){//如果不是白名单启动的进程就添加到关闭列表中
if (procsToKill == null) {
procsToKill = new ArrayList();
}
procsToKill.add(proc);
}
}
}
//从mPidsSelfLocked中找到那些先于AMS启动的进程,哪些进程有如此能耐,
//在AMS还未启动完毕就启动完了呢?对,那些声明了persistent为true的进程有可能
synchronized(this) {
if (procsToKill != null) {
for (int i=procsToKill.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ProcessRecord proc = procsToKill.get(i);
Slog.i(TAG, "Removing system update proc: " + proc);
removeProcessLocked(proc, true, false, "system update done");
}
}
// Now that we have cleaned up any update processes, we
// are ready to start launching real processes and know that
// we won't trample on them any more.
mProcessesReady = true;//进程准备完成
}
Slog.i(TAG, "System now ready");
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.BOOT_PROGRESS_AMS_READY,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
/// M: Boot time profiling @{
sMtkSystemServerIns.addBootEvent("AMS:AMS_READY");
/// M: @}
synchronized(this) {
// Make sure we have no pre-ready processes sitting around.
//工厂模式
if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
ResolveInfo ri = mContext.getPackageManager()
.resolveActivity(new Intent(Intent.ACTION_FACTORY_TEST),
STOCK_PM_FLAGS);
CharSequence errorMsg = null;
if (ri != null) {
ActivityInfo ai = ri.activityInfo;
ApplicationInfo app = ai.applicationInfo;
if ((app.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_SYSTEM) != 0) {
mTopAction = Intent.ACTION_FACTORY_TEST;
mTopData = null;
mTopComponent = new ComponentName(app.packageName,
ai.name);
} else {
errorMsg = mContext.getResources().getText(
com.android.internal.R.string.factorytest_not_system);
}
} else {
errorMsg = mContext.getResources().getText(
com.android.internal.R.string.factorytest_no_action);
}
if (errorMsg != null) {
mTopAction = null;
mTopData = null;
mTopComponent = null;
Message msg = Message.obtain();
msg.what = SHOW_FACTORY_ERROR_UI_MSG;
msg.getData().putCharSequence("msg", errorMsg);
mUiHandler.sendMessage(msg);
}
}
}
retrieveSettings();
final int currentUserId;
synchronized (this) {
currentUserId = mUserController.getCurrentUserIdLocked();
readGrantedUriPermissionsLocked();//读取授权的uri文件
}
//到了此处,应用进程需要运行的环境以及完成,开始启动一些系统核心apk,比如systemui
if (goingCallback != null) goingCallback.run();
traceLog.traceBegin("ActivityManagerStartApps");
mBatteryStatsService.noteEvent(BatteryStats.HistoryItem.EVENT_USER_RUNNING_START,
Integer.toString(currentUserId), currentUserId);
mBatteryStatsService.noteEvent(BatteryStats.HistoryItem.EVENT_USER_FOREGROUND_START,
Integer.toString(currentUserId), currentUserId);
mSystemServiceManager.startUser(currentUserId);
synchronized (this) {
// Only start up encryption-aware persistent apps; once user is
// unlocked we'll come back around and start unaware apps
//哪些APK是persistent APP?
//com.mediatek.ims android com.android.phone com.android.systemui
//条件是目录是priv-app下面的apk,2.在AndroidManifest里面声明android:persistent="true"
startPersistentApps(PackageManager.MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_AWARE);//开启Persistent 的apk
// Start up initial activity.
mBooting = true;//启动apk
// Enable home activity for system user, so that the system can always boot. We don't
// do this when the system user is not setup since the setup wizard should be the one
// to handle home activity in this case.
if (UserManager.isSplitSystemUser() &&
Settings.Secure.getInt(mContext.getContentResolver(),
Settings.Secure.USER_SETUP_COMPLETE, 0) != 0) {
ComponentName cName = new ComponentName(mContext, SystemUserHomeActivity.class);
try {
AppGlobals.getPackageManager().setComponentEnabledSetting(cName,
PackageManager.COMPONENT_ENABLED_STATE_ENABLED, 0,
UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowAsRuntimeException();
}
}
startHomeActivityLocked(currentUserId, "systemReady");//启动桌面
try {
if (AppGlobals.getPackageManager().hasSystemUidErrors()) {
Slog.e(TAG, "UIDs on the system are inconsistent, you need to wipe your"
+ " data partition or your device will be unstable.");
mUiHandler.obtainMessage(SHOW_UID_ERROR_UI_MSG).sendToTarget();
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
}
if (!Build.isBuildConsistent()) {
Slog.e(TAG, "Build fingerprint is not consistent, warning user");
mUiHandler.obtainMessage(SHOW_FINGERPRINT_ERROR_UI_MSG).sendToTarget();
}
long ident = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
try {
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_USER_STARTED);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER_HANDLE, currentUserId);
broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, intent,
null, null, 0, null, null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE,
null, false, false, MY_PID, SYSTEM_UID,
currentUserId);
intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_USER_STARTING);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER_HANDLE, currentUserId);
broadcastIntentLocked(null, null, intent,
null, new IIntentReceiver.Stub() {
@Override
public void performReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode, String data,
Bundle extras, boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int sendingUser)
throws RemoteException {
}
}, 0, null, null,
new String[] {INTERACT_ACROSS_USERS}, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE,
null, true, false, MY_PID, SYSTEM_UID, UserHandle.USER_ALL);
} catch (Throwable t) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Failed sending first user broadcasts", t);
} finally {
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(ident);
}
//恢复栈顶的activity
mStackSupervisor.resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
//发送广播切换到userid
mUserController.sendUserSwitchBroadcastsLocked(-1, currentUserId);
traceLog.traceEnd(); // ActivityManagerStartApps
traceLog.traceEnd(); // PhaseActivityManagerReady
}
} 3.3.2 SystemServer :在goingCallback的回调中可以看出有很多的服务被启动,其中就有我们熟悉的systemui,startSystemUi(context, windowManagerF)
mActivityManagerService.systemReady(() -> {
Slog.i(TAG, "Making services ready");
traceBeginAndSlog("StartActivityManagerReadyPhase");
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(
SystemService.PHASE_ACTIVITY_MANAGER_READY);
traceEnd();
traceBeginAndSlog("StartObservingNativeCrashes");
try {
mActivityManagerService.startObservingNativeCrashes();
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("observing native crashes", e);
}
traceEnd();
// No dependency on Webview preparation in system server. But this should
// be completed before allowring 3rd party
final String WEBVIEW_PREPARATION = "WebViewFactoryPreparation";
Future webviewPrep = null;
if (!mOnlyCore) {
webviewPrep = SystemServerInitThreadPool.get().submit(() -> {
Slog.i(TAG, WEBVIEW_PREPARATION);
TimingsTraceLog traceLog = new TimingsTraceLog(
SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_ASYNC_TAG, Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);
traceLog.traceBegin(WEBVIEW_PREPARATION);
ConcurrentUtils.waitForFutureNoInterrupt(mZygotePreload, "Zygote preload");
mZygotePreload = null;
mWebViewUpdateService.prepareWebViewInSystemServer();
traceLog.traceEnd();
}, WEBVIEW_PREPARATION);
}
if (mPackageManager.hasSystemFeature(PackageManager.FEATURE_AUTOMOTIVE)) {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartCarServiceHelperService");
mSystemServiceManager.startService(CarServiceHelperService.class);
traceEnd();
}
traceBeginAndSlog("StartSystemUI");
try {
startSystemUi(context, windowManagerF);
} catch (Throwable e) {
reportWtf("starting System UI", e);
}3.3.3 startHomeActivityLocked
代码不难,就是向packageservice查询带有Intent.CATEGORY_HOME的intent。然后返回查询结果的Intent,启动它。
boolean startHomeActivityLocked(int userId, String reason) {
if (mFactoryTest == FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL
&& mTopAction == null) {
// We are running in factory test mode, but unable to find
// the factory test app, so just sit around displaying the
// error message and don't try to start anything.
return false;
}
Intent intent = getHomeIntent();
ActivityInfo aInfo = resolveActivityInfo(intent, STOCK_PM_FLAGS, userId);
if (aInfo != null) {
intent.setComponent(new ComponentName(aInfo.applicationInfo.packageName, aInfo.name));
// Don't do this if the home app is currently being
// instrumented.
aInfo = new ActivityInfo(aInfo);
aInfo.applicationInfo = getAppInfoForUser(aInfo.applicationInfo, userId);
//在正常情况下,app应该为null,因为刚开机,Home进程肯定还没启动
ProcessRecord app = getProcessRecordLocked(aInfo.processName,
aInfo.applicationInfo.uid, true);
if (app == null || app.instr == null) {
intent.setFlags(intent.getFlags() | Intent.FLAG_ACTIVITY_NEW_TASK);
final int resolvedUserId = UserHandle.getUserId(aInfo.applicationInfo.uid);
// For ANR debugging to verify if the user activity is the one that actually
// launched.
final String myReason = reason + ":" + userId + ":" + resolvedUserId;
mActivityStarter.startHomeActivityLocked(intent, aInfo, myReason);
}
} else {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "No home screen found for " + intent, new Throwable());
}
return true;
} Intent getHomeIntent() {
Intent intent = new Intent(mTopAction, mTopData != null ? Uri.parse(mTopData) : null);
intent.setComponent(mTopComponent);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_DEBUG_TRIAGED_MISSING);
if (mFactoryTest != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL) {
intent.addCategory(Intent.CATEGORY_HOME);
}
return intent;
}3.3.4 startHomeActivityLocked :
startHomeActivityLocked 的调用规则是:AMS在systemReady时候回调用它,然后会启动符号规则的Intent,如果此Intent的Actiivity不能正常显示在用户前面(什么情况不能正常显示呢?oncreat完后被自身finish了或者disbale了),系统会再次调用startHomeActivityLocked 直到找到可以正常显示的Intent。当这个Activity显示完成后,开始发送系统开机广播(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED)
void startHomeActivityLocked(Intent intent, ActivityInfo aInfo, String reason) {
mSupervisor.moveHomeStackTaskToTop(reason);
//启动一个activity
mLastHomeActivityStartResult = startActivityLocked(null /*caller*/, intent,
null /*ephemeralIntent*/, null /*resolvedType*/, aInfo, null /*rInfo*/,
null /*voiceSession*/, null /*voiceInteractor*/, null /*resultTo*/,
null /*resultWho*/, 0 /*requestCode*/, 0 /*callingPid*/, 0 /*callingUid*/,
null /*callingPackage*/, 0 /*realCallingPid*/, 0 /*realCallingUid*/,
0 /*startFlags*/, null /*options*/, false /*ignoreTargetSecurity*/,
false /*componentSpecified*/, mLastHomeActivityStartRecord /*outActivity*/,
null /*inTask*/, "startHomeActivity: " + reason);
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "startHomeActivityLocked:"+mSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity );
if (mSupervisor.inResumeTopActivity) {
// If we are in resume section already, home activity will be initialized, but not
// resumed (to avoid recursive resume) and will stay that way until something pokes it
// again. We need to schedule another resume.
mSupervisor.scheduleResumeTopActivities();
}
}3.4 开机广播的流程
我们之前有说过开机广播是第一个app进程启动完成才发送的,那app进程的启动入口是哪里?ActivityThread main方法。至于为什么是ActivityThread main呢?后面会讲,因为这个涉及到进程的创建和Activity的启动
3.4.1 ActivityThread main
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ActivityThreadMain");
// CloseGuard defaults to true and can be quite spammy. We
// disable it here, but selectively enable it later (via
// StrictMode) on debug builds, but using DropBox, not logs.
CloseGuard.setEnabled(false);
Environment.initForCurrentUser();
// Set the reporter for event logging in libcore
EventLogger.setReporter(new EventLoggingReporter());
// Make sure TrustedCertificateStore looks in the right place for CA certificates
final File configDir = Environment.getUserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId());
TrustedCertificateStore.setDefaultUserDirectory(configDir);
//设置进程名为""
Process.setArgV0("");
Looper.prepareMainLooper();//准备主线程消息循环
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();//创建一个ActivityThread对象
thread.attach(false);
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {//app 进程第一次启动sMainThreadHandler=null,这也是主线程的handler
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
if (false) {
Looper.myLooper().setMessageLogging(new
LogPrinter(Log.DEBUG, "ActivityThread"));
}
// End of event ActivityThreadMain.
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
/// M: ANR Debug Mechanism
mAnrAppManager.setMessageLogger(Looper.myLooper());
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
3.4.2 ActivityThread attach
private void attach(boolean system) {
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityThread attach system:"+system );
sCurrentActivityThread = this;
mSystemThread = system;
if (!system) {//应用进程的处理流程
//view在绘画的时候回调
ViewRootImpl.addFirstDrawHandler(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
ensureJitEnabled();//启动即使编译
}
});
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("",
UserHandle.myUserId());
RuntimeInit.setApplicationObject(mAppThread.asBinder());//设置IBinder,主要是为后续跨进程使用
//获取和AMS交互的Binder客户端
final IActivityManager mgr = ActivityManager.getService();
try {
//①调用AMS的attachApplication,mAppThread为ApplicationThread类型,它是应用进程和AMS交互的接口
mgr.attachApplication(mAppThread);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
// Watch for getting close to heap limit.
BinderInternal.addGcWatcher(new Runnable() {
@Override public void run() {
if (!mSomeActivitiesChanged) {
return;
}
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long dalvikMax = runtime.maxMemory();
long dalvikUsed = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
if (dalvikUsed > ((3*dalvikMax)/4)) {
if (DEBUG_MEMORY_TRIM) Slog.d(TAG, "Dalvik max=" + (dalvikMax/1024)
+ " total=" + (runtime.totalMemory()/1024)
+ " used=" + (dalvikUsed/1024));
mSomeActivitiesChanged = false;
try {
mgr.releaseSomeActivities(mAppThread);//清除这个进程中不活跃的ActivityRecord
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}
});
} else {
// Don't set application object here -- if the system crashes,
// we can't display an alert, we just want to die die die.
//系统进程的处理流程
//设置DDM的进程名称system_process
android.ddm.DdmHandleAppName.setAppName("system_process",
UserHandle.myUserId());
try {
// 一个工具类,系统和组件之间的交互也将通过Instrumentation来传递,这样,Instrumentation就能监测系统和这些组件的交互情况了
mInstrumentation = new Instrumentation();
//创建属于这个进程的context
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(
this, getSystemContext().mPackageInfo);
//启动application oncreate 方法
//Application是Android中的一个概念,可理解为一种容器,它内部包含四大组件。另外,一个进程可以运行多个Application。
mInitialApplication = context.mPackageInfo.makeApplication(true, null);
mInitialApplication.onCreate();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e);
}
}
// add dropbox logging to libcore
DropBox.setReporter(new DropBoxReporter());
//注册Configuration变化的回调通知
ViewRootImpl.ConfigChangedCallback configChangedCallback
= (Configuration globalConfig) -> {
synchronized (mResourcesManager) {
// We need to apply this change to the resources immediately, because upon returning
// the view hierarchy will be informed about it.
if (mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(globalConfig,
null /* compat */)) {
updateLocaleListFromAppContext(mInitialApplication.getApplicationContext(),
mResourcesManager.getConfiguration().getLocales());
// This actually changed the resources! Tell everyone about it.
if (mPendingConfiguration == null
|| mPendingConfiguration.isOtherSeqNewer(globalConfig)) {
mPendingConfiguration = globalConfig;
sendMessage(H.CONFIGURATION_CHANGED, globalConfig);
}
}
}
};
ViewRootImpl.addConfigCallback(configChangedCallback);
} 3.4.3 AMS attachApplication
private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,
int pid) {
// Find the application record that is being attached... either via
// the pid if we are running in multiple processes, or just pull the
// next app record if we are emulating process with anonymous threads.
ProcessRecord app;
long startTime = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//MY_PID是AMS的服务进程id,这个判断就是不是系统进程
if (pid != MY_PID && pid >= 0) {
//mPidsSelfLocked管理所有的application进程
//那这个app进程是什么时候添加到mPidsSelfLocked?
//答案是:startProcessLocked函数中创建了新的进程,并且执行了this.mPidsSelfLocked.put(startResult.pid, app);
synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {
app = mPidsSelfLocked.get(pid);
}
} else {
app = null;
}
/*
如果该应用进程由AMS启动,则它一定在AMS中有对应的ProcessRecord,读者可回顾前面创建
应用进程的代码:AMS先创建了一个ProcessRecord对象,然后才发命令给Zygote。
如果此处app为null,表示AMS没有该进程的记录,故需要“杀死”它
*/
if (app == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "No pending application record for pid " + pid
+ " (IApplicationThread " + thread + "); dropping process");
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_DROP_PROCESS, pid);
if (pid > 0 && pid != MY_PID) {
killProcessQuiet(pid);
//TODO: killProcessGroup(app.info.uid, pid);
} else {
try {
//调用ApplicationThread的scheduleExit函数。应用进程完成处理工作
//将退出运行
thread.scheduleExit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// Ignore exceptions.
}
}
return false;
}
// If this application record is still attached to a previous
// process, clean it up now.
//app进程存在,并且之前也有主线程,清空已经存在的线程
if (app.thread != null) {
handleAppDiedLocked(app, true, true);
}
// Tell the process all about itself.
if (DEBUG_ALL) Slog.v(
TAG, "Binding process pid " + pid + " to record " + app);
/*
创建一个应用进程讣告接收对象。当应用进程退出时,该对象的binderDied将被调
用。这样,AMS就能做相应处理。binderDied函数将在另外一个线程中执行,其内部也会
调用handleAppDiedLocked。
*/
final String processName = app.processName;
try {
//app死亡监听服务
AppDeathRecipient adr = new AppDeathRecipient(
app, pid, thread);
thread.asBinder().linkToDeath(adr, 0);
app.deathRecipient = adr;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
app.resetPackageList(mProcessStats);
startProcessLocked(app, "link fail", processName);
return false;
}
EventLog.writeEvent(EventLogTags.AM_PROC_BOUND, app.userId, app.pid, app.processName);
//设置该进程的调度优先级和oom_adj等成员
app.makeActive(thread, mProcessStats);
app.curAdj = app.setAdj = app.verifiedAdj = ProcessList.INVALID_ADJ;
app.curSchedGroup = app.setSchedGroup = ProcessList.SCHED_GROUP_DEFAULT;
app.forcingToImportant = null;
updateProcessForegroundLocked(app, false, false);//更新作为前台进程
//在这个阶段是不允许进程被杀死。
app.hasShownUi = false;
app.debugging = false;
app.cached = false;
app.killedByAm = false;
app.killed = false;
// We carefully use the same state that PackageManager uses for
// filtering, since we use this flag to decide if we need to install
// providers when user is unlocked later
app.unlocked = StorageManager.isUserKeyUnlocked(app.userId);
//启动成功,从消息队列中撤销PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG消息
//那么这个广播是在什么时候发送的?
//startProcessLocked->Process.start 进程创建的时候就开始发送的。
mHandler.removeMessages(PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG, app);
//SystemServer早就启动完毕,所以normalMode为true
boolean normalMode = mProcessesReady || isAllowedWhileBooting(app.info);
//在该函数内部将查询(根据进程名,uid确定)PKMS以获取需运行在该进程中的ContentProvider
List providers = normalMode ? generateApplicationProvidersLocked(app) : null;
if (providers != null && checkAppInLaunchingProvidersLocked(app)) {
Message msg = mHandler.obtainMessage(CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = app;
mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(msg, CONTENT_PROVIDER_PUBLISH_TIMEOUT);
}
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: before bindApplication");
if (!normalMode) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Launching preboot mode app: " + app);
}
if (DEBUG_ALL) Slog.v(
TAG, "New app record " + app
+ " thread=" + thread.asBinder() + " pid=" + pid);
try {
int testMode = ApplicationThreadConstants.DEBUG_OFF;
if (mDebugApp != null && mDebugApp.equals(processName)) {
testMode = mWaitForDebugger
? ApplicationThreadConstants.DEBUG_WAIT
: ApplicationThreadConstants.DEBUG_ON;
app.debugging = true;
if (mDebugTransient) {
mDebugApp = mOrigDebugApp;
mWaitForDebugger = mOrigWaitForDebugger;
}
}
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo = null;
String agent = null;
//用于记录性能文件
if (mProfileApp != null && mProfileApp.equals(processName)) {
mProfileProc = app;
profilerInfo = (mProfilerInfo != null && mProfilerInfo.profileFile != null) ?
new ProfilerInfo(mProfilerInfo) : null;
agent = mProfilerInfo != null ? mProfilerInfo.agent : null;
} else if (app.instr != null && app.instr.mProfileFile != null) {
profilerInfo = new ProfilerInfo(app.instr.mProfileFile, null, 0, false, false,
null);
}
boolean enableTrackAllocation = false;
if (mTrackAllocationApp != null && mTrackAllocationApp.equals(processName)) {
enableTrackAllocation = true;
mTrackAllocationApp = null;
}
// If the app is being launched for restore or full backup, set it up specially
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode = false;
if (mBackupTarget != null && mBackupAppName.equals(processName)) {
isRestrictedBackupMode = mBackupTarget.appInfo.uid >= FIRST_APPLICATION_UID
&& ((mBackupTarget.backupMode == BackupRecord.RESTORE)
|| (mBackupTarget.backupMode == BackupRecord.RESTORE_FULL)
|| (mBackupTarget.backupMode == BackupRecord.BACKUP_FULL));
}
if (app.instr != null) {
notifyPackageUse(app.instr.mClass.getPackageName(),
PackageManager.NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_INSTRUMENTATION);
}
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG_CONFIGURATION, "Binding proc "
+ processName + " with config " + getGlobalConfiguration());
ApplicationInfo appInfo = app.instr != null ? app.instr.mTargetInfo : app.info;
app.compat = compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(appInfo);
if (profilerInfo != null && profilerInfo.profileFd != null) {
profilerInfo.profileFd = profilerInfo.profileFd.dup();
}
// We deprecated Build.SERIAL and it is not accessible to
// apps that target the v2 security sandbox. Since access to
// the serial is now behind a permission we push down the value.
String buildSerial = appInfo.targetSandboxVersion < 2
? sTheRealBuildSerial : Build.UNKNOWN;
// Check if this is a secondary process that should be incorporated into some
// currently active instrumentation. (Note we do this AFTER all of the profiling
// stuff above because profiling can currently happen only in the primary
// instrumentation process.)
if (mActiveInstrumentation.size() > 0 && app.instr == null) {
for (int i = mActiveInstrumentation.size() - 1; i >= 0 && app.instr == null; i--) {
ActiveInstrumentation aInstr = mActiveInstrumentation.get(i);
if (!aInstr.mFinished && aInstr.mTargetInfo.uid == app.uid) {
if (aInstr.mTargetProcesses.length == 0) {
// This is the wildcard mode, where every process brought up for
// the target instrumentation should be included.
if (aInstr.mTargetInfo.packageName.equals(app.info.packageName)) {
app.instr = aInstr;
aInstr.mRunningProcesses.add(app);
}
} else {
for (String proc : aInstr.mTargetProcesses) {
if (proc.equals(app.processName)) {
app.instr = aInstr;
aInstr.mRunningProcesses.add(app);
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
// If we were asked to attach an agent on startup, do so now, before we're binding
// application code.
if (agent != null) {
thread.attachAgent(agent);
}
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: immediately before bindApplication");
mStackSupervisor.mActivityMetricsLogger.notifyBindApplication(app);
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "bindApplication" );
if (app.isolatedEntryPoint != null) {
// This is an isolated process which should just call an entry point instead of
// being bound to an application.
thread.runIsolatedEntryPoint(app.isolatedEntryPoint, app.isolatedEntryPointArgs);
} else if (app.instr != null) {
//①通过ApplicationThread和应用进程交互,调用其bindApplication函数
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers,
app.instr.mClass,
profilerInfo, app.instr.mArguments,
app.instr.mWatcher,
app.instr.mUiAutomationConnection, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
} else {
thread.bindApplication(processName, appInfo, providers, null, profilerInfo,
null, null, null, testMode,
mBinderTransactionTrackingEnabled, enableTrackAllocation,
isRestrictedBackupMode || !normalMode, app.persistent,
new Configuration(getGlobalConfiguration()), app.compat,
getCommonServicesLocked(app.isolated),
mCoreSettingsObserver.getCoreSettingsLocked(),
buildSerial);
}
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: immediately after bindApplication");
updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);//更新进程
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after updateLruProcessLocked");
//记录两个时间
app.lastRequestedGc = app.lastLowMemory = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
} catch (Exception e) {
// todo: Yikes! What should we do? For now we will try to
// start another process, but that could easily get us in
// an infinite loop of restarting processes...
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown during bind of " + app, e);
app.resetPackageList(mProcessStats);
app.unlinkDeathRecipient();
startProcessLocked(app, "bind fail", processName);
return false;
}
// Remove this record from the list of starting applications.
mPersistentStartingProcesses.remove(app);
if (DEBUG_PROCESSES && mProcessesOnHold.contains(app)) Slog.v(TAG_PROCESSES,
"Attach application locked removing on hold: " + app);
mProcessesOnHold.remove(app);
boolean badApp = false;
boolean didSomething = false;
// See if the top visible activity is waiting to run in this process...
if (normalMode) {
try {
if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {
didSomething = true;
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown launching activities in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
// Find any services that should be running in this process...
if (!badApp) {
try {
didSomething |= mServices.attachApplicationLocked(app, processName);
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after mServices.attachApplicationLocked");
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown starting services in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
// Check if a next-broadcast receiver is in this process...
if (!badApp && isPendingBroadcastProcessLocked(pid)) {
try {
didSomething |= sendPendingBroadcastsLocked(app);
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after sendPendingBroadcastsLocked");
} catch (Exception e) {
// If the app died trying to launch the receiver we declare it 'bad'
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown dispatching broadcasts in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
// Check whether the next backup agent is in this process...
if (!badApp && mBackupTarget != null && mBackupTarget.app == app) {
if (DEBUG_BACKUP) Slog.v(TAG_BACKUP,
"New app is backup target, launching agent for " + app);
notifyPackageUse(mBackupTarget.appInfo.packageName,
PackageManager.NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_BACKUP);
try {
thread.scheduleCreateBackupAgent(mBackupTarget.appInfo,
compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(mBackupTarget.appInfo),
mBackupTarget.backupMode);
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Exception thrown creating backup agent in " + app, e);
badApp = true;
}
}
if (badApp) {
app.kill("error during init", true);
handleAppDiedLocked(app, false, true);
return false;
}
if (!didSomething) {
updateOomAdjLocked();
checkTime(startTime, "attachApplicationLocked: after updateOomAdjLocked");
}
return true;
}
3.4.4 ActivityThread bindApplication
public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,
List providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,
ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,
IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,
IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,
boolean enableBinderTracking, boolean trackAllocation,
boolean isRestrictedBackupMode, boolean persistent, Configuration config,
CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map services, Bundle coreSettings,
String buildSerial) {
if (services != null) {//保存AMS传递过来的系统Service信息
// Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager
ServiceManager.initServiceCache(services);
}
setCoreSettings(coreSettings);//向主线程消息队列添加SET_CORE_SETTINGS消息
AppBindData data = new AppBindData();//将AMS传过来的参数保存到AppBindData中
data.processName = processName;
data.appInfo = appInfo;
data.providers = providers;
data.instrumentationName = instrumentationName;
data.instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs;
data.instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher;
data.instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection;
data.debugMode = debugMode;
data.enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking;
data.trackAllocation = trackAllocation;
data.restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode;
data.persistent = persistent;
data.config = config;
data.compatInfo = compatInfo;
data.initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo;
data.buildSerial = buildSerial;
sendMessage(H.BIND_APPLICATION, data);//绑定data
}
3.4.5 ActivityThread handleResumeActivity
final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,
boolean clearHide, boolean isForward, boolean reallyResume, int seq, String reason) {
ActivityClientRecord r = mActivities.get(token);
if (!checkAndUpdateLifecycleSeq(seq, r, "resumeActivity")) {
return;
}
// If we are getting ready to gc after going to the background, well
// we are back active so skip it.
unscheduleGcIdler();
mSomeActivitiesChanged = true;
// TODO Push resumeArgs into the activity for consideration
//内部调用目标Activity的onResume函数
r = performResumeActivity(token, clearHide, reason);
if (r != null) {
final Activity a = r.activity;
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Resume " + r + " started activity: " +
a.mStartedActivity + ", hideForNow: " + r.hideForNow
+ ", finished: " + a.mFinished);
final int forwardBit = isForward ?
WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION : 0;
// If the window hasn't yet been added to the window manager,
// and this guy didn't finish itself or start another activity,
// then go ahead and add the window.
boolean willBeVisible = !a.mStartedActivity;
if (!willBeVisible) {
try {
willBeVisible = ActivityManager.getService().willActivityBeVisible(
a.getActivityToken());
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {
r.window = r.activity.getWindow();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
decor.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
a.mDecor = decor;
l.type = WindowManager.LayoutParams.TYPE_BASE_APPLICATION;
l.softInputMode |= forwardBit;
if (r.mPreserveWindow) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
r.mPreserveWindow = false;
// Normally the ViewRoot sets up callbacks with the Activity
// in addView->ViewRootImpl#setView. If we are instead reusing
// the decor view we have to notify the view root that the
// callbacks may have changed.
ViewRootImpl impl = decor.getViewRootImpl();
if (impl != null) {
impl.notifyChildRebuilt();
}
}
if (a.mVisibleFromClient) {
if (!a.mWindowAdded) {
a.mWindowAdded = true;
wm.addView(decor, l);//添加window,现在开始显示
} else {
// The activity will get a callback for this {@link LayoutParams} change
// earlier. However, at that time the decor will not be set (this is set
// in this method), so no action will be taken. This call ensures the
// callback occurs with the decor set.
a.onWindowAttributesChanged(l);
}
}
// If the window has already been added, but during resume
// we started another activity, then don't yet make the
// window visible.
} else if (!willBeVisible) {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Launch " + r + " mStartedActivity set");
r.hideForNow = true;
}
// Get rid of anything left hanging around.
cleanUpPendingRemoveWindows(r, false /* force */);
// The window is now visible if it has been added, we are not
// simply finishing, and we are not starting another activity.
if (!r.activity.mFinished && willBeVisible
&& r.activity.mDecor != null && !r.hideForNow) {
if (r.newConfig != null) {
performConfigurationChangedForActivity(r, r.newConfig);
if (DEBUG_CONFIGURATION) Slog.v(TAG, "Resuming activity "
+ r.activityInfo.name + " with newConfig " + r.activity.mCurrentConfig);
r.newConfig = null;
}
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Resuming " + r + " with isForward="
+ isForward);
WindowManager.LayoutParams l = r.window.getAttributes();
if ((l.softInputMode
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION)
!= forwardBit) {
l.softInputMode = (l.softInputMode
& (~WindowManager.LayoutParams.SOFT_INPUT_IS_FORWARD_NAVIGATION))
| forwardBit;
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
ViewManager wm = a.getWindowManager();
View decor = r.window.getDecorView();
wm.updateViewLayout(decor, l);
}
}
r.activity.mVisibleFromServer = true;
mNumVisibleActivities++;
if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {
r.activity.makeVisible();
}
}
//将上面完成onResume的Activity保存到mNewActivities中
if (!r.onlyLocalRequest) {
r.nextIdle = mNewActivities;
mNewActivities = r;
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Scheduling idle handler for " + r);
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "ActivityThread handleResumeActivity ddIdleHandler" );
Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new Idler()); //①向消息队列中添加一个Idler对象
}
r.onlyLocalRequest = false;
// Tell the activity manager we have resumed.
if (reallyResume) {
try {
ActivityManager.getService().activityResumed(token);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
} else {
// If an exception was thrown when trying to resume, then
// just end this activity.
try {
ActivityManager.getService()
.finishActivity(token, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null,
Activity.DONT_FINISH_TASK_WITH_ACTIVITY);
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
}3.4.6 ActivityThread Looper.myQueue().addIdleHandler(new Idler())
private class Idler implements MessageQueue.IdleHandler {
@Override
public final boolean queueIdle() {
ActivityClientRecord a = mNewActivities;
boolean stopProfiling = false;
if (mBoundApplication != null && mProfiler.profileFd != null
&& mProfiler.autoStopProfiler) {
stopProfiling = true;
}
if (a != null) {
mNewActivities = null;
IActivityManager am = ActivityManager.getService();
ActivityClientRecord prev;
do {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(
TAG, "Reporting idle of " + a +
" finished=" +
(a.activity != null && a.activity.mFinished));
if (a.activity != null && !a.activity.mFinished) {
try {
//调用AMS的activityIdle
am.activityIdle(a.token, a.createdConfig, stopProfiling);
a.createdConfig = null;
} catch (RemoteException ex) {
throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
prev = a;
a = a.nextIdle;
prev.nextIdle = null;
} while (a != null);
}
if (stopProfiling) {
mProfiler.stopProfiling();
}
ensureJitEnabled();
return false;
}
}3.4.7 AMS activityIdle
public final void activityIdle(IBinder token, Configuration config, boolean stopProfiling) {
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
synchronized (this) {
ActivityStack stack = ActivityRecord.getStackLocked(token);
if (stack != null) {
ActivityRecord r =
mStackSupervisor.activityIdleInternalLocked(token, false /* fromTimeout */,
false /* processPausingActivities */, config);
if (stopProfiling) {
if ((mProfileProc == r.app) && mProfilerInfo != null) {
clearProfilerLocked();
}
}
/// M: onEndOfActivityIdle @{
mAmsExt.onEndOfActivityIdle(mContext, r.intent);
/// M: onEndOfActivityIdle @}
}
}
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
}3.4.8 ActivityStackSupervisor activityIdleInternalLocked
final ActivityRecord activityIdleInternalLocked(final IBinder token, boolean fromTimeout,
boolean processPausingActivities, Configuration config) {
if (DEBUG_ALL) Slog.v(TAG, "Activity idle: " + token);
ArrayList finishes = null;
ArrayList startingUsers = null;
int NS = 0;
int NF = 0;
boolean booting = false;
boolean activityRemoved = false;
ActivityRecord r = ActivityRecord.forTokenLocked(token);
if (r != null) {
if (DEBUG_IDLE) Slog.d(TAG_IDLE, "activityIdleInternalLocked: Callers="
+ Debug.getCallers(4));
mHandler.removeMessages(IDLE_TIMEOUT_MSG, r);
r.finishLaunchTickingLocked();
if (fromTimeout) {
reportActivityLaunchedLocked(fromTimeout, r, -1, -1);
}
// This is a hack to semi-deal with a race condition
// in the client where it can be constructed with a
// newer configuration from when we asked it to launch.
// We'll update with whatever configuration it now says
// it used to launch.
if (config != null) {
r.setLastReportedGlobalConfiguration(config);
}
// We are now idle. If someone is waiting for a thumbnail from
// us, we can now deliver.
r.idle = true;
//Slog.i(TAG, "IDLE: mBooted=" + mBooted + ", fromTimeout=" + fromTimeout);
if (isFocusedStack(r.getStack()) || fromTimeout) {
booting = checkFinishBootingLocked();
}
}
if (allResumedActivitiesIdle()) {
if (r != null) {
mService.scheduleAppGcsLocked();
}
if (mLaunchingActivity.isHeld()) {
mHandler.removeMessages(LAUNCH_TIMEOUT_MSG);
if (VALIDATE_WAKE_LOCK_CALLER &&
Binder.getCallingUid() != Process.myUid()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Calling must be system uid");
}
mLaunchingActivity.release();
}
ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked(null, 0, !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);
}
// Atomically retrieve all of the other things to do.
final ArrayList stops = processStoppingActivitiesLocked(r,
true /* remove */, processPausingActivities);
NS = stops != null ? stops.size() : 0;
if ((NF = mFinishingActivities.size()) > 0) {
finishes = new ArrayList<>(mFinishingActivities);
mFinishingActivities.clear();
}
if (mStartingUsers.size() > 0) {
startingUsers = new ArrayList<>(mStartingUsers);
mStartingUsers.clear();
}
// Stop any activities that are scheduled to do so but have been
// waiting for the next one to start.
for (int i = 0; i < NS; i++) {
r = stops.get(i);
final ActivityStack stack = r.getStack();
if (stack != null) {
if (r.finishing) {
stack.finishCurrentActivityLocked(r, ActivityStack.FINISH_IMMEDIATELY, false);
} else {
stack.stopActivityLocked(r);
}
}
}
// Finish any activities that are scheduled to do so but have been
// waiting for the next one to start.
for (int i = 0; i < NF; i++) {
r = finishes.get(i);
final ActivityStack stack = r.getStack();
if (stack != null) {
activityRemoved |= stack.destroyActivityLocked(r, true, "finish-idle");
}
}
if (!booting) {//如果还没有启动完成就发送启动完成广播
// Complete user switch
if (startingUsers != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < startingUsers.size(); i++) {
mService.mUserController.finishUserSwitch(startingUsers.get(i));
}
}
}
mService.trimApplications();
//dump();
//mWindowManager.dump();
if (activityRemoved) {
resumeFocusedStackTopActivityLocked();
}
return r;
} 3.4.9 ActivityStackSupervisor checkFinishBootingLocked
private boolean checkFinishBootingLocked() {
final boolean booting = mService.mBooting;
boolean enableScreen = false;
mService.mBooting = false;
if (!mService.mBooted) {
mService.mBooted = true;
enableScreen = true;
}
if (booting || enableScreen) {
mService.postFinishBooting(booting, enableScreen);
}
return booting;
}3.5.0 AMS postFinishBooting 发送一个FINISH_BOOTING_MSG message 最终会调用finishBooting()
void postFinishBooting(boolean finishBooting, boolean enableScreen) {
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(FINISH_BOOTING_MSG,
finishBooting ? 1 : 0, enableScreen ? 1 : 0));
}3.5.1 AMS finishBooting()
final void finishBooting() {
synchronized (this) {
if (!mBootAnimationComplete) {
mCallFinishBooting = true;
return;
}
mCallFinishBooting = false;
}
ArraySet completedIsas = new ArraySet();
for (String abi : Build.SUPPORTED_ABIS) {
zygoteProcess.establishZygoteConnectionForAbi(abi);
final String instructionSet = VMRuntime.getInstructionSet(abi);
if (!completedIsas.contains(instructionSet)) {
try {
mInstaller.markBootComplete(VMRuntime.getInstructionSet(abi));
} catch (InstallerException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unable to mark boot complete for abi: " + abi + " (" +
e.getMessage() +")");
}
completedIsas.add(instructionSet);
}
}
//处理package 重启广播
IntentFilter pkgFilter = new IntentFilter();
pkgFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_QUERY_PACKAGE_RESTART);
pkgFilter.addDataScheme("package");
mContext.registerReceiver(new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
String[] pkgs = intent.getStringArrayExtra(Intent.EXTRA_PACKAGES);
if (pkgs != null) {
for (String pkg : pkgs) {
synchronized (ActivityManagerService.this) {
if (forceStopPackageLocked(pkg, -1, false, false, false, false, false,
0, "query restart")) {
setResultCode(Activity.RESULT_OK);
return;
}
}
}
}
}
}, pkgFilter);
IntentFilter dumpheapFilter = new IntentFilter();
dumpheapFilter.addAction(DumpHeapActivity.ACTION_DELETE_DUMPHEAP);
mContext.registerReceiver(new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
if (intent.getBooleanExtra(DumpHeapActivity.EXTRA_DELAY_DELETE, false)) {
mHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(POST_DUMP_HEAP_NOTIFICATION_MSG, 5*60*1000);
} else {
mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(POST_DUMP_HEAP_NOTIFICATION_MSG);
}
}
}, dumpheapFilter);
// Let system services know.
//调用所有的注册在mSystemServiceManager的service ->onBootPhase
mSystemServiceManager.startBootPhase(SystemService.PHASE_BOOT_COMPLETED);
synchronized (this) {
// Ensure that any processes we had put on hold are now started
// up.
final int NP = mProcessesOnHold.size();
if (NP > 0) {
ArrayList procs =
new ArrayList(mProcessesOnHold);//启动那些等待启动的进程
for (int ip=0; ip 3.5.2 UserController finishUserBoot(),可能大家会觉得这个方法肯定是发送开机广播的,但是整个方法看完发现并没有。只要类似开机广播的ACTION_LOCKED_BOOT_COMPLETED。那大家一定会以为,那开机广播在哪里发送呢?接着往后看。
private void finishUserBoot(UserState uss, IIntentReceiver resultTo) {
final int userId = uss.mHandle.getIdentifier();
Slog.d(TAG, "Finishing user boot " + userId);
Log.i("ActivityManagerService-xiao", "UserController finishUserBoot uss:"+uss );
synchronized (mLock) {
// Bail if we ended up with a stale user
if (mStartedUsers.get(userId) != uss) return;
// We always walk through all the user lifecycle states to send
// consistent developer events. We step into RUNNING_LOCKED here,
// but we might immediately step into RUNNING below if the user
// storage is already unlocked.
if (uss.setState(STATE_BOOTING, STATE_RUNNING_LOCKED)) {
mInjector.getUserManagerInternal().setUserState(userId, uss.state);
// Do not report secondary users, runtime restarts or first boot/upgrade
if (userId == UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM
&& !mInjector.isRuntimeRestarted() && !mInjector.isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
int uptimeSeconds = (int)(SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() / 1000);
MetricsLogger.histogram(mInjector.getContext(),
"framework_locked_boot_completed", uptimeSeconds);
final int MAX_UPTIME_SECONDS = 120;
if (uptimeSeconds > MAX_UPTIME_SECONDS) {
Slog.wtf("SystemServerTiming",
"finishUserBoot took too long. uptimeSeconds=" + uptimeSeconds);
}
}
mHandler.sendMessage(mHandler.obtainMessage(REPORT_LOCKED_BOOT_COMPLETE_MSG,
userId, 0));
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_LOCKED_BOOT_COMPLETED, null);
intent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER_HANDLE, userId);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_NO_ABORT
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_INCLUDE_BACKGROUND);
mInjector.broadcastIntentLocked(intent, null, resultTo, 0, null, null,
new String[] { android.Manifest.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED },
AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, true, false, MY_PID, SYSTEM_UID, userId);
}
// We need to delay unlocking managed profiles until the parent user
// is also unlocked.
if (mInjector.getUserManager().isManagedProfile(userId)) {
final UserInfo parent = mInjector.getUserManager().getProfileParent(userId);
if (parent != null
&& isUserRunningLocked(parent.id, ActivityManager.FLAG_AND_UNLOCKED)) {
Slog.d(TAG, "User " + userId + " (parent " + parent.id
+ "): attempting unlock because parent is unlocked");
maybeUnlockUser(userId);
} else {
String parentId = (parent == null) ? "" : String.valueOf(parent.id);
Slog.d(TAG, "User " + userId + " (parent " + parentId
+ "): delaying unlock because parent is locked");
}
} else {
maybeUnlockUser(userId);
}
}
} 3.5.2 UserController maybeUnlockUser()
boolean maybeUnlockUser(final int userId) {
// Try unlocking storage using empty token
return unlockUserCleared(userId, null, null, null);
}
boolean unlockUserCleared(final int userId, byte[] token, byte[] secret,
IProgressListener listener) {
UserState uss;
synchronized (mLock) {
// TODO Move this block outside of synchronized if it causes lock contention
if (!StorageManager.isUserKeyUnlocked(userId)) {
final UserInfo userInfo = getUserInfo(userId);
final IStorageManager storageManager = getStorageManager();
try {
// We always want to unlock user storage, even user is not started yet
storageManager.unlockUserKey(userId, userInfo.serialNumber, token, secret);
} catch (RemoteException | RuntimeException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Failed to unlock: " + e.getMessage());
}
}
// Bail if user isn't actually running, otherwise register the given
// listener to watch for unlock progress
uss = mStartedUsers.get(userId);
if (uss == null) {
notifyFinished(userId, listener);
return false;
} else {
uss.mUnlockProgress.addListener(listener);
uss.tokenProvided = (token != null);
}
}
finishUserUnlocking(uss);
final ArraySet childProfilesToUnlock = new ArraySet<>();
synchronized (mLock) {
// We just unlocked a user, so let's now attempt to unlock any
// managed profiles under that user.
for (int i = 0; i < mStartedUsers.size(); i++) {
final int testUserId = mStartedUsers.keyAt(i);
final UserInfo parent = mInjector.getUserManager().getProfileParent(testUserId);
if (parent != null && parent.id == userId && testUserId != userId) {
Slog.d(TAG, "User " + testUserId + " (parent " + parent.id
+ "): attempting unlock because parent was just unlocked");
childProfilesToUnlock.add(testUserId);
}
}
}
final int size = childProfilesToUnlock.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
maybeUnlockUser(childProfilesToUnlock.valueAt(i));
}
return true;
} 3.5.2 UserController finishUserUnlocking()这个方法最尾端有发送一个广播 mHandler.obtainMessage(SYSTEM_USER_UNLOCK_MSG, userId, 0, uss)
.sendToTarget()
private void finishUserUnlocking(final UserState uss) {
final int userId = uss.mHandle.getIdentifier();
boolean proceedWithUnlock = false;
synchronized (mLock) {
// Bail if we ended up with a stale user
if (mStartedUsers.get(uss.mHandle.getIdentifier()) != uss) return;
// Only keep marching forward if user is actually unlocked
if (!StorageManager.isUserKeyUnlocked(userId)) return;
if (uss.setState(STATE_RUNNING_LOCKED, STATE_RUNNING_UNLOCKING)) {
mInjector.getUserManagerInternal().setUserState(userId, uss.state);
proceedWithUnlock = true;
}
}
if (proceedWithUnlock) {
uss.mUnlockProgress.start();
// Prepare app storage before we go any further
uss.mUnlockProgress.setProgress(5,
mInjector.getContext().getString(R.string.android_start_title));
mInjector.getUserManager().onBeforeUnlockUser(userId);
uss.mUnlockProgress.setProgress(20);
// Dispatch unlocked to system services; when fully dispatched,
// that calls through to the next "unlocked" phase
mHandler.obtainMessage(SYSTEM_USER_UNLOCK_MSG, userId, 0, uss)
.sendToTarget();
}
}3.5.2 AMS SYSTEM_USER_UNLOCK_MSG ,也就是说SYSTEM_USER_UNLOCK_MSG message的处理是在AMS。但是后续它又会条用UserController finishUserUnlocked
case SYSTEM_USER_UNLOCK_MSG: {
final int userId = msg.arg1;
mSystemServiceManager.unlockUser(userId);
synchronized (ActivityManagerService.this) {
mRecentTasks.loadUserRecentsLocked(userId);
}
if (userId == UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM) {
startPersistentApps(PackageManager.MATCH_DIRECT_BOOT_UNAWARE);
}
installEncryptionUnawareProviders(userId);
mUserController.finishUserUnlocked((UserState) msg.obj);
/// M: DuraSpeed
mAmsExt.onSystemUserUnlock();
break;
}3.5.3 UserController finishUserUnlocked
void finishUserUnlocked(final UserState uss) {
final int userId = uss.mHandle.getIdentifier();
synchronized (mLock) {
// Bail if we ended up with a stale user
if (mStartedUsers.get(uss.mHandle.getIdentifier()) != uss) return;
// Only keep marching forward if user is actually unlocked
if (!StorageManager.isUserKeyUnlocked(userId)) return;
if (uss.setState(STATE_RUNNING_UNLOCKING, STATE_RUNNING_UNLOCKED)) {
mInjector.getUserManagerInternal().setUserState(userId, uss.state);
uss.mUnlockProgress.finish();
// Dispatch unlocked to external apps
final Intent unlockedIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_USER_UNLOCKED);
unlockedIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER_HANDLE, userId);
unlockedIntent.addFlags(
Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY | Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
mInjector.broadcastIntentLocked(unlockedIntent, null, null, 0, null,
null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, false, false, MY_PID, SYSTEM_UID,
userId);
if (getUserInfo(userId).isManagedProfile()) {
UserInfo parent = mInjector.getUserManager().getProfileParent(userId);
if (parent != null) {
final Intent profileUnlockedIntent = new Intent(
Intent.ACTION_MANAGED_PROFILE_UNLOCKED);
profileUnlockedIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER, UserHandle.of(userId));
profileUnlockedIntent.addFlags(
Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_REGISTERED_ONLY
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND);
mInjector.broadcastIntentLocked(profileUnlockedIntent,
null, null, 0, null, null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE,
null, false, false, MY_PID, SYSTEM_UID,
parent.id);
}
}
// Send PRE_BOOT broadcasts if user fingerprint changed; we
// purposefully block sending BOOT_COMPLETED until after all
// PRE_BOOT receivers are finished to avoid ANR'ing apps
final UserInfo info = getUserInfo(userId);
if (!Objects.equals(info.lastLoggedInFingerprint, Build.FINGERPRINT)) {
// Suppress double notifications for managed profiles that
// were unlocked automatically as part of their parent user
// being unlocked.
final boolean quiet;
if (info.isManagedProfile()) {
quiet = !uss.tokenProvided
|| !mLockPatternUtils.isSeparateProfileChallengeEnabled(userId);
} else {
quiet = false;
}
mInjector.sendPreBootBroadcast(userId, quiet,
() -> finishUserUnlockedCompleted(uss));
} else {
finishUserUnlockedCompleted(uss);
}
}
}
}3.5.4 UserController finishUserUnlockedCompleted
private void finishUserUnlockedCompleted(UserState uss) {
final int userId = uss.mHandle.getIdentifier();
synchronized (mLock) {
// Bail if we ended up with a stale user
if (mStartedUsers.get(uss.mHandle.getIdentifier()) != uss) return;
final UserInfo userInfo = getUserInfo(userId);
if (userInfo == null) {
return;
}
// Only keep marching forward if user is actually unlocked
if (!StorageManager.isUserKeyUnlocked(userId)) return;
// Remember that we logged in
mInjector.getUserManager().onUserLoggedIn(userId);
if (!userInfo.isInitialized()) {
if (userId != UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Initializing user #" + userId);
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_USER_INITIALIZE);
intent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_FOREGROUND
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_INCLUDE_BACKGROUND);
mInjector.broadcastIntentLocked(intent, null,
new IIntentReceiver.Stub() {
@Override
public void performReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode,
String data, Bundle extras, boolean ordered,
boolean sticky, int sendingUser) {
// Note: performReceive is called with mService lock held
mInjector.getUserManager().makeInitialized(userInfo.id);
}
}, 0, null, null, null, AppOpsManager.OP_NONE,
null, true, false, MY_PID, SYSTEM_UID, userId);
}
}
Slog.i(TAG, "Sending BOOT_COMPLETE user #" + userId);
// Do not report secondary users, runtime restarts or first boot/upgrade
if (userId == UserHandle.USER_SYSTEM
&& !mInjector.isRuntimeRestarted() && !mInjector.isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
int uptimeSeconds = (int) (SystemClock.elapsedRealtime() / 1000);
MetricsLogger.histogram(mInjector.getContext(), "framework_boot_completed",
uptimeSeconds);
}
final Intent bootIntent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED, null);
bootIntent.putExtra(Intent.EXTRA_USER_HANDLE, userId);
bootIntent.addFlags(Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_NO_ABORT
| Intent.FLAG_RECEIVER_INCLUDE_BACKGROUND);
mInjector.broadcastIntentLocked(bootIntent, null, new IIntentReceiver.Stub() {
@Override
public void performReceive(Intent intent, int resultCode, String data,
Bundle extras, boolean ordered, boolean sticky, int sendingUser)
throws RemoteException {
Slog.i(UserController.TAG, "Finished processing BOOT_COMPLETED for u" + userId);
}
}, 0, null, null,
new String[] { android.Manifest.permission.RECEIVE_BOOT_COMPLETED },
AppOpsManager.OP_NONE, null, true, false, MY_PID, SYSTEM_UID, userId);
}
}最终我们在这个方法里面找到发送Intent.ACTION_BOOT_COMPLETED的开机广播的代码,至此android系统就启动完成了