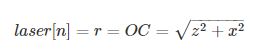深度图转激光原理
深度图转激光在ROS包depthimage_to_laserscan中实现,本篇讲解其计算过程。关于点云转激光数据的思路也是类似的,只需要将一定高度范围内的数据进行投影即可。
1. 深度图转激光原理
原理如图(1)所示。深度图转激光中,对任意给定的一个深度图像点m(u,v,z),其转换激光的步骤为:
a.将深度图像的点m(u,v,z)转换到深度相机坐标系下的坐标点M(x,y,z),具体求解过程请参考“深度图转点云的原理”;
b.计算直线AO和CO的夹角AOC,计算公式如下:
c.将角AOC影射到相应的激光数据槽中.已知激光的最小最大范围[α,β],激光束共细分为N分,那么可用数组laser[N]表示激光数据。那么点M投影到数组laser中的索引值n可如下计算:
laser[n]的值为M在x轴上投影的点C到相机光心O的距离r,即
2. 代码
以下为添加注释说明的实现代码(另可参阅原始代码),
/**
* Converts the depth image to a laserscan using the DepthTraits to assist.
*
* This uses a method to inverse project each pixel into a LaserScan angular increment. This method first projects the pixel
* forward into Cartesian coordinates, then calculates the range and angle for this point. When multiple points coorespond to
* a specific angular measurement, then the shortest range is used.
*
* @param depth_msg The UInt16 or Float32 encoded depth message.
* @param cam_model The image_geometry camera model for this image.
* @param scan_msg The output LaserScan.
* @param scan_height The number of vertical pixels to feed into each angular_measurement.
*
*/
template
void convert(const sensor_msgs::ImageConstPtr& depth_msg, const image_geometry::PinholeCameraModel& cam_model,
const sensor_msgs::LaserScanPtr& scan_msg, const int& scan_height) const{
// Use correct principal point from calibration
float center_x = cam_model.cx();//图像中心位置x
float center_y = cam_model.cy();//图像中心位置y
// Combine unit conversion (if necessary) with scaling by focal length for computing (X,Y)
double unit_scaling = depthimage_to_laserscan::DepthTraits::toMeters( T(1) );
float constant_x = unit_scaling / cam_model.fx();
float constant_y = unit_scaling / cam_model.fy();
const T* depth_row = reinterpret_cast(&depth_msg->data[0]);
int row_step = depth_msg->step / sizeof(T);
int offset = (int)(cam_model.cy()-scan_height/2);
depth_row += offset*row_step; // Offset to center of image
for(int v = offset; v < offset+scan_height_; v++, depth_row += row_step){
for (int u = 0; u < (int)depth_msg->width; u++) // Loop over each pixel in row
{
T depth = depth_row[u];
double r = depth; // Assign to pass through NaNs and Infs
double th = -atan2((double)(u - center_x) * constant_x, unit_scaling); // 计算夹角AOC,Atan2(x, z),实际上这里省略了深度值,因为分子分母都有,所以就略去了 but depth divides out
int index = (th - scan_msg->angle_min) / scan_msg->angle_increment;//计算对应激光数据的索引
if (depthimage_to_laserscan::DepthTraits::valid(depth)){ // Not NaN or Inf
// Calculate in XYZ,计算XYZ
double x = (u - center_x) * depth * constant_x;
double z = depthimage_to_laserscan::DepthTraits::toMeters(depth);
// Calculate actual distance,计算激光的真实距离
r = sqrt(pow(x, 2.0) + pow(z, 2.0));
}
// Determine if this point should be used.判断激光距离是否超出预设的有效范围
if(use_point(r, scan_msg->ranges[index], scan_msg->range_min, scan_msg->range_max)){
scan_msg->ranges[index] = r;
}
}
}
}
image_geometry::PinholeCameraModel cam_model_; ///< image_geometry helper class for managing sensor_msgs/CameraInfo messages.
float scan_time_; ///< Stores the time between scans.
float range_min_; ///< Stores the current minimum range to use.
float range_max_; ///< Stores the current maximum range to use.
int scan_height_; ///< Number of pixel rows to use when producing a laserscan from an area.
std::string output_frame_id_; ///< Output frame_id for each laserscan. This is likely NOT the camera's frame_id.
};
深圳辰视智能科技有限公司
深圳辰视智能科技有限公司是一家提供机器视觉、工业智能化设备的国家高新技术企业,是由中国科学院机器视觉技术研究团队创立,公司拥有快速三维建模、机器人运动控制、工件目标的分类与6D识别等方面的核心技术。
公司的主要产品有:机器人三维视觉引导系统、深度学习分类与检测系统、二维/三维视觉定位系统等,产品解决了机器人没有视觉感知与目标识别功能,影响机器人便捷应用的关键问题;使机器人拥有“双眼”和“大脑”。
目前,公司产品已广泛应用到自动上下料、组装、分类分拣、铸造、喷涂与焊接引导等多种不同工业场景,极大地提高生产效果、节约人力成本。
深圳辰视智能科技有限公司专注于工业视觉应用领域,致力于技术的不断研究、创新、突破,为合作伙伴提供全球领先的机器视觉产品及技术。
更多资讯, 联系我们!
联系方式:0755-26920296 199 2871 0160 / 181 2401 9365
www.cosmosvisiontech.com