Input子系统框架之InputDispatcher
原始链接:http://gityuan.com/2016/12/17/input-dispatcher/
一. InputDispatcher起点
上篇文章输入系统之InputReader线程,介绍InputReader利用EventHub获取数据后生成EventEntry事件,加入到InputDispatcher的mInboundQueue队列,再唤醒InputDispatcher线程。本文将介绍InputDispatcher,同样从threadLoop为起点开始分析。
1.1 threadLoop
先来回顾一下InputDispatcher对象的初始化过程:
InputDispatcher::InputDispatcher(const sp<InputDispatcherPolicyInterface>& policy) :
mPolicy(policy),
mPendingEvent(NULL), mLastDropReason(DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED),
mAppSwitchSawKeyDown(false), mAppSwitchDueTime(LONG_LONG_MAX),
mNextUnblockedEvent(NULL),
mDispatchEnabled(false), mDispatchFrozen(false), mInputFilterEnabled(false),
mInputTargetWaitCause(INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE) {
//创建Looper对象
mLooper = new Looper(false);
mKeyRepeatState.lastKeyEntry = NULL;
//获取分发超时参数
policy->getDispatcherConfiguration(&mConfig);
}
该方法主要工作:
创建属于自己线程的Looper对象;
超时参数来自于IMS,参数默认值keyRepeatTimeout = 500,keyRepeatDelay = 50。
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
bool InputDispatcherThread::threadLoop() {
mDispatcher->dispatchOnce(); //【见小节1.2】
return true;
}
整个过程不断循环地调用InputDispatcher的dispatchOnce()来分发事件
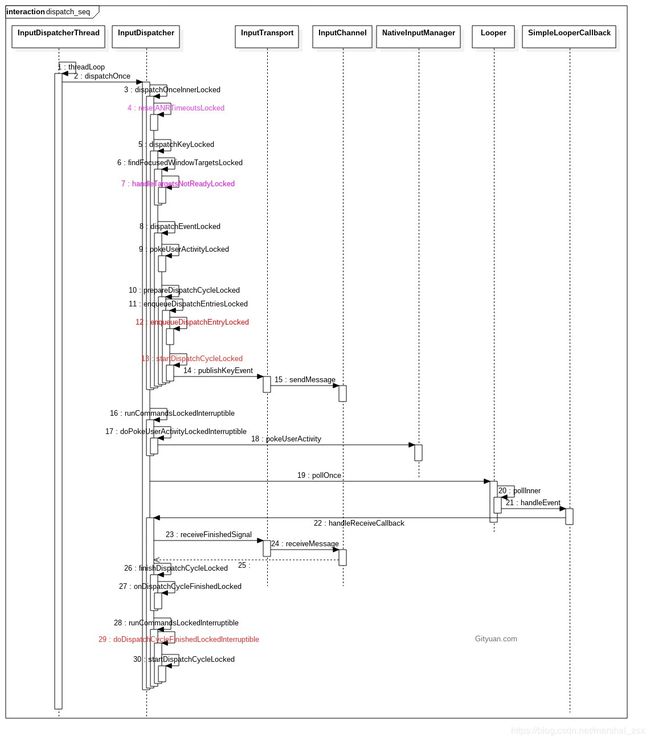
1.2 dispatchOnce
[-> InputDispatcher.cpp]
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
//唤醒等待线程,monitor()用于监控dispatcher是否发生死锁
mDispatcherIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {
//当mCommandQueue不为空时处理【见小节2.1】
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);
}
//【见小节3.1】
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {
nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;
}
}
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis); //进入epoll_wait
}
线程执行Looper->pollOnce,进入epoll_wait等待状态,当发生以下任一情况则退出等待状态:
callback:通过回调方法来唤醒;
timeout:到达nextWakeupTime时间,超时唤醒;
wake: 主动调用Looper的wake()方法;
二. InputDispatcher
2.1 dispatchOnceInnerLocked
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
nsecs_t currentTime = now(); //当前时间,也是后面ANR计时的起点
if (!mDispatchEnabled) { //默认值为false
resetKeyRepeatLocked(); //重置操作
}
if (mDispatchFrozen) { //默认值为false
return; //当分发被冻结,则不再处理超时和分发事件的工作,直接返回
}
//优化app切换延迟,当切换超时,则抢占分发,丢弃其他所有即将要处理的事件。
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime;
...
if (!mPendingEvent) {
if (mInboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
if (!mPendingEvent) {
return; //没有事件需要处理,则直接返回
}
} else {
//从mInboundQueue取出头部的事件
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.dequeueAtHead();
}
...
resetANRTimeoutsLocked(); //重置ANR信息[见小节2.1.1]
}
bool done = false;
DropReason dropReason = DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED;
if (!(mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER)) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_POLICY;
} else if (!mDispatchEnabled) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_DISABLED;
}
...
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
KeyEntry* typedEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(mPendingEvent);
if (isAppSwitchDue) {
if (isAppSwitchKeyEventLocked(typedEntry)) {
resetPendingAppSwitchLocked(true);
isAppSwitchDue = false;
} else if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_APP_SWITCH;
}
}
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED
&& isStaleEventLocked(currentTime, typedEntry)) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_STALE;
}
if (dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED && mNextUnblockedEvent) {
dropReason = DROP_REASON_BLOCKED;
}
// 分发按键事件[见小节2.2]
done = dispatchKeyLocked(currentTime, typedEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
...
}
...
//分发操作完成,则进入该分支
if (done) {
if (dropReason != DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
//[见小节2.1.2]
dropInboundEventLocked(mPendingEvent, dropReason);
}
mLastDropReason = dropReason;
releasePendingEventLocked(); //释放pending事件见小节2.10]
*nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; //强制立刻执行轮询
}
}
在enqueueInboundEventLocked()的过程中已设置mAppSwitchDueTime等于eventTime加上500ms:
mAppSwitchDueTime = keyEntry->eventTime + APP_SWITCH_TIMEOUT;
该方法主要功能:
mDispatchFrozen用于决定是否冻结事件分发工作不再往下执行;
当事件分发的时间点距离该事件加入mInboundQueue的时间超过500ms,则认为app切换过期,即isAppSwitchDue=true;
mInboundQueue不为空,则取出头部的事件,放入mPendingEvent变量;并重置ANR时间;
根据EventEntry的type类型分别处理,比如按键调用dispatchKeyLocked分发事件;再根据分发结果来决定是否进入done;
执行完成(done)的处理:
根据dropReason(默认NOT_DROPPED不处理)来决定是否丢失事件; dropInboundEventLocked
释放当前正在处理的事件(即mPendingEvent); releasePendingEventLocked
关于dispatchKeyLocked分发事件,
不会执行done过情况:
当前Event时间小于唤醒时间;
让policy有机会执行拦截操作;
调用findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked方法的返回结果是INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING, 即targets没有处于Ready状态;
会执行done的情况:
该事件需要丢弃, 即dropReason != DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED;
findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked的返回结果不是INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING(没有正在处理的事件);
接下来以按键为例来展开说明, 则进入[小节2.2] dispatchKeyLocked.
2.1.1 resetANRTimeoutsLocked
void InputDispatcher::resetANRTimeoutsLocked() {
// 重置等待超时cause和handle
mInputTargetWaitCause = INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_NONE;
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle.clear();
}
2.1.2 dropInboundEventLocked
void InputDispatcher::dropInboundEventLocked(EventEntry* entry, DropReason dropReason) {
const char* reason;
switch (dropReason) {
case DROP_REASON_POLICY:
reason = "inbound event was dropped because the policy consumed it";
break;
case DROP_REASON_DISABLED:
if (mLastDropReason != DROP_REASON_DISABLED) {
ALOGI("Dropped event because input dispatch is disabled.");
}
reason = "inbound event was dropped because input dispatch is disabled";
break;
case DROP_REASON_APP_SWITCH:
ALOGI("Dropped event because of pending overdue app switch.");
reason = "inbound event was dropped because of pending overdue app switch";
break;
case DROP_REASON_BLOCKED:
ALOGI("Dropped event because the current application is not responding and the user "
"has started interacting with a different application.");
reason = "inbound event was dropped because the current application is not responding "
"and the user has started interacting with a different application";
break;
case DROP_REASON_STALE:
ALOGI("Dropped event because it is stale.");
reason = "inbound event was dropped because it is stale";
break;
default:
return;
}
switch (entry->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
CancelationOptions options(CancelationOptions::CANCEL_NON_POINTER_EVENTS, reason);
synthesizeCancelationEventsForAllConnectionsLocked(options);
break;
}
...
}
}
2.2 dispatchKeyLocked
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchKeyLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, KeyEntry* entry,
DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
...
if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_TRY_AGAIN_LATER) {
// case1: 当前时间小于唤醒时间,则进入等待状态。
if (currentTime < entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime) {
if (entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime < *nextWakeupTime) {
*nextWakeupTime = entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime;
}
return false; //直接返回
}
entry->interceptKeyResult = KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_UNKNOWN;
entry->interceptKeyWakeupTime = 0;
}
if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_UNKNOWN) {
//case2: 让policy有机会执行拦截操作
if (entry->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {
CommandEntry* commandEntry = postCommandLocked(
& InputDispatcher::doInterceptKeyBeforeDispatchingLockedInterruptible);
if (mFocusedWindowHandle != NULL) {
commandEntry->inputWindowHandle = mFocusedWindowHandle;
}
commandEntry->keyEntry = entry;
entry->refCount += 1;
return false; //直接返回
} else {
entry->interceptKeyResult = KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_CONTINUE;
}
} else if (entry->interceptKeyResult == KeyEntry::INTERCEPT_KEY_RESULT_SKIP) {
if (*dropReason == DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
*dropReason = DROP_REASON_POLICY;
}
}
//case3: 如果需要丢弃该事件,则执行清理操作
if (*dropReason != DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
setInjectionResultLocked(entry, *dropReason == DROP_REASON_POLICY
? INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_SUCCEEDED : INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_FAILED);
return true; //直接返回
}
Vector<InputTarget> inputTargets;
//case4: 寻找焦点 【见小节2.3】
int32_t injectionResult = findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime,
entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime);
if (injectionResult == INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING) {
return false; //直接返回
}
setInjectionResultLocked(entry, injectionResult);
if (injectionResult != INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_SUCCEEDED) {
return true; //直接返回
}
addMonitoringTargetsLocked(inputTargets);
//只有injectionResult是成功,才有机会执行分发事件【见小节2.4】
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);
return true;
}
在以下场景下,有可能无法分发事件:
当前时间小于唤醒时间(nextWakeupTime)的情况;
policy需要提前拦截事件的情况;
需要drop事件的情况;
寻找聚焦窗口失败的情况;
如果成功跳过以上所有情况,则会进入执行事件分发的过程。
2.3 findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked
int32_t InputDispatcher::findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const EventEntry* entry, Vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
int32_t injectionResult;
String8 reason;
if (mFocusedWindowHandle == NULL) {
if (mFocusedApplicationHandle != NULL) {
//【见小节2.3.2】
injectionResult = handleTargetsNotReadyLocked(currentTime, entry,
mFocusedApplicationHandle, NULL, nextWakeupTime,
"Waiting because no window has focus but there is a "
"focused application that may eventually add a window "
"when it finishes starting up.");
goto Unresponsive;
}
ALOGI("Dropping event because there is no focused window or focused application.");
injectionResult = INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_FAILED;
goto Failed;
}
//权限检查
if (! checkInjectionPermission(mFocusedWindowHandle, entry->injectionState)) {
injectionResult = INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PERMISSION_DENIED;
goto Failed;
}
//检测窗口是否为更多的输入操作而准备就绪【见小节2.3.1】
reason = checkWindowReadyForMoreInputLocked(currentTime,
mFocusedWindowHandle, entry, "focused");
if (!reason.isEmpty()) {
//【见小节2.3.2】
injectionResult = handleTargetsNotReadyLocked(currentTime, entry,
mFocusedApplicationHandle, mFocusedWindowHandle, nextWakeupTime, reason.string());
goto Unresponsive;
}
injectionResult = INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_SUCCEEDED;
//成功找到目标窗口,添加到目标窗口 [见小节2.3.3]
addWindowTargetLocked(mFocusedWindowHandle,
InputTarget::FLAG_FOREGROUND | InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS, BitSet32(0),
inputTargets);
Failed:
Unresponsive:
//TODO: 统计等待时长信息,目前没有实现,这个方法还是很值得去改造
nsecs_t timeSpentWaitingForApplication = getTimeSpentWaitingForApplicationLocked(currentTime);
updateDispatchStatisticsLocked(currentTime, entry,
injectionResult, timeSpentWaitingForApplication);
return injectionResult;
}
此处mFocusedWindowHandle是何处赋值呢?是在InputDispatcher.setInputWindows()方法,具体见下一篇文章Input系统—UI线程.
寻找聚焦窗口失败的情况:
无窗口,无应用:Dropping event because there is no focused window or focused application.(这并不导致ANR的情况,因为没有机会调用handleTargetsNotReadyLocked)
无窗口, 有应用:Waiting because no window has focus but there is a focused application that may eventually add a window when it finishes starting up.
另外,还有更多的失败场景见checkWindowReadyForMoreInputLocked的过程,如下:
2.3.1 checkWindowReadyForMoreInputLocked
String8 InputDispatcher::checkWindowReadyForMoreInputLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle, const EventEntry* eventEntry,
const char* targetType) {
//当窗口暂停的情况,则保持等待
if (windowHandle->getInfo()->paused) {
return String8::format("Waiting because the %s window is paused.", targetType);
}
//当窗口连接未注册,则保持等待
ssize_t connectionIndex = getConnectionIndexLocked(windowHandle->getInputChannel());
if (connectionIndex < 0) {
return String8::format("Waiting because the %s window's input channel is not "
"registered with the input dispatcher. The window may be in the process "
"of being removed.", targetType);
}
//当窗口连接已死亡,则保持等待
sp<Connection> connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
if (connection->status != Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {
return String8::format("Waiting because the %s window's input connection is %s."
"The window may be in the process of being removed.", targetType,
connection->getStatusLabel());
}
// 当窗口连接已满,则保持等待
if (connection->inputPublisherBlocked) {
return String8::format("Waiting because the %s window's input channel is full. "
"Outbound queue length: %d. Wait queue length: %d.",
targetType, connection->outboundQueue.count(), connection->waitQueue.count());
}
if (eventEntry->type == EventEntry::TYPE_KEY) {
// 按键事件,输出队列或事件等待队列不为空
if (!connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty() || !connection->waitQueue.isEmpty()) {
return String8::format("Waiting to send key event because the %s window has not "
"finished processing all of the input events that were previously "
"delivered to it. Outbound queue length: %d. Wait queue length: %d.",
targetType, connection->outboundQueue.count(), connection->waitQueue.count());
}
} else {
// 非按键事件,事件等待队列不为空且头事件分发超时500ms
if (!connection->waitQueue.isEmpty()
&& currentTime >= connection->waitQueue.head->deliveryTime
+ STREAM_AHEAD_EVENT_TIMEOUT) {
return String8::format("Waiting to send non-key event because the %s window has not "
"finished processing certain input events that were delivered to it over "
"%0.1fms ago. Wait queue length: %d. Wait queue head age: %0.1fms.",
targetType, STREAM_AHEAD_EVENT_TIMEOUT * 0.000001f,
connection->waitQueue.count(),
(currentTime - connection->waitQueue.head->deliveryTime) * 0.000001f);
}
}
return String8::empty();
}
2.3.2 handleTargetsNotReadyLocked
int32_t InputDispatcher::handleTargetsNotReadyLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const EventEntry* entry,
const sp<InputApplicationHandle>& applicationHandle,
const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle,
nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime, const char* reason) {
if (applicationHandle == NULL && windowHandle == NULL) {
if (mInputTargetWaitCause != INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY) {
mInputTargetWaitCause = INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY;
mInputTargetWaitStartTime = currentTime; //当前时间
mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
mInputTargetWaitTimeoutExpired = false;
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle.clear();
}
} else {
if (mInputTargetWaitCause != INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY) {
nsecs_t timeout;
if (windowHandle != NULL) {
timeout = windowHandle->getDispatchingTimeout(DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT);
} else if (applicationHandle != NULL) {
timeout = applicationHandle->getDispatchingTimeout(DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT);
} else {
timeout = DEFAULT_INPUT_DISPATCHING_TIMEOUT; // 5s
}
mInputTargetWaitCause = INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY;
//这里的currentTime是指执行dispatchOnceInnerLocked方法体的起点
mInputTargetWaitStartTime = currentTime;
mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime = currentTime + timeout;
mInputTargetWaitTimeoutExpired = false;
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle.clear();
if (windowHandle != NULL) {
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle = windowHandle->inputApplicationHandle;
}
if (mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle == NULL && applicationHandle != NULL) {
mInputTargetWaitApplicationHandle = applicationHandle;
}
}
}
if (mInputTargetWaitTimeoutExpired) {
return INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_TIMED_OUT; //等待超时已过期,则直接返回
}
//当超时5s,则进入ANR流程
if (currentTime >= mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime) {
onANRLocked(currentTime, applicationHandle, windowHandle,
entry->eventTime, mInputTargetWaitStartTime, reason);
*nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; //强制立刻执行轮询来执行ANR策略
return INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING;
} else {
if (mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime < *nextWakeupTime) {
*nextWakeupTime = mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime; //当触发超时则强制执行轮询
}
return INPUT_EVENT_INJECTION_PENDING;
}
}
ANR超时时间点为mInputTargetWaitTimeoutTime,该值等于currentTime + 5s, 这里的currentTime是指执行dispatchOnceInnerLocked方法体的起点。此处设置mInputTargetWaitCause等于INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY(应用没有准备就绪),而前面resetANRTimeoutsLocked()过程是唯一用于重置等待理由的地方。
可见,ANR时间区间是从dispatchOnceInnerLocked方法体的起点,直到下次执行handleTargetsNotReadyLocked()方法的这段应用未准备就绪的时间段,该时间段是否超过5s来决定是否触发ANR。
当前这次的事件dispatch过程中执行findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked()方法到下一次执行resetANRTimeoutsLocked()的时间区间。
handleTargetsNotReadyLocked()的判断过程:
当applicationHandle和windowHandle同时为空, 且system准备就绪的情况下
设置等待理由 INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_SYSTEM_NOT_READY;
设置超时等待时长为无限大;
设置TimeoutExpired= false
清空等待队列;
当applicationHandle和windowHandle至少一个不为空, 且application准备就绪的情况下:
设置等待理由 INPUT_TARGET_WAIT_CAUSE_APPLICATION_NOT_READY;
设置超时等待时长为5s;
设置TimeoutExpired= false
清空等待队列;
继续回到[小节2.3]findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked,如果没有发生ANR,则addWindowTargetLocked()将该事件添加到inputTargets。
2.3.3 addWindowTargetLocked
void InputDispatcher::addWindowTargetLocked(const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle,
int32_t targetFlags, BitSet32 pointerIds, Vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
inputTargets.push();
const InputWindowInfo* windowInfo = windowHandle->getInfo();
InputTarget& target = inputTargets.editTop();
target.inputChannel = windowInfo->inputChannel;
target.flags = targetFlags;
target.xOffset = - windowInfo->frameLeft;
target.yOffset = - windowInfo->frameTop;
target.scaleFactor = windowInfo->scaleFactor;
target.pointerIds = pointerIds;
}
将当前聚焦窗口mFocusedWindowHandle的inputChannel传递到inputTargets。
2.4 dispatchEventLocked
void InputDispatcher::dispatchEventLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
EventEntry* eventEntry, const Vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
//【见小节2.4.1】向mCommandQueue队列添加doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible命令
pokeUserActivityLocked(eventEntry);
for (size_t i = 0; i < inputTargets.size(); i++) {
const InputTarget& inputTarget = inputTargets.itemAt(i);
//[见小节2.4.3]
ssize_t connectionIndex = getConnectionIndexLocked(inputTarget.inputChannel);
if (connectionIndex >= 0) {
sp<Connection> connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
//找到目标连接[见小节2.5]
prepareDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, &inputTarget);
}
}
}
该方法主要功能是将eventEntry发送到目标inputTargets.
其中pokeUserActivityLocked(eventEntry)方法最终会调用到Java层的PowerManagerService.java中的userActivityFromNative()方法. 这也是PMS中唯一的native call方法.
2.4.1 pokeUserActivityLocked
void InputDispatcher::pokeUserActivityLocked(const EventEntry* eventEntry) {
if (mFocusedWindowHandle != NULL) {
const InputWindowInfo* info = mFocusedWindowHandle->getInfo();
if (info->inputFeatures & InputWindowInfo::INPUT_FEATURE_DISABLE_USER_ACTIVITY) {
return;
}
}
...
//【见小节2.4.2】
CommandEntry* commandEntry = postCommandLocked(
& InputDispatcher::doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible);
commandEntry->eventTime = eventEntry->eventTime;
commandEntry->userActivityEventType = eventType;
}
2.4.2 postCommandLocked
InputDispatcher::CommandEntry* InputDispatcher::postCommandLocked(Command command) {
CommandEntry* commandEntry = new CommandEntry(command);
// 将命令加入mCommandQueue队尾
mCommandQueue.enqueueAtTail(commandEntry);
return commandEntry;
}
2.4.3 getConnectionIndexLocked
ssize_t InputDispatcher::getConnectionIndexLocked(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) {
ssize_t connectionIndex = mConnectionsByFd.indexOfKey(inputChannel->getFd());
if (connectionIndex >= 0) {
sp<Connection> connection = mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
if (connection->inputChannel.get() == inputChannel.get()) {
return connectionIndex;
}
}
return -1;
}
根据inputChannel的fd从mConnectionsByFd队列中查询目标connection.
2.5 prepareDispatchCycleLocked
void InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection, EventEntry* eventEntry, const InputTarget* inputTarget) {
if (connection->status != Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {
return; //当连接已破坏,则直接返回
}
...
//[见小节2.6]
enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);
}
当connection状态不正确,则直接返回。
2.6 enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection, EventEntry* eventEntry, const InputTarget* inputTarget) {
bool wasEmpty = connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty();
//[见小节2.7]
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_EXIT);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_ENTER);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER);
if (wasEmpty && !connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
//当原先的outbound队列为空, 且当前outbound不为空的情况执行.[见小节2.8]
startDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection);
}
}
该方法主要功能:
根据dispatchMode来分别执行DispatchEntry事件加入队列的操作。
当起初connection.outboundQueue等于空, 经enqueueDispatchEntryLocked处理后, outboundQueue不等于空情况下, 则执行startDispatchCycleLocked()方法.
2.7 enqueueDispatchEntryLocked
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(
const sp<Connection>& connection, EventEntry* eventEntry, const InputTarget* inputTarget,
int32_t dispatchMode) {
int32_t inputTargetFlags = inputTarget->flags;
if (!(inputTargetFlags & dispatchMode)) {
return; //分发模式不匹配,则直接返回
}
inputTargetFlags = (inputTargetFlags & ~InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_MASK) | dispatchMode;
//生成新的事件, 加入connection的outbound队列
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = new DispatchEntry(eventEntry,
inputTargetFlags, inputTarget->xOffset, inputTarget->yOffset,
inputTarget->scaleFactor);
switch (eventEntry->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
KeyEntry* keyEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(eventEntry);
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction = keyEntry->action;
dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags = keyEntry->flags;
if (!connection->inputState.trackKey(keyEntry,
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags)) {
delete dispatchEntry;
return; //忽略不连续的事件
}
break;
}
...
}
...
//添加到outboundQueue队尾
connection->outboundQueue.enqueueAtTail(dispatchEntry);
}
该方法主要功能:
根据dispatchMode来决定是否需要加入outboundQueue队列;
根据EventEntry,来生成DispatchEntry事件;
将dispatchEntry加入到connection的outbound队列.
执行到这里,其实等于由做了一次搬运的工作,将InputDispatcher中mInboundQueue中的事件取出后, 找到目标window后,封装dispatchEntry加入到connection的outbound队列.
2.8 startDispatchCycleLocked
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection) {
//当Connection状态正常,且outboundQueue不为空
while (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL
&& !connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.head;
dispatchEntry->deliveryTime = currentTime; //设置deliveryTime时间
status_t status;
EventEntry* eventEntry = dispatchEntry->eventEntry;
switch (eventEntry->type) {
case EventEntry::TYPE_KEY: {
KeyEntry* keyEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(eventEntry);
//发布Key事件 [见小节2.9]
status = connection->inputPublisher.publishKeyEvent(dispatchEntry->seq,
keyEntry->deviceId, keyEntry->source,
dispatchEntry->resolvedAction, dispatchEntry->resolvedFlags,
keyEntry->keyCode, keyEntry->scanCode,
keyEntry->metaState, keyEntry->repeatCount, keyEntry->downTime,
keyEntry->eventTime);
break;
}
...
}
if (status) { //publishKeyEvent失败情况
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
if (connection->waitQueue.isEmpty()) {
//pipe已满,但waitQueue为空. 不正常的行为
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, true /*notify*/);
} else {
// 处于阻塞状态
connection->inputPublisherBlocked = true;
}
} else {
//不不正常的行为
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, true /*notify*/);
}
return;
}
//从outboundQueue中取出事件,重新放入waitQueue队列
connection->outboundQueue.dequeue(dispatchEntry);
connection->waitQueue.enqueueAtTail(dispatchEntry);
}
}
startDispatchCycleLocked的主要功能: 从outboundQueue中取出事件,重新放入waitQueue队列
startDispatchCycleLocked触发时机:当起初connection.outboundQueue等于空, 经enqueueDispatchEntryLocked处理后, outboundQueue不等于空。
startDispatchCycleLocked主要功能: 从outboundQueue中取出事件,重新放入waitQueue队列
publishKeyEvent执行结果status不等于OK的情况下:
WOULD_BLOCK,且waitQueue等于空,则调用abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked(),该方法最终会调用到Java层的IMS.notifyInputChannelBroken().
WOULD_BLOCK,且waitQueue不等于空,则处于阻塞状态,即inputPublisherBlocked=true
其他情况,则调用abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked
abortBrokenDispatchCycleLocked()方法最终会调用到Java层的IMS.notifyInputChannelBroken().
2.9 inputPublisher.publishKeyEvent
[-> InputTransport.cpp]
status_t InputPublisher::publishKeyEvent(...) {
if (!seq) {
return BAD_VALUE;
}
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::TYPE_KEY;
msg.body.key.seq = seq;
msg.body.key.deviceId = deviceId;
msg.body.key.source = source;
msg.body.key.action = action;
msg.body.key.flags = flags;
msg.body.key.keyCode = keyCode;
msg.body.key.scanCode = scanCode;
msg.body.key.metaState = metaState;
msg.body.key.repeatCount = repeatCount;
msg.body.key.downTime = downTime;
msg.body.key.eventTime = eventTime;
//通过InputChannel来发送消息
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}
InputChannel通过socket向远端的socket发送消息。socket通道是如何建立的呢? InputDispatcher又是如何与前台的window通信的呢? 见下一篇文章Input系统—进程交互, 从文章的小节2.1开始继续往下说.
2.10 releasePendingEventLocked
void InputDispatcher::releasePendingEventLocked() {
if (mPendingEvent) {
resetANRTimeoutsLocked(); //重置ANR超时时间
releaseInboundEventLocked(mPendingEvent); //释放mPendingEvent对象,并记录到mRecentQueue队列
mPendingEvent = NULL; //置空mPendingEvent变量.
}
}
三. 处理Comand
3.1 runCommandsLockedInterruptible
bool InputDispatcher::runCommandsLockedInterruptible() {
if (mCommandQueue.isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
do {
//从mCommandQueue队列的头部取出第一个元素
CommandEntry* commandEntry = mCommandQueue.dequeueAtHead();
Command command = commandEntry->command;
//此处调用的命令隐式地包含'LockedInterruptible'
(this->*command)(commandEntry);
commandEntry->connection.clear();
delete commandEntry;
} while (! mCommandQueue.isEmpty());
return true;
}
通过循环方式处理完mCommandQueue队列的所有命令,处理过程从mCommandQueue中取出CommandEntry.
typedef void (InputDispatcher::*Command)(CommandEntry* commandEntry);
struct CommandEntry : Link<CommandEntry> {
CommandEntry(Command command);
Command command;
sp<Connection> connection;
nsecs_t eventTime;
KeyEntry* keyEntry;
sp<InputApplicationHandle> inputApplicationHandle;
sp<InputWindowHandle> inputWindowHandle;
String8 reason;
int32_t userActivityEventType;
uint32_t seq;
bool handled;
};
前面小节【2.4.1】添加的doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible命令. 接下来进入该方法:
3.2 doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible
[-> InputDispatcher]
void InputDispatcher::doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible(CommandEntry* commandEntry) {
mLock.unlock();
//【见小节4.3】
mPolicy->pokeUserActivity(commandEntry->eventTime, commandEntry->userActivityEventType);
mLock.lock();
}
3.3 pokeUserActivity
[-> com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp]
void NativeInputManager::pokeUserActivity(nsecs_t eventTime, int32_t eventType) {
//[见小节4.4]
android_server_PowerManagerService_userActivity(eventTime, eventType);
}
3.4 android_server_PowerManagerService_userActivity
[-> com_android_server_power_PowerManagerService.cpp]
void android_server_PowerManagerService_userActivity(nsecs_t eventTime, int32_t eventType) {
// Tell the power HAL when user activity occurs.
if (gPowerModule && gPowerModule->powerHint) {
gPowerModule->powerHint(gPowerModule, POWER_HINT_INTERACTION, NULL);
}
if (gPowerManagerServiceObj) {
...
//[见小节4.5]
env->CallVoidMethod(gPowerManagerServiceObj,
gPowerManagerServiceClassInfo.userActivityFromNative,
nanoseconds_to_milliseconds(eventTime), eventType, 0);
}
}
3.5 PMS.userActivityFromNative
[-> PowerManagerService.java]
private void userActivityFromNative(long eventTime, int event, int flags) {
userActivityInternal(eventTime, event, flags, Process.SYSTEM_UID);
}
private void userActivityInternal(long eventTime, int event, int flags, int uid) {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (userActivityNoUpdateLocked(eventTime, event, flags, uid)) {
updatePowerStateLocked();
}
}
}
runCommandsLockedInterruptible是不断地从mCommandQueue队列取出命令,然后执行直到全部执行完成。 除了doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible,还有其他如下命令:
- doNotifyANRLockedInterruptible
- doInterceptKeyBeforeDispatchingLockedInterruptible
- doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible
- doNotifyInputChannelBrokenLockedInterruptible
- doNotifyConfigurationChangedInterruptible