Netty源码(五):keepalive和Idle处理
1.keepalive和Idle检测
keepalive机制:如果对方突然无响应,我们需要发送一个探测帧去查看对方是是否下线。
Idle检测:如果你发送数据给对方,对方无响应,你会等一段时间(Idle检测),如果对方无响应,你就会发送心跳包(Idle检测)
2. 两种设置keepalive的方式
下面两行代码都可以开启keepalive模式,keepalive模式默认是关闭的

跟进childOption源码,发现它是ServerBootstrap里面的一个LinkedHashMap,用于保存与客户端的socketChannel的操作。
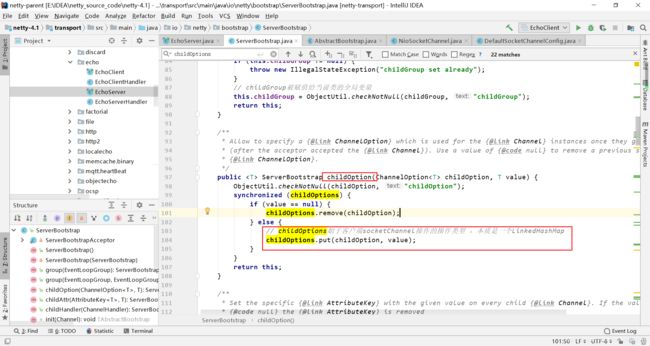
在该类中搜索发现在init()方法中,childOptions在初始化ServerBootstrapAcceptor被当作参数传入。
ServerBootstrapAcceptor的是在连接建立完成之后的以下列操作的一个封装类
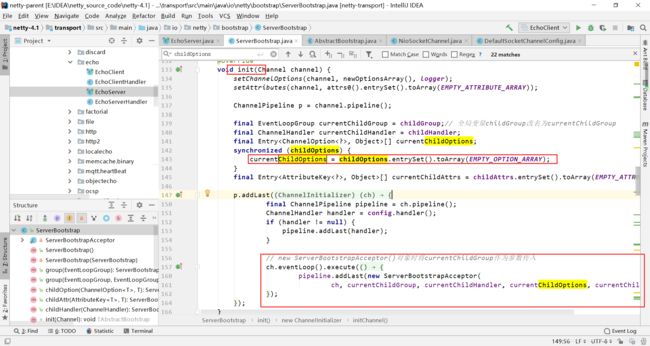
在里面的channelRead()方法中使用了setChannelOptions方法去完成socketChannel的相关option的设置
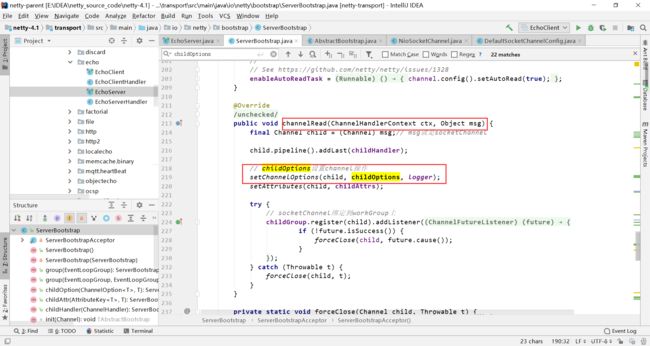
继续跟进源码,setChannelOptions方法使用了setChannelOption将map中的操作都设置到socketChannel中,setChannelOption又使用了setOption去完成此操作。
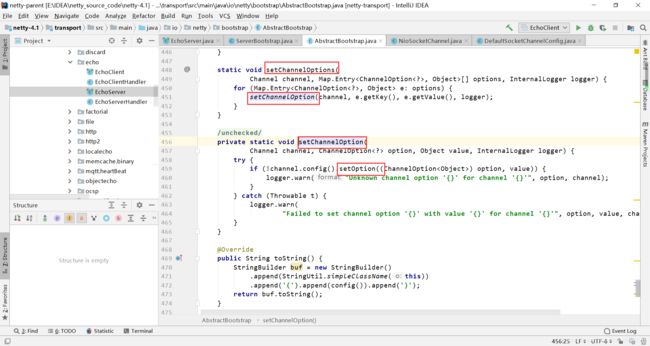
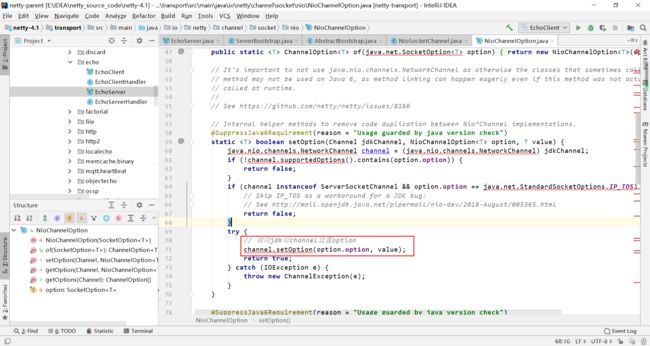
因为我们讨论的是NioSocketChannel,所以我们查看其setOption方法
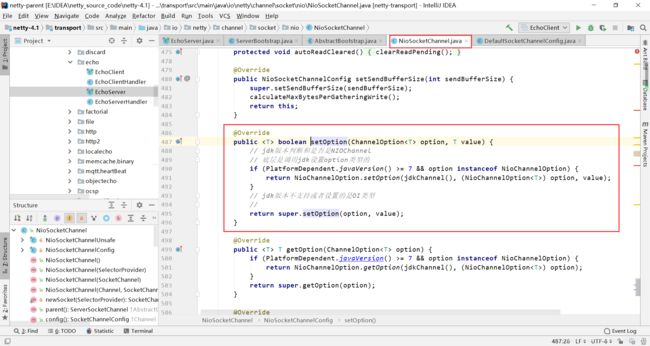
2.1 如果java版本大于7并且option是NioChannelOption
2.2 jdk版本不支持或者设置的是OIO类型
手动使用if else完成对channel中的option的设置,如果遇到了if else中不存在的option类型,需要手动在if else上添加判断分支。
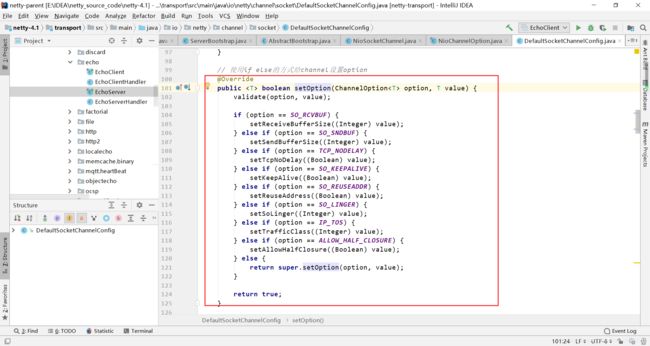
总结:下面两个代码的区别是,一个通过if else的方式手动设置channel的option,NioChannelOption则是另一种方式是,它使用的是jdk的设置option的方式设置的,不需要手动增加if else判断。
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true )
.childOption(NioChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE,true )
3. IdleStateHandler如何处理Idle
ReaderIdle处理逻辑
private final class ReaderIdleTimeoutTask extends AbstractIdleTask {
ReaderIdleTimeoutTask(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
super(ctx);
}
@Override
protected void run(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
long nextDelay = readerIdleTimeNanos;// 空闲的延迟时间
if (!reading) {
// 下一个需要定时的任务的延迟时间
nextDelay -= ticksInNanos() - lastReadTime;
}
if (nextDelay <= 0) {// 发生空闲,创建一个schedule任务,延时时间为readerIdleTimeNanos
// Reader is idle - set a new timeout and notify the callback.
readerIdleTimeout = schedule(ctx, this, readerIdleTimeNanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
boolean first = firstReaderIdleEvent;
firstReaderIdleEvent = false;
try {
IdleStateEvent event = newIdleStateEvent(IdleState.READER_IDLE, first);
// 发生事件的回调,将事件放入pipeline
channelIdle(ctx, event);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(t);
}
} else {
// 没有发生空闲,创建一个schedule任务,延时时间为nextDelay
// Read occurred before the timeout - set a new timeout with shorter delay.
readerIdleTimeout = schedule(ctx, this, nextDelay, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
}
}
}
WriterIdle事件,多了一个hasOutputChanged()方法
private final class WriterIdleTimeoutTask extends AbstractIdleTask {
WriterIdleTimeoutTask(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
super(ctx);
}
@Override
protected void run(ChannelHandlerContext ctx) {
long lastWriteTime = IdleStateHandler.this.lastWriteTime;
long nextDelay = writerIdleTimeNanos - (ticksInNanos() - lastWriteTime);
if (nextDelay <= 0) {
// Writer is idle - set a new timeout and notify the callback.
writerIdleTimeout = schedule(ctx, this, writerIdleTimeNanos, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
boolean first = firstWriterIdleEvent;
firstWriterIdleEvent = false;
try {
// 和ReaderIdle不同之处
if (hasOutputChanged(ctx, first)) {
return;
}
IdleStateEvent event = newIdleStateEvent(IdleState.WRITER_IDLE, first);
channelIdle(ctx, event);
} catch (Throwable t) {
ctx.fireExceptionCaught(t);
}
} else {
// Write occurred before the timeout - set a new timeout with shorter delay.
writerIdleTimeout = schedule(ctx, this, nextDelay, TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS);
}
}
}
查看hasOutputChanged()方法
/**
* Returns {@code true} if and only if the {@link IdleStateHandler} was constructed
* with {@link #observeOutput} enabled and there has been an observed change in the
* {@link ChannelOutboundBuffer} between two consecutive calls of this method.
*
* https://github.com/netty/netty/issues/6150
*/
private boolean hasOutputChanged(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, boolean first) {
// 正常情况下:false,即写空闲的判断中的写指的是写成功,但实际可能遇到以下情况
// (1)写了,缓存区满了,没有写成功
// (2)写了一个大数据,写了,但没有完成
// 这个参数是判断写的意图,而不是判断是否写成功
if (observeOutput) {
// We can take this shortcut if the ChannelPromises that got passed into write()
// appear to complete. It indicates "change" on message level and we simply assume
// that there's change happening on byte level. If the user doesn't observe channel
// writability events then they'll eventually OOME and there's clearly a different
// problem and idleness is least of their concerns.
// 上一次写的时间和上一次发生变化的时间不同,说明正在写
if (lastChangeCheckTimeStamp != lastWriteTime) {
lastChangeCheckTimeStamp = lastWriteTime;
// But this applies only if it's the non-first call.
if (!first) {
return true;
}
}
Channel channel = ctx.channel();
Unsafe unsafe = channel.unsafe();
ChannelOutboundBuffer buf = unsafe.outboundBuffer();
if (buf != null) {
int messageHashCode = System.identityHashCode(buf.current());
long pendingWriteBytes = buf.totalPendingWriteBytes();
// pendingWriteBytes和上一次lastPendingWriteBytes不相同,说明正在追加数据
if (messageHashCode != lastMessageHashCode || pendingWriteBytes != lastPendingWriteBytes) {
lastMessageHashCode = messageHashCode;
lastPendingWriteBytes = pendingWriteBytes;
if (!first) {
return true;
}
}
// flush的进度不同说明正在写
long flushProgress = buf.currentProgress();
if (flushProgress != lastFlushProgress) {
lastFlushProgress = flushProgress;
if (!first) {
return true;
}
}
}
}
return false;
}
其中两个Idle异常:
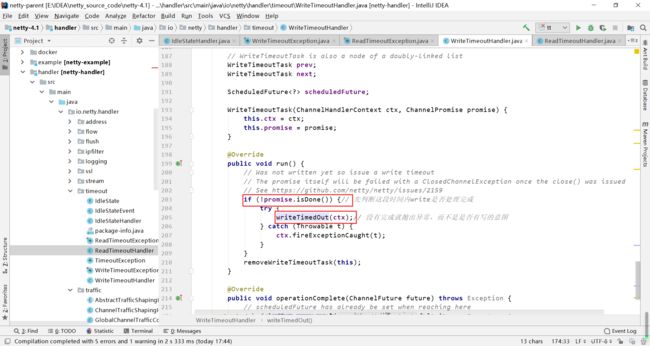
发生ReadIdle问题时,ReadTimeoutHandler是这样处理的,直接抛出异常。
发生WriteIdle问题时,系统自带的处理类WriteTimeoutHandler会先判断一段时间内wirte任务是否完成。