ML之Kmeans:利用自定义Kmeans函数实现对多个坐标点(自定义四个点)进行自动(最多迭代10次)分类
ML之Kmeans:利用自定义Kmeans函数实现对多个坐标点(自定义四个点)进行自动(最多迭代10次)分类
目录
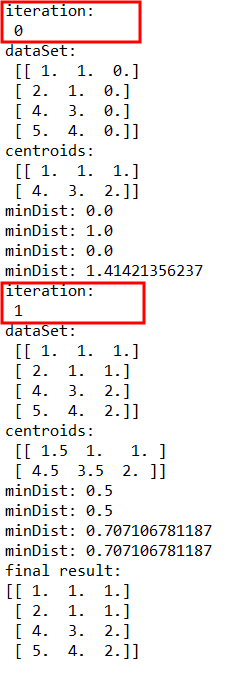
输出结果
核心代码
输出结果
核心代码
#!/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
#ML之Kmeans:利用自定义Kmeans函数实现对多个坐标点(自定义四个点)进行自动(最多迭代10次)分类
def kmeans(X, k, maxIt):
numPoints, numDim = X.shape
dataSet = np.zeros((numPoints, numDim + 1))
dataSet[:, :-1] = X
centroids = dataSet[np.random.randint(numPoints, size = k), :]
#centroids = dataSet[0:2, :]
#Randomly assign labels to initial centorid给初始中心随机分配标签
centroids[:, -1] = range(1, k +1)
iterations = 0
oldCentroids = None
# Run the main k-means algorithm
while not shouldStop(oldCentroids, centroids, iterations, maxIt):
print ("iteration: \n", iterations)
print ("dataSet: \n", dataSet)
print ("centroids: \n", centroids)
# Save old centroids for convergence test. Book keeping.
oldCentroids = np.copy(centroids)
iterations += 1
# Assign labels to each datapoint based on centroids
updateLabels(dataSet, centroids)
# Assign centroids based on datapoint labels
centroids = getCentroids(dataSet, k)
# We can get the labels too by calling getLabels(dataSet, centroids)
return dataSet
# Function: Should Stop
# -------------
# Returns True or False if k-means is done. K-means terminates either
# because it has run a maximum number of iterations OR the centroids
# stop changing.
def shouldStop(oldCentroids, centroids, iterations, maxIt):
if iterations > maxIt:
return True
return np.array_equal(oldCentroids, centroids)
# Function: Get Labels
# -------------
# Update a label for each piece of data in the dataset.
def updateLabels(dataSet, centroids):
# For each element in the dataset, chose the closest centroid.
# Make that centroid the element's label.
numPoints, numDim = dataSet.shape
for i in range(0, numPoints):
dataSet[i, -1] = getLabelFromClosestCentroid(dataSet[i, :-1], centroids)
def getLabelFromClosestCentroid(dataSetRow, centroids):
label = centroids[0, -1];
minDist = np.linalg.norm(dataSetRow - centroids[0, :-1])
for i in range(1 , centroids.shape[0]):
dist = np.linalg.norm(dataSetRow - centroids[i, :-1])
if dist < minDist:
minDist = dist
label = centroids[i, -1]
print ("minDist:", minDist)
return label
# Function: Get Centroids
# -------------
# Returns k random centroids, each of dimension n.
def getCentroids(dataSet, k):
# Each centroid is the geometric mean of the points that
# have that centroid's label. Important: If a centroid is empty (no points have
# that centroid's label) you should randomly re-initialize it.
result = np.zeros((k, dataSet.shape[1]))
for i in range(1, k + 1):
oneCluster = dataSet[dataSet[:, -1] == i, :-1]
result[i - 1, :-1] = np.mean(oneCluster, axis = 0)
result[i - 1, -1] = i
x1 = np.array([1, 1])
x2 = np.array([2, 1])
x3 = np.array([4, 3])
x4 = np.array([5, 4])
testX = np.vstack((x1, x2, x3, x4))
result = kmeans(testX, 2, 10)
print ("final result:")
print (result)
相关文章
ML之Kmeans:利用自定义Kmeans函数实现对多个坐标点(自定义四个点)进行自动(最多迭代10次)分类