Game with Pearls
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/65536 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 1923 Accepted Submission(s): 677
Problem Description
Tom and Jerry are playing a game with tubes and pearls. The rule of the game is:
1) Tom and Jerry come up together with a number K.
2) Tom provides N tubes. Within each tube, there are several pearls. The number of pearls in each tube is at least 1 and at most N.
3) Jerry puts some more pearls into each tube. The number of pearls put into each tube has to be either 0 or a positive multiple of K. After that Jerry organizes these tubes in the order that the first tube has exact one pearl, the 2nd tube has exact 2 pearls, …, the Nth tube has exact N pearls.
4) If Jerry succeeds, he wins the game, otherwise Tom wins.
Write a program to determine who wins the game according to a given N, K and initial number of pearls in each tube. If Tom wins the game, output “Tom”, otherwise, output “Jerry”.
Input
The first line contains an integer M (M<=500), then M games follow. For each game, the first line contains 2 integers, N and K (1 <= N <= 100, 1 <= K <= N), and the second line contains N integers presenting the number of pearls in each tube.
Output
For each game, output a line containing either “Tom” or “Jerry”.
Sample Input
2 5 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 1 2 3 4 5 5
Sample Output
Source
2014上海全国邀请赛——题目重现(感谢上海大学提供题目)
题目大意:
Tom和Jerry玩游戏。
Tom给定N个管子,里面有一些珍珠。
Jerry可以往里面放一些珍珠,必须的K的倍数,或者选择不放。
最后将管子排序,如果能使得第i个管子里刚好有i颗珍珠,则Jerry赢得胜利,否则Tom赢。
解题思路:
一、贪心:
将N个管子按管内的珍珠数量升序排序。
对每个管子进行遍历,如果第i个管子内的珍珠刚好等于i,则进行下一个循环,
如果当前管内珍珠数量
如果当前管内珍珠数量>i,则说明不满足条件,即最少的珍珠数量已经大于i。
二、模拟:
用num数组记录每个数共有几种可能被组成出现。
例如:
4 3
1 1 2 3
num[1]=2,num[2]=1,num[3]=1,num[4]=2
从1到N遍历,如果num[i]不为0,说明有管子可以放在第i个位置,管内珍珠数量为i,
那么之后的num[i+n*k](i+n*k
如果num[i]==0,则说明没有可以构成i的管子存在了,Tom胜出。
前两个解题思路参考-》》http://www.cnblogs.com/Enumz/p/4071631.html
三、二分匹配:
以第二个样例为例:
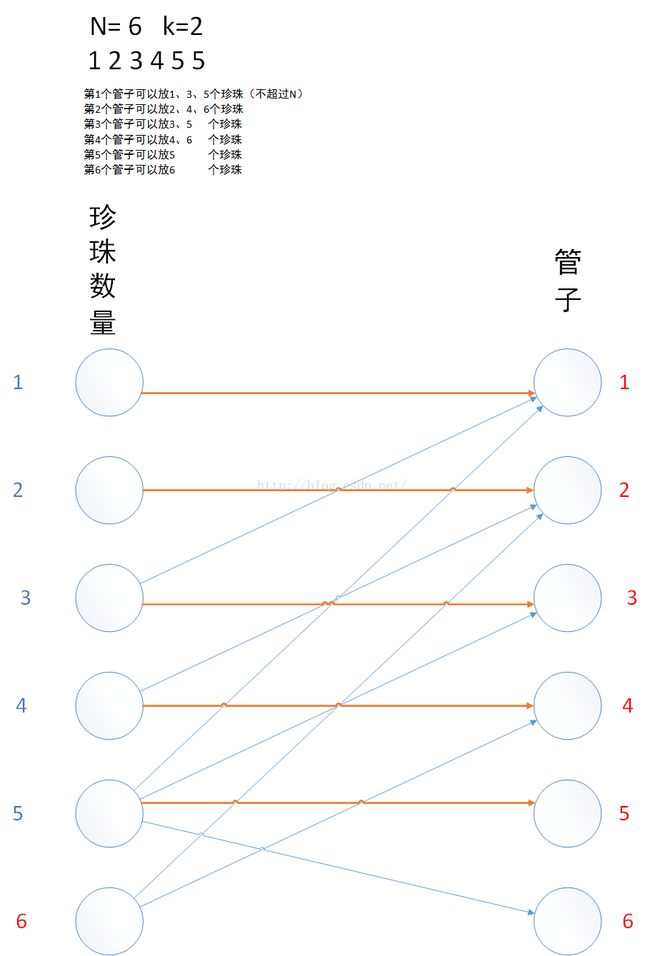
建边时,我们定义edge[j][i],表示第i个管子可以放j个珍珠。
二分匹配时,我们从珍珠数量出发。
如果第i个管子没被使用,那么我们就把当前的n个珍珠放在第i个管子里。
如果第i个管子被使用了,我们就查找其他管子是否可以放。
最后所有珍珠都可以被放置,即二分图里的最大匹配,恰好count==N,
那么就是Jerry胜利,否则Tom胜利。
/*贪心*/
#include
#include
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 110;
int num[maxn];
int n,k;
int main()
{
int m,i;
bool flag;
scanf("%d",&m);
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
scanf("%d",&num[i]);
flag=false;
sort(num+1,num+n+1); //下标从1开始,注意排序的起始地址和范围
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
if(num[i]!=i)
{
if(num[i]>i)
{
flag=true;
break;
}
num[i]+=k;
sort(num+i,num+n+1);
--i; //要--i,因为下次循环前要执行++i
}
}
if(flag) printf("Tom\n");
else printf("Jerry\n");
}
return 0;
}
/*模拟*/
#include
#include
const int maxn = 110;
int num[maxn];
int n,k;
int main()
{
int m,i,j,a;
bool flag;
scanf("%d",&m);
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
memset(num,0,sizeof(num));
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
scanf("%d",&a);
for(j=a;j<=n;j+=k)
num[j]++;
}
flag=false;
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
if(!num[i])
{
flag=true;
break;
}
else
{
for(j=i;j<=n;j+=k)
num[j]--;
}
}
if(flag) printf("Tom\n");
else printf("Jerry\n");
}
return 0;
}
/*二分匹配*/
#include
#include
const int maxn = 110;
bool edge[maxn][maxn],vis[maxn];
int num[maxn],a;
int n,k,count;
void init()
{
int i,j,a;
memset(edge,0,sizeof(edge));
memset(num,-1,sizeof(num));
for(i=1;i<=n;++i)
{
scanf("%d",&a);
for(j=a;j<=n;j+=k) //注意是edge[j][i],第i个盒子可以放j个珍珠
edge[j][i]=true;
}
}
bool find(int p)
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=n;++i) //遍历管子
{
if(edge[p][i]==true&&!vis[i])
{
vis[i]=true;
if(num[i]==-1||find(num[i])) //如果找到管子可以放,则把p个珍珠放在这个管子里。
{
num[i]=p;
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void hungry()
{
int i;
for(i=1;i<=n;++i) //以珍珠数量去找管子
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
if(find(i))
count++;
}
}
int main()
{
int m,i;
scanf("%d",&m);
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&k);
init();
count=0;
hungry();
if(count==n) printf("Jerry\n");
else printf("Tom\n");
}
return 0;
}
