Service、系统服务(震动器举例)、自定义服务(一)【安卓学习笔记七】
目录
一、什么是服务
系统服务
自定义服务
二、StartService()和BindService()两种启动方式的生命周期
三、启动service的两种方式
一、什么是服务
1、服务是四大组件之一,新建了一个service子类,在AndroidManifest.xml中就会生成
2、做一些耗时的工作或者一些跨进程的工作,不适合交给主线程,我们可以用自定义service
3、不需要界面只需要默默在后面做的工作我们可以放在后台进行
4、如果我们把一些不用放在前台,不需要界面的工作放在主线程中,就可能出现ANR(Application Not Responding),我们可以放在子线程中处理
5、我们可以通过activity,broadcast receiver,甚至一些其他的service来启动
6、不同启动方式的service的生命周期不同
**系统服务:**比如短信拦截、手机识别信息、震动、闹铃等系统服务,是系统封装好的,我们只需要去“召唤”它们就好了。
①设置权限uses-permission,对于不同版本的API注册权限的方式可能不同,我们可能需要用到动态注册权限
②获取系统服务context.getSyetemService(Service name)
③使用系统服务:调用系统服务提供的一些方法
例子:振动器进行震动
修改布局页面(点击按钮,启动震动器),用按钮button1来启动振动器
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Vibrator"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.49"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.335" />
</androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout>
①设置权限uses-permission,振动器的系统权限android.permission.VIBRATE
AndroidManifest.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.systemservice">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.VIBRATE"/>
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
②获取系统服务context.getSyetemService(Service name)
③使用系统服务:调用系统服务提供的一些方法
②获取系统的震动服务VIBRATOR_SERVICE
Vibrator vibrator = (Vibrator)getSystemService(VIBRATOR_SERVICE);//这里用getSystemService()方法获取的数据是Object类型,所以要进行强转
③使用服务:vibrator.vibrate(500);//设置震动时间500ms
vibrator还有很多方法,比如hasVibrator(),cancel(),
MainActivity.java
package com.example.systemservice;
import androidx.annotation.RequiresApi;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.app.AlarmManager;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.VibrationEffect;
import android.os.Vibrator;
import android.telephony.TelephonyManager;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
import static android.os.VibrationEffect.DEFAULT_AMPLITUDE;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
private Button button1,button2,button3;
private final static String TAG="Vibrator";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
button1 =(Button)findViewById(R.id.button1);
button1.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.button1:
Vibrator vibrator = (Vibrator)getSystemService(VIBRATOR_SERVICE);
vibrator.vibrate(500);//设置震动时间500ms
Log.d("Vibrator","振动器震动 500ms");
break;
}
}
}
**自定义服务:**自定义服务最大的任务就是减轻主线程的工作量,主线程主要负责与用户界面进行互动,如果这时候再把一些耗时的工作加到主线程中,就容易崩。我们可以把一些在后台默默做的耗时的工作放在service子类中做。
①创建一个service类
②重写service的回调方法
③start/bind service
二、StartService()和BindService()两种启动方式的生命周期
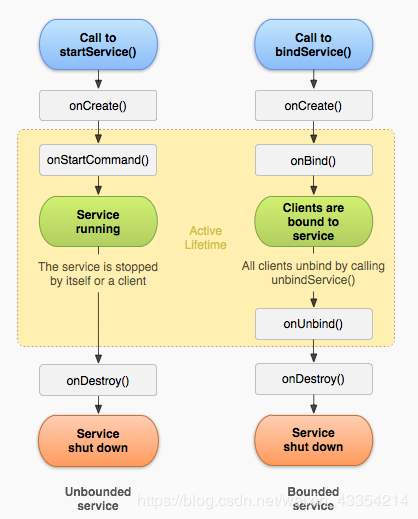
StartService()的生命周期是:onCreate()→onStartCommand()→onDestory()
StartService():由任意组件的独立intent来启动,不依赖与任何组件,意思就是它一旦启动就会一直运行,即使启动它的组件被销毁,它也会一直运行,停止它的方式只有两种:自己调用stopSelf()或者由其他组件调用stopService()
方法:
startService(intent)-
回调方法:onCreate()/onStartCommand()
stopService(intent)-
回调方法:onDestory()
BindService()的生命周期是:onCreate()→onBind()→onUnbind()→onDestory()
BindService():由service关联的组件的intent和ServiceConnection object来启动,它的生命周期依赖于绑定的组件,如果组件销毁那么service也停止了
方法:
ServiceConnection sc = new ServiceConnection(){}
bindService(intent,sc,null);
回调方法:onCreate(),onBind()
unbindService(sc);
回调方法:onUnbind(),onDestory()
三、启动service的两种方式
StartService“撒手不管”型:一种方式是告诉它做什么,然后就不管了
BindService“拴在裤腰带上”型:另一种方式是告诉它做什么,然后还一直在旁边观察着,不断进行监管交流
这里我们先介绍StartService(),BindService()将再下篇笔记中介绍
首先, 创建一个MyService类
MyService.java
package com.example.systemservice;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.util.Log;
public class MyService extends Service {
private final static String TAG="MyService";
public MyService() {
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
Log.i(TAG,"onCreate()-service instance created in memory");
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
// TODO: Return the communication channel to the service.
//throw new UnsupportedOperationException("Not yet implemented");
return null;
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.i(TAG,"onStartCommand()-service instance started");
return super.onStartCommand(intent, flags, startId);
}
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
Log.i(TAG,"onUnbind()-service instance unbind");
return super.onUnbind(intent);
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.i(TAG,"onDestory()-service instance destoryed");
}
}
我们用按钮startService和按钮stopService来控制service的启动和停止
修改页面布局文件
activity_main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<androidx.constraintlayout.widget.ConstraintLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/button4"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="32dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="181dp"
android:text="startService"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/button1"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toStartOf="@+id/button5"
app:layout_constraintHorizontal_bias="0.488"
app:layout_constraintStart_toStartOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.0" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/button5"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginEnd="60dp"
android:layout_marginRight="60dp"
android:text="stopService"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toTopOf="@+id/button1"
app:layout_constraintEnd_toEndOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintVertical_bias="0.176" />
然后,为按钮设置监听事件
MainActivity.java:
package com.example.systemservice;
import androidx.annotation.RequiresApi;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.app.AlarmManager;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Build;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.VibrationEffect;
import android.os.Vibrator;
import android.telephony.TelephonyManager;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.Toast;
import static android.os.VibrationEffect.DEFAULT_AMPLITUDE;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnClickListener{
private Button button1,button2,button3,button4,button5;
private final static String TAG="Vibrator";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
button4 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button4);
button4.setOnClickListener(this);
button5 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.button5);
button5.setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
switch (v.getId()){
case R.id.button4:
Intent service = new Intent();
service.setClass(this,MyService.class);
startService(service);//启动service
break;
case R.id.button5:
Intent intent =new Intent(this,MyService.class);//与button4中的intent没有必然联系
stopService(intent);//停止service
}
}
需要注意的是:button4里的service与button5中的intent没有必然的联系,因为StartService()不依赖于任何组件,所以停止service的组件不一定就是启动它的组件。
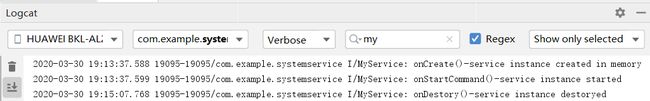
然后我们点击startService按钮,可以在Logcat中看到onCreate()和onStartCommand()方法被调用
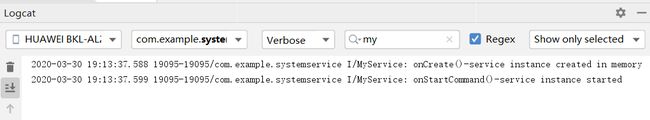
然后点击stopService按钮,可以在Logcat中看到onDestory()方法被调用