【Leetcode 225】 Implement Stack using Queues - EASY
【Leetcode 225】 Implement Stack using Queues - EASY
- 题目
- 思路
- 题解
- 反思
- 复杂度分析
- 思路反思
- 扩展学习
- 方法1
- 方法2
题目
Implement the following operations of a stack using queues.
push(x) – Push element x onto stack.
pop() – Removes the element on top of the stack.
top() – Get the top element.
empty() – Return whether the stack is empty.
用队列实现栈的以下方法:
push(x) – 将元素x入栈
pop() – 弹出栈顶元素
top() – 返回栈顶元素
empty() – 判断栈中是否为空
Example:
MyStack stack = new MyStack();
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.top(); // returns 2
stack.pop(); // returns 2
stack.empty(); // returns false
Notes:
You must use only standard operations of a queue – which means only push to back, peek/pop from front, size, and is empty operations are valid.
Depending on your language, queue may not be supported natively. You may simulate a queue by using a list or deque (double-ended queue), as long as you use only standard operations of a queue.
You may assume that all operations are valid (for example, no pop or top operations will be called on an empty stack).
思路
队列的特点是先进先出,而栈的特点是后进先出。
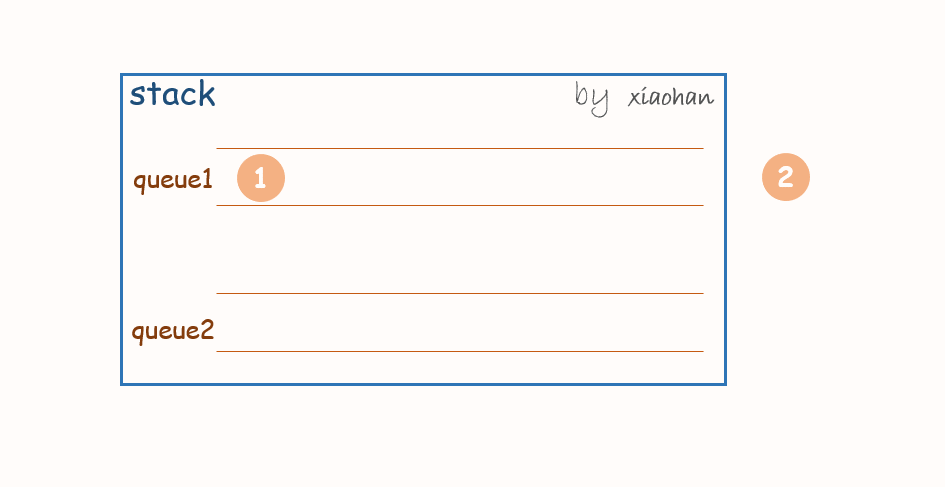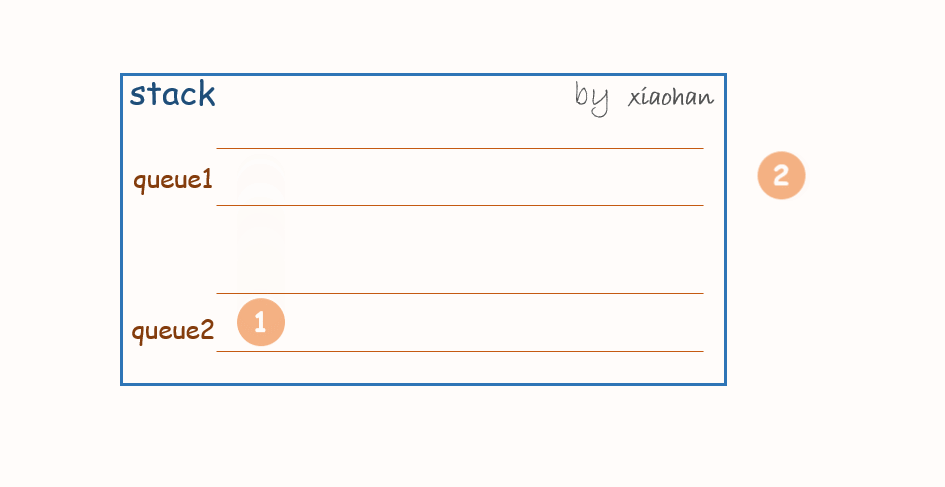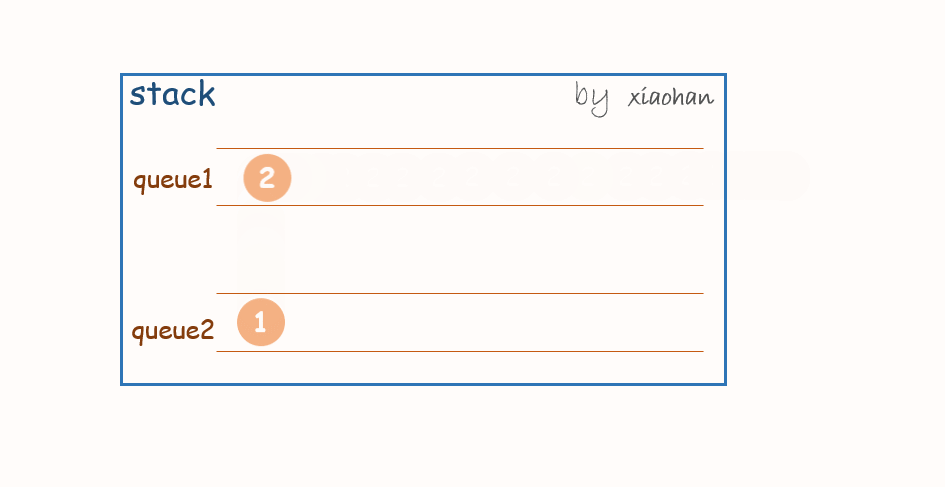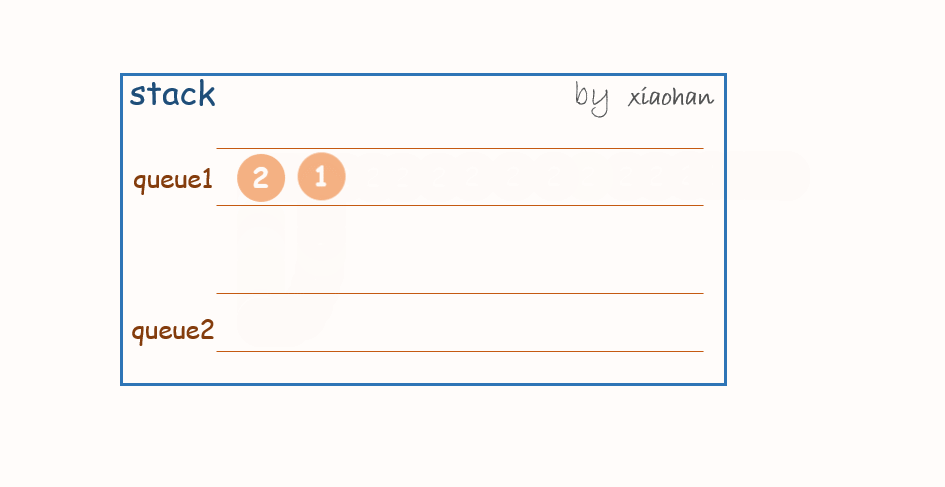
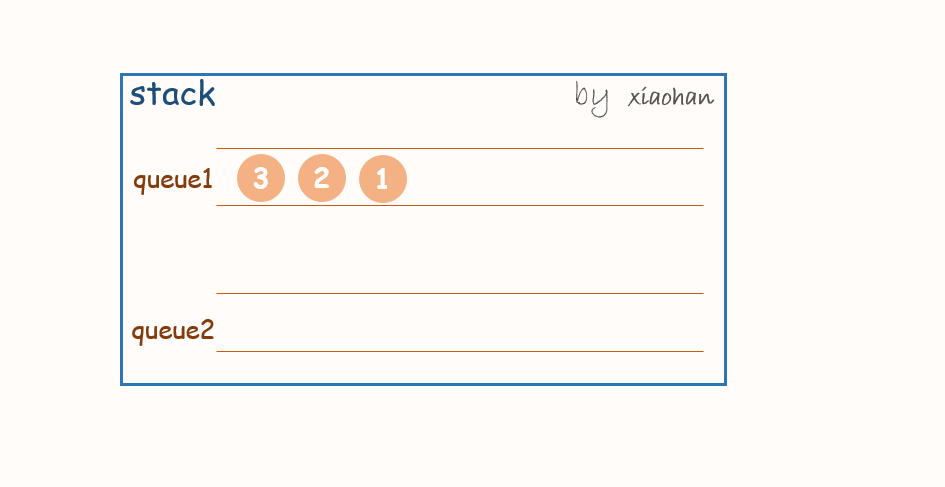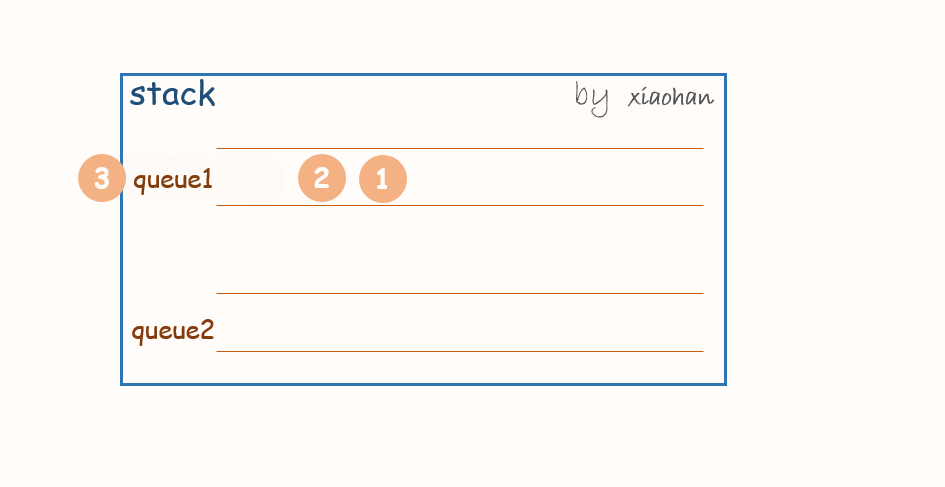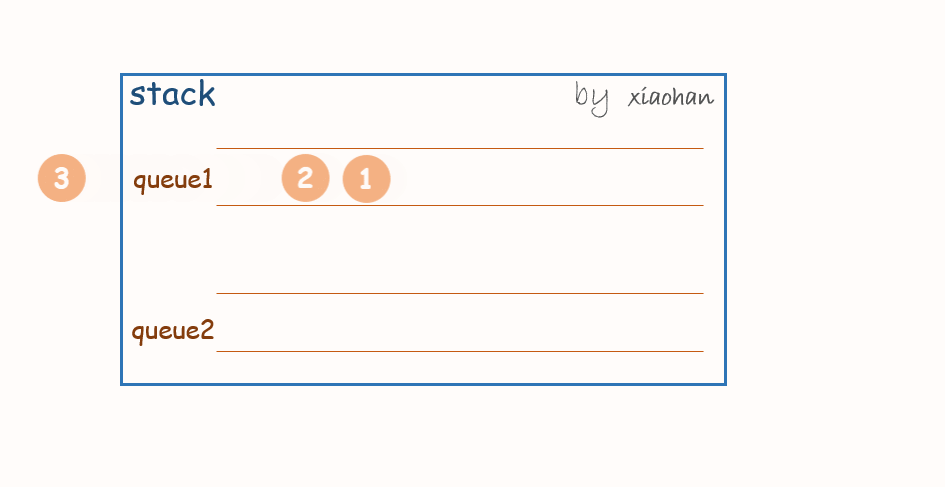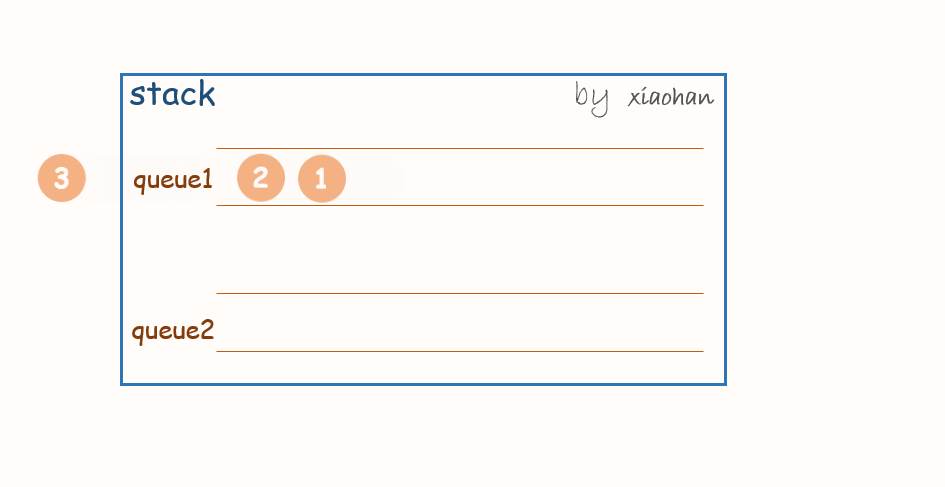
考虑用两个队列来实现栈,队列1用来存储值,队列2用来倒置。
(后续有对该思路进行反思)
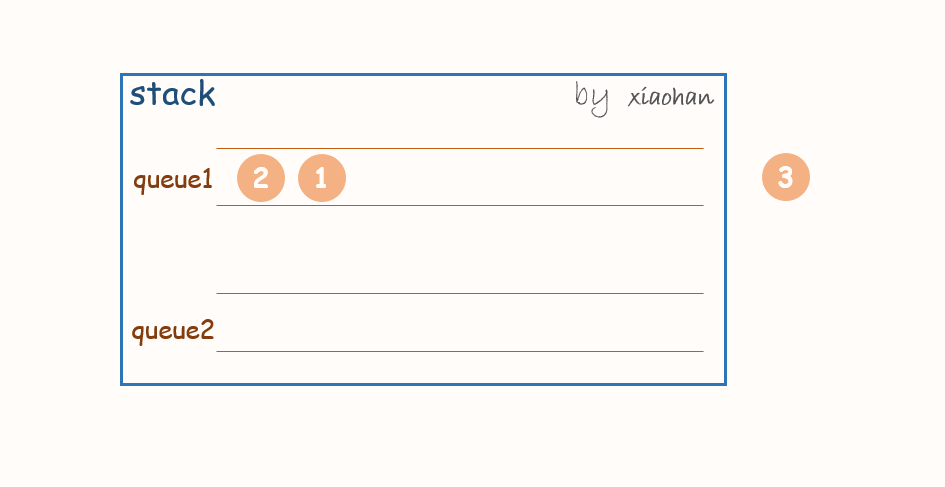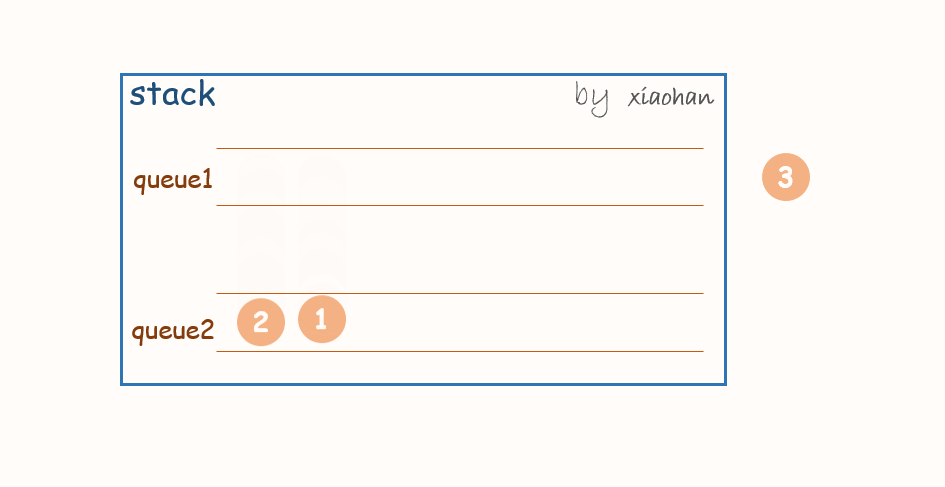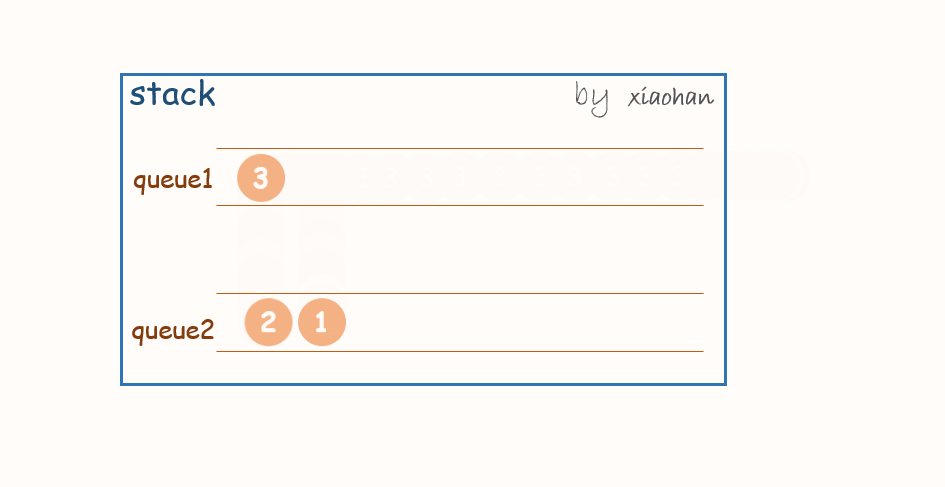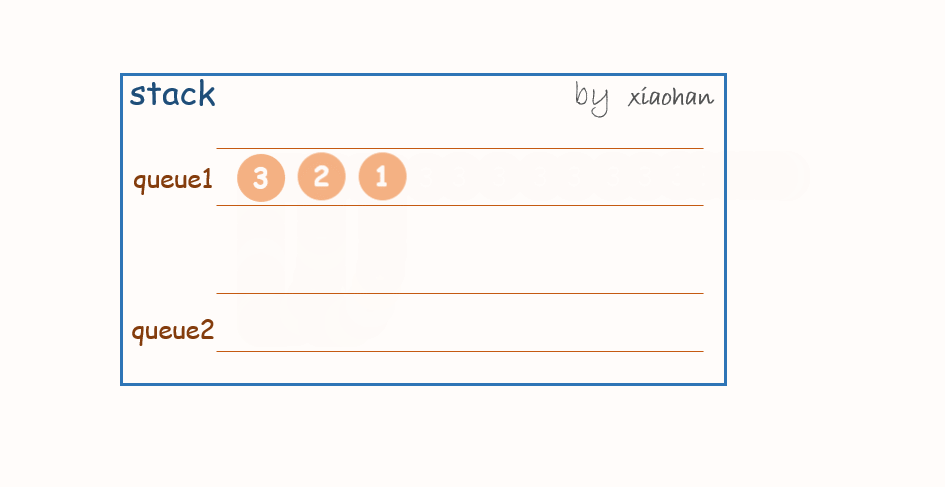
push(x):
每次有新的元素增加,都先将队列1中所有元素转移到队列2中,将新元素添加到队列1,然后再将队列2中的值转移到队列1中。
pop():
从队列1取出中一个元素
top():
获取队列1的队首元素
empty():
判断队列1是否为空
示例:
一个stack初始状态为空。
依次执行
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
stack.top();
stack.pop();
题解
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue1;// = new LinkedList<>();
private Queue<Integer> queue2;// = new LinkedList<>();
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
while(queue1.size()>0){
queue2.add(queue1.remove());
}
queue1.add(x);
while(queue2.size()>0){
queue1.add(queue2.remove());
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue1.remove();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue1.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.size()==0;
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
反思
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:
- push:O(n)
- pop:O(1)
- top:O(1)
- empty:O(1)
空间复杂度:
- O(1)
思路反思
首先有一点,我们上面所使用的方法是认为队列1和队列2有差别,永远往队列1中插入数据,用队列2进行倒置。那么能否认为两个队列无差别,只往空的那个队列中插入数据,另一个队列用来作其他数据的中转站呢?
当然是可以的,这样我们便可以节省掉在插入一个元素时,将当前n-1种先转移到队列2,腾出队列1位置的过程。
第二点,当前方式是push时就将队列倒置,push()的时间复杂度是O(n),pop()的时间复杂度是O(1)。
当然,如果push()操作较多,pop()操作较少,我们可以考虑使用一种push()时间复杂度为O(1),pop()复杂度为O(n)的方法。(扩展学习中的方法1)
另外,我们是否可以仅仅使用一个队列来实现栈呢?这样能够减少空间浪费,提升空间利用率。(扩展学习中的方法2)
扩展学习
方法1
考虑使用一种push()时间复杂度为O(1),pop()复杂度为O(n)的方法。
队列1用来存储值,队列2用作中转站。
push(x):
每次有新的元素增加,就直接添加到队列1中,并将该元素的值赋给top。
pop():
从队列1中转移n-1个元素到队列2,从队列1中取出栈顶元素。然后交换队列1、队列2。
top():
获取top值。
empty():
判断队列1是否为空
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue1;// = new LinkedList<>();
private Queue<Integer> queue2;// = new LinkedList<>();
private int top;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue1 = new LinkedList<>();
queue2 = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
queue1.add(x);
top = x;
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
int oldTop = top;
while(queue1.size() > 1){
top = queue1.remove();
queue2.add(top);
}
queue1.remove();
Queue<Integer> temp = queue1;
queue1 = queue2;
queue2 = temp;
return oldTop;
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return top;
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue1.size()==0;
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
- push:O(1)
- pop:O(n)
- top:O(1)
- empty:O(1)
空间复杂度:
- O(1)
方法2
用两个队列来实现势必会造成空间利用率低。那么我们可以考虑如何使用一个队列来实现。
push(x):
每次有新的元素增加,就直接添加到队列尾部中,然后取出队首元素放到队尾,如此执行n-1次。
pop():
移除队首元素。
top():
获取队首元素。
empty():
判断队列是否为空。
代码如下:
class MyStack {
private Queue<Integer> queue;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
public MyStack() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
}
/** Push element x onto stack. */
public void push(int x) {
int i = queue.size();
queue.add(x);
while(i>0){
queue.add(queue.remove());
i--;
}
}
/** Removes the element on top of the stack and returns that element. */
public int pop() {
return queue.remove();
}
/** Get the top element. */
public int top() {
return queue.peek();
}
/** Returns whether the stack is empty. */
public boolean empty() {
return queue.size()==0;
}
}
/**
* Your MyStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyStack obj = new MyStack();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
- push:O(n)
- pop:O(1)
- top:O(1)
- empty:O(1)
空间复杂度:
- O(1)
类似的题还有【Leetcode 232】 Implement Queues using Stacks - EASY。