Android自定义ImageView(二)——实现双击放大与缩小图片
效果图:
首先设置图片依据控件的大小来显示在ImageVeiw中
也就是当图片的宽与高小于控件的宽与高的时候,默认不进行对图片进行放大的操作,但是会将图片居中显示,当然使用的时候可以使用自定义的属性isScale=“true”,来设置,在加载图片的时候,如果图片的宽与高小于控件的宽与高的时候,会对图片进行适当 的放大
操作源码:具体可以参考http://blog.csdn.net/zl18603543572/article/details/50811771
public class ScaleAttrsImageView extends ImageView implements ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener {
private Matrix mMatrix;
public ScaleAttrsImageView(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public ScaleAttrsImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
private boolean isScale = false;
public ScaleAttrsImageView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
//获取所有的自定义属性和样式
final TypedArray typedArray = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ScaleImageView, defStyleAttr, 0);
//获取自定义属性的个数
final int indexCount = typedArray.getIndexCount();
//获取相关设定的值
for (int i = 0; i < indexCount; i++) {
final int attr = typedArray.getIndex(i);
switch (attr){
case R.styleable.ScaleImageView_isScaleImage:
isScale = typedArray.getBoolean(attr,false);
}
}
mMatrix = new Matrix();
}
@Override
protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener(this);
}
@Override
protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
super.onDetachedFromWindow();
getViewTreeObserver().removeOnGlobalLayoutListener(this);
}
private boolean mOnce = false;
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
if (!mOnce) {
final int width = getWidth();
final int height = getHeight();
final Drawable drawable = getDrawable();
if (drawable==null){
return;
}
final int intrinsicWidth = drawable.getIntrinsicWidth();
final int intrinsicHeight = drawable.getIntrinsicHeight();
float scale = 1.0f;
//如果图片宽度大于控件宽度,图片高度小于控件高度 图片缩小
if (intrinsicWidth > width && intrinsicHeight < height) {
scale = intrinsicWidth * 1.0f / width;
}
//如果图片的高度大于控件的高度,图片的宽度小于控件的宽度 图片缩小
if (intrinsicHeight > height && intrinsicWidth < width) {
scale = intrinsicHeight * 1.0f / height;
}
//如果图片的宽与高都大于控件的宽与高 或者 图片的宽与高都小于控件的宽与高
if ((intrinsicHeight > height && intrinsicWidth > width) ) {
scale = Math.min(width * 1.0f / intrinsicWidth, height * 1.0f / intrinsicHeight);
}
if (isScale&&(intrinsicHeight < height && intrinsicWidth < width)) {
scale = Math.min(width * 1.0f / intrinsicWidth, height * 1.0f / intrinsicHeight);
}
//得到初始化时图片需要进行缩放的值
final int moveX = getWidth() / 2 - intrinsicWidth / 2;
final int moveY = getHeight() / 2 - intrinsicHeight / 2;
mMatrix.postTranslate(moveX, moveY);
mMatrix.postScale(scale,scale,getWidth()/2,getHeight()/2);
setImageMatrix(mMatrix);
mOnce=true;
}
}
}实现双击图片,进行缩放的操作
当图片是在放大的状态的时候,双击图片,将其进行缩小
当图片是在缩小状态的时候,双击图片,将其进行放大的操作
当进行双击操作的时候,我们可以使用GestureDetector的方法onDoubleTap方法来监听双击的操作
在构造方法中初始化GestureDetector监听接口
private GestureDetector mGestureDetector1;
mGestureDetector1 = new GestureDetector(context,new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener(){
@Override
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
return true;
}
});当我们双击图片的时候,会调用到GestureDetector接口中的onDoubleTap,方法,那么当我们双击的时候,就可以在其中进行相应的缩放操作了
当然使用的时候,我们需要将我们的控件的点击事件传递给mGestureDetector1
所以使用我们的控件实现OnTouchListener接口,并在构造方法中进行设置事件监听
在onTouch方法中,将点击事件传递给mGestureDetector1
实现OnTouchListener接口,并实现其onTouch方法
在构造方法中进行OnTouchListener接口
setOnTouchListener(this);在其onTouch中将点击事件传递给mGestureDetector1
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
if (mGestureDetector1.onTouchEvent(event)){
return true;
}
return true;
}基本双击缩放逻辑
首先获取当前的缩放比例,如果当前的缩放比例大于初始的缩放比例,那么就将其进缩小操作
如果当前的缩放比例小于等于初始缩放比例,我们就将其进行放大的操作
获取当前图片的缩放值
public float getInitScale() {
final float[] floats = new float[9];
mMatrix.getValues(floats);
//获取当前的缩放值
return floats[Matrix.MSCALE_X];
}进行图片缩放的逻辑操作
//在mGestureDetector1的方法onDoubleTap中进行相关操作
mGestureDetector1 = new GestureDetector(context,new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener(){
@Override
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
//获取当前的点击点的坐标
float x = e.getX();
float y = e.getY();
//获取当前的缩放值
final float initScale = getInitScale();
//当前缩放值大于初使的缩放值,对其进行缩小操作
if(getInitScale()>mInitScale){
mMatrix.postScale(mInitScale/5.0f,mInitScale/5.0f,x,y);
setImageMatrix(mMatrix);
}else{
//当前的缩放值小于等于初始的缩放值,对其进行放大的操作
mMatrix.postScale(mInitScale*5.0f,mInitScale*5.0f,x,y);
setImageMatrix(mMatrix);
}
return true;
}
});走到这里,我们可以看到双击进行缩放操作的图片是瞬间放大或者缩小的,在这里,我们可以进行一些显示效果的优化操作
双击缓慢进行图片的放大与缩小的操作过程
效果图
这里进行操作的原理:
放大的原理,判断当前的广大比例是否大于指定的最大放大的值,如果大于等于,就设置显示此时的显示大小,如果不大于,那么就再次进行放大操作,
缩小图片的原理与放大图片的操作原理一致
编写操作缓慢缩放的过程()
(这个操作方法是参考了鸿洋大神的方法)
private class AutoScaleRunnable implements Runnable {
/**
* 缩放的目标值
*/
private float mTargetScale;
/**
* 缩放的中心点
*/
private float x;
private float y;
public AutoScaleRunnable(float targetScale, float x, float y) {
//将要进行缩放的大小值
mTargetScale = targetScale;
//缩放的中心点
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
//getInitScale方法获得当前的缩放值
//依据当前的缩放值设置将要进行的缩放比例操作
if (getInitScale() < mTargetScale) {
tmpScale = BIGGET;
}
if (getInitScale() > mTargetScale) {
tmpScale = SMALL;
}
}
/**
* 缩放过程中的梯度
*/
private float BIGGET = 1.07F;
private float SMALL = 0.83F;
private float tmpScale;
@Override
public void run() {
//将图片进行缩放的操作
mMatrix.postScale(tmpScale, tmpScale, x, y);
//进行缩放过程中的边界控制
checkBorderAndCenter();
setImageMatrix(mMatrix);
//获取当前的缩放值
float currentScale = getInitScale();
if ((tmpScale>1.0f&¤tScalemTargetScale)){
//再次进行缩放
postDelayed(this,16);
}else {
float scale = mTargetScale/currentScale;
mMatrix.postScale(scale,scale,x,y);
setImageMatrix(mMatrix);
mIsAutoScale = false;
}
}
} 在上面注册的GestureDetector接口中的onDoubleTap中进行操作
mGestureDetector1 = new GestureDetector(context,new GestureDetector.SimpleOnGestureListener(){
@Override
public boolean onDoubleTap(MotionEvent e) {
if (mIsAutoScale){
return true;
}
float x = e.getX();
float y = e.getY();
if (getInitScale()上面使用到 mMidScale mInitScale
//初始化缩放的值
private float mInitScale;
//双击放大到达的值
private float mMidScale;
//放大到最大的值
private float mMaxScale;这是初始化的一进行缩放大小程度的控制变量
可以在onGlobalLayout中进行初始化默认附值操作
mInitScale = scale;
mMidScale = scale*3.5f;
mMaxScale = scale*5.0f;其中scale是进行比较后根据图片与控件的大小而确定的缩放值,这里只设置了默认值,当然也可以自定义属性,对放大与缩小控制变量的值进行指定的设置
使用自定义属性来设置控制缩放变量的值
在values的attrs.xml文件中
其中属性isCaleToValue 是标识用户是否设定了指定放大到的比例倍数,true,使用属性中设定的值,false使用默认的值
在构造中获取我们所用到的自定义属性
//获取所有的自定义属性和样式
final TypedArray typedArray = context.getTheme().obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.ScaleImageView, defStyleAttr, 0);
//获取自定义属性的个数
final int indexCount = typedArray.getIndexCount();
//获取相关设定的值
for (int i = 0; i < indexCount; i++) {
final int attr = typedArray.getIndex(i);
switch (attr){
case R.styleable.ScaleImageView_isScaleImage:
isScale = typedArray.getBoolean(attr,false);
break;
case R.styleable.ScaleImageView_isScaleToValue:
isScaleToValue = typedArray.getBoolean(attr,false);
break;
case R.styleable.ScaleImageView_scaleMaxValue:
mMaxScale = typedArray.getFloat(attr, 2.0f);
break;
case R.styleable.ScaleImageView_scaleMidValue:
mMidScale = typedArray.getFloat(attr, 1.5f);
break;
}
}在onGlobalLayout中进行附值操作
//判断如果属性中没有定义设定放大操作控制变量值,这里进行默认附值的操作
if (!isScaleToValue){
mMidScale = scale*3.5f;
mMaxScale = scale*5.0f;
}注:在进行图片的缩放过程中,会出现图片恢复不到原位,出现上下左右四面中的某一面的空白边隙,所以在进行缩放的过程中,要时时控制缩放的边界
控制图片缩放的边界(处理空白问题)
图片解析空白计算说明(当然,只有图片的宽度或高度大于控件的宽度于高度的时候才需要处理边界空白问题,当图片的宽度或者是高度小于控件的宽度于高度的时候,我们设置让图片居中进行显示)
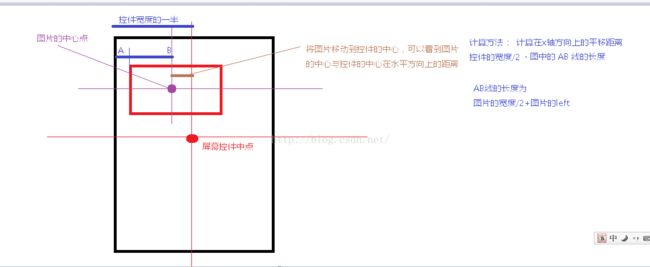
当图片的宽度大于控件的宽度的时候,进行边界控制说明:(高度方向边界控制原理一至)
当图片的宽度小于控件的宽度的时候 :
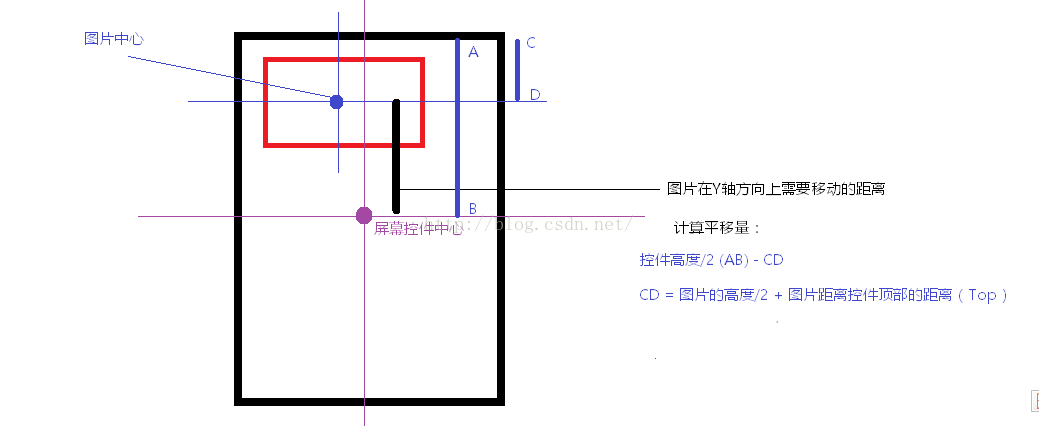
高度方向移动计算
操作逻辑编写
//进行边界控制的逻辑
private void checkBorderAndCenter() {
//得到放大或者缩小后的图片的宽与高
final RectF matrixRectF = getMatrixRectF();
float deltaX = 0;
float deltaY = 0;
//得到控件的宽与高
final int width = getWidth();
final int height = getHeight();
if (matrixRectF.width() >= width) {
//当图片距控件左边的距离left>0那说明图片距离左边出现的空白,需要将图片向左面移动
if (matrixRectF.left > 0) {
deltaX = -matrixRectF.left;
}
//当图片距控件右边的距离right小于控件的width的时候,说明图片距离控件的右面会出现空白,需要将图片向右面移动
if (matrixRectF.right < width) {
deltaX = width - matrixRectF.right;
}
}
if (matrixRectF.height() >= height) {
if (matrixRectF.top > 0) {
deltaY = -matrixRectF.top;
}
if (matrixRectF.bottom < height) {
deltaY = height - matrixRectF.bottom;
}
}
//如果 宽度 与高度小于控件的宽与高,则让图片居中
if (matrixRectF.width() < width) {
deltaX = width / 2 - matrixRectF.right + matrixRectF.width() / 2;
}
if (matrixRectF.height() < height) {
deltaY = height / 2 - matrixRectF.bottom + matrixRectF.height() / 2;
}
mScaleMatrix.postTranslate(deltaX, deltaY);
}这里就是控制图片缩放过程中与控件边界出现空白消除的处理逻辑,只需要在每次进行缩放图片后,在setImageMatrix()方法前调用边界控制方法checkBorderAndCenter就可以了