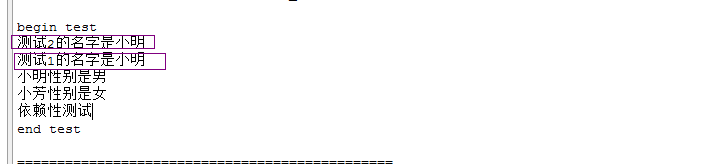TestNG按顺序执行case
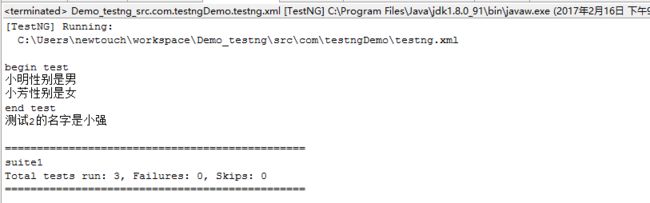
package com.testngDemo; import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.Test; public class DemoTestng { @BeforeClass public void setup() { System.out.println("begin test"); } @Test public void test1() { System.out.println("at test1"); } @Test public void test2() { System.out.println("at test2"); } @Test public void test3() { System.out.println("at test3"); } @AfterClass public void teardown() { System.out.println("end test"); } }
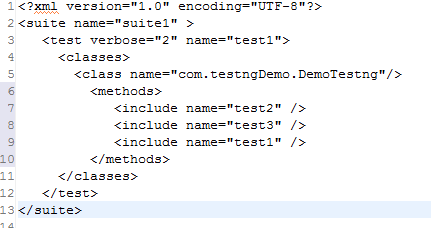
在xml文件中配置:
执行一下:
TestNG参数化执行case
我们在测试中经常会遇到参数化执行case的情况, TestNG为我们提供了两种参数化的方式:
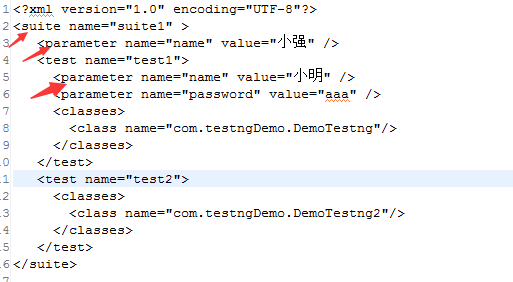
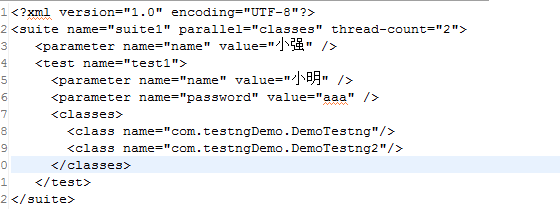
1.在xml文件中传递参数
2.使用@DataProvider传递参数
第一种方式:
在这两种测试范围定义的参数,满足如下规律:
1)在Suite范围内定义某个参数的值,对所有的Test都有效。
2)在Test范围内定义某个参数的值,只是针对该Test有效。
3)如果同时在Suite和Test中定义某个参数,Test范围的值会屏蔽Suite的值。
示例代码如下:
xml文件:
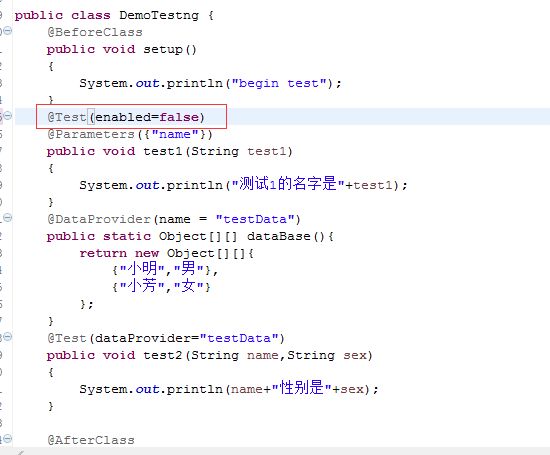
package com.testngDemo; import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.Parameters; import org.testng.annotations.Test; public class DemoTestng { @BeforeClass public void setup() { System.out.println("begin test"); } @Test @Parameters({"name"}) public void test1(String test1) { System.out.println("测试1的名字是"+test1); } @AfterClass public void teardown() { System.out.println("end test"); } }
package com.testngDemo; import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass; import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass; import org.testng.annotations.Parameters; import org.testng.annotations.Test; public class DemoTestng2 { @BeforeClass public void setup() { } @Test @Parameters("name") public void test(String name) { System.out.println("测试2的名字是"+name); } @AfterClass public void teardown() { } }
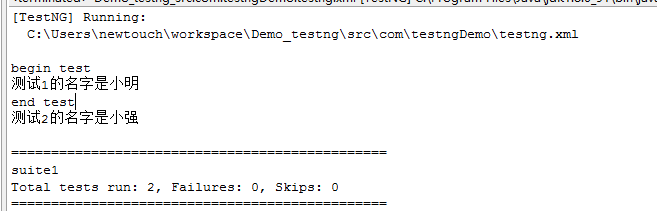
执行完成的结果是:
第二种方式:
执行结果是:
TestNG忽略性测试
测试结果:
TestNG依赖性测试
在@Test后面添加dependsOnMethods={"testName"},则这个case依赖于testName这个case,如下图,我忽略了test1测试,那么dependTest也没法执行。
TesNG多线程并发执行
执行结果: