Android Binder分析二:Natvie Service的注册
这一章我们通过MediaPlayerService的注册来说明如何在Native层通过binder向ServiceManager注册一个service,以及client如何通过binder向ServiceManager获得一个service,并调用这个Service的方法。
Native Service的注册
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
signal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
char value[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
bool doLog = (property_get("ro.test_harness", value, "0") > 0) && (atoi(value) == 1);
if (doLog) {
prctl(PR_SET_PDEATHSIG, SIGKILL); // if parent media.log dies before me, kill me also
setpgid(0, 0); // but if I die first, don't kill my parent
}
sp proc(ProcessState::self());
sp sm = defaultServiceManager();
ALOGI("ServiceManager: %p", sm.get());
AudioFlinger::instantiate();
MediaPlayerService::instantiate();
CameraService::instantiate();
AudioPolicyService::instantiate();
registerExtensions();
ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
} 这里首先通过ProcessState::self()获得一个ProcessState对象,ProcessState是与进程相关对象,在一个进程中只会存在一个ProcessState对象。首先来看ProcessState::self()和构造函数:
sp ProcessState::self()
{
Mutex::Autolock _l(gProcessMutex);
if (gProcess != NULL) {
return gProcess;
}
gProcess = new ProcessState;
return gProcess;
}
ProcessState::ProcessState()
: mDriverFD(open_driver())
, mVMStart(MAP_FAILED)
, mManagesContexts(false)
, mBinderContextCheckFunc(NULL)
, mBinderContextUserData(NULL)
, mThreadPoolStarted(false)
, mThreadPoolSeq(1)
{
if (mDriverFD >= 0) {
mVMStart = mmap(0, BINDER_VM_SIZE, PROT_READ, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_NORESERVE, mDriverFD, 0);
if (mVMStart == MAP_FAILED) {
// *sigh*
ALOGE("Using /dev/binder failed: unable to mmap transaction memory.\n");
close(mDriverFD);
mDriverFD = -1;
}
}
} gProcess的定义是在Static.cpp文件里面,当main_mediaservice的main函数第一次调用ProcessState::self()方法时,gProcess为空,所以首先会构造一个ProcessState对象。在ProcessState的构造函数中,首先会调用open_driver()方法去打开/dev/binder设备:
static int open_driver()
{
int fd = open("/dev/binder", O_RDWR);
if (fd >= 0) {
fcntl(fd, F_SETFD, FD_CLOEXEC);
int vers;
status_t result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_VERSION, &vers);
if (result == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to obtain version failed: %s", strerror(errno));
close(fd);
fd = -1;
}
if (result != 0 || vers != BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION) {
ALOGE("Binder driver protocol does not match user space protocol!");
close(fd);
fd = -1;
}
size_t maxThreads = 15;
result = ioctl(fd, BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS, &maxThreads);
if (result == -1) {
ALOGE("Binder ioctl to set max threads failed: %s", strerror(errno));
}
} else {
ALOGW("Opening '/dev/binder' failed: %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
return fd;
}打开/dev/binder设备会调用到binder驱动中的binder_open方法,在前面分析ServiceManager中我们已经分析过,这个方法首先会创建一个binder_proc对象,并初始化它的pid和task_struct结构,并把它自己链接到全局的binder_procs链表中。在成功打开/dev/binder设备后,会往binder驱动中通过ioctl发送BINDER_VERSION和BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS两个命令,我们到binder_ioctl去分析:
static long binder_ioctl(struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int ret;
struct binder_proc *proc = filp->private_data;
struct binder_thread *thread;
unsigned int size = _IOC_SIZE(cmd);
void __user *ubuf = (void __user *)arg;
binder_lock(__func__);
thread = binder_get_thread(proc);
if (thread == NULL) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto err;
}
switch (cmd) {
case BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS:
if (copy_from_user(&proc->max_threads, ubuf, sizeof(proc->max_threads))) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
break;
case BINDER_VERSION:
if (size != sizeof(struct binder_version)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
if (put_user(BINDER_CURRENT_PROTOCOL_VERSION, &((struct binder_version *)ubuf)->protocol_version)) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto err;
}
break;与前面分析ServiceManager一样,这里首先调用binder_get_thread为meidaservcie构造一个binder_thread对象,并把它链接到前面创建的binder_proc数据结构的threads红黑树上。接下来处理BINDER_SET_MAX_THREADS和BINDER_VERSION都比较简单。回到ProcessState的构造函数中,接着会调用mmap方法去为分配实际的物理页面,并为用户空间和内核空间映射内存。
在main_mediaservice.cpp接着会调用defaultServiceManager()获得一个ServiceManager的binder指针,我们在后面再来分析这个方法。接着会分别实例化几个不同的service,我们这里只分析AudioFlinger和MediaPlayerService两个service。AudioFlinger继承于BinderService,如下:
class AudioFlinger :
public BinderService,
public BnAudioFlinger
{
friend class BinderService; // for AudioFlinger()
public:
static const char* getServiceName() ANDROID_API { return "media.audio_flinger"; } BinderService是一个类模板,并实现了instantiate()方法,如下:
template
class BinderService
{
public:
static status_t publish(bool allowIsolated = false) {
sp sm(defaultServiceManager());
return sm->addService(
String16(SERVICE::getServiceName()),
new SERVICE(), allowIsolated);
}
static void publishAndJoinThreadPool(bool allowIsolated = false) {
publish(allowIsolated);
joinThreadPool();
}
static void instantiate() { publish(); }
static status_t shutdown() { return NO_ERROR; }
private:
static void joinThreadPool() {
sp ps(ProcessState::self());
ps->startThreadPool();
ps->giveThreadPoolName();
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool();
}
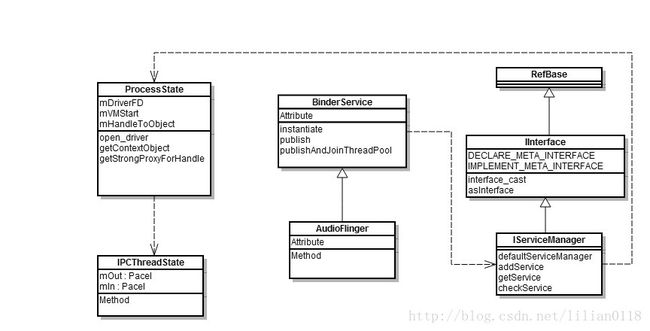
}; instantiate()方法调用publish()函数实现向ServiceManager 注册服务。在介绍defaultServiceManager()函数之前,我们先来看一下刚刚讲到的几个类的关系:
从上图可以看到,IServiceManager是继承于IInterface类,而在IInterface有两个重要的宏定义,DECLARE_META_INTERFACE和IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE,这两个宏定义声明和定义了两个比较重要的函数:descriptor和asInterface,后面我们在使用的过程中再来详细解释每个函数。
我们先来看defaultServiceManager()函数:
sp defaultServiceManager()
{
if (gDefaultServiceManager != NULL) return gDefaultServiceManager;
{
AutoMutex _l(gDefaultServiceManagerLock);
while (gDefaultServiceManager == NULL) {
gDefaultServiceManager = interface_cast(
ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL));
if (gDefaultServiceManager == NULL)
sleep(1);
}
}
return gDefaultServiceManager;
} 和ProcessState一样,这里的gDefaultServiceManager也是定义在Static.cpp中,所以在一个进程中只会存在一份实例。当第一次调用defaultServiceManager()函数时,会调用ProcessState的getContextObject方法去获取一个Bpbinder(首先我们要有个概念,BpBinder就是一个代理binder,BnBinder才是真正实现服务的地方),我们先来看getContextObject的实现:
sp ProcessState::getContextObject(const sp& caller)
{
return getStrongProxyForHandle(0);
}
sp ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle(int32_t handle)
{
sp result;
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
handle_entry* e = lookupHandleLocked(handle);
if (e != NULL) {
IBinder* b = e->binder;
if (b == NULL || !e->refs->attemptIncWeak(this)) {
if (handle == 0) {
Parcel data;
status_t status = IPCThreadState::self()->transact(
0, IBinder::PING_TRANSACTION, data, NULL, 0);
if (status == DEAD_OBJECT)
return NULL;
}
b = new BpBinder(handle);
e->binder = b;
if (b) e->refs = b->getWeakRefs();
result = b;
} else {
result.force_set(b);
e->refs->decWeak(this);
}
}
return result;
}
ProcessState::handle_entry* ProcessState::lookupHandleLocked(int32_t handle)
{
const size_t N=mHandleToObject.size();
if (N <= (size_t)handle) {
handle_entry e;
e.binder = NULL;
e.refs = NULL;
status_t err = mHandleToObject.insertAt(e, N, handle+1-N);
if (err < NO_ERROR) return NULL;
}
return &mHandleToObject.editItemAt(handle);
} getContextObject会直接调用getStrongProxyForHandle()方法去获取一个BpBinder,传入的handler id是0,在ServiceManager那章讲过,在binder驱动中ServiceManager的handle值为0,所以这里即是要获得ServiceManager这个BpBinder,我们后面慢慢来分析。接着看getStrongProxyForHandle的实现,先通过lookupHandleLocked(0)去查找在mHandeToObject数组中有没有存在hande等于0的BpBinder,如果不存在就新建一个entry,并把它的binder和refs都设为NULL。回到getStrongProxyForHandle中,因为binder等于NULL并且hande等于0,所以调用IPCThreadState的transact方法来测试ServiceManager是否已经注册或者ServiceManager是否还存活在。关于这里给ServiceManager发送PING_TRANSACTION来检查ServiceManager是否注册的代码,我们后面分析注册Service时一起来分析,先假设这里ServiceManager已经注册到系统中了并且是存活着。接着会创建一个BpBinder(0)并返回。
回到defaultServiceManager()函数,ProcessState::self()->getContextObject(NULL)其实就是返回一个BpBinder(0),然后我们来看interface_cast 的实现,这个模板函数是定义在IIterface.h中:
template
inline sp interface_cast(const sp& obj)
{
return INTERFACE::asInterface(obj);
} #define DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE) \
static const android::String16 descriptor; \
static android::sp asInterface( \
const android::sp& obj); \
virtual const android::String16& getInterfaceDescriptor() const; \
I##INTERFACE(); \
virtual ~I##INTERFACE(); \
#define IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(INTERFACE, NAME) \
const android::String16 I##INTERFACE::descriptor(NAME); \
const android::String16& \
I##INTERFACE::getInterfaceDescriptor() const { \
return I##INTERFACE::descriptor; \
} \
android::sp I##INTERFACE::asInterface( \
const android::sp& obj) \
{ \
android::sp intr; \
if (obj != NULL) { \
intr = static_cast( \
obj->queryLocalInterface( \
I##INTERFACE::descriptor).get()); \
if (intr == NULL) { \
intr = new Bp##INTERFACE(obj); \
} \
} \
return intr; \
} \
I##INTERFACE::I##INTERFACE() { } \
I##INTERFACE::~I##INTERFACE() { } \ DECLARE_META_INTERFACE宏声明了4个函数,其中包含构造和析构函数;另外包含asInterface和asInterface。这两个宏都带有参数,其中INTERFACE为函数的类名,例如IServiceManager.cpp中,就定义INTERFACE为ServiceManager;NAME为"android.os.IServiceManager",通过宏定义中的"##"将INTERFACE名字前面加上“I",如IServiceManager.cpp中的定义:
DECLARE_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager);
IMPLEMENT_META_INTERFACE(ServiceManager, "android.os.IServiceManager");我们将上面的两个宏展开,就可以得到如下的代码:
static const android::String16 descriptor;
static android::sp asInterface(
const android::sp& obj);
virtual const android::String16& getInterfaceDescriptor() const;
IServiceManager();
virtual ~IServiceManager();
const android::String16 IServiceManager::descriptor("android.os.IServiceManager");
const android::String16&
IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor() const {
return IServiceManager::descriptor;
}
android::sp IServiceManager::asInterface(
const android::sp& obj)
{
android::sp intr;
if (obj != NULL) {
intr = static_cast(
obj->queryLocalInterface(
IServiceManager::descriptor).get());
if (intr == NULL) {
intr = new BpServiceManager(obj);
}
}
return intr;
}
IServiceManager::IServiceManager() { }
IServiceManager::~IServiceManager() { } 所以在defaultServiceManager()函数调用interface_cast
sp IBinder::queryLocalInterface(const String16& descriptor)
{
return NULL;
} 所以前面的defaultServiceManager()可以改写为:
sp defaultServiceManager()
{
if (gDefaultServiceManager != NULL) return gDefaultServiceManager;
{
AutoMutex _l(gDefaultServiceManagerLock);
while (gDefaultServiceManager == NULL) {
gDefaultServiceManager = new BpServiceManager(
BpBinder(0));
if (gDefaultServiceManager == NULL)
sleep(1);
}
}
return gDefaultServiceManager;
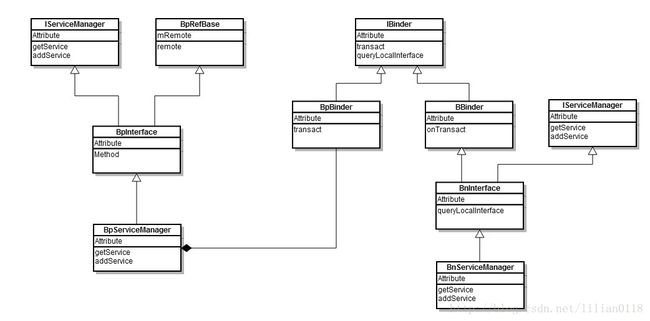
} 至此,gDefaultServiceManager其实就是一个BpServiceManager,先来看一下上面的类图关系:
我们来看BpServiceManager的构造函数:
class BpServiceManager : public BpInterface
{
public:
BpServiceManager(const sp& impl)
: BpInterface(impl)
{
}
template
inline BpInterface::BpInterface(const sp& remote)
: BpRefBase(remote)
{
}
BpRefBase::BpRefBase(const sp& o)
: mRemote(o.get()), mRefs(NULL), mState(0)
{
extendObjectLifetime(OBJECT_LIFETIME_WEAK);
if (mRemote) {
mRemote->incStrong(this); // Removed on first IncStrong().
mRefs = mRemote->createWeak(this); // Held for our entire lifetime.
}
} 通过一系列的调用,最后把BpBinder(0)记录在mRemote变量中,并增加它的强弱指针引用计数。回到BinderService的instantiate()方法,sm即是BpServiceManager(BpBinder(0)),接着调用它的addService方法,将BinderService的publish方法展开如下:
static status_t publish(bool allowIsolated = false) {
sp sm(defaultServiceManager());
return sm->addService(
String16("media.audio_flinger"),
new AudioFlinger (), false);
} 接着来看addService的实现:
virtual status_t addService(const String16& name, const sp& service,
bool allowIsolated)
{
Parcel data, reply;
data.writeInterfaceToken(IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor());
data.writeString16(name);
data.writeStrongBinder(service);
data.writeInt32(allowIsolated ? 1 : 0);
status_t err = remote()->transact(ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION, data, &reply);
return err == NO_ERROR ? reply.readExceptionCode() : err;
} 首先定义两个Parcel对象,一个用于存储发送的数据,一个用于接收response。首先来看writeInterfaceToken()方法,我们知道IServiceManager::getInterfaceDescriptor()会返回"android.os.IServiceManager":
status_t Parcel::writeInterfaceToken(const String16& interface)
{
writeInt32(IPCThreadState::self()->getStrictModePolicy() |
STRICT_MODE_PENALTY_GATHER);
// currently the interface identification token is just its name as a string
return writeString16(interface);
}首先向Parcel中写入strict mode,这个会被binder驱动用于做PRC检验,接着会把"android.os.IServiceManager"和”media.audio_flinger"也写入到Parcel对象中。下面来看一下writeStrongBinder方法,参数是AudioFlinger对象:
status_t Parcel::writeStrongBinder(const sp& val)
{
return flatten_binder(ProcessState::self(), val, this);
}
status_t flatten_binder(const sp& proc,
const sp& binder, Parcel* out)
{
flat_binder_object obj;
obj.flags = 0x7f | FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS;
if (binder != NULL) {
IBinder *local = binder->localBinder();
if (!local) {
BpBinder *proxy = binder->remoteBinder();
if (proxy == NULL) {
ALOGE("null proxy");
}
const int32_t handle = proxy ? proxy->handle() : 0;
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE;
obj.handle = handle;
obj.cookie = NULL;
} else {
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = local->getWeakRefs();
obj.cookie = local;
}
} else {
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = NULL;
obj.cookie = NULL;
}
return finish_flatten_binder(binder, obj, out);
} 先来看flat_binder_object的结构,定义在binder驱动的binder.h中:
struct flat_binder_object {
/* 8 bytes for large_flat_header. */
unsigned long type;
unsigned long flags;
/* 8 bytes of data. */
union {
void *binder; /* local object */
signed long handle; /* remote object */
};
/* extra data associated with local object */
void *cookie;
};flat_binder_object数据结构中,根据type的不同,分别binder和handle保存不同的对象。如果是type是BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE,就表示flat_binder_object存储的是binder驱动中的一个handle id值,所以会把handle id记录在handle中;如果type是BINDER_TYPE_BINDER,表示flat_binder_object存储的是一个binder对象,所以会把binder对象放在binder中。这里的AudioFlinger对象是继承于BBinder,所以它的localBinder不会为空,就将flat_binder_object的binder置为RefBase的mRefs变量,并将cookie置为AudioFlinger本身。接着调用finish_flatten_binder将flat_binder_object写入到Parcel中。来看一下finish_flatten_binder的实现:
inline static status_t finish_flatten_binder(
const sp& binder, const flat_binder_object& flat, Parcel* out)
{
return out->writeObject(flat, false);
}
status_t Parcel::writeObject(const flat_binder_object& val, bool nullMetaData)
{
const bool enoughData = (mDataPos+sizeof(val)) <= mDataCapacity;
const bool enoughObjects = mObjectsSize < mObjectsCapacity;
if (enoughData && enoughObjects) {
restart_write:
*reinterpret_cast(mData+mDataPos) = val;
// Need to write meta-data?
if (nullMetaData || val.binder != NULL) {
mObjects[mObjectsSize] = mDataPos;
acquire_object(ProcessState::self(), val, this);
mObjectsSize++;
}
return finishWrite(sizeof(flat_binder_object));
}
} 上面的代码中先检验现在Parcel中分配的数组空间是否足够,如果不足够就去扩大分配的数组;假设这里数组空间大小足够,就将上面的flat_binder_object写入到mData+mDataPos处,并在mObjects中的记录下这个数据结构写入的起始地址。因为Parcel不仅存在整形、string,还存在flat_binder_object数据结构,为了快速的找到所有的binder,这里利用mObjects数组存下写入到Parcel中的所有flat_binder_object数据结构的偏移地址,mObjectSize存写入的flat_binder_object数据结构个数。把上面所有的数据都写入到Parcel中,现在Parcel中的数据结构如下:
| Strict Mode | 0 | |
| interface | "android.os.IServiceManager" | |
| name | ”media.audio_flinger" | |
| flat_binder_object | type | BINDER_TYPE_BINDER |
| flags | 0 | |
| binder | local->getWeakRefs | |
| cookie | local | |
接着调用remote()->transact方法,我们知道这里的remote()返回BpBinder(0),所以这里会调用BpBinder的transact方法:
status_t BpBinder::transact(
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
// Once a binder has died, it will never come back to life.
if (mAlive) {
status_t status = IPCThreadState::self()->transact(
mHandle, code, data, reply, flags);
if (status == DEAD_OBJECT) mAlive = 0;
return status;
}
return DEAD_OBJECT;
}这里会调用IPCThreadState的transact方法,这里的mHandle等于0,表示数据要发往ServiceManager,code是ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION,data是上面画出来的Parcel数据。来看IPCThreadState的transact的实现:
status_t IPCThreadState::transact(int32_t handle,
uint32_t code, const Parcel& data,
Parcel* reply, uint32_t flags)
{
status_t err = data.errorCheck();
flags |= TF_ACCEPT_FDS;
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
LOG_ONEWAY(">>>> SEND from pid %d uid %d %s", getpid(), getuid(),
(flags & TF_ONE_WAY) == 0 ? "READ REPLY" : "ONE WAY");
err = writeTransactionData(BC_TRANSACTION, flags, handle, code, data, NULL);
}
if ((flags & TF_ONE_WAY) == 0) {
if (reply) {
err = waitForResponse(reply);
} else {
Parcel fakeReply;
err = waitForResponse(&fakeReply);
}
} else {
err = waitForResponse(NULL, NULL);
}
return err;
}首先做参数加入,如果参数无误,就调用writeTransactionData将数据写入到IPCThreadState的mOut这个Parcel对象中等待发送出去。在IPCThreadState中有两个Parcel对象,一个是mOut;一个是mIn。分别用于记录发往binder驱动的数据和回收binder写给上层的数据,我们后面分析会看到。先来看writeTransactionData的实现:
status_t IPCThreadState::writeTransactionData(int32_t cmd, uint32_t binderFlags,
int32_t handle, uint32_t code, const Parcel& data, status_t* statusBuffer)
{
binder_transaction_data tr;
tr.target.handle = handle;
tr.code = code;
tr.flags = binderFlags;
tr.cookie = 0;
tr.sender_pid = 0;
tr.sender_euid = 0;
const status_t err = data.errorCheck();
if (err == NO_ERROR) {
tr.data_size = data.ipcDataSize();
tr.data.ptr.buffer = data.ipcData();
tr.offsets_size = data.ipcObjectsCount()*sizeof(size_t);
tr.data.ptr.offsets = data.ipcObjects();
} else if (statusBuffer) {
tr.flags |= TF_STATUS_CODE;
*statusBuffer = err;
tr.data_size = sizeof(status_t);
tr.data.ptr.buffer = statusBuffer;
tr.offsets_size = 0;
tr.data.ptr.offsets = NULL;
} else {
return (mLastError = err);
}
mOut.writeInt32(cmd);
mOut.write(&tr, sizeof(tr));
return NO_ERROR;
}首先声明一个binder_transaction_data数据结构,它的定义是在binder驱动的binder.h中:
struct binder_transaction_data {
/* The first two are only used for bcTRANSACTION and brTRANSACTION,
* identifying the target and contents of the transaction.
*/
union {
size_t handle; /* target descriptor of command transaction */
void *ptr; /* target descriptor of return transaction */
} target;
void *cookie; /* target object cookie */
unsigned int code; /* transaction command */
/* General information about the transaction. */
unsigned int flags;
pid_t sender_pid;
uid_t sender_euid;
size_t data_size; /* number of bytes of data */
size_t offsets_size; /* number of bytes of offsets */
/* If this transaction is inline, the data immediately
* follows here; otherwise, it ends with a pointer to
* the data buffer.
*/
union {
struct {
/* transaction data */
const void *buffer;
/* offsets from buffer to flat_binder_object structs */
const void *offsets;
} ptr;
uint8_t buf[8];
} data;
};binder_transaction_data结构中的target记录着这个数据要发往哪里,如果从用户层发往binder驱动,就设置handle为要发往的那个service在binder驱动中的handle id;如果由kernel发回上层,则设置ptr为要发送的binder的weak refs,cookie设置为binder本身。回到writeTransactionData中,将所有的数据记录在binder_transaction_data的buffer指针;所有的flat_binder_object数据结构偏移地址保存在offsets上;data_size记录整个Pacel对象的大小;offsets_size记录保存的flat_binder_object个数。接着把上面的cmd和binder_transaction_data写入到mOut对象中。这里mOut对象中的数据结构组织如下:
| cmd | BC_TRANSACTION | |
| binder_transaction_data | target(handle) | 0 |
| cookie | 0 | |
| code | ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION | |
| flags | 0 | |
| sender_pid | 0 | |
| sender_euid | 0 | |
| data_size | ||
| offsets_size | ||
| buffer | Strict Mode 0 interface "android.os.IServiceManager" name ”media.audio_flinger" flat_binder_object type BINDER_TYPE_BINDER flags 0 binder local->getWeakRefs cookie local |
|
| offsets | 26 | |
回到IPCThreadState的transact方法,接着会调用waitForResponse于binder驱动交互并获取reply结果。TF_ONE_WAY表示这是一个异步消息或者不需要等待回复,这里没有设置。
status_t IPCThreadState::waitForResponse(Parcel *reply, status_t *acquireResult)
{
int32_t cmd;
int32_t err;
while (1) {
if ((err=talkWithDriver()) < NO_ERROR) break;
err = mIn.errorCheck();
if (err < NO_ERROR) break;
if (mIn.dataAvail() == 0) continue;
cmd = mIn.readInt32();
IF_LOG_COMMANDS() {
alog << "Processing waitForResponse Command: "
<< getReturnString(cmd) << endl;
}
switch (cmd) {
case BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE:
if (!reply && !acquireResult) goto finish;
break;
case BR_DEAD_REPLY:
err = DEAD_OBJECT;
goto finish;
case BR_FAILED_REPLY:
err = FAILED_TRANSACTION;
goto finish;
case BR_REPLY:
{
binder_transaction_data tr;
err = mIn.read(&tr, sizeof(tr));
ALOG_ASSERT(err == NO_ERROR, "Not enough command data for brREPLY");
if (err != NO_ERROR) goto finish;
if (reply) {
if ((tr.flags & TF_STATUS_CODE) == 0) {
reply->ipcSetDataReference(
reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.buffer),
tr.data_size,
reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.offsets),
tr.offsets_size/sizeof(size_t),
freeBuffer, this);
} else {
}
} else {
}
}
goto finish;
default:
err = executeCommand(cmd);
if (err != NO_ERROR) goto finish;
break;
}
}
finish:
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
if (acquireResult) *acquireResult = err;
if (reply) reply->setError(err);
mLastError = err;
}
return err;
} 上面的代码中,循环的调用talkWithDriver与binder驱动交互,并获取reply,直至获取到的回复cmd是BR_REPLY或者出错才退出。首先来看talkWithDriver如何把数据发往binder驱动并从binder驱动中获取reply:
status_t IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver(bool doReceive)
{
binder_write_read bwr;
// Is the read buffer empty?
const bool needRead = mIn.dataPosition() >= mIn.dataSize();
const size_t outAvail = (!doReceive || needRead) ? mOut.dataSize() : 0;
bwr.write_size = outAvail;
bwr.write_buffer = (long unsigned int)mOut.data();
// This is what we'll read.
if (doReceive && needRead) {
bwr.read_size = mIn.dataCapacity();
bwr.read_buffer = (long unsigned int)mIn.data();
} else {
bwr.read_size = 0;
bwr.read_buffer = 0;
}
// Return immediately if there is nothing to do.
if ((bwr.write_size == 0) && (bwr.read_size == 0)) return NO_ERROR;
bwr.write_consumed = 0;
bwr.read_consumed = 0;
status_t err;
do {
if (ioctl(mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr) >= 0)
err = NO_ERROR;
else
err = -errno;
} while (err == -EINTR);
if (err >= NO_ERROR) {
if (bwr.write_consumed > 0) {
if (bwr.write_consumed < (ssize_t)mOut.dataSize())
mOut.remove(0, bwr.write_consumed);
else
mOut.setDataSize(0);
}
if (bwr.read_consumed > 0) {
mIn.setDataSize(bwr.read_consumed);
mIn.setDataPosition(0);
}
return NO_ERROR;
}
return err;
}talkWithDriver首先声明一个binder_write_read数据结构,前面我们已经介绍过这个数据结构了,它是用来和binder驱动交互的数据类型。再判断mIn中是否还有未读出的数据。如果mIn中有未读的数据,并且这是一个同步的请求,需要等待binder的回复,则先将write_size置为0,不往binder驱动中写入数据和读出数据,先处理完mIn中的reply。因为这里是第一次进入到talkWithDriver,所以这里的mIn初始化为空。将write_buffer指向上面的mOut数据,read_buffer指向mIn数据,并设置write_size和read_size。binder驱动会判断write_size和read_size分别执行write和read请求。接着调用ioctl向binder驱动写入数据,这里的write_size和read_size都不为0,mOut中带有BC_TRANSACTION 的命令和binder_transaction_data数据。在binder_ioctl中,先调用binder_thread_write去处理写请求,再调用binder_thread_read处理读请求。先来看binder_thread_write的实现:
int binder_thread_write(struct binder_proc *proc, struct binder_thread *thread,
void __user *buffer, int size, signed long *consumed)
{
uint32_t cmd;
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;
void __user *end = buffer + size;
while (ptr < end && thread->return_error == BR_OK) {
if (get_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
trace_binder_command(cmd);
if (_IOC_NR(cmd) < ARRAY_SIZE(binder_stats.bc)) {
binder_stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]++;
proc->stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]++;
thread->stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]++;
}
switch (cmd) {
case BC_TRANSACTION:
case BC_REPLY: {
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
if (copy_from_user(&tr, ptr, sizeof(tr)))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(tr);
binder_transaction(proc, thread, &tr, cmd == BC_REPLY);
break;
}处理BC_TRANSACTION和BC_REPLY是在同一个case语句,都是先从buffer中获取到binder_transaction_data数据结构后,这里tr内容是:
| binder_transaction_data | target(handle) | 0 |
| cookie | 0 | |
| code | ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION | |
| flags | 0 | |
| sender_pid | 0 | |
| sender_euid | 0 | |
| data_size | ||
| offsets_size | ||
| buffer | Strict Mode 0 interface "android.os.IServiceManager" name ”media.audio_flinger" flat_binder_object type BINDER_TYPE_BINDER flags 0 binder local->getWeakRefs cookie local |
|
| offsets | 26 |
调用binder_transaction来处理:
static void binder_transaction(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
struct binder_transaction_data *tr, int reply)
{
struct binder_transaction *t;
struct binder_work *tcomplete;
size_t *offp, *off_end;
struct binder_proc *target_proc;
struct binder_thread *target_thread = NULL;
struct binder_node *target_node = NULL;
struct list_head *target_list;
wait_queue_head_t *target_wait;
struct binder_transaction *in_reply_to = NULL;
struct binder_transaction_log_entry *e;
uint32_t return_error;
if (reply) {
} else {
if (tr->target.handle) {
} else {
target_node = binder_context_mgr_node;
if (target_node == NULL) {
}
}
e->to_node = target_node->debug_id;
target_proc = target_node->proc;
if (target_proc == NULL) {
}
if (security_binder_transaction(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk) < 0) {
}
if (!(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY) && thread->transaction_stack) {
}
}
if (target_thread) {
} else {
target_list = &target_proc->todo;
target_wait = &target_proc->wait;
}
e->to_proc = target_proc->pid;
/* TODO: reuse incoming transaction for reply */
t = kzalloc(sizeof(*t), GFP_KERNEL);
if (t == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_alloc_t_failed;
}
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION);
tcomplete = kzalloc(sizeof(*tcomplete), GFP_KERNEL);
if (tcomplete == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_alloc_tcomplete_failed;
}
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE);
t->debug_id = ++binder_last_id;
e->debug_id = t->debug_id;
if (!reply && !(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY))
t->from = thread;
else
t->from = NULL;
t->sender_euid = proc->tsk->cred->euid;
t->to_proc = target_proc;
t->to_thread = target_thread;
t->code = tr->code;
t->flags = tr->flags;
t->priority = task_nice(current);
t->buffer = binder_alloc_buf(target_proc, tr->data_size,
tr->offsets_size, !reply && (t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY));
if (t->buffer == NULL) {
}
t->buffer->allow_user_free = 0;
t->buffer->debug_id = t->debug_id;
t->buffer->transaction = t;
t->buffer->target_node = target_node;
trace_binder_transaction_alloc_buf(t->buffer);
if (target_node)
binder_inc_node(target_node, 1, 0, NULL);
offp = (size_t *)(t->buffer->data + ALIGN(tr->data_size, sizeof(void *)));
if (copy_from_user(t->buffer->data, tr->data.ptr.buffer, tr->data_size)) {
}
if (copy_from_user(offp, tr->data.ptr.offsets, tr->offsets_size)) {
}
if (!IS_ALIGNED(tr->offsets_size, sizeof(size_t))) {
}
off_end = (void *)offp + tr->offsets_size;
for (; offp < off_end; offp++) {
struct flat_binder_object *fp;
if (*offp > t->buffer->data_size - sizeof(*fp) ||
t->buffer->data_size < sizeof(*fp) ||
!IS_ALIGNED(*offp, sizeof(void *))) {
}
fp = (struct flat_binder_object *)(t->buffer->data + *offp);
switch (fp->type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER:
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER: {
struct binder_ref *ref;
struct binder_node *node = binder_get_node(proc, fp->binder);
if (node == NULL) {
node = binder_new_node(proc, fp->binder, fp->cookie);
if (node == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_new_node_failed;
}
node->min_priority = fp->flags & FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_PRIORITY_MASK;
node->accept_fds = !!(fp->flags & FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS);
}
if (fp->cookie != node->cookie) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d sending u%p "
"node %d, cookie mismatch %p != %p\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid,
fp->binder, node->debug_id,
fp->cookie, node->cookie);
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
if (security_binder_transfer_binder(proc->tsk, target_proc->tsk)) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
ref = binder_get_ref_for_node(target_proc, node);
if (ref == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_binder_get_ref_for_node_failed;
}
if (fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_BINDER)
fp->type = BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE;
else
fp->type = BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE;
fp->handle = ref->desc;
binder_inc_ref(ref, fp->type == BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE,
&thread->todo);
} break;
case BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE:
case BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE: {
} break;
case BINDER_TYPE_FD: {
} break;
default:
}
}
if (reply) {
} else if (!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) {
BUG_ON(t->buffer->async_transaction != 0);
t->need_reply = 1;
t->from_parent = thread->transaction_stack;
thread->transaction_stack = t;
} else {
}
t->work.type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION;
list_add_tail(&t->work.entry, target_list);
tcomplete->type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE;
list_add_tail(&tcomplete->entry, &thread->todo);
if (target_wait)
wake_up_interruptible(target_wait);
return;首先,传入到binder_transaction的reply参数为false,只有在cmd等于BC_REPLY时才为true;接着看tr->target.handle,因为我们现在要请求ServiceManager为我们服务,hande id肯定是0,从上面的binder_transaction_data第一个数据也可以看到,所以代码中会设置target_node = binder_context_mgr_node,binder_context_mgr_node就是我们在启动ServiceManager构造的。target_proc设置为ServiceManager的上下文信息;因为当前thread(即注册AudioFlinger服务的线程)的transaction_stack为空,所以不会进到if (!(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY) && thread->transaction_stack) 这个if中;因为target_thread也为空,所以会设置target_list和target_wait为ServiceManager的todo和wait列表。接下来就会去分配这次事务的binder_transaction结构,我们先来看binder_transaction数据结构:
struct binder_transaction {
int debug_id;
struct binder_work work; //连接binder_proc的todo链表中
struct binder_thread *from; //从哪个thread调用的
struct binder_transaction *from_parent;
struct binder_proc *to_proc; //被调用的binder_proc信息
struct binder_thread *to_thread; //被调用的binder_thread
struct binder_transaction *to_parent; //
unsigned need_reply:1;
/* unsigned is_dead:1; */ /* not used at the moment */
struct binder_buffer *buffer; //这次事务的数据
unsigned int code; //这次事务的cmd类型
unsigned int flags; //这次事务的flag参数
long priority;
long saved_priority;
uid_t sender_euid;
};
因为当前事务是需要等待回复的(没有设置TF_ONE_WAY的flag),ServiceManager处理完这个transaction后,需要通知注册AudioFlinger服务的线程,这里设置t->from = thread。接着调用binder_alloc_buf从free_buffer红黑树中分配内存,并将用户空间的数据拷贝到内核空间。如果在传入的binder_transaction_data数据中有binder类型的数据,接下来就会一个个处理binder数据。因为这次注册AudioFinger服务传入的binder type是BINDER_TYPE_BINDER,我们来看这个case分支。因为是第一次注册AuidoFlinger服务,所以通过binder_get_node查找当前binder_proc中的nodes红黑树,会返回NULL,这里就先调用binder_new_node创建一个binder_node,在前面讲ServiceManager启动过程中已经讲过binder_new_node和binder_node数据结构了。接着调用binder_get_ref_for_node为刚创建的binder_node再创建一个binder_ref对象,binder_ref对象中的desc数据就是后面我们在获取binder中返回的handle id值:
static struct binder_ref *binder_get_ref_for_node(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_node *node)
{
struct rb_node *n;
struct rb_node **p = &proc->refs_by_node.rb_node;
struct rb_node *parent = NULL;
struct binder_ref *ref, *new_ref;
while (*p) {
parent = *p;
ref = rb_entry(parent, struct binder_ref, rb_node_node);
if (node < ref->node)
p = &(*p)->rb_left;
else if (node > ref->node)
p = &(*p)->rb_right;
else
return ref;
}
new_ref = kzalloc(sizeof(*ref), GFP_KERNEL);
if (new_ref == NULL)
return NULL;
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_REF);
new_ref->debug_id = ++binder_last_id;
new_ref->proc = proc;
new_ref->node = node;
rb_link_node(&new_ref->rb_node_node, parent, p);
rb_insert_color(&new_ref->rb_node_node, &proc->refs_by_node);
new_ref->desc = (node == binder_context_mgr_node) ? 0 : 1;
for (n = rb_first(&proc->refs_by_desc); n != NULL; n = rb_next(n)) {
ref = rb_entry(n, struct binder_ref, rb_node_desc);
if (ref->desc > new_ref->desc)
break;
new_ref->desc = ref->desc + 1;
}
p = &proc->refs_by_desc.rb_node;
while (*p) {
parent = *p;
ref = rb_entry(parent, struct binder_ref, rb_node_desc);
if (new_ref->desc < ref->desc)
p = &(*p)->rb_left;
else if (new_ref->desc > ref->desc)
p = &(*p)->rb_right;
else
BUG();
}
rb_link_node(&new_ref->rb_node_desc, parent, p);
rb_insert_color(&new_ref->rb_node_desc, &proc->refs_by_desc);
if (node) {
hlist_add_head(&new_ref->node_entry, &node->refs);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_INTERNAL_REFS,
"binder: %d new ref %d desc %d for "
"node %d\n", proc->pid, new_ref->debug_id,
new_ref->desc, node->debug_id);
} else {
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_INTERNAL_REFS,
"binder: %d new ref %d desc %d for "
"dead node\n", proc->pid, new_ref->debug_id,
new_ref->desc);
}
return new_ref;
}首先去target_proc(ServiceManager)中的refs_by_node红黑树中查找有没有node对应的binder_refs对象,如果有则返回,这里会返回空并创建一个新的binder_refs对象,并设置它的一些变量。接着查找refs_by_desc红黑树,为刚创建的binder_refs分配一个独一无二的desc值并把这个binder_refs插入到refs_by_desc红黑树中。
回到binder_transaction中,接下来会把传入的flat_binder_object结构中的type和handle改变,还记得在最开始设置flat_binder_object的type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER,handle(binder) = binder.getWeakRefs();这里将type改为BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE,将handle设为ref->desc(这里就是一个id值)。所以后面ServiceManager再来处理这个binder_transaction结构时,只能得到在Binder驱动中的desc值,通过这个desc值可以从binder驱动中获取到实际binder_node节点。在处理完这些后,先将刚创建binder_transaction加入到注册AudioFlinger服务的线程的transaction_stack中,表示当中thread有事务正在等待处理。然后将刚创建binder_transaction添加到ServiceManager所在的binder_proc的todo列表中等待处理。并创建一个binder_work结构的tcomplete对象添加到注册AudioFlinger服务的线程的binder_proc的todo列表中,表示事务已经发送完成了。最后调用wake_up_interruptible去唤醒ServiceManager。
当处理完binder_thread_write后,就会调用binder_thread_read来处理读请求了,首先来看binder_thread_read的实现:
static int binder_thread_read(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
void __user *buffer, int size,
signed long *consumed, int non_block)
{
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;
void __user *end = buffer + size;
int ret = 0;
int wait_for_proc_work;
if (*consumed == 0) {
if (put_user(BR_NOOP, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
}
retry:
wait_for_proc_work = thread->transaction_stack == NULL &&
list_empty(&thread->todo);
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads++;
binder_unlock(__func__);
if (wait_for_proc_work) {
} else {
if (non_block) {
} else
ret = wait_event_freezable(thread->wait, binder_has_thread_work(thread));
}
binder_lock(__func__);
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads--;
thread->looper &= ~BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
if (ret)
return ret;
while (1) {
uint32_t cmd;
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
struct binder_work *w;
struct binder_transaction *t = NULL;
if (!list_empty(&thread->todo))
w = list_first_entry(&thread->todo, struct binder_work, entry);
else if (!list_empty(&proc->todo) && wait_for_proc_work)
w = list_first_entry(&proc->todo, struct binder_work, entry);
else { if (ptr - buffer == 4 && !(thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_NEED_RETURN)) /* no data added */
goto retry;
break;
}
if (end - ptr < sizeof(tr) + 4)
break;
switch (w->type) {
case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION: {
t = container_of(w, struct binder_transaction, work);
} break;
case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE: {
cmd = BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE;
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, cmd);
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE,
"binder: %d:%d BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
list_del(&w->entry);
kfree(w);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE);
} break;
case BINDER_WORK_NODE: {
} break;
}
if (!t)
continue;
}
done:
*consumed = ptr - buffer;
return 0;
}binder_thread_read首先向user space写入BR_NOOP命令。因为此时的transaction_stack和todo链表都不为空,所以wait_for_proc_work为false,并且wait_event_freezable会直接返回。接下来从todo链表中取出头一个元素即tcomplete对象。前面看到tcomplete对象的type是BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE,处理它的case只是很简单的往usespace的buffer写入一个BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE命令,并将这个tcomplete对象从todo链表中删除。因为tcomplete对象没有要处理的binder_transaction数据结构,也就是上面的t是空,会继续while循环,最终在else处跳出整个大循环。
回到talkWithDriver函数中,通过ioctrl执行完命令后并返回0:,看接下来的处理流程:
if (err >= NO_ERROR) {
if (bwr.write_consumed > 0) {
if (bwr.write_consumed < (ssize_t)mOut.dataSize())
mOut.remove(0, bwr.write_consumed);
else
mOut.setDataSize(0);
}
if (bwr.read_consumed > 0) {
mIn.setDataSize(bwr.read_consumed);
mIn.setDataPosition(0);
}
return NO_ERROR;
}上面的write_consumed会在binder_thread_write被置为0,而read_consumed会在binder_thread_read被置为8(因为有BR_NOOP和BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE两个命令)。所以上面的代码中首先将mOut的大小设置为0,并将mIn设置为8。回到waitForResponse函数中,首先从mIn中读出BR_NOOP命令,这个命令什么也不做。然后waitForResponse接着调用talkWithDriver,这次进入到talkWithDriver时mOut中还有个命令没有处理,所有设置write_size和read_size都为0,通过ioctrl发送到bindr驱动后,binder驱动什么也不做,直接返回。接着再从mOut中读出BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE命令,BR_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE也是什么都不做,waitForResponse再调用talkWithDriver函数等待ServiceManager执行后ADD_SEVICE的返回。这时通过ioctrl发送到binder驱动的binder_write_read对象的write_size为0,read_size不为0。所以调用binder_thread_read函数去处理读指令,又因为当前thread的transaction_stack不为空,所以最后调用wait_event_freezable(thread->wait, binder_has_thread_work(thread))等待。
回到ServieManager中,它会在wait_event_freezable_exclusive中等待客户端的请求,首先来看前面分析过的代码:
static int binder_thread_read(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
void __user *buffer, int size,
signed long *consumed, int non_block)
{
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;
void __user *end = buffer + size;
int ret = 0;
int wait_for_proc_work;
if (*consumed == 0) {
if (put_user(BR_NOOP, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
}
retry:
wait_for_proc_work = thread->transaction_stack == NULL &&
list_empty(&thread->todo);
if (thread->return_error != BR_OK && ptr < end) {
}
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads++;
binder_unlock(__func__);
trace_binder_wait_for_work(wait_for_proc_work,
!!thread->transaction_stack,
!list_empty(&thread->todo));
if (wait_for_proc_work) {
binder_set_nice(proc->default_priority);
if (non_block) {
} else
ret = wait_event_freezable_exclusive(proc->wait, binder_has_proc_work(proc, thread));
} else {
}
binder_lock(__func__);
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads--;
thread->looper &= ~BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
if (ret)
return ret;
while (1) {
uint32_t cmd;
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
struct binder_work *w;
struct binder_transaction *t = NULL;
if (!list_empty(&thread->todo))
w = list_first_entry(&thread->todo, struct binder_work, entry);
else if (!list_empty(&proc->todo) && wait_for_proc_work)
w = list_first_entry(&proc->todo, struct binder_work, entry);
else {
if (ptr - buffer == 4 && !(thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_NEED_RETURN)) /* no data added */
goto retry;
break;
}
if (end - ptr < sizeof(tr) + 4)
break;
switch (w->type) {
case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION: {
t = container_of(w, struct binder_transaction, work);
} break;
}
if (!t)
continue;
BUG_ON(t->buffer == NULL);
if (t->buffer->target_node) {
struct binder_node *target_node = t->buffer->target_node;
tr.target.ptr = target_node->ptr;
tr.cookie = target_node->cookie;
t->saved_priority = task_nice(current);
if (t->priority < target_node->min_priority &&
!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY))
binder_set_nice(t->priority);
else if (!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY) ||
t->saved_priority > target_node->min_priority)
binder_set_nice(target_node->min_priority);
cmd = BR_TRANSACTION;
} else {
}
tr.code = t->code;
tr.flags = t->flags;
tr.sender_euid = t->sender_euid;
if (t->from) {
struct task_struct *sender = t->from->proc->tsk;
tr.sender_pid = task_tgid_nr_ns(sender,
current->nsproxy->pid_ns);
} else {
}
tr.data_size = t->buffer->data_size;
tr.offsets_size = t->buffer->offsets_size;
tr.data.ptr.buffer = (void *)t->buffer->data +
proc->user_buffer_offset;
tr.data.ptr.offsets = tr.data.ptr.buffer +
ALIGN(t->buffer->data_size,
sizeof(void *));
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
if (copy_to_user(ptr, &tr, sizeof(tr)))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(tr);
list_del(&t->work.entry);
t->buffer->allow_user_free = 1;
if (cmd == BR_TRANSACTION && !(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) {
t->to_parent = thread->transaction_stack;
t->to_thread = thread;
thread->transaction_stack = t;
} else {
}
break;
}
done:
*consumed = ptr - buffer;
if (proc->requested_threads + proc->ready_threads == 0 &&
proc->requested_threads_started < proc->max_threads &&
(thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED |
BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) /* the user-space code fails to */
/*spawn a new thread if we leave this out */) {
proc->requested_threads++;
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS,
"binder: %d:%d BR_SPAWN_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
if (put_user(BR_SPAWN_LOOPER, (uint32_t __user *)buffer))
return -EFAULT;
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, BR_SPAWN_LOOPER);
}
return 0;
}首先从todo链表中取出前面添加的binder_transaction数据结构,t->buffer->target_node即是binder_context_mgr_node。binder_transaction_data结构我们在前面讲过,并复制binder_transaction结构中的target_node、code、flags、sender_euid、data_size、offsets_size、buffer和offsets到binder_transaction_data结构中。另外,因为注册AudioFlinger的线程需要等待ServiceManager的回复,所以在sender_pid记录注册线程的pid号。然后拷贝BR_TRANSACTION命令和binder_transaction_data结构到用户空间,并将binder_transaction数据结构从todo链表中删除。因为cmd == BR_TRANSACTION && !(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)为true,表示ServieManager 在处理完这个事务后需要给binder驱动回复,所以这里先将binder_transaction数据结构放在transaction_stack链表中。在done这个标志处,计算是否需要让Service去创建线程来处理事务,以后再来分析这一点。
回到ServiceManager的binder_loop处,返回到用户层的数据如下:
| cmd | BR_TRANSACTION | |
| binder_transaction_data | target(ptr) | binder_context_mgr_node.local().getWeakRefs() |
| cookie | binder_context_mgr_node.local() | |
| code | ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION | |
| flags | 0 | |
| sender_pid | 注册AudioFlinger的线程的pid | |
| sender_euid | 0 | |
| data_size | ||
| offsets_size | ||
| buffer | Strict Mode 0 interface "android.os.IServiceManager" name ”media.audio_flinger" flat_binder_object type BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE flags 0 handle ref->desc cookie local |
|
| offsets | 26 | |
首先调用binder_parse去解析收到的指令:
int binder_parse(struct binder_state *bs, struct binder_io *bio,
uint32_t *ptr, uint32_t size, binder_handler func)
{
int r = 1;
uint32_t *end = ptr + (size / 4);
while (ptr < end) {
uint32_t cmd = *ptr++;
switch(cmd) {
case BR_TRANSACTION: {
struct binder_txn *txn = (void *) ptr;
if ((end - ptr) * sizeof(uint32_t) < sizeof(struct binder_txn)) {
ALOGE("parse: txn too small!\n");
return -1;
}
binder_dump_txn(txn);
if (func) {
unsigned rdata[256/4];
struct binder_io msg;
struct binder_io reply;
int res;
bio_init(&reply, rdata, sizeof(rdata), 4);
bio_init_from_txn(&msg, txn);
res = func(bs, txn, &msg, &reply);
binder_send_reply(bs, &reply, txn->data, res);
}
ptr += sizeof(*txn) / sizeof(uint32_t);
break;
}
default:
ALOGE("parse: OOPS %d\n", cmd);
return -1;
}
}
return r;
}这里的cmd前面设置的BR_TRANSACTION,然后txn执行上面的binder_transaction_data结构,来看一下binder_txn的结构,它是和binder_transaction_data数据结构完全一一对应的。
struct binder_txn
{
void *target;
void *cookie;
uint32_t code;
uint32_t flags;
uint32_t sender_pid;
uint32_t sender_euid;
uint32_t data_size;
uint32_t offs_size;
void *data;
void *offs;
};这里首先调用bio_init和bio_init_from_txn去初始化msg和reply两个binder_io数据结构,调用bio_init_from_txn后,然后msg的数据内容如下:
| data | Strict Mode 0 interface "android.os.IServiceManager" name ”media.audio_flinger" flat_binder_object type BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE flags 0 handle ref->desc cookie local |
| offs | 26 |
| data_avail | data_size |
| offs_avail | offs_size |
| data0 | |
| offs0 | |
| flags | BIO_F_SHARED |
| unused |
再调用svcmgr_handler去处理具体的事务:
int svcmgr_handler(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_txn *txn,
struct binder_io *msg,
struct binder_io *reply)
{
struct svcinfo *si;
uint16_t *s;
unsigned len;
void *ptr;
uint32_t strict_policy;
int allow_isolated;
if (txn->target != svcmgr_handle)
return -1;
strict_policy = bio_get_uint32(msg);
s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len);
if ((len != (sizeof(svcmgr_id) / 2)) ||
memcmp(svcmgr_id, s, sizeof(svcmgr_id))) {
fprintf(stderr,"invalid id %s\n", str8(s));
return -1;
}
switch(txn->code) {
case SVC_MGR_ADD_SERVICE:
s = bio_get_string16(msg, &len);
ptr = bio_get_ref(msg);
allow_isolated = bio_get_uint32(msg) ? 1 : 0;
if (do_add_service(bs, s, len, ptr, txn->sender_euid, allow_isolated))
return -1;
break;
}
bio_put_uint32(reply, 0);
return 0;
}我们前面讲过在数据的开始会写入strict mode和"android.os.IServiceManager",这里会读出这两个数据用于RPC检查。处理SVC_MGR_ADD_SERVICE中首先从msg取出”media.audio_flinger" 字串,ptr指针指向binder_transaction_data中的target结构,然后调用do_add_service来添加service。
int do_add_service(struct binder_state *bs,
uint16_t *s, unsigned len,
void *ptr, unsigned uid, int allow_isolated)
{
struct svcinfo *si;
if (!ptr || (len == 0) || (len > 127))
return -1;
if (!svc_can_register(uid, s)) {
ALOGE("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d - PERMISSION DENIED\n",
str8(s), ptr, uid);
return -1;
}
si = find_svc(s, len);
if (si) {
if (si->ptr) {
ALOGE("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d - ALREADY REGISTERED, OVERRIDE\n",
str8(s), ptr, uid);
svcinfo_death(bs, si);
}
si->ptr = ptr;
} else {
si = malloc(sizeof(*si) + (len + 1) * sizeof(uint16_t));
if (!si) {
ALOGE("add_service('%s',%p) uid=%d - OUT OF MEMORY\n",
str8(s), ptr, uid);
return -1;
}
si->ptr = ptr;
si->len = len;
memcpy(si->name, s, (len + 1) * sizeof(uint16_t));
si->name[len] = '\0';
si->death.func = svcinfo_death;
si->death.ptr = si;
si->allow_isolated = allow_isolated;
si->next = svclist;
svclist = si;
}
binder_acquire(bs, ptr);
binder_link_to_death(bs, ptr, &si->death);
return 0;
}首先调用svc_can_register查看能否能注册这个service,能注册service的条件是注册AudioFlinger服务的进程uid是0或者是AID_SYSTEM,或者在allowed数组中有指定。再调用find_svc通过服务名字去查找是否已经注册,这里是第一次注册,所以返回空。然后创建一个svcinfo对象,并设置它的一些变量,这里将ptr指针指向flat_binder_object 的handle id值。最后将创建的svcinfo对象加入到全局的svclist链表中。
在svcmgr_handler方法的最后,通过bio_put_uint32(reply, 0)写一个0到reply中。回到binder_parse方法中会调用binder_send_reply向binder驱动返回执行结果,如下:
void binder_send_reply(struct binder_state *bs,
struct binder_io *reply,
void *buffer_to_free,
int status)
{
struct {
uint32_t cmd_free;
void *buffer;
uint32_t cmd_reply;
struct binder_txn txn;
} __attribute__((packed)) data;
data.cmd_free = BC_FREE_BUFFER;
data.buffer = buffer_to_free;
data.cmd_reply = BC_REPLY;
data.txn.target = 0;
data.txn.cookie = 0;
data.txn.code = 0;
if (status) {
data.txn.flags = TF_STATUS_CODE;
data.txn.data_size = sizeof(int);
data.txn.offs_size = 0;
data.txn.data = &status;
data.txn.offs = 0;
} else {
data.txn.flags = 0;
data.txn.data_size = reply->data - reply->data0;
data.txn.offs_size = ((char*) reply->offs) - ((char*) reply->offs0);
data.txn.data = reply->data0;
data.txn.offs = reply->offs0;
}
binder_write(bs, &data, sizeof(data));
}这里填充data 数据结构如下:
| cmd_free | BC_FREE_BUFFER | |
| buffer | buffer_to_free | |
| cmd_reply | BC_REPLY | |
| binder_txn | target | 0 |
| cookie | 0 | |
| code | 0 | |
| flags | 0 | |
| sender_pid | 0 | |
| sender_euid | 0 | |
| data_size | 4 | |
| offs_size | 0 | |
| data | 0 | |
| offs | 0 | |
我们可以看到上面有两个cmd,一个是BC_FREE_BUFFER,一个是BC_REPLY。BC_FREE_BUFFER就是释放前面我们申请t->buffer = binder_alloc_buf()内存;BC_REPLY就是执行ADD_SEVICE的结果。binder_write前面我们分析过,通过ioctrl将上面的data数据发送给binder驱动,我们直接到binder驱动中去分析binder_thread_write方法:
int binder_thread_write(struct binder_proc *proc, struct binder_thread *thread,
void __user *buffer, int size, signed long *consumed)
{
uint32_t cmd;
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;
void __user *end = buffer + size;
while (ptr < end && thread->return_error == BR_OK) {
if (get_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
trace_binder_command(cmd);
if (_IOC_NR(cmd) < ARRAY_SIZE(binder_stats.bc)) {
binder_stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]++;
proc->stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]++;
thread->stats.bc[_IOC_NR(cmd)]++;
}
switch (cmd) {
case BC_FREE_BUFFER: {
void __user *data_ptr;
struct binder_buffer *buffer;
if (get_user(data_ptr, (void * __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(void *);
buffer = binder_buffer_lookup(proc, data_ptr);
if (buffer == NULL) {
}
if (!buffer->allow_user_free) {
}
if (buffer->transaction) {
buffer->transaction->buffer = NULL;
buffer->transaction = NULL;
}
if (buffer->async_transaction && buffer->target_node) {
BUG_ON(!buffer->target_node->has_async_transaction);
if (list_empty(&buffer->target_node->async_todo))
buffer->target_node->has_async_transaction = 0;
else
list_move_tail(buffer->target_node->async_todo.next, &thread->todo);
}
binder_transaction_buffer_release(proc, buffer, NULL);
binder_free_buf(proc, buffer);
break;
}
case BC_TRANSACTION:
case BC_REPLY: {
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
if (copy_from_user(&tr, ptr, sizeof(tr)))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(tr);
binder_transaction(proc, thread, &tr, cmd == BC_REPLY);
break;
}
}
*consumed = ptr - buffer;
}
return 0;
}首先处理BC_FREE_BUFFER命令,从BC_FREE_BUFFER指令后取出buffer的地址,并在binder_proc查找相应的的binder_buffer,最后调用binder_transaction_buffer_release和binder_free_buf来释放这块binder_buffer。接着处理BC_REPLY命令,通过copy_from_user将ptr中的数据拷贝到tr数据结构中,这时tr中的数据如下:
| binder_transaction_data | target | 0 |
| cookie | 0 | |
| code | 0 | |
| flags | 0 | |
| sender_pid | 0 | |
| sender_euid | 0 | |
| data_size | 4 | |
| offset_size | 0 | |
| data | 0 | |
| offsets | 0 |
接着来看binder_transaction方法,这个函数在前面处理BC_TRANSACTION命名时分析过。不同的是这里的最后一个参数cmd == BC_REPLY是true。
static void binder_transaction(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
struct binder_transaction_data *tr, int reply)
{
struct binder_transaction *t;
struct binder_work *tcomplete;
size_t *offp, *off_end;
struct binder_proc *target_proc;
struct binder_thread *target_thread = NULL;
struct binder_node *target_node = NULL;
struct list_head *target_list;
wait_queue_head_t *target_wait;
struct binder_transaction *in_reply_to = NULL;
struct binder_transaction_log_entry *e;
uint32_t return_error;
e = binder_transaction_log_add(&binder_transaction_log);
e->call_type = reply ? 2 : !!(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY);
e->from_proc = proc->pid;
e->from_thread = thread->pid;
e->target_handle = tr->target.handle;
e->data_size = tr->data_size;
e->offsets_size = tr->offsets_size;
if (reply) {
in_reply_to = thread->transaction_stack;
if (in_reply_to == NULL) {
}
binder_set_nice(in_reply_to->saved_priority);
if (in_reply_to->to_thread != thread) {
}
thread->transaction_stack = in_reply_to->to_parent;
target_thread = in_reply_to->from;
if (target_thread == NULL) {
}
if (target_thread->transaction_stack != in_reply_to) {
}
target_proc = target_thread->proc;
} else {
}
}
if (target_thread) {
e->to_thread = target_thread->pid;
target_list = &target_thread->todo;
target_wait = &target_thread->wait;
} else {
target_list = &target_proc->todo;
target_wait = &target_proc->wait;
}
e->to_proc = target_proc->pid;
/* TODO: reuse incoming transaction for reply */
t = kzalloc(sizeof(*t), GFP_KERNEL);
if (t == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_alloc_t_failed;
}
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION);
tcomplete = kzalloc(sizeof(*tcomplete), GFP_KERNEL);
if (tcomplete == NULL) {
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_alloc_tcomplete_failed;
}
binder_stats_created(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE);
t->debug_id = ++binder_last_id;
e->debug_id = t->debug_id;
if (reply)
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_TRANSACTION,
"binder: %d:%d BC_REPLY %d -> %d:%d, "
"data %p-%p size %zd-%zd\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, t->debug_id,
target_proc->pid, target_thread->pid,
tr->data.ptr.buffer, tr->data.ptr.offsets,
tr->data_size, tr->offsets_size);
else
if (!reply && !(tr->flags & TF_ONE_WAY))
t->from = thread;
else
t->from = NULL;
t->sender_euid = proc->tsk->cred->euid;
t->to_proc = target_proc;
t->to_thread = target_thread;
t->code = tr->code;
t->flags = tr->flags;
t->priority = task_nice(current);
trace_binder_transaction(reply, t, target_node);
t->buffer = binder_alloc_buf(target_proc, tr->data_size,
tr->offsets_size, !reply && (t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY));
if (t->buffer == NULL) {
}
t->buffer->allow_user_free = 0;
t->buffer->debug_id = t->debug_id;
t->buffer->transaction = t;
t->buffer->target_node = target_node;
trace_binder_transaction_alloc_buf(t->buffer);
if (target_node)
binder_inc_node(target_node, 1, 0, NULL);
offp = (size_t *)(t->buffer->data + ALIGN(tr->data_size, sizeof(void *)));
if (copy_from_user(t->buffer->data, tr->data.ptr.buffer, tr->data_size)) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with invalid "
"data ptr\n", proc->pid, thread->pid);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_copy_data_failed;
}
if (copy_from_user(offp, tr->data.ptr.offsets, tr->offsets_size)) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with invalid "
"offsets ptr\n", proc->pid, thread->pid);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_copy_data_failed;
}
if (!IS_ALIGNED(tr->offsets_size, sizeof(size_t))) {
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d got transaction with "
"invalid offsets size, %zd\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid, tr->offsets_size);
return_error = BR_FAILED_REPLY;
goto err_bad_offset;
}
off_end = (void *)offp + tr->offsets_size;
for (; offp < off_end; offp++) {
}
if (reply) {
BUG_ON(t->buffer->async_transaction != 0);
binder_pop_transaction(target_thread, in_reply_to);
} else if (!(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) {
} else {
}
t->work.type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION;
list_add_tail(&t->work.entry, target_list);
tcomplete->type = BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION_COMPLETE;
list_add_tail(&tcomplete->entry, &thread->todo);
if (target_wait)
wake_up_interruptible(target_wait);
return;首先从thread->transaction_stack中取出开始处理ADD_SERVICE时创建的binder_transaction对象,这时的thread是ServiceManager所在的thread,而target_thread和target_proc都是注册AudioFlinger所在的thread。然后在创建一个binder_transaction对象t,这时t对象的buffer数据里面讲没有binder数据,并且t->buffer->target_node为NULL,其from设置为NULL,表示不需要等待回复。再调用binder_pop_transaction(target_thread, in_reply_to)去释放in_reply_to所在的内存。然后发送给注册AudioFlinger所在的thread;并往ServiceManager所在的thread的todo队列中加入一个tcomplete对象表示完成。先到注册AudioFlinger所在的thread看如何处理:
static int binder_thread_read(struct binder_proc *proc,
struct binder_thread *thread,
void __user *buffer, int size,
signed long *consumed, int non_block)
{
void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;
void __user *end = buffer + size;
int ret = 0;
int wait_for_proc_work;
if (*consumed == 0) {
if (put_user(BR_NOOP, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
}
retry:
wait_for_proc_work = thread->transaction_stack == NULL &&
list_empty(&thread->todo);
if (thread->return_error != BR_OK && ptr < end) {
}
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads++;
binder_unlock(__func__);
trace_binder_wait_for_work(wait_for_proc_work,
!!thread->transaction_stack,
!list_empty(&thread->todo));
if (wait_for_proc_work) {
} else {
if (non_block) {
} else
ret = wait_event_freezable(thread->wait, binder_has_thread_work(thread));
}
binder_lock(__func__);
if (wait_for_proc_work)
proc->ready_threads--;
thread->looper &= ~BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_WAITING;
while (1) {
uint32_t cmd;
struct binder_transaction_data tr;
struct binder_work *w;
struct binder_transaction *t = NULL;
if (!list_empty(&thread->todo))
w = list_first_entry(&thread->todo, struct binder_work, entry);
else if (!list_empty(&proc->todo) && wait_for_proc_work)
w = list_first_entry(&proc->todo, struct binder_work, entry);
else {
if (ptr - buffer == 4 && !(thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_NEED_RETURN)) /* no data added */
goto retry;
break;
}
if (end - ptr < sizeof(tr) + 4)
break;
switch (w->type) {
case BINDER_WORK_TRANSACTION: {
t = container_of(w, struct binder_transaction, work);
} break;
}
if (!t)
continue;
BUG_ON(t->buffer == NULL);
if (t->buffer->target_node) {
} else {
tr.target.ptr = NULL;
tr.cookie = NULL;
cmd = BR_REPLY;
}
tr.code = t->code;
tr.flags = t->flags;
tr.sender_euid = t->sender_euid;
if (t->from) {
} else {
tr.sender_pid = 0;
}
tr.data_size = t->buffer->data_size;
tr.offsets_size = t->buffer->offsets_size;
tr.data.ptr.buffer = (void *)t->buffer->data +
proc->user_buffer_offset;
tr.data.ptr.offsets = tr.data.ptr.buffer +
ALIGN(t->buffer->data_size,
sizeof(void *));
if (put_user(cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(uint32_t);
if (copy_to_user(ptr, &tr, sizeof(tr)))
return -EFAULT;
ptr += sizeof(tr);
list_del(&t->work.entry);
t->buffer->allow_user_free = 1;
if (cmd == BR_TRANSACTION && !(t->flags & TF_ONE_WAY)) {
} else {
t->buffer->transaction = NULL;
kfree(t);
binder_stats_deleted(BINDER_STAT_TRANSACTION);
}
break;
}
done:
*consumed = ptr - buffer;
return 0;
}因为t->buffer->target_node为NULL,所以这里的cmd = BR_REPLY,回到waitForResponse来看如何处理BR_REPLY:
status_t IPCThreadState::waitForResponse(Parcel *reply, status_t *acquireResult)
{
int32_t cmd;
int32_t err;
while (1) {
if ((err=talkWithDriver()) < NO_ERROR) break;
err = mIn.errorCheck();
if (err < NO_ERROR) break;
if (mIn.dataAvail() == 0) continue;
cmd = mIn.readInt32();
switch (cmd) {
case BR_REPLY:
{
binder_transaction_data tr;
err = mIn.read(&tr, sizeof(tr));
if (reply) {
if ((tr.flags & TF_STATUS_CODE) == 0) {
reply->ipcSetDataReference(
reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.buffer),
tr.data_size,
reinterpret_cast(tr.data.ptr.offsets),
tr.offsets_size/sizeof(size_t),
freeBuffer, this);
} else {
}
}
}
goto finish;
default:
err = executeCommand(cmd);
if (err != NO_ERROR) goto finish;
break;
}
}
finish:
if (err != NO_ERROR) {
if (acquireResult) *acquireResult = err;
if (reply) reply->setError(err);
mLastError = err;
}
return err;
} 首先从mIn中读出binder_transaction_data数据,然后调用Parcel的ipcSetDataReference来释放内存:
void Parcel::ipcSetDataReference(const uint8_t* data, size_t dataSize,
const size_t* objects, size_t objectsCount, release_func relFunc, void* relCookie)
{
freeDataNoInit();
mError = NO_ERROR;
mData = const_cast(data);
mDataSize = mDataCapacity = dataSize;
//ALOGI("setDataReference Setting data size of %p to %lu (pid=%d)\n", this, mDataSize, getpid());
mDataPos = 0;
ALOGV("setDataReference Setting data pos of %p to %d\n", this, mDataPos);
mObjects = const_cast(objects);
mObjectsSize = mObjectsCapacity = objectsCount;
mNextObjectHint = 0;
mOwner = relFunc;
mOwnerCookie = relCookie;
scanForFds();
} 这里设置mData是前面申请的binder_buffer的地址,mOwner为freeBuffer函数指针,在Parcel的析构函数中调用freeDataNoInit去释放binder_buffer数据结构:
Parcel::~Parcel()
{
freeDataNoInit();
}
void Parcel::freeDataNoInit()
{
if (mOwner) {
mOwner(this, mData, mDataSize, mObjects, mObjectsSize, mOwnerCookie);
} else {
}
}
void IPCThreadState::freeBuffer(Parcel* parcel, const uint8_t* data, size_t dataSize,
const size_t* objects, size_t objectsSize,
void* cookie)
{
if (parcel != NULL) parcel->closeFileDescriptors();
IPCThreadState* state = self();
state->mOut.writeInt32(BC_FREE_BUFFER);
state->mOut.writeInt32((int32_t)data);
}前面我们分析过处理BC_FREE_BUFFER的流程,这里就不再介绍了。到这里AudioFlinger::instantiate方法就执行完了,接着执行MediaPlayerService::instantiate的方法,与前面类似,主要过程大致如下:
1.通过defaultServiceManager()方法构造一个BpServiceManager的对象,其中的mRemote为BpBinder(0)
2.调用BpServiceManager的addService方法,它其实是调用BpBinder的transact方法,code是ADD_SERVICE_TRANSACTION
3.BpBinder通过IPCThreadState的transact发送BC_TRANSACTION的cmd给binder驱动,并等待binder驱动的BR_REPLY回复
4.binder驱动收到BC_TRANSACTION指令后,为MediaPlayerService构造一个binder_node,并加入到binder_proc的nodes红黑树上(这是nodes上面就有两个节点了,一个AudioFlinger,一个MeidaPlayerService),然后通过binder_node构造一个binder_refs结构,并改写传入的type和handle值。并构造一个binder_transaction加入到ServiceManager的todo队列中。
5.ServiceManager取出binder_transaction对象,并根据里面的name和refs(handle id),构造一个svcinfo对象并加入到全局的svclist链表中
6.做reply和释放前面申请的内存
启动事务处理线程
当在main_mediaservice.cpp注册完所有的Service后,会调用后面两个函数: ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool(),IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool()。首先来看ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool()方法:
void ProcessState::startThreadPool()
{
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
if (!mThreadPoolStarted) {
mThreadPoolStarted = true;
spawnPooledThread(true);
}
}
void ProcessState::spawnPooledThread(bool isMain)
{
if (mThreadPoolStarted) {
String8 name = makeBinderThreadName();
ALOGV("Spawning new pooled thread, name=%s\n", name.string());
sp t = new PoolThread(isMain);
t->run(name.string());
}
}
virtual bool threadLoop()
{
IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool(mIsMain);
return false;
} startThreadPool直接调用spawnPooledThread来启动线程池,makeBinderThreadName顺序的构造一个"Binder_%X"字串作为thread的名字。然后新建一个PoolThread线程并调用其run方法。thread的run方法最后会调用threadLoop方法,也就是调用IPCThreadState::self()->joinThreadPool(true)。所以这里会启动两个线程来不断的处理事务,先来看joinThreadPool的实现:
void IPCThreadState::joinThreadPool(bool isMain)
{
LOG_THREADPOOL("**** THREAD %p (PID %d) IS JOINING THE THREAD POOL\n", (void*)pthread_self(), getpid());
mOut.writeInt32(isMain ? BC_ENTER_LOOPER : BC_REGISTER_LOOPER);
set_sched_policy(mMyThreadId, SP_FOREGROUND);
status_t result;
do {
processPendingDerefs();
result = getAndExecuteCommand();
if (result < NO_ERROR && result != TIMED_OUT && result != -ECONNREFUSED && result != -EBADF) {
ALOGE("getAndExecuteCommand(fd=%d) returned unexpected error %d, aborting",
mProcess->mDriverFD, result);
abort();
}
if(result == TIMED_OUT && !isMain) {
break;
}
} while (result != -ECONNREFUSED && result != -EBADF);
LOG_THREADPOOL("**** THREAD %p (PID %d) IS LEAVING THE THREAD POOL err=%p\n",
(void*)pthread_self(), getpid(), (void*)result);
mOut.writeInt32(BC_EXIT_LOOPER);
talkWithDriver(false);
}
status_t IPCThreadState::getAndExecuteCommand()
{
status_t result;
int32_t cmd;
result = talkWithDriver();
if (result >= NO_ERROR) {
size_t IN = mIn.dataAvail();
if (IN < sizeof(int32_t)) return result;
cmd = mIn.readInt32();
IF_LOG_COMMANDS() {
alog << "Processing top-level Command: "
<< getReturnString(cmd) << endl;
}
result = executeCommand(cmd);
set_sched_policy(mMyThreadId, SP_FOREGROUND);
}
return result;
}传入到joinThreadPool中的默认参数为true,所以会发送BC_ENTER_LOOPER命令到binder驱动中,我们在分析ServiceManager的时候,已经看过处理的代码了,只是设置thread->looper属性为BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED。所以上面启动两个线程会一直循环的调用getAndExecuteCommand去等待事务,永不退出;而如果调用joinThreadPool(false)创建的thread在没有事务处理时,会在没有事务处理时退出。我们再来看一下什么时候会调用joinThreadPool(false) 去创建thread呢。在binder驱动中的binder_thread_read方法中曾说过下面这段code:
*consumed = ptr - buffer;
if (proc->requested_threads + proc->ready_threads == 0 &&
proc->requested_threads_started < proc->max_threads &&
(thread->looper & (BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED |
BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED)) /* the user-space code fails to */
/*spawn a new thread if we leave this out */) {
proc->requested_threads++;
binder_debug(BINDER_DEBUG_THREADS,
"binder: %d:%d BR_SPAWN_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
if (put_user(BR_SPAWN_LOOPER, (uint32_t __user *)buffer))
return -EFAULT;
binder_stat_br(proc, thread, BR_SPAWN_LOOPER);
}当requested_threads(binder驱动请求增加的thread数)+ready_threads(处于等待客户端请求的空闲线程数)等于0,并且requested_threads_started(binder驱动请求成功增加的thread数)小于max_threads数目,就会向用户层发送一个BR_SPAWN_LOOPER命令,并将requested_threads加一。来看Service端收到BR_SPAWN_LOOPER的处理,代码在IPCThreadState::executeCommand方法中:
case BR_SPAWN_LOOPER:
mProcess->spawnPooledThread(false);
break;这里调用ProcessState::self()->startThreadPool(false)来启动一个thread,并发送BC_REGISTER_LOOPER命令到binder驱动,我们来看处理的代码:
case BC_REGISTER_LOOPER:
if (thread->looper & BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_ENTERED) {
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_INVALID;
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d ERROR:"
" BC_REGISTER_LOOPER called "
"after BC_ENTER_LOOPER\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
} else if (proc->requested_threads == 0) {
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_INVALID;
binder_user_error("binder: %d:%d ERROR:"
" BC_REGISTER_LOOPER called "
"without request\n",
proc->pid, thread->pid);
} else {
proc->requested_threads--;
proc->requested_threads_started++;
}
thread->looper |= BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_REGISTERED;
break;因为不同的线程调用binder_ioctrl时通过binder_get_thread会返回不同的binder_thread对象,所以这里的thread->looper的属性是BINDER_LOOPER_STATE_NEED_RETURN。后面将requested_threads减一,并将成功增加的thread数目requested_threads_started增加一。这样就增加了一个Service服务处理线程,当在Service比较繁忙时,线程池中的线程数据会增加,当然不会超过max_threads+2的数目;当Service比较空闲的时候,线程池中的线程会自动退出,也不会少于2。