Linux内核:安装kdb
一、下载kdb
kdb以补丁的形式打包到Linux内核源码中。
文件名:kdb-v4.4-2.6.32-common-6.bz2
kdb-v4.4-2.6.32-x86-6.bz2
下载地址:ftp://oss.sgi.com/www/projects/kdb/download
二、打包kdb补丁到内核源码
将kdb补丁包放到Linux内核源码目录下:/usr/src/linux-2.6.32
2.1 解压缩kdb文件
bzip2 -d kdb-v4.4-2.6.32-common-6.bz2
bzip2 -d kdb-v4.4-2.6.32-x86-6.bz2
2.2 打包kdb文件
patch -p1 < kdb-v4.4-2.6.32-common-6
patch -p1 < kdb-v4.4-2.6.32-x86-6
三、配置Linux内核参数(使用KDB)
3.1 进入内核参数配置页面
cd /usr/src/linux-2.6.32
make menuconfig
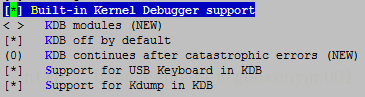
3.2 设置内核参数
Kernel hacking --->
![]()
保存退出,即可看到.config。
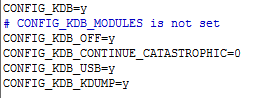
3.3 查看内核参数
vim .config
确保.config文件选项有如下:
CONFIG_KDB=y
CONFIG_KDB_MODULES=n
CONFIG_KDB_OFF=n (y、n均可)
CONFIG_KDB_CONTINUE_CATASTROPHIC=0
CONFIG_KDB_USB=y
CONFIG_KDB_KDUMP=y
CONFIG_KALLSYMS=y
CONFIG_FRAME_POINTER=y
四、编译中可能遇到的问题
以下错误是Linux 2.6.32内核中的错误。
(参考资料,Linux 2.6.3.32内核编译安装kdb-v4.4-2.6.32)
4.1 错误:/arch/x86/kernel/traps.c
错误:
解决办法:
去掉arch/x86/kernel/traps.c 文件中,415行的“}”。
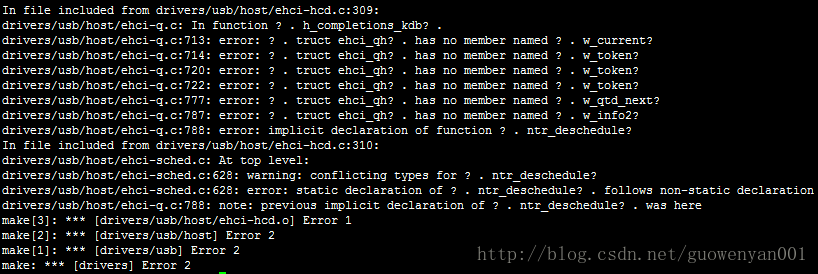
4.2 错误:drivers/usb/host/ehci-hcd.c
错误:
解决办法:
打一个手写的补丁,自己取名:ehci-q--echi_qh--patch
patch -p1 < ehci-q--echi_qh--patch
补丁ehci-q--echi_qh--patch中的内容:
diff --git a/drivers/usb/host/ehci-q.c b/drivers/usb/host/ehci-q.c
index dca7b17..52b4651 100644
--- a/drivers/usb/host/ehci-q.c
+++ b/drivers/usb/host/ehci-q.c
@@ -594,6 +594,7 @@ qh_completions_kdb(struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct ehci_qh *qh, struct urb *kdburb
int do_status = 0;
u8 state;
u32 halt = HALT_BIT(ehci);
+ struct ehci_qh_hw *hw = qh->hw;
/* verify params are valid */
if (!qh || !kdburb)
@@ -612,6 +613,11 @@ qh_completions_kdb(struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct ehci_qh *qh, struct urb *kdburb
qh->qh_state = QH_STATE_COMPLETING;
stopped = (state == QH_STATE_IDLE);
+ rescan:
+ last = NULL;
+ last_status = -EINPROGRESS;
+ qh->needs_rescan = 0;
+
/* remove de-activated QTDs from front of queue.
* after faults (including short reads), cleanup this urb
* then let the queue advance.
@@ -621,7 +627,6 @@ qh_completions_kdb(struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct ehci_qh *qh, struct urb *kdburb
struct ehci_qtd *qtd;
struct urb *urb;
u32 token = 0;
- int qtd_status;
qtd = list_entry (entry, struct ehci_qtd, qtd_list);
urb = qtd->urb;
@@ -651,10 +656,10 @@ qh_completions_kdb(struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct ehci_qh *qh, struct urb *kdburb
spin_unlock (&ehci->lock);
count++;
+ last_status = -EINPROGRESS;
}
ehci_qtd_free (ehci, last);
last = NULL;
- last_status = -EINPROGRESS;
}
/* ignore urbs submitted during completions we reported */
@@ -663,7 +668,7 @@ qh_completions_kdb(struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct ehci_qh *qh, struct urb *kdburb
/* hardware copies qtd out of qh overlay */
rmb ();
- token = hc32_to_cpu(ehci, qtd->hw_token);
+ token = hc32_to_cpu(ehci, hw->hw_token);
/* always clean up qtds the hc de-activated */
if ((token & QTD_STS_ACTIVE) == 0) {
@@ -710,37 +715,60 @@ qh_completions_kdb(struct ehci_hcd *ehci, struct ehci_qh *qh, struct urb *kdburb
/* token in overlay may be most current */
if (state == QH_STATE_IDLE
&& cpu_to_hc32(ehci, qtd->qtd_dma)
- == qh->hw_current)
- token = hc32_to_cpu(ehci, qh->hw_token);
+ == hw->hw_current)
+ token = hc32_to_cpu(ehci, hw->hw_token);
/* force halt for unlinked or blocked qh, so we'll
* patch the qh later and so that completions can't
* activate it while we "know" it's stopped.
*/
- if ((halt & qh->hw_token) == 0) {
+ if ((halt & hw->hw_token) == 0) {
halt:
- qh->hw_token |= halt;
+ hw->hw_token |= halt;
wmb ();
}
}
- /* remove it from the queue */
- qtd_status = qtd_copy_status(ehci, urb, qtd->length, token);
- if (unlikely(qtd_status == -EREMOTEIO)) {
- do_status = (!urb->unlinked &&
- usb_pipecontrol(urb->pipe));
- qtd_status = 0;
+ if (likely(last_status == -EINPROGRESS)) {
+ last_status = qtd_copy_status(ehci, urb,
+ qtd->length, token);
+ if (last_status == -EREMOTEIO
+ && (qtd->hw_alt_next
+ & EHCI_LIST_END(ehci)))
+ last_status = -EINPROGRESS;
+
+ /* As part of low/full-speed endpoint-halt processing
+ * we must clear the TT buffer (11.17.5).
+ */
+ if (unlikely(last_status != -EINPROGRESS &&
+ last_status != -EREMOTEIO)) {
+ /* The TT's in some hubs malfunction when they
+ * receive this request following a STALL (they
+ * stop sending isochronous packets). Since a
+ * STALL can't leave the TT buffer in a busy
+ * state (if you believe Figures 11-48 - 11-51
+ * in the USB 2.0 spec), we won't clear the TT
+ * buffer in this case. Strictly speaking this
+ * is a violation of the spec.
+ */
+ if (last_status != -EPIPE)
+ ehci_clear_tt_buffer(ehci, qh, urb,
+ token);
+ }
}
- if (likely(last_status == -EINPROGRESS))
- last_status = qtd_status;
if (stopped && qtd->qtd_list.prev != &qh->qtd_list) {
last = list_entry (qtd->qtd_list.prev,
struct ehci_qtd, qtd_list);
last->hw_next = qtd->hw_next;
}
+
+ /* remove qtd; it's recycled after possible urb completion */
list_del (&qtd->qtd_list);
last = qtd;
+
+ /* reinit the xacterr counter for the next qtd */
+ qh->xacterrs = 0;
}
/* last urb's completion might still need calling */
@@ -767,6 +795,21 @@ halt:
ehci_qtd_free (ehci, last);
}
+ /* Do we need to rescan for URBs dequeued during a giveback? */
+ if (unlikely(qh->needs_rescan)) {
+ /* If the QH is already unlinked, do the rescan now. */
+ if (state == QH_STATE_IDLE)
+ goto rescan;
+
+ /* Otherwise we have to wait until the QH is fully unlinked.
+ * Our caller will start an unlink if qh->needs_rescan is
+ * set. But if an unlink has already started, nothing needs
+ * to be done.
+ */
+ if (state != QH_STATE_LINKED)
+ qh->needs_rescan = 0;
+ }
+
/* restore original state; caller must unlink or relink */
qh->qh_state = state;
@@ -774,21 +817,26 @@ halt:
* it after fault cleanup, or recovering from silicon wrongly
* overlaying the dummy qtd (which reduces DMA chatter).
*/
- if (stopped != 0 || qh->hw_qtd_next == EHCI_LIST_END(ehci)) {
+ if (stopped != 0 || hw->hw_qtd_next == EHCI_LIST_END(ehci)) {
switch (state) {
case QH_STATE_IDLE:
qh_refresh(ehci, qh);
break;
case QH_STATE_LINKED:
- /* should be rare for periodic transfers,
- * except maybe high bandwidth ...
- */
- if ((cpu_to_hc32(ehci, QH_SMASK)
- & qh->hw_info2) != 0) {
- intr_deschedule (ehci, qh);
- (void) qh_schedule (ehci, qh);
- } else
- unlink_async (ehci, qh);
+ /* We won't refresh a QH that's linked (after the HC
+ * stopped the queue). That avoids a race:
+ * - HC reads first part of QH;
+ * - CPU updates that first part and the token;
+ * - HC reads rest of that QH, including token
+ * Result: HC gets an inconsistent image, and then
+ * DMAs to/from the wrong memory (corrupting it).
+ *
+ * That should be rare for interrupt transfers,
+ * except maybe high bandwidth ...
+ */
+
+ /* Tell the caller to start an unlink */
+ qh->needs_rescan = 1;
break;
/* otherwise, unlink already started */
}五、编译内核
参考:http://blog.csdn.net/guowenyan001/article/details/38704775
六、启动KDB
6.1 激活KDB
echo "1" >/proc/sys/kernel/kdb
6.2 启动KDB
1. KDB处于激活状态,内核中有紧急情况时,会自动调用KDB。
2. 按下Pause键,手动调用KDB。(需要在单用户模式下 ,sudo init 1进入单用户模式)(参考资料,KDB使用2)
参考资料:
Linux内核调试器内幕:http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-kdbug/
KDB使用2:http://blog.csdn.net/cybertan/article/details/6574023(单用户模式下,按下Pause,手动调用KDB)
Linux 2.6.3.32内核编译安装kdb-v4.4-2.6.32:http://babybandf.blog.163.com/blog/static/61993532010715990178/ (解决2个错误问题)