时序行为检测和分类
一 数据集
ActivityNet
发展简介
ActivityNet是15年年cvpr,16年年开始举办的竞赛。
16-19年,
- 16:只有detection和classification(untrimmed) -
- 17:classification(trimmed和untrimmed) proposals captioning
- 18:从-18年年开始去掉了了untrimmed的分类,
任务A: 视频动作分类 (trimmed)改⽤用Kinetics数据集
新加的Task B
时空⾏行行为定位(Spatio-temporal Action Localization)依据 AVA 数据集,试图评估算法对⼈人类⾏行行为时空信息的定位能⼒力力,其中每个标注的视频⽚片 段连续且超过 15 分钟,包含多个主体,每个主体有多个⾏行行为;
Task B 分为
#1 (Vision Only) 以及 #2 (Full) 两个⼦子挑战赛。
总体来说,这⼀一任务做⼤大的难点是 将动作细化到了了原⼦子级别,需要在任务中判断⼈人类⾏行行为主体的位置,发⽣生了了什什么 动作,⼜又与其他物体/⼈人发⽣生了了什什么交互。 AVA的两个任务( AVA atomic visual actions dataset)The long term goal of this dataset is to enable modeling of complex activities by building on top of current work in recognizing atomic actions. This task will be divided into two challenges.
Challenge #1 is strictly computer vision, i.e. participants are requested not to use signals derived from audio, metadata, etc. Challenge #2 lifts this restriction, allowing creative solutions that leverage any input modalities. We ask only that users document the additional data and features they use. Performance will be ranked separately for the two challenges.
19年
任务C改为egocentric activity understanding 该任务适⽤用于online,即处理理的是⼀一个视频流,需要在线的检测(or 预测未来) 发⽣生的动作类别,但⽆无法知道检测时间点之后的内容。online的问题设定更更符合 surveillance的需求,需要做实时的检测或者预警,⽐比如 anomaly detection ; offline的设定更更符合视频搜索的需求,⽐比如youtube可能⽤用到的 highlight detection / preview generation。 这篇⽂文章主要聚焦在 online action detection & anticipation(预测) This task is intended to evaluate the ability of algorithms to understand daily activities in egocentric videos. There will be three tracks focus on classifying actions on trimmed segments, detecting objects in egocentric videos and anticipating future actions Challenge #1 - Object Detection: Detect and localise objects in individual images out of 290 classes, with a long-tail distribution. Challenge #2 - Action Recognition: Given a start-end time in an untrimmed video, classify the varying-length segments into verb classes (125 verb classes, 331 noun classes). Challenge #3 - Action Anticipation: Given an action segment, predict the action class (125 verb classes and 331 noun classes) by observing the video segment preceding the action start time by a preselected anticipation time duration of 1 second. Task D:Activity Detection in Extended Videos (ActEV-PC) ActEV-PC task has two phases: ActEV-PC Open Leaderboard Evaluation (Phase 1): challenge participants will run their activity detection software on their compute hardware and submit system output defined by the ActEV-PC evaluation plan to the NIST ActEV Scoring Server . This phase will serve as a qualifying stage where the top 6 participants will proceed to phase 2. ActEV-PC Independent Evaluation (Phase 2): invited challenge participants will submit their runnable activity detection software to NIST using the forthcoming Evaluation Commandline Interface Submission Instructions. NIST will then evaluate system performance on sequestered data using NIST hardware.
ActivityNet (v1.3):200类、19,994未剪辑视频(10,024训练,4,926 验证,5,044测试)、共648⼩小时。内容包括饮⻝⾷食、运动、家庭活动等。
(a) Untrimmed Classification Challenge: Given a long video, predict the labels of the activities present in the video;
(b) Detection Challenge: Given a long video, predict the labels and temporal extents of the activities present in the video.
仅提供视频的youtube链接,⽽而不不能直接下载视频,所以还需要⽤用 python中的youtube下载⼯工具来⾃自动下载
including Kinetics (Google DeepMind), AVA (Google), EPIC-Kitchens (University of Bristol), and VIRAT (NIST)
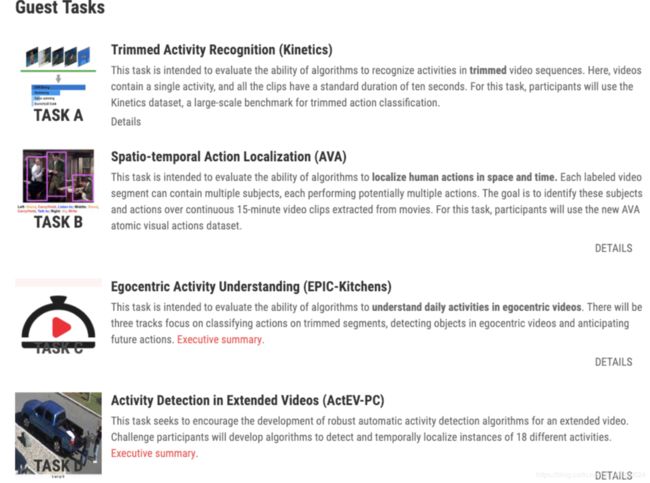
其中任务1-3基于ActivityNet数据集,任务A,B,C则为其他视频理理解领域 内重要的数据集。⽬目前ActivityNet数据集的版本为1.3,包括20000个 Youtube 视频,共计约700⼩小时,平均每个视频上有1.5个动作⽚片段,涵 盖了了共200个动作类别。这些⽐比赛项⽬目具体包括:
任务1: 时序动作提名⽣生成;
任务2: 时序动作定位;
任务3: 视频密集描述⽣生成;
任务A: 视频动作分类(Kinetics数据集);
任务B: 时空动作定位(AVA数据集);
任务C: 视频事件分类(Moments-in-time 数据集) 在时序动作定位问题中,mean Average Precision(mAP) 是最常⽤用的 评估指标。此次竞赛计算0.5到0.95, 以0.05为步⻓长的多个IoU阈值下的 mAP,称为 Average mAP,作为最终的测评以及排名指标。相较于使 ⽤用[email protected] 作为测评指标,Average mAP 更更看重在较严格IoU阈值下 的检测精度。时序动作提名任务由于⽆无需对时序⽚片段进⾏行行分类,所以通
常使⽤用average recall (AR) 来进⾏行行评估。在此次竞赛中,Average Recall vs. Average Number of Proposals per Video (AR-AN) 曲线下的 ⾯面积被作为最终的评测指标
HMDB-51:
51类、6,766剪辑视频、每个视频不不超过10秒、分辨率320 K. Soomro, et al. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human action classes from videos in the wild. CoRR, abs/1212.0402, 2012.
240、共2 GB。视频源于YouTube和⾕谷歌视频,内容包括⼈人⾯面部、肢 体、和物体交互的动作这⼏几⼤大类。
UCF-101:
101类、13,320视频剪辑、每个视频不不超过10秒、共27⼩时、分辨率320
240、共6.5 GB。视频源于YouTube
The action categories : 1)Human-Object Interaction 2) Body-Motion Only 3) Human- Human Interaction 4) Playing Musical Instruments 5) Sports.
每类动作由25个⼈人做动作,每⼈人做4-7组。
Kinetics:
400类、246k训练视频、20k验证视频、每个视频⼤大约10 秒。视频源于YouTube。Kinetics是⼀一个⼤大规模数据集,其在视频理理解 中的作⽤用有些类似于ImageNet在图像识别中的作⽤用,有些⼯工作⽤用 Kinetics预训练模型迁移到其他视频数据集。
其他小数据集
50 Salads dataset
contains 50 videos with 17 action classes. On average, each video contains 20 action instances and is 6.4 minutes long. 50 Salads数据集旨在激发对识别操纵⼿手势的研究。它捕获了了25个⼈人,每个⼈人准 备2个混合沙拉,包含超过4⼩小时的注释加速度计和RGB-D视频数据。包括详细 注释,多种传感器器类型和每个参与者的两个序列列,50 Salads数据集可⽤用于活动 识别,活动定位,序列列分析等领域的研究, 数据集包括 RGB视频数据,640 x 480像素,30 Hz 深度以30 Hz的频率映射640x480像素 连接到⼑刀具,混合勺,⼩小勺⼦子,削⽪皮器器,玻璃,油瓶和胡椒分配器器的50赫 兹设备的3轴加速度计数据。 ⽤用于视频和加速度计数据的时间对⻬齐的同步参数 注释作为与配⽅方中的步骤对应的活动的前核和后期的时间间隔
GTEA dataset
contains 28 videos corresponding to 7 different activities, like preparing coffee or cheese sandwich, performed by 4 subjects. All the videos were recorded by a camera that is mounted on the actor’s head. The frames of the videos are annotated with 11 action classes including background. On average, each video has 20 action instances. We use cross-validation for evaluation by leaving one subject out. The Breakfast Actions Dataset 1, 712 videos. The videos were recorded in 18 different kitchens showing breakfast preparation related activities. Overall, there are 48 different actions where each video contains 6 action instances on average coffee (n=200) orange juice (n=187) chocolate milk (n=224) tea (n=223) bowl of cereals (n=214) fried eggs (n=198) pancakes (n=173) fruit salad (n=185) sandwich (n=197) scrambled eggs (n=188)**
论文
2th I3D Quo Vadis, Action Recognition? A New Model and the
Kinetics Dataset
基于inception-V1模型,将2D卷积扩展到3D卷积。 https://github.com/deepmind/kinetics-i3d
A. Karpathy, G. Toderici, S. Shetty, T. Leung, R. Sukthankar, and F.-F.
Li. Large-scale video classification with convolutional neural networks. In CVPR, pages 1725-1732, 2014.
S. Abu-El-Haija, N. Kothari, J. Lee, P. Natsev, G. Toderici, B. Varadarajan, and S. Vijayanarasimhan.
YouTube-8M: A large-scale video classification benchmark. CoRR, abs/1609.08675, 2016.
How temporal information should be fed into convo- lutional networks, various fusion schemes are investigated? 逐帧处理理融合
Spatio temporal networks 2850(NIPS2014)
Large-scale Video Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks
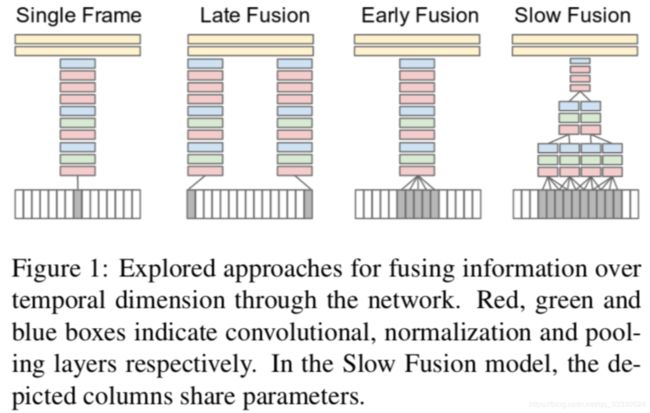
proposed the concept of slow fusion to increase the temporal awareness of a convolutional network. In slow fusion, a convolutional network accepts several, yet consecutive, parts of a video and processes them through the very same set of layers to produce responses across temporal domain. These responses are then processed by fully connected layers to produce the video descriptor Karpathy等⼈人把视频划分成很多固定⻓长度的⽚片段(clip),并设计了了多种 融合⽅方法
ECCV 2018 M. Zolfaghari, et al. ECO: Efficient Convolutional network for Online video understanding. arXiv:1804.09066.
王恒
H. Wang, et al. Dense trajectories and motion boundary descriptors for action recognition. IJCV’13.
H. Wang and C. Schmid. Action recognition with improved trajectories. ICCV’13.
Wang等⼈人提出DT和iDT⽅方法。DT利利⽤用光流得到视频中的运动轨迹,再 沿着轨迹提取特征
Before deep learning came along, most of the traditional CV algorithm variants for action recognition can be broken down into the following 3 broad steps:
- Local high-dimensional visual features that describe a region of the video are extracted either densely or at a sparse set of interest points. 2.The extracted features get combined into a fixed-sized video level description. One popular variant to the step is to bag of visual words (derived using hierarchical or k-means clustering) for encoding features at video-level.
3.A classifier, like SVM or RF, is trained on bag of visual words for final prediction
deep learning methods
Trajectories (iDT) which uses densely sampled trajectory features was the state-of-the-art. Simultaneously, 3D convolutions were used as is for action recognition without much help in 2013. Soon after this in 2014, two breakthrough research papers were released which form the backbone for all the papers we are going to discuss in this post. The major differences between them was the design choice around combining spatiotemporal information.
Approach 1: Single Stream Network
Large-scale Video Classification with Convolutional Neural Networks
Karpathy等⼈人把视频划分成很多固定⻓长度的⽚片段(clip),并设计了了多种 融合⽅方法。
explore multiple ways to fuse temporal information from consecutive frames using 2D pre-trained convolutions
Approach 2: Two Stream Networks
Two-Stream Convolutional Networks for Action
Recognition in Videos

Given the toughness of deep architectures to learn motion features,
authors explicitly modeled motion features in the form of stacked optical flow vectors.
Two Stream方法最初在这篇文章中被提出:
在空间部分,以单个帧上的外观形式,携带了视频描绘的场景和目标信息。其自身静态外表是一个很有用的线索,因为一些动作很明显地与特定的目标有联系。
在时间部分,以多帧上的运动形式,表达了观察者(摄像机)和目标者的运动。
基本原理为:
1. 对视频序列中每两帧计算密集光流,得到密集光流的序列(即temporal信息)。
2. 然后对于视频图像(spatial)和密集光流(temporal)分别训练CNN模型,
两个分支的网络分别对动作的类别进行判断,
3. 最后直接对两个网络的class score进行fusion(包括直接平均和svm两种方法),得到最终的分类结果。
注意,对与两个分支使用了相同的2D CNN网络结构,其网络结构见下图。
实验效果:UCF101-88.0%,HMDB51-59.4%

LRCN(Long-term Recurrent Convolutional Networks for Visual Recognition and Description 2014CVPR)
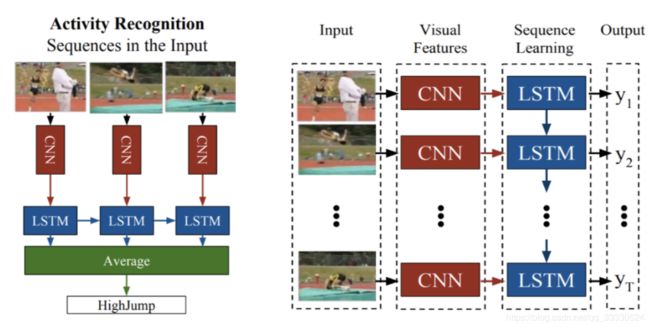
During training, 16 frame clips are sampled from video. The architecture is trained end-to-end with input as RGB or optical flow of 16 frame clips. Final prediction for each clip is the average of predictions across each time step.
The final prediction at video level is average of predictions from each clip.
C3D LearningSpatiotemporalFeatureswith3DConvolutional
Networks (2015ICCV) Facebook AI Research
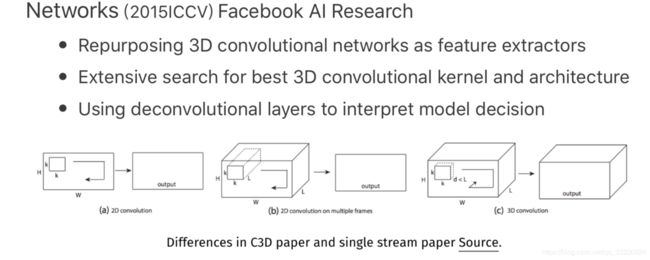
Repurposing 3D convolutional networks as feature extractors
Extensive search for best 3D convolutional kernel and architecture Using deconvolutional layers to interpret model decision
Conv3D TwoStreamFusion
Convolutional Two-Stream Network Fusion for Video Action
Recognition“(2016CVPR)
这篇论⽂文的主要⼯工作为:
- 在two stream network的基础上, 利利⽤用CNN⽹网络进⾏行行了了spatial以及temporal的融合,从⽽而进⼀一步提⾼高了了效
果。 - 此外,该⽂文章还将基础的spatial和temporal⽹网络都换成了了VGG-16 network。 实验效果:UCF101-92.5%,HMDB51-65.4%
TSN
Temporal Segment Networks: Towards Good Practices for Deep Action Recognition(eccv2017)
这篇⽂文章是港中⽂文Limin Wang⼤大神的⼯工作,他在这⽅方⾯面做了了很多很棒的⼯工作, 可以followt他的主⻚页:http://wanglimin.github.io/ 。 这篇⽂文章提出的TSN⽹网络也算是spaital+temporal fusion,结构图⻅见下图。 这篇⽂文章对如何进⼀一步提⾼高two stream⽅方法进⾏行行了了详尽的讨论,主要包括⼏几个⽅方⾯面 (完整内容请看原⽂文):
-
据的类型:除去two stream原本的RGB image和 optical flow field 这两种输⼊入外,
章中还尝试了了RGB difference及 warped optical flow field两种输 ⼊入。
终结果是 RGB+optical flow+warped optical flow的组合效果最 好。 -
结构:尝试了了GoogLeNet,VGGNet-16及BN-Inception三种⽹网络结构,其 中BN-Inception的效果最好。
-
包括 跨模态预训练,正则化,数据增强等。 4. 果:UCF101-94.2%,HMDB51-69.4%
two-stream 卷积⽹网络对于⻓长范围时间结构的建模⽆无能为⼒力力, 主要因为它仅仅操作⼀一帧(空间⽹网络)或者操作短⽚片段中的单堆帧(时间⽹网络), 因此对时间上下⽂文的访问是有限的。 视频级框架TSN可以从整段视频中建模动作。
和two-stream⼀一样,TSN也是由空间流卷积⽹网络和时间流卷积⽹网络构成。 但不不同于two-stream采⽤用单帧或者单堆帧,TSN使⽤用从整个视频中稀疏地采样⼀一系列列 短⽚片段, 每个⽚片段都将给出其本身对于⾏行行为类别的初步预测,从这些⽚片段的“共识”来得到视频级 的预测结果。 在学习过程中,通过迭代更更新模型参数来优化视频级预测的损失值(loss value)。
HiddenTwoStream Hidden Two-Stream Convolutional Networks for
Action Recognition
该论⽂文主要参考了了flownet,即使⽤用神经⽹网络学习⽣生成光流图,然后作为temporal⽹网 络的输⼊入。
该⽅方法提升了了光流的质量量,⽽而且模型⼤大⼩小也⽐比flownet⼩小很多。 有论⽂文证明,光流质量量的提⾼高,尤其是对于边缘微⼩小运动光流的提升,对分类有关键作 ⽤用。
另⼀一⽅方⾯面,该论⽂文中也⽐比较了了其余的输⼊入格式,如RGB diff。但效果没有光流好。 ⽬目前,除了了可以考虑尝试新的数据增强⽅方法外,如何训练出替代光流的运动特征应该是
接下来的发展趋势之⼀一。
I3D[Facebook] 即基于inception-V1模型,将2D卷积扩展到3D卷积
T3D 时空 3d卷积
Temporal 3D ConvNets:New Architecture and Transfer Learning for
Video Classification
⼀一⽅方⾯面是采⽤用了了3D densenet,区别于之前的inception和Resnet结构; 另⼀一⽅方⾯面,TTL层,即使⽤用不不同尺度的卷积(inception思想)来捕捉讯息。

Given the difficulty of training deep networks when it comes to video data, knowl- edge transfer, i.e. benefiting from models trained on images or other sources
Considering deep architectures for action recognition, the key- words to remember would be 3D convolutions, temporal pooling, optical flow frames, and LSTMs
To boost the performance, carefully engineered approaches are needed. For instance, data aug- mentation techniques [144], foveated architecture [56] and distinct frame sampling strategies [29,115] have been shown to be essential.
改进:
- 输⼊入的数据类型和格式,也包括数据增强的相关操作 双流⽹网络中,空间⽹网络通道的输⼊入格式通常为单RGB图像或者是多帧RGB堆叠。 ⽽而空间⽹网络⼀一般是直接对ImageNet上经典的⽹网络进⾏行行finetune。 虽然近年年来对motion信息的关注逐渐上升,指责⾏行行为识别过度依赖背景和外貌特征, ⽽而缺少对运动本身的建模,但是,事实上,运动既不不是名词, 也不不应该是动词,⽽而应该是动词+名词的形式,例例如:play+basketball,也可以是 play+football。
所以,个⼈人认为,虽然应该加⼤大的时间信息的关注,但不不可否认空间特征的重要作⽤用。 - 时间流 上输⼊入的改进 光流信息 ⾸首先,光流的提取需要消耗⼤大量量的计算⼒力力和时间(有论⽂文中提到⼏几乎占据整个训练时间 的90%);
其次,光流包含的未必是最优的的运动特征。 - 信息的融合 这⾥里里连接主要是指双流⽹网络中时空信息的交互。 ⼀一种是双流⽹网络之间的交互,包括不不同fusion⽅方式的探索,
金字塔 双流融合
Spatiotemporal Pyramid Network for Video Action Recognition
行为识别的关键就在于如何很好的融合空间和时序上的特征。 作者发现,传统双流⽹网络虽然在最后有fusion的过程,但训练中确实单独训练的, 最终结果的失误预测往往仅来源于某⼀一⽹网络,并且空间/时序⽹网络各有所⻓长。 论⽂分析了错误分类的原因:
空间⽹网络在视频背景相似度⾼高的时候容易失误, 时序网络在long-term⾏为中因为snippets length的⻓度限制容易失误。 那么能否通过交互,实现两个⽹网络的互补呢?
该论⽂重点在于STCB模块,详情请参阅论⽂文。 交互方面,在保留空间、时序流的同时,对时空信息进⾏了一次融合,最后三路路融合, 得出最后结果
SSN(structured segment network,结构化的段⽹网络) 通过结构化的时间⾦字塔对每个⾏行行为实例例的时间结构进⾏行行建模。 ⾦字塔顶层有decomposed discriminative model(分解判别模型), 包含两个分类器器:⽤用于分类⾏行行为(针对recognition)和确定完整性(针对 localization)。 集成到统一的⽹网络中,可以以端到端的⽅式⾼效地进⾏训练。 为了了提取⾼质量,⾏为时间proposal,采⽤用temporal actionness grouping (TAG)算法。
Spatial Temporal Graph Convolutional Networks for Skeleton-Based Action Recognition (AAAI2018)
https://github.com/yysijie/st-gcn
Temporal Action Detection(时序⾏为检测)
THUMOS 2014:在时序⾏行行为检测任务中,只有20类动作的未分割视频 是有时序⾏行行为⽚片段标注的, 包括200个验证集视频(包含3007个⾏行行为 ⽚片段)和213个测试集视频(包含3358个⾏行行为⽚片段)。这些经过标注 的未分割视频可以被⽤用于训练和测试时序⾏行行为检测模型。实际上之后 还有THUMOS Challenge 2015,包括更更多的动作类别和视频数,但由于 上⾯面可以⽐比较的⽅方法不不是很多,所以⽬目前看到的⽂文章基本上还是在THUMOS14上进⾏行行实验。
测试集解压缩密码:The passwords of THUMOS15 and 14 are “THUMOS15_challenge_REGISTERED” and “THUMOS14_REGISTERED”, respectively. 1080显卡,按照我论⽂文中所述的间隔提取光流⼤大概需要12-15天。。硬盘的 话,我没有测试过(因为⽂文件数量量太⼤大),估计在400G左右吧。
ActivityNet
Rethinking the Faster R-CNN Architecture for Temporal Action Localization TAL-Net

第二名: SSN
Temporal Action Detection with Structured Segment
Networks(2017ICCV)
Yue Zhao1, Yuanjun Xiong1, Limin Wang2, Zhirong Wu1, Xiaoou Tang1,
and Dahua Lin1 The Chinese University of Hong Kong
https://github.com/yjxiong/action-detection
End-to-end Learning of Action Detection from Frame Glimpses in Videos(CVPR2016)
这篇⽂文章是李李⻜飞⻜飞实验室的⼯工作。这篇⽂文章使⽤用强化学习的⽅方法 训练了了⼀一个基于RNN的代理理(agent,不不太确定应该怎么翻译)。这个 agent不不断观察视频帧并不不断决定接下来要看哪⾥里里以及什什么时候要 ⽣生成⼀一个动作预测。与后⾯面很多基于proposal的⽅方法不不同,该⽅方法 是end-to-end且是直接⽣生成⾏行行为预测的。
CDC: Convolutional-De-Convolutional Networks for Precise Temporal Action Localization in Untrimmed Videos
发表会议:CVPR 2017 (oral)
性能:THUMOS14 上的[email protected] 为 24.7%,ActvitiyNet 1.3测 试集上的average mAP为 22.9%
@Showthem 寿政
在CVPR17上的⼯工作。基于C3D(3D CNN网络)设计了了⼀一个卷积逆卷积⽹络,输⼊⼀⼩小段视频,输出frame-level的动作类别概率。该⽹络 主要是⽤来对temporal action detection中的动作边界进⾏微调,使得 动作边界更加准确,从⽽而提⾼mAP。由于基于了了层数不不多的C3D⽹络,该⽅方法的速度⾮常快,可以达到500FPS。
R-C3D(Region 3-Dimensional Convolution)⽹网络
R-C3D- Region Convolutional 3D Network for Temporal Activity Detection(2017ICCV)84
是基于Faster R-CNN和C3D⽹网络思想。 对于任意的输⼊入视频L,先进⾏行行Proposal,然后⽤用3D-pooling,最后进⾏行行分类和回归 操作。
⽂文章主要贡献点有以下3个。
1、可以针对任意⻓长度视频、任意⻓长度⾏行行为进⾏行行端到端的检测
2、速度很快(是⽬目前⽹网络的5倍),通过共享proposal generation 和 Classification⽹网络的C3D参数
3、作者测试了了3个不不同的数据集,效果都很好,显示了了通⽤用性。
Temporal action localization in untrimmed videos via multi-stage cnns (CVPR2016)
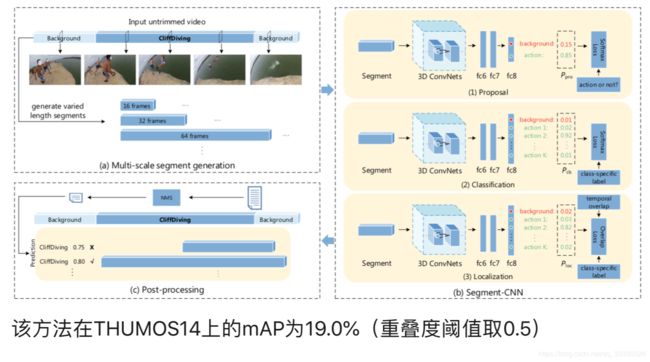
该方法首先使用滑窗的方法生成多种尺寸的视频片段(segment),再使用多阶段的网络(Segment-CNN)来处理。SCNN主要包括三个子网络,均使用了C3D network。第一个是proposal network,用来判断当前输入的视频片段是一个动作的概率;第二个为classification network,该网络用于给视频片段分类,但该网络不用于测试环节,而只是用作初始化localization network;第三个子网络为localization network,该网络的输出形式依旧为类别的概率,但在训练时加入了重叠度相关的损失函数,使得网络能更好的估计一个视频片段的类别和重叠度。最后采用了非极大化抑制(NMS)来去除重叠的片段,完成预测。
该方法实际上采用了类似于R-CNN的思路,后面有不少文章也采用了类似的思想,即先提proposal,再分类。这篇文章的封面图为该paper最后的效果展示图。
该⽅方法在THUMOS14上的mAP为19.0%(重叠度阈值取0.5)
(一) 关于弱监督的视频时序动作检测(Weakly Supervised Action Detection/Localization)
“视频时序动作检测”是指在可能包含一个或多个动作片段的未剪辑长视频中,定位出这些动作片段的起止时间,并指出片段具体属于哪一类动作。“全监督”指的是训练标签中包含了片段级别的动作类别,以及动作片段的时间信息,详见上述的知乎文章;“弱监督”则是指训练集中只标记整段视频包含的动作类别,并没有片段级别的时间信息。
弱监督的动作识别与时序检测
Temporal Localization of Fine-Grained Actions in Videos by Domain Transfer from Web Images (ACM MM’15)
mAP@tIoU=0.5 on THUMOS’14: 4.4%
这是上古时代的工作,应用了领域迁移(静态图片→动态视频)的思想。根据动作的名称,在Flickr 和Google上搜出这些包含动作的图片,然后过滤掉不适合迁移的搜索结果,并用剩下的图片辅助弱监督的视频时序检测。
UntrimmedNets for Weakly Supervised Action Recognition and Detection (CVPR’17)
Limin Wang The Chinese University of Hong Kong
比较正式地提出“弱监督的动作识别与时序检测”这两个任务,引领了后来基于这两个任务的一系列工作。该方法可以视为王利民教授、熊元骏研究员、乔宇研究员、林达华
教授、汤晓鸥教授团队在ECCV’16的工作Temporal Segment Network (TSN)的拓展,得到片段级别的动作概率后,用soft selection模块——给出每个片段样本得分对应的attention权重,然后加权融合为video-level的动作分类输出,根据该输出与视频标签做梯度反传。在测试阶段,用attention权重排除掉不包含动作的视频片段,并选取动作概率大于0.5的片段作为结果。
mAP@tIoU=0.5 on THUMOS’14: 13.7%mAP@tIoU=0.5 on ActivityNet-v1.2 val: 7.4%
Segregated Temporal Assembly Recurrent Networks for Weakly Supervised Multiple Action Detection (18浙大) mAP@tIoU=0.5 on THUMOS‘14: 23.0% mAP@tIoU=0.5 on ActivityNet-v1.3 val: 31.1%
Temporal Action Proposal Generation
该任务的目标是生成一批有可能包含动作片断的时间区域,而不需要对时间区域进行动作分类。常用的数据库同样是THUMOS14以及ActivityNet 1.3 等。常用的测评指标为AR( Average Recall)。注意,实际上时序动作检测模型去掉分类功能一般都能用来做时序提名生成,此处则主要讨论独立的时序提名生成模型。
average recall (AR) ,Average Recall vs. Average Number of Proposals per Video (AR-AN) 即曲线下的面积
找proposals的方法:
- (1) 单纯的滑动窗口(SCNN提出):
固定一些尺寸在视频长度上滑窗,重叠度越高,效果越好,但是计算量大。
理论上这种方法只要重叠度够高,是找的最全的,但是冗余多。 - (2)时序动作分组(TAG提出):
逐个视频帧分类(CNN网络),把相邻的类别一样的分成一组,设置一些阈值防止噪声干扰,一般设置多组阈值防止漏掉proposal。这种方法对于边界比较灵活,但是可能会因为分类错误漏掉proposal。 - (3)单元回归(TURN提出):
把视频分成固定大小单元,比如16视频帧一组,每组学一个特征(放C3D里),然后每组或者多组作为中心anchor单元(参照faster-rcnn)向两端扩展找不同长度proposal。
如果刚开始看这方面,17工作直接看SSN(TAG找proposal)、R-C3D、CBR(TURN找proposal)就好了,找proposal方法简单看看TAG和TURN(网络其他部分不用看),github也有代码,对性能要求不高可以试试SSN(用到了光流),不然的话可以用一下R-C3D。
SSN代码:https://github.com/yjxiong/action-detection
Temporal Action Detection with Structured Segment Networks
Yue Zhao1, Yuanjun Xiong1, Limin Wang2, Zhirong Wu1, Xiaoou Tang1, and Dahua Lin1
CDC代码:https://github.com/ColumbiaDVMM/CDC
R-C3D代码:https://github.com/VisionLearningGroup/R-C3D
CBR代码:https://github.com/jiyanggao/CBR
Learning Latent Super-Events to Detect Multiple Activities in Videos
代码:https://github.com/piergiaj/super-events-cvpr18
常用特征
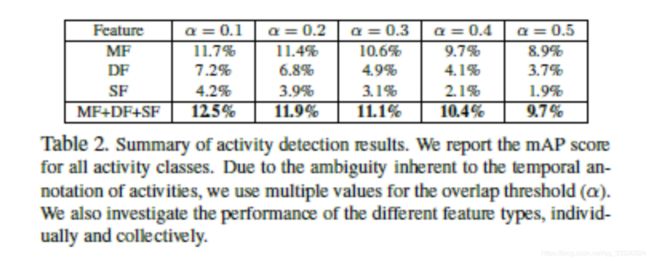
DF(Deep Features):For the network implementation,we adopt the AlexNet architecture trained
on ILSVRC-2012 [32] as provided by Caffe. We retain activations of the network associated with the top-3 fullyconnected layers (fc-6, fc-7, and fc-8). We retain activations of the network associated with the top-3 fullyconnected layers (fc-6, fc-7, and fc-8).We encode temporal information in the activity by averaging activations across several frames. In practice, we compute these deep features every ten frames for all the videos in our dataset
SF(Static Features):capture contextual scene information by extracting
SIFT features every ten frames. These features are encoded
using FV with a GMM of 1024 components, which is then
reduced to a feature size of 48 dimensions using PCA. The
final representation for each video aggregates all descriptors
in a single FV.
MF(Motion Features):we first extract
improved trajectories to obtain a set of local descriptors
i.e. HOG, HOF, and MBH. We encode these descriptors using
the Fisher vector (FV) coding scheme , where each
descriptor type is represented separately. In all our experiments,
we first learn a GMM with 512 components and reduce
the dimensionality of the final encoding to half using PCA
Detection
hard negative mining
得分较高的这些false positive当做所谓的Hard negative,既然mining出了这些Hard negative,就把这些扔进网络再训练一次,从而加强分类器判别假阳性的能力。ps:Fast中把IOU小于0.1的作为hard example mining
- 目标检测中如何根据有标签的数据划分正负训练集?
用带标签的图像随机生成图像块,iou大于某一个阈值的图像块做为正样本,否则为负样本。但一般负样本远远多于正样本,为避免训练出来的模型会偏向预测为负例,需要保持样本均衡,所以初始负样本训练集需要选择负样本集的子集,一般正:负=1:3。 - 有了正负训练集集就可以训练神经网络了。经过一轮训练,就可以用这个训练出的模型预测其余的负样本了(就是没有加入训练集的那些负样本)。模型在预测一张图像块后会给出其属于正负的概率,在这里设置一个阈值,预测为正的概率大于这个阈值,就可以把这个图像块加入负样本训练集了。
- 正样本训练集不变,负样本训练集除了初始的那些,还有新加入的。拿着这个新的训练集,就可以开始新的一轮训练了。
跳到第二步(这个过程是重复的)