易筋SpringBoot 2.1 | 第七篇:JPA访问MySQL
写作时间:2019-01-04
Spring Boot: 2.1 ,JDK: 1.8, IDE: IntelliJ IDEA, MySQL 8.0.13
JPA说明
对数据的操作无非CRUD(增加查询修改删除),每次写的SQL都类似,是否可以交由框架处理。JPA就是为释放程序员不用谢CRUD而出来的规范。2006年5月11号,JPA 1.0 规范作为 JCP JSR 220 的一部分最终被发布。
JPA(Java Persistence API)是Sun官方提出的Java持久化规范。它为Java开发人员提供了一种对象/关联映射工具来管理Java应用中的关系数据。他的出现主要是为了简化现有的持久化开发工作和整合ORM技术,结束现在Hibernate,TopLink,JDO等ORM框架各自为营的局面。
注意:JPA是一套规范,不是一套产品,那么像Hibernate,TopLink,JDO他们是一套产品,如果说这些产品实现了这个JPA规范,那么我们就可以叫它们为JPA的实现产品。
对象与关系的范式不匹配
| 属性 | Object | RDBMS |
|---|---|---|
| 粒度 | 类 | 表 |
| 继承 | 有 | 没有 |
| 唯一性 | a == b, a.equals(b) | 主键 |
| 关联 | 引用 | 外键 |
| 数据访问 | 逐级访问 | SQL 表间关联Join,数量要少 |
MySQL准备
笔者的MySQL版本为8.0.13,搭建环境可参考文章JdbcTemplate访问MySQL。
工程建立
工程建立的时候,需要勾选SQL的JPA和MySQL两项:
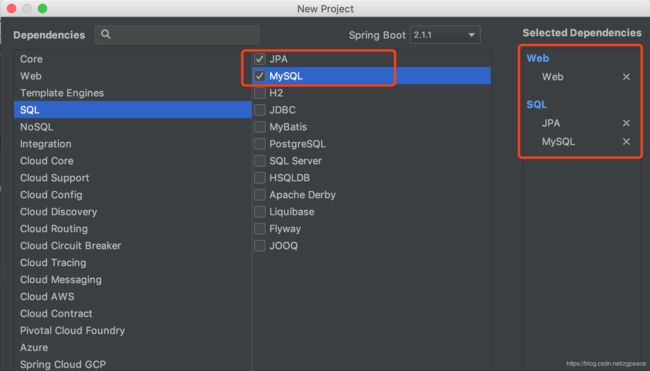
参照教程【SpringBoot 2.1 | 第一篇:构建第一个SpringBoot工程】新建一个Spring Boot项目,名字叫demojpa, 在目录src/main/java/resources 下找到配置文件application.properties,重命名为application.yml。
配置文件
pom.xml 依赖配置修改,mysql-connector-java改为如下 :
<dependency>
<groupId>mysqlgroupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-javaartifactId>
<version>8.0.13version>
dependency>
数据库连接信息配置src/main/resources/application.yml:
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_example
username: springuser
password: ThePassword
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create # 第一次简表create 后面用update
show-sql: true
database-platform: org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect
配置信息解析:
- spring.jpa.show-sql=true 配置在日志中打印出执行的 SQL 语句信息。
- spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5InnoDBDialect 。在 SrpingBoot 2.0 版本中,Hibernate 创建数据表的时候,默认的数据库存储引擎选择的是 MyISAM (之前好像是 InnoDB,这点比较诡异)。这个参数是在建表的时候,将默认的存储引擎切换为 InnoDB 用的。
- spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto是hibernate的配置属性,其主要作用是:自动创建、更新、验证数据库表结构。该参数的几种配置如下:
1)create:每次加载hibernate时都会删除上一次的生成的表,然后根据你的model类再重新来生成新表,哪怕两次没有任何改变也要这样执行,这就是导致数据库表数据丢失的一个重要原因。
2)create-drop:每次加载hibernate时根据model类生成表,但是sessionFactory一关闭,表就自动删除。
3)update:最常用的属性,第一次加载hibernate时根据model类会自动建立起表的结构(前提是先建立好数据表),以后加载hibernate时根据model类自动更新表结构,即使表结构改变了但表中的行仍然存在不会删除以前的行。要注意的是当部署到服务器后,表结构是不会被马上建立起来的,是要等应用第一次运行起来后才会。
4)validate:每次加载hibernate时,验证创建数据库表结构,只会和数据库中的表进行比较,不会创建新表,但是会插入新值。
其它配置项解析请参考文章JdbcTemplate访问MySQL。
实体类
新建实体类com.zgpeace.demojpa.bean.Customer
package com.zgpeace.demojpa.bean;
import javax.persistence.Entity;
import javax.persistence.GeneratedValue;
import javax.persistence.GenerationType;
import javax.persistence.Id;
@Entity
public class Customer {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public Customer() {}
public Customer(String firstName, String lastName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return String.format(
"Customer[id=%d, firstName='%s', lastName='%s']",
id, firstName, lastName
);
}
//getter... setter...
}
实体类解析:
- 默认构造方法
Customer()是为JPA要求的,如果代码中未用到,可以修饰为protected。 - Customer类用注解 @Entity表示JPA的实体类。缺少 @Table表示实体类跟数据库表的名字一样。
- @Id 声明了实体唯一标识对应的属性,@GeneratedValue表示ID会自增长。
- @Column(length = 32) 用来声明实体属性的表字段的定义。默认的实体每个属性都对应了表的一个字段。字段的名称默认和属性名称保持一致(并不一定相等)。字段的类型根据实体属性类型自动推断。这里主要是声明了字符字段的长度。如果不这么声明,则系统会采用 255 作为该字段的长度。
DAO层接口
新建数据库操作接口com.zgpeace.demojpa.dao.CustomerRepository
package com.zgpeace.demojpa.dao;
import com.zgpeace.demojpa.bean.Customer;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import java.util.List;
public interface CustomerRepository extends JpaRepository<Customer, Long> {
List<Customer> findByLastName(String lastName);
}
接口解析:
JpaRepository实现了PagingAndSortingRepository接口,PagingAndSortingRepository接口实现了CrudRepository接口,CrudRepository接口实现了Repository接口;
简单说明下:
- Repository接口是一个标识接口,里面是空的;
- CrudRepository接口定义了增删改查方法;
- PagingAndSortingRepository接口用于分页和排序;
由于JpaRepository接口继承了以上所有接口,所以拥有它们声明的所有方法;
另外注意下,以findAll方法为例,JpaRepository接口返回的是List, PagingAndSortingRepository和CrudRepository返回的是迭代器;
Application初始化数据
初始化数据,完善项目启动类:com.zgpeace.demojpa.DemojpaApplication
package com.zgpeace.demojpa;
import com.zgpeace.demojpa.bean.Customer;
import com.zgpeace.demojpa.dao.CustomerRepository;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemojpaApplication {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DemojpaApplication.class);
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemojpaApplication.class, args);
}
@Bean
public CommandLineRunner demo(CustomerRepository repository) {
return (args) -> {
// save a couple of customers
repository.save(new Customer("Jack", "Bauer"));
repository.save(new Customer("Chloe", "O'Brian"));
repository.save(new Customer("Kim", "Bauer"));
repository.save(new Customer("David", "Palmer"));
repository.save(new Customer("Michelle", "Dessler"));
// fetch all customers
log.info("Customers found with findAll():");
log.info("-------------------------------");
for (Customer customer: repository.findAll()) {
log.info(customer.toString());
}
log.info("");
// fetch an individual customer by ID
repository.findById(1L)
.ifPresent(customer -> {
log.info("Customer found with findById(1L):");
log.info("--------------------------------");
log.info(customer.toString());
log.info("");
});
// fetch customers by last name
log.info("Customer found with findByLastName('Bauer'):");
log.info("--------------------------------------------");
repository.findByLastName("Bauer").forEach(customer -> {
log.info(customer.toString());
});
log.info("");
};
}
}
代码解析:
- 新插入5条数据到数据库
- 查询数据库全部数据
- 根据ID查询数据
- 根据LastName查询数据
运行项目,控制台打印如下:
== Customers found with findAll():
Customer[id=1, firstName='Jack', lastName='Bauer']
Customer[id=2, firstName='Chloe', lastName='O'Brian']
Customer[id=3, firstName='Kim', lastName='Bauer']
Customer[id=4, firstName='David', lastName='Palmer']
Customer[id=5, firstName='Michelle', lastName='Dessler']
== Customer found with findOne(1L):
Customer[id=1, firstName='Jack', lastName='Bauer']
== Customer found with findByLastName('Bauer'):
Customer[id=1, firstName='Jack', lastName='Bauer']
Customer[id=3, firstName='Kim', lastName='Bauer']
上面代码没有分层,逻辑不清晰,下面用MVC实现Restful的增删改查。
新建Service类
新建Service类com.zgpeace.demojpa.service.CustomerService
package com.zgpeace.demojpa.service;
import com.zgpeace.demojpa.bean.Customer;
import com.zgpeace.demojpa.dao.CustomerRepository;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
@Service
public class CustomerService {
@Autowired
private CustomerRepository customerRepository;
public List<Customer> getCustomers() {
return (List<Customer>) customerRepository.findAll();
}
public Customer getCustomerById(long id) {
return customerRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
public Customer addCustomer(Customer customer) {
return customerRepository.save(customer);
}
public Customer updateCustomer(Customer customer) {
return customerRepository.saveAndFlush(customer);
}
public void deleteCustomerById(long id) {
customerRepository.deleteById(id);
}
}
代码解析:
- 注入对象CustomerRepository
- 方法是增删改查的实现
customerRepository.findById(id)返回的是一个Optional对象。
1)Optional 类是一个可以为null的容器对象。如果值存在则isPresent()方法会返回true,调用get()方法会返回该对象。
2)Optional 是个容器:它可以保存类型T的值,或者仅仅保存null。
3)Optional提供很多有用的方法,这样我们就不用显式进行空值检测。Optional 类的引入很好的解决空指针异常。
Optional 类的常用方式
I) 设置默认值,如果不是泛型对象则用默认值
public T orElse(T other) {
return value != null ? value : other;
}
II) 如果值存在,则在闭包里调用泛型对象
public void ifPresent(Consumer<? super T> consumer) {
if (value != null)
consumer.accept(value);
}
Controller的实现
新建类com.zgpeace.demojpa.web.CustomerController
package com.zgpeace.demojpa.web;
import com.zgpeace.demojpa.bean.Customer;
import com.zgpeace.demojpa.service.CustomerService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/customer")
public class CustomerController {
@Autowired
private CustomerService customerService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/list", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<Customer> getCustomers() {
return customerService.getCustomers();
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Customer getCustomerById(@PathVariable("id") long id) {
return customerService.getCustomerById(id);
}
@RequestMapping(value = "", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String addCustomer(@RequestParam(value = "firstName", required = true) String firstName,
@RequestParam(value = "lastName", required = true) String lastName) {
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setFirstName(firstName);
customer.setLastName(lastName);
Customer result = customerService.addCustomer(customer);
return result.toString();
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String updateCustomer(@PathVariable("id") long id, @RequestParam(value = "firstName", required = true) String firstName,
@RequestParam(value = "lastName", required = true) String lastName) {
Customer customer = new Customer();
customer.setId(id);
customer.setFirstName(firstName);
customer.setLastName(lastName);
Customer result = customerService.updateCustomer(customer);
return result.toString();
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteCustomerById(@PathVariable("id") long id) {
customerService.deleteCustomerById(id);
return "finish delete, Please check whether is success";
}
}
上面代码用Postman全部测试通过,Postman用法可点击链接。
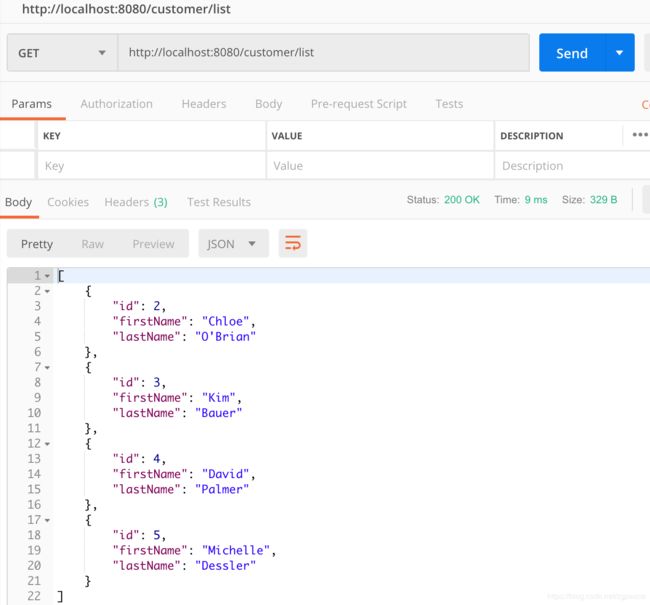
获取全部数据截图:
分页、排序查询
实际项目中经常用到分页、排序查询,spring data jpa已经帮我们实现了分页的功能,在查询的方法中,需要传入参数Pageable ,当查询中有多个参数的时候Pageable建议做为最后一个参数传入。
Service类com.zgpeace.demojpa.service.CustomerService
public List<Customer> getCustomersByPage(Pageable pageable) {
return (List<Customer>) customerRepository.findAll(pageable).getContent();
}
代码解析:
findAll(Pageable) 返回的是Page对象,需要.getContent()获取List
Controller类com.zgpeace.demojpa.web.CustomerController
@RequestMapping(value = "/listPageable", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<Customer> getCustomersByPage() {
int page = 0, size =3;
Sort sort = new Sort(Sort.Direction.DESC, "lastName");
Pageable pageable = PageRequest.of(page, size, sort);
return customerService.getCustomersByPage(pageable);
}
头文件为
import org.springframework.data.domain.PageRequest;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Pageable;
import org.springframework.data.domain.Sort;
代码解析:
- 根据lastName倒序排序
- 每页3条记录,获取第一页的数据。
命令行测试:
$ curl http://localhost:8080/customer/listPageable
[{"id":4,"firstName":"David","lastName":"Palmer"},
{"id":2,"firstName":"Chloe","lastName":"O'Brian"},
{"id":5,"firstName":"Michelle","lastName":"Dessler"}]
自定义SQL查询
有的需求比较复杂,需要写SQL,spring data也是完美支持的;在SQL的查询方法上面使用@Query注解,如涉及到删除和修改在需要加上@Modifying.也可以根据需要添加 @Transactional 对事物的支持,查询超时的设置等
Dao添加com.zgpeace.demojpa.dao.CustomerRepository
@Transactional(timeout = 10)
@Modifying
@Query("delete from Customer where id = ?1")
void deleteCustomerWithSqlByUserId(Long id);
头文件
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Modifying;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.Query;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
Service添加com.zgpeace.demojpa.service.CustomerService
public void deleteCustomerWithSqlByUserId(long id) {
customerRepository.deleteCustomerWithSqlByUserId(id);
}
Controller添加com.zgpeace.demojpa.web.CustomerController
@RequestMapping(value = "/sql/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteCustomerWithSqlById(@PathVariable("id") long id) {
customerService.deleteCustomerWithSqlByUserId(id);
return "finish sql delete, Please check whether is success";
}
命令行测试
删除id为2的记录
$ curl --request DELETE \
--url 'http://localhost:8080/customer/sql/2'
finish sql delete, Please check whether is success%
查询id为2的记录为空,验证通过
$ curl http://localhost:8080/customer/2
常用JPA注解
实体
- @Entity
表明这个类是个实体 - @MappedSuperclass
有多个实体的类,有个父类 - @Table(name)
把表和实体关联起来
主键
- @Id
表的主键 - @GeneratedValue(strategy, generator)
自动生成主键(生成策略, 生成器) - SequenceGenerator(name, sequenceName)
序列生成(名字, 序列名字)
映射
- @Column(name, nullable, length, insertable, updatable)
字段(名字,是否为空,长度多少,插入后能不能改,更新以后能不能改) - @JoinTable(name), @JoinColumn(name)
关联表的时候设置的字段
关系
- @OneToOne
一对一 - @OneToMany
一对多 - @ManyToOne
多对一 - @ManyToMany
多对多 - @OrderBy
排序
总结
恭喜你!学会了SPA的增删改查,分页排序查询,自定义SQL查询。
代码下载:
https://github.com/zgpeace/Spring-Boot2.1/tree/master/db/demojpa
参考:
https://spring.io/guides/gs/accessing-data-jpa/
https://www.cnblogs.com/ityouknow/p/5891443.html
http://blog.didispace.com/springbootdata2/
https://blog.csdn.net/forezp/article/details/70545038
https://juejin.im/post/5aa733af518825558a0646fb
https://www.cnblogs.com/chenpi/p/6357527.html