DirectX11学习笔记十一 法线映射
回顾光照公式
前面学的局部光照里用到了与法线有关的计算公式,也就是漫反射,以点光源为例回顾一下:
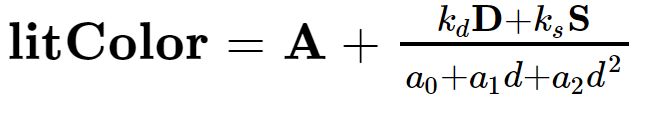
其中 漫反射光D = 漫反射材质系数 点乘 (入射光反方向 点乘 法向量) 点乘 入射光颜色,如下图所示

镜面高光S = 镜面高光材质系数 点乘 (出射光向量 点乘 顶点或像素到摄像机向量)^高光系数 点乘 入射光颜色,如下图所示:

之前计算光照用到的法线都是网格上根据三角形两条边叉乘得到的,但这样的缺点是相邻像素插值得到的法线之间变化非常小,导致整个plane看起来像一个光滑的平面,如果能为texture的每一个像素都提前规定一个法线,就可以表现出平面上凹凸不平的光照现象。
法线纹理
办法就是用一张图片存储法线信息,在渲染时两张图都采样,一张为texture纹理,一张为normal纹理,光照公式不需要动,只需要处理法线。
而法线纹理分Object-space和Tangent-space两种。
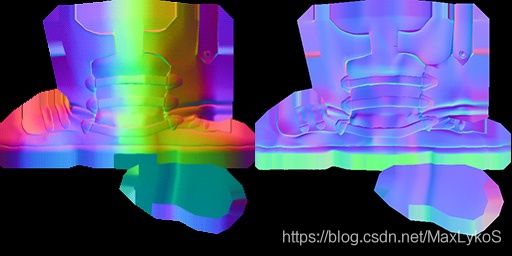
前者(左边)颜色信息代表模型空间,后者为切线空间,数据范围[0,1],通过rgb*2-1来扩大值域范围到[-1,1]。
具体的含义就是,模型空间下的法线纹理,与模型本身密切相关;举个例子,比如有一面竖着的墙(plane),其模型空间下的法线纹理大多朝向-z轴(对着摄像机),而墙的网格本身也是正面对着摄像机,那么法线经过采样并做model变换后,渲染出来的结果就是正确的。However, 如果我又找了一个地板的模型,想套用墙的法线纹理,但是地板的网格法线在模型空间下的的朝向是+y,而墙的法线纹理还是超向-z,那么两者的方向就会不一致,渲染的结果就错了。可以理解为,模型空间下的法线纹理只能跟特定的网格配合渲染。

而切线空间下的法线纹理,其坐标系是以像素在以网格法线为z轴,UV方向为X轴和Y轴所组成的某种局部坐标系,知乎大佬说可以理解为是对像素网格法线的扰动。因此,由图像可以看到,其颜色普遍偏蓝,就是因为其z轴靠近1。

那么就可以根据切线坐标系将法线转换到世界坐标系。
数学原理
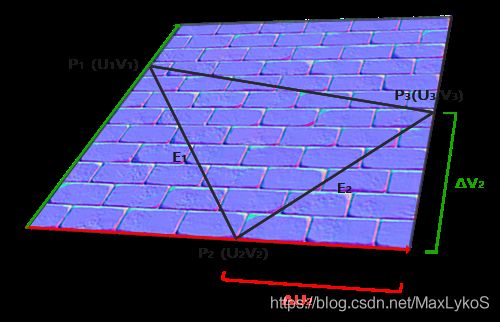
P1P2P3代表网格中的一个三角形,T和B分别代表tangent和bitangent轴,与UV轴对其,UV坐标和三个顶点的模型坐标皆已知。
P 1 − P 2 = E 1 = Δ U 1 T + Δ V 1 B P 3 − P 2 = E 2 = Δ U 2 T + Δ V 2 B P_1 - P_2 = E_1 = \Delta U_1T + \Delta V_1B \newline P_3 - P_2 = E_2 = \Delta U_2T + \Delta V_2B P1−P2=E1=ΔU1T+ΔV1BP3−P2=E2=ΔU2T+ΔV2B
可变为
( E 1 x , E 1 y , E 1 z ) = Δ U 1 ( T x , T y , T z ) + Δ V 1 ( B x , B y , B z ) ( E 2 x , E 2 y , E 2 z ) = Δ U 2 ( T x , T y , T z ) + Δ V 2 ( B x , B y , B z ) (E_{1x}, E_{1y}, E_{1z}) = \Delta U_1(T_x, T_y, T_z) + \Delta V_1(B_x, B_y, B_z)\newline (E_{2x}, E_{2y}, E_{2z}) = \Delta U_2(T_x, T_y, T_z) + \Delta V_2(B_x, B_y, B_z) (E1x,E1y,E1z)=ΔU1(Tx,Ty,Tz)+ΔV1(Bx,By,Bz)(E2x,E2y,E2z)=ΔU2(Tx,Ty,Tz)+ΔV2(Bx,By,Bz)
表示为矩阵
[ E 1 x E 1 y E 1 z E 2 x E 2 y E 2 z ] = [ Δ U 1 Δ V 1 Δ U 2 Δ V 2 ] [ T x T y T z B x B y B z ] \begin{bmatrix} E_{1x} & E_{1y} & E_{1z} \\ E_{2x} & E_{2y} & E_{2z} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} \Delta U_1 & \Delta V_1 \\ \Delta U_2 & \Delta V_2 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} T_x & T_y & T_z \\ B_x & B_y & B_z \end{bmatrix} [E1xE2xE1yE2yE1zE2z]=[ΔU1ΔU2ΔV1ΔV2][TxBxTyByTzBz]
左乘逆矩阵,得
[ Δ U 1 Δ V 1 Δ U 2 Δ V 2 ] − 1 [ E 1 x E 1 y E 1 z E 2 x E 2 y E 2 z ] = [ T x T y T z B x B y B z ] \begin{bmatrix} \Delta U_1 & \Delta V_1 \\ \Delta U_2 & \Delta V_2 \end{bmatrix}^{-1} \begin{bmatrix} E_{1x} & E_{1y} & E_{1z} \\ E_{2x} & E_{2y} & E_{2z} \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} T_x & T_y & T_z \\ B_x & B_y & B_z \end{bmatrix} [ΔU1ΔU2ΔV1ΔV2]−1[E1xE2xE1yE2yE1zE2z]=[TxBxTyByTzBz]
由
可以推出
[ T x T y T z B x B y B z ] = 1 Δ U 1 Δ V 2 − Δ U 2 Δ V 1 [ Δ V 2 − Δ V 1 − Δ U 2 Δ U 1 ] [ E 1 x E 1 y E 1 z E 2 x E 2 y E 2 z ] \begin{bmatrix} T_x & T_y & T_z \\ B_x & B_y & B_z \end{bmatrix} = \frac{1}{\Delta U_1 \Delta V_2 - \Delta U_2 \Delta V_1} \begin{bmatrix} \Delta V_2 & -\Delta V_1 \\ -\Delta U_2 & \Delta U_1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} E_{1x} & E_{1y} & E_{1z} \\ E_{2x} & E_{2y} & E_{2z} \end{bmatrix} [TxBxTyByTzBz]=ΔU1ΔV2−ΔU2ΔV11[ΔV2−ΔU2−ΔV1ΔU1][E1xE2xE1yE2yE1zE2z]
求出T三个分量即可
float f = 1.0f / (deltaUV1.x * deltaUV2.y - deltaUV2.x * deltaUV1.y);
tangent.x = f * (deltaUV2.y * edge1.x - deltaUV1.y * edge2.x);
tangent.y = f * (deltaUV2.y * edge1.y - deltaUV1.y * edge2.y);
tangent.z = f * (deltaUV2.y * edge1.z - deltaUV1.y * edge2.z);
tangent = normalize(tangent);
bitangent.x = f * (-deltaUV2.x * edge1.x + deltaUV1.x * edge2.x);
bitangent.y = f * (-deltaUV2.x * edge1.y + deltaUV1.x * edge2.y);
bitangent.z = f * (-deltaUV2.x * edge1.z + deltaUV1.x * edge2.z);
bitangent = normalize(bitangent);
左手坐标系还是右手坐标系的区别一般不用考虑。
B可以在着色器中通过法线与施密特正交化后的+T叉乘得到。
float3 B = cross(N, T);
计算出来的T将会保存作为每个顶点的属性,一个三角形上三个顶点共享一个T,但是考虑到三角形与三角形之间会共用顶点,所以可以在每个顶点的TB做平均(assimp应该可以吧)。
计算完之后,在像素着色器里通过法线纹理采样 * TBN矩阵完成法线从切线空间到世界空间的转换。
下面的代码里用了个技巧,计算都是在视图空间进行的,顶点着色器进行MV变换,可以将摄像机放到0,0点,任何坐标都是从摄像机出发指向该坐标的向量。
// PS
cbuffer LightCBuf
{
float3 lightPos;
float3 ambient;
float3 diffuseColor;
float diffuseIntensity;
float attConst;
float attLin;
float attQuad;
};
cbuffer ObjectCBuf
{
float specularIntensity;
float specularPower;
bool normalMapEnabled;
float padding[1];
};
Texture2D tex;
Texture2D nmap : register(t2);
SamplerState splr;
float4 main(float3 viewPos : Position, float3 n : Normal, float3 tan : Tangent, float3 bitan : Bitangent, float2 tc : Texcoord) : SV_Target
{
// sample normal from map if normal mapping enabled
if (normalMapEnabled)
{
// Orthogonalization
float3 T = normalize(tan - dot(tan , n) * n);
// build the tranform (rotation) into tangent space
const float3x3 tanToView = float3x3(
normalize(T),
normalize(bitan),
normalize(n)
);
// unpack the normal from map into tangent space
const float3 normalSample = nmap.Sample(splr, tc).xyz;
n = normalSample * 2.0f - 1.0f;
// bring normal from tanspace into view space
n = mul(n, tanToView);
}
// fragment to light vector data
const float3 vToL = lightPos - viewPos;
const float distToL = length(vToL);
const float3 dirToL = vToL / distToL;
// attenuation
const float att = 1.0f / (attConst + attLin * distToL + attQuad * (distToL * distToL));
// diffuse intensity
const float3 diffuse = diffuseColor * diffuseIntensity * att * max(0.0f, dot(dirToL, n));
// calculate specular intensity based on angle between viewing vector and reflection vector, narrow with power function
const float3 specular = att * (diffuseColor * diffuseIntensity) * specularIntensity * pow(max(0.0f, dot(normalize(reflect(vToL, n)), normalize(viewPos))), specularPower);
// final color
return float4(saturate((diffuse + ambient) * tex.Sample(splr, tc).rgb + specular), 1.0f);
}
//VS
cbuffer CBuf
{
matrix modelView;
matrix modelViewProj;
};
struct VSOut
{
float3 viewPos : Position;
float3 normal : Normal;
float3 tan : Tangent;
float3 bitan : Bitangent;
float2 tc : Texcoord;
float4 pos : SV_Position;
};
VSOut main(float3 pos : Position, float3 n : Normal, float3 tan : Tangent, float3 bitan : Bitangent, float2 tc : Texcoord)
{
VSOut vso;
vso.viewPos = (float3) mul(float4(pos, 1.0f), modelView);
vso.normal = mul(n, (float3x3) modelView);
vso.tan = mul(tan, (float3x3) modelView);
vso.bitan = mul(bitan, (float3x3) modelView);
vso.pos = mul(float4(pos, 1.0f), modelViewProj);
vso.tc = tc;
return vso;
}
施密特正交化

t = normalize(t - n * dot(n, t));
原理是将t减去t在n上的分量,则t可与n垂直
模型读取
用assimp
Assimp::Importer imp;
const auto pScene = imp.ReadFile(fileName.c_str(),
aiProcess_Triangulate |
aiProcess_JoinIdenticalVertices |
aiProcess_ConvertToLeftHanded |
aiProcess_GenNormals |
aiProcess_CalcTangentSpace // calculate T and B
);
然后数据就都在pScene的各个mesh里了。
效果
