Android 自定义View系列之PathMeasure+Loading效果+小车跑道移动效果
- PathMeasure详解
- 源码分析
- API说明
- 代码效果
- 正切值
- getPosTan和getMatrix实现的Loading效果
- getSegment实现的Loading效果
- 小车跑道移动效果
PathMeasure详解
源码分析
要理解一件事物,我们要观其外,也要观其内,因此我们这里先看看PathMeasure的源码,先知其然,PathMeasure源码的内容不多,只有一百多行,因此这里将其贴了出来:
package android.graphics;
public class PathMeasure {
private Path mPath;
/**
* Create an empty PathMeasure object. To uses this to measure the length
* of a path, and/or to find the position and tangent along it, call
* setPath.
*
* Note that once a path is associated with the measure object, it is
* undefined if the path is subsequently modified and the the measure object
* is used. If the path is modified, you must call setPath with the path.
*/
public PathMeasure() {
mPath = null;
native_instance = native_create(0, false);
}
/**
* Create a PathMeasure object associated with the specified path object
* (already created and specified). The measure object can now return the
* path's length, and the position and tangent of any position along the
* path.
*
* Note that once a path is associated with the measure object, it is
* undefined if the path is subsequently modified and the the measure object
* is used. If the path is modified, you must call setPath with the path.
*
* @param path The path that will be measured by this object
* @param forceClosed If true, then the path will be considered as "closed"
* even if its contour was not explicitly closed.
*/
public PathMeasure(Path path, boolean forceClosed) {
// The native implementation does not copy the path, prevent it from being GC'd
mPath = path;
native_instance = native_create(path != null ? path.readOnlyNI() : 0,
forceClosed);
}
/**
* Assign a new path, or null to have none.
*/
public void setPath(Path path, boolean forceClosed) {
mPath = path;
native_setPath(native_instance,
path != null ? path.readOnlyNI() : 0,
forceClosed);
}
/**
* Return the total length of the current contour, or 0 if no path is
* associated with this measure object.
*/
public float getLength() {
return native_getLength(native_instance);
}
/**
* Pins distance to 0 <= distance <= getLength(), and then computes the
* corresponding position and tangent. Returns false if there is no path,
* or a zero-length path was specified, in which case position and tangent
* are unchanged.
*
* @param distance The distance along the current contour to sample
* @param pos If not null, returns the sampled position (x==[0], y==[1])
* @param tan If not null, returns the sampled tangent (x==[0], y==[1])
* @return false if there was no path associated with this measure object
*/
public boolean getPosTan(float distance, float pos[], float tan[]) {
if (pos != null && pos.length < 2 ||
tan != null && tan.length < 2) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
return native_getPosTan(native_instance, distance, pos, tan);
}
public static final int POSITION_MATRIX_FLAG = 0x01; // must match flags in SkPathMeasure.h
public static final int TANGENT_MATRIX_FLAG = 0x02; // must match flags in SkPathMeasure.h
/**
* Pins distance to 0 <= distance <= getLength(), and then computes the
* corresponding matrix. Returns false if there is no path, or a zero-length
* path was specified, in which case matrix is unchanged.
*
* @param distance The distance along the associated path
* @param matrix Allocated by the caller, this is set to the transformation
* associated with the position and tangent at the specified distance
* @param flags Specified what aspects should be returned in the matrix.
*/
public boolean getMatrix(float distance, Matrix matrix, int flags) {
return native_getMatrix(native_instance, distance, matrix.native_instance, flags);
}
/**
* Given a start and stop distance, return in dst the intervening
* segment(s). If the segment is zero-length, return false, else return
* true. startD and stopD are pinned to legal values (0..getLength()).
* If startD >= stopD then return false (and leave dst untouched).
* Begin the segment with a moveTo if startWithMoveTo is true.
*
* On {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#KITKAT} and earlier
* releases, the resulting path may not display on a hardware-accelerated
* Canvas. A simple workaround is to add a single operation to this path,
* such as dst.rLineTo(0, 0).
*/
public boolean getSegment(float startD, float stopD, Path dst, boolean startWithMoveTo) {
// Skia used to enforce this as part of it's API, but has since relaxed that restriction
// so to maintain consistency in our API we enforce the preconditions here.
float length = getLength();
if (startD < 0) {
startD = 0;
}
if (stopD > length) {
stopD = length;
}
if (startD >= stopD) {
return false;
}
return native_getSegment(native_instance, startD, stopD, dst.mutateNI(), startWithMoveTo);
}
/**
* Return true if the current contour is closed()
*/
public boolean isClosed() {
return native_isClosed(native_instance);
}
/**
* Move to the next contour in the path. Return true if one exists, or
* false if we're done with the path.
*/
public boolean nextContour() {
return native_nextContour(native_instance);
}
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
native_destroy(native_instance);
native_instance = 0; // Other finalizers can still call us.
}
private static native long native_create(long native_path, boolean forceClosed);
private static native void native_setPath(long native_instance, long native_path, boolean forceClosed);
private static native float native_getLength(long native_instance);
private static native boolean native_getPosTan(long native_instance, float distance, float pos[], float tan[]);
private static native boolean native_getMatrix(long native_instance, float distance, long native_matrix, int flags);
private static native boolean native_getSegment(long native_instance, float startD, float stopD, long native_path, boolean startWithMoveTo);
private static native boolean native_isClosed(long native_instance);
private static native boolean native_nextContour(long native_instance);
private static native void native_destroy(long native_instance);
/* package */private long native_instance;
}
API说明
我们先看看构造函数1:
PathMeasure():
创建一个空的PathMeasure对象, 但是要使用它来测量路径的长度,或查找位置和切线的时候,必须要先调用setPath函数来指定一个路径,当参数path改变时,需要重新调用setPath来重新指定:
public void setPath(Path path, boolean forceClosed);构造函数2
PathMeasure(Path path, boolean forceClosed)
创建一个与指定的path对象关联的PathMeasure对象,要求path创建完毕,这时PathMeasure对象可以返回path的长度以及沿着路径的任何位置的位置和切线,当参数path改变时,需要重新调用setPath来重新指定。
第二个参数:boolean forceClosed
代表在测量的时候是否闭合,ture闭合,false不闭合。forceCloseed不会对Path本身有任何影响,只是影响PathMeasure的测量
setPath(Path path, boolean forceClosed)
设置一个path,参数与第二个构造函数相同,即
setPath(Path path, boolean forceClosed) == new PathMeasure(Path path, boolean forceClosed)
float getLength()
返回当前测量得到的轮廓的总长度,如果没有setPath(),则返回0
boolean getPosTan(float distance, float pos[], float tan[])
获取path上的点的坐标和该点的正切值
distance:即距离path起点的距离, 值为0 <= distance <= getLength()
pos[]:如果不为null,则返回点坐标(x == [0],y == [1])
tan[]:如果不为null,则返回点的正切值(x == [0],y == [1])
返回值:true表示获取成功,并将值保存到pos和tan中,false表示获取失败,pos和tan不变
boolean getMatrix(float distance, Matrix matrix, int flags)
根据flags获取对应的矩阵
distance:即距离path起点的距离, 值为0 <= distance <= getLength()
matrix:flags指定返回点坐标矩阵/点正切值矩阵
flags:PathMeasure.POSITION_MATRIX_FLAG点坐标矩阵,PathMeasure.POSITION_MATRIX_FLAG点正切值
返回值:true表示获取成功,并将值保存到matrix,false表示获取失败,matrix不变
boolean getSegment(float startD, float stopD, Path dst, boolean startWithMoveTo)
指定其实distance和结束distance,用来截取path,被截取的 Path 片段会添加到 dst 中,而不是替换 dst 中到内容。
float startD 距离path起点开始截取的距离,0 <= startD <= getLength()
float stopD 距离path起点完成截取的距离,0 <= startD < stopD <= getLength()
Path dst 截取到
boolean startWithMove 起始点是否使用moveTo的点,用来设置截取的path的第一个点位置不变
在Build.VERSION_CODES.KITKAT和更早版本上,生成的路径可能不会显示在硬件加速中canvas上。 一个简单的解决方法是向此path添加单个操作,如dst.rLineTo(0,0)。
boolean isClosed()
判断PathMeasure是否闭合
boolean nextContour()
path可由多个轮廓组成,例如通过addRect, addRoundRect, addOval, addCircle, addPath, addArc, arcTo等方法添加的矩形, 圆角矩形, 椭圆, 圆, 路径, 圆弧等轮廓,像 getLength , getgetSegment,getPosTan,getMatrix这些方法,都只是在其中一个轮廓中执行,nextContour 作用就是跳转到下一条轮廓中
如果还有下一条轮廓,返回true,否则返回false。
我们来证明一下,代码如下
//画两个矩形测试path轮廓的添加顺序对nextContour的影响
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(centerX, centerY); //移动canvas坐标系到中心点
path = new Path();
path.addRect(-100, -100, 100, 100, Path.Direction.CW); // 添加周长为800的第一个矩形
canvas.drawPath(path, paint); //先画一个矩形
path.addRect(-200, -200, 200, 200, Path.Direction.CW); // 添加周长为1600的第二个矩形
canvas.drawPath(path, paint); //再画一个矩形
canvas.restore();
//不闭合
PathMeasure pathMeasure = new PathMeasure(path, false);
//我们这里添加了两个轮廓,因此打印了两次
while(pathMeasure.nextContour()){
Log.e(TAG, "getLength: "+ pathMeasure.getLength());
}我们这里添加了两条轮廓,一条为周长为800的矩形,一条为周长为1600的矩形,我们通过while来打印所有的轮廓的长度,得出长度为:

我们看到打印的顺序为先打印第一次添加的矩形轮廓,再打印第二次添加的矩形轮廓,假如我们将添加的位置调换,看看长度打印是什么:
![]()
我们可以看到打印的值调换了,证明path添加轮廓的顺序会影响nextContour()的顺序。
可以看到PathMeasure还隐藏了身份,即内部还是调用了底层native方法来实现path的测量。
PathMeasure类源码地址
代码效果
我们接下来写代码来看看详细的接口效果,
//测试闭合/不闭合效果
canvas.save();
canvas.translate(centerX, centerY); //移动canvas坐标系到中心点
path = new Path();
path.lineTo( - 200, - 200); //画一条线
path.lineTo(-200, 200); //画第二条线
// path.close(); //代表path本身闭合
PathMeasure pathMeasure1 = new PathMeasure(path, false); //不闭合测量
PathMeasure pathMeasure2 = new PathMeasure(path, true); //闭合测量
float length1 = pathMeasure1.getLength(); //获取轮廓长度
float length2 = pathMeasure2.getLength(); //获取轮廓长度
Log.e(TAG, "pathMeasure1 length: " + length1);
Log.e(TAG, "pathMeasure2 length: " + length2);
// canvas.drawPath(path, paint); //绘制原path轮廓
//画不闭合
// for (float dis = 0; dis < length1; dis++){
// float pos[] = new float[2];
// float tan[] = new float[2];
//
// pathMeasure1.getPosTan(dis, pos, tan);
// canvas.drawPoint(pos[0], pos[1], paint);
// }
//画闭合
for (float dis = 0; dis < length2; dis++){
float pos[] = new float[2];
float tan[] = new float[2];
pathMeasure2.getPosTan(dis, pos, tan);
canvas.drawPoint(pos[0], pos[1], paint);
}
canvas.restore();
//=============================================
//=============================================我们再看看canvas.drawPath(path, paint)的效果为:
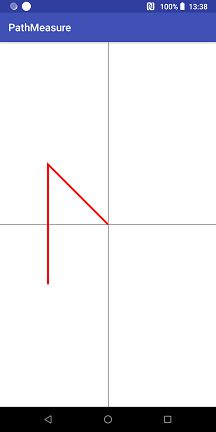
可以看到原本的轮廓闭合了,增加了一条使原本轮廓闭合的直线,并且创建PathMeasure并指定闭合的话,是不会影响path自身的,PathMeasure只是通过path来计算以获取坐标和正切值。那么这时候可能会有疑问,如果是一条直线呢,会闭合吗?答案是不会的,path和PathMeasure只会闭合可以闭合的轮廓。
我们上面通过代码
pathMeasure1.getPosTan(dis, pos, tan);
pathMeasure2.getPosTan(dis, pos, tan);再通过canvas.drawPoint()方法来进行画点。
通过上面例子我们可以知道,通过getPosTan()方法根据distance长度来获取对应长度的xy坐标并画到画布上面,我们知道pos记录了该长度的坐标,那么tan又代表什么呢?
正切值
我们先了解一下什么是切线:
几何上,切线指的是一条刚好触碰到曲线上某一点的直线。更准确地说,当切线经过曲线上的某点(即切点)时,切线的方向与曲线上该点的方向是相同的。平面几何中,将和圆只有一个公共交点的直线叫做圆的切线。
AD直径垂直于AB切线
那么我们这里的正切值是什么?
正切函数
tangent
tan
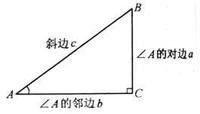
a/b
∠A的对边比邻边
在Rt△ABC(直角三角形)中,∠C=90°,AB是∠C的对边c,BC是∠A的对边a,AC是∠B的对边b,正切函数就是tanB=b/a,即tanB=AC/BC
tan[]记录的就是根据distance计算得到的点的正切值的xy值,这里的xy值可当做为对边和邻边
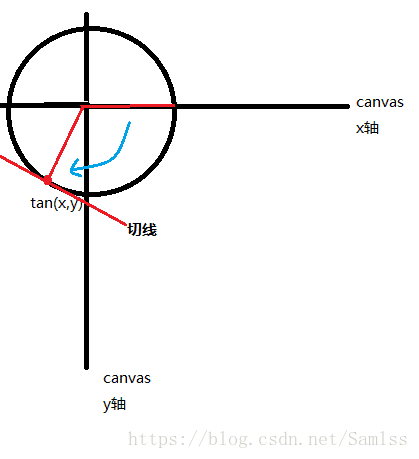
正切函数在直角三角形中,对边与邻边的比值叫做正切。放在直角坐标系中(如图)即 tanθ=y/x。
图中红色线的角度为当前角度,我们可以通过公式即反正切计算:
float degree = (float) (Math.atan2(tan[1], tan[0]) * 180 / Math.PI);来获取红色线角度。
安卓中,Math.atan2(double y, double x),代表根据y(纵坐标),x(横坐标)来获取反正切的值,Math.atan2()函数返回点(x,y)和原点(0,0)之间直线的倾斜角,不过这样我们得到的是一个弧度值,因此还需要 * 180 / Math.PI来获取最终的角度。
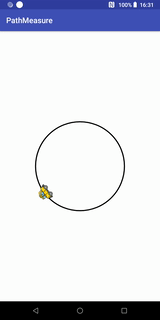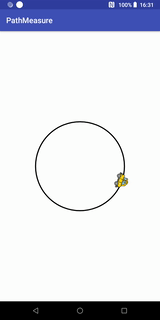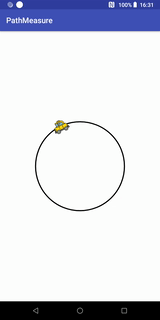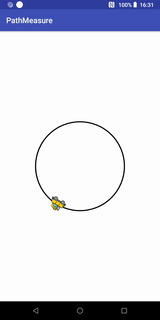
getPosTan和getMatrix实现的Loading效果
代码实现:
public class Loading1View extends View {
private final static float RADIUS = 200; //圆的半径
private final static float SPEED_RATIO = 0.006f; //控制速度
private Bitmap carBitmap;
private float[] pos = new float[2]; //记录位置
private float[] tan = new float[2]; //记录切点值xy
private Path path;
private PathMeasure pathMeasure; //路径计算
private float distanceRatio = 0;
private Paint circlePaint; //画圆圈的画笔
private Paint carPaint; //画小车的画笔
private Matrix carMatrix; //针对car bitmap图片操作的矩阵
public Loading1View(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public Loading1View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public Loading1View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init(){
carBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.icon_car);
path = new Path();
path.addCircle(0, 0, RADIUS, Path.Direction.CW);
pathMeasure = new PathMeasure(path, false);
circlePaint = new Paint();
circlePaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
circlePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
circlePaint.setAntiAlias(true);
circlePaint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
carPaint = new Paint();
carPaint.setColor(Color.DKGRAY);
carPaint.setStrokeWidth(2);
carPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
carMatrix = new Matrix();
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawColor(Color.WHITE);
int width = canvas.getWidth();
int height = canvas.getHeight();
//移动canvas坐标系到中心
canvas.translate(width / 2, height / 2);
carMatrix.reset();
distanceRatio += SPEED_RATIO;
if(distanceRatio >=1){
distanceRatio = 0;
}
float distance = pathMeasure.getLength() * distanceRatio;
{
//使用getPosTan方法
pathMeasure.getPosTan(distance, pos, tan);
float degree = (float) (Math.atan2(tan[1], tan[0]) * 180 / Math.PI); //计算小车本身要旋转的角度
carMatrix.postRotate(degree, carBitmap.getWidth() / 2, carBitmap.getHeight() / 2); //设置旋转角度和旋转中心
//这里要将设置到小车的中心点
carMatrix.postTranslate(pos[0] - carBitmap.getWidth() / 2, pos[1] - carBitmap.getHeight() / 2);
//使用getMatrix方法
//再次重新计算坐标和正切值
//该方法内部已帮我们实现实现上面的计算,包括坐标点和正切值获得的角度
// pathMeasure.getMatrix(distance, carMatrix, PathMeasure.TANGENT_MATRIX_FLAG | PathMeasure.POSITION_MATRIX_FLAG); //获取
// carMatrix.preTranslate(-carBitmap.getWidth() / 2, -carBitmap.getHeight() / 2);//这里要将设置到小车的中心点
/*
这里我们讲一下postTranslate和preTranslate的差别,
Postconcats the matrix with the specified translation. M' = T(dx, dy) * M 代表指定平移之后再进行矩阵拼接
Preconcats the matrix with the specified translation. M' = M * T(dx, dy) 代表指定平移之前就要进行矩阵拼接
我们这里,使用getPosTan方法时,调用的是postTranslate:
这是因为,在调用postRotate接口的时候,已经指定了旋转中心,然后再调用postTranslate进行平移,若调用
preTranslate的话,则会导致旋转的时候由于平移使旋转中心发生改变,导致小车旋转角度不正确。
而在调用getMatrix方法时,调用的是preTranslate,这是由于,
getMatrix将坐标和角度信息拼接到矩阵carMatrix的时候并没有指定旋转中心,因此这里需要先使用preTranslate进行移动和矩阵拼接,
然后getMatrix内部对carMatrix矩阵赋值进行角度旋转的时候会以移动后的位置为中心
*/
}
canvas.drawPath(path, circlePaint);
canvas.drawBitmap(carBitmap, carMatrix, carPaint);
invalidate();
}
}这里我们可以将getPosTan 替换为 getMatrix方法,
pathMeasure.getMatrix(distance, carMatrix, PathMeasure.TANGENT_MATRIX_FLAG | PathMeasure.POSITION_MATRIX_FLAG); //获取
carMatrix.preTranslate(-carBitmap.getWidth() / 2, -carBitmap.getHeight() / 2);//这里要将设置到小车的中心点这样就不需要我们自己去计算。
我们定义的path添加圆圈的时候,调用了如下代码:
path.addCircle(0, 0, RADIUS, Path.Direction.CW);Path.Direction.CW代表顺时针,Path.Direction.CCW代表逆时针,我们现在来看看逆时针的效果:
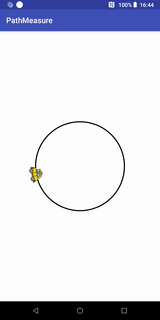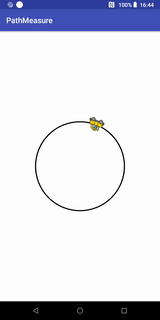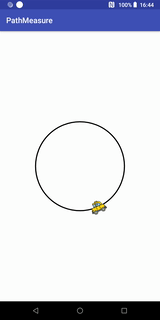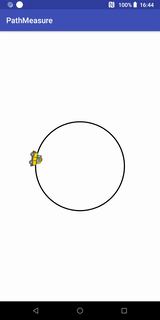
getSegment实现的Loading效果
我们这里用getSegment来实现,我们先看看他的方法
boolean getSegment(float startD, float stopD, Path dst, boolean startWithMoveTo);api说明可在上面看到,我们这里写代码来实现一下:
代码+说明:
/**
* 测试getSegment函数
*
* @param canvas 画布
* @param startWithMoveTo 起始点是否使用moveTo的点
*/
private void testGetSegment(Canvas canvas, boolean startWithMoveTo) {
Path path = new Path();
//添加一个觉醒
path.addRect(-200, -200, 200, 200, Path.Direction.CW);
Path dst = new Path();
//原本存在的轮廓
dst.lineTo(-300, -300);
// 将Path 与 PathMeasure 关联
PathMeasure measure = new PathMeasure(path, false);
// 截取一部分轮廓存入dst中,并设置moveTo保持截取得到的 Path 第一个点的位置是否不变,取决于startWithMoveTo
measure.getSegment(300, 600, dst, startWithMoveTo);
//原图画笔
Paint srcPaint = new Paint();
srcPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
srcPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
srcPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
//截取后的图的画笔
Paint dstPaint = new Paint();
dstPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
dstPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
dstPaint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
//绘制原图
canvas.drawPath(path,srcPaint);
// 绘制 dst
canvas.drawPath(dst, dstPaint);
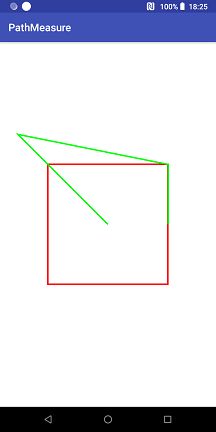
}我们来看看testGetSegment(canvas, true)和testGetSegment(canvas, false)的效果分别是怎样的,
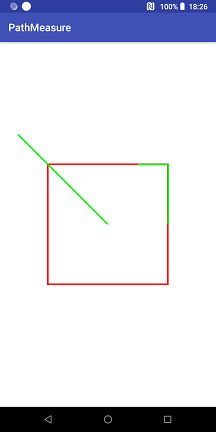
可见被截取的 Path 片段会添加到 dst 中,而不是替换 dst 中到内容。
因此我们可以知道当startWithMoveTo的值为:
true 使截取的内容不会改变
false 使截取的内容和原本的内容连接起来。
接下来我们用getSegment接口来实现一个Loading动画:
代码+说明:
public class Loading2View extends View {
private final static float RADIUS = 150; //圆的半径
private Path path;
private PathMeasure pathMeasure; //路径计算
private Paint paint; //画笔
private float pathDistanceRatio; //路径长度的比值 (0 - 1)
public Loading2View(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public Loading2View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public Loading2View(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init(){
path = new Path();
path.addCircle(0, 0, RADIUS, Path.Direction.CW);
pathMeasure = new PathMeasure(path, false);
paint = new Paint();
paint.setStrokeWidth(10);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
paint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
//计算比例的动画
ValueAnimator ratioAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(0, 1);
ratioAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator valueAnimator) {
pathDistanceRatio = (float) valueAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
invalidate();
}
});
ratioAnimator.setDuration(1500);
ratioAnimator.setRepeatMode(ValueAnimator.RESTART);
ratioAnimator.setRepeatCount(ValueAnimator.INFINITE);
ratioAnimator.setInterpolator(new DecelerateInterpolator());
ratioAnimator.start();
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawColor(Color.WHITE);
int width = canvas.getWidth();
int height = canvas.getHeight();
canvas.translate(width / 2, height / 2); //移动canvas坐标系到中心点
float stopD = pathMeasure.getLength() * pathDistanceRatio; //当前截取的结束点
float startD = (float) (stopD - ((0.5 - Math.abs(pathDistanceRatio - 0.5)) * pathMeasure.getLength())); //当前截取的开始点
Path dst = new Path();
dst.moveTo(RADIUS, 0); //移动起始点
pathMeasure.getSegment(startD, stopD, dst, true);
canvas.drawPath(dst, paint);
// testGetSegment(canvas, true);
}
/**
* 测试getSegment函数
*
* @param canvas 画布
* @param startWithMoveTo 起始点是否使用moveTo的点
*/
private void testGetSegment(Canvas canvas, boolean startWithMoveTo) {
Path path = new Path();
//添加一个觉醒
path.addRect(-200, -200, 200, 200, Path.Direction.CW);
Path dst = new Path();
//原本存在的轮廓
dst.lineTo(-300, -300);
// 将Path 与 PathMeasure 关联
PathMeasure measure = new PathMeasure(path, false);
// 截取一部分轮廓存入dst中,并设置moveTo保持截取得到的 Path 第一个点的位置是否不变,取决于startWithMoveTo
measure.getSegment(300, 600, dst, startWithMoveTo);
//原图画笔
Paint srcPaint = new Paint();
srcPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
srcPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
srcPaint.setColor(Color.RED);
//截取后的图的画笔
Paint dstPaint = new Paint();
dstPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
dstPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
dstPaint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
//绘制原图
canvas.drawPath(path,srcPaint);
// 绘制 dst
canvas.drawPath(dst, dstPaint);
}
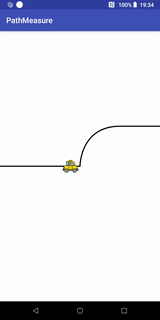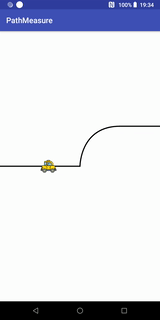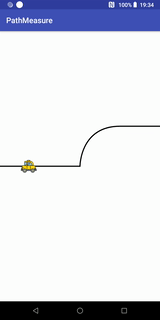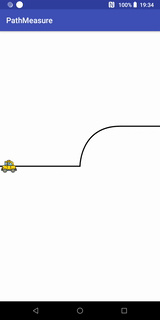
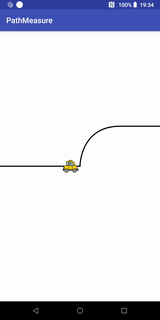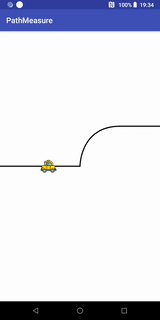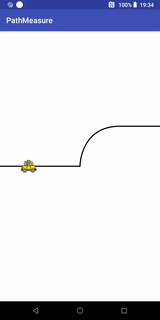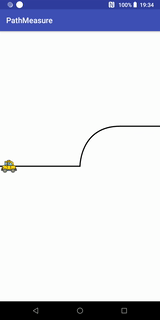
}小车跑道移动效果
代码+说明
public class CarTrackView extends View {
private static final String TAG = "CarTrackView";
private final static float SPEED_RATIO = 0.006f; //控制速度
private Bitmap carBitmap; //小车bitmap
private Paint contourPaint; //轮廓画笔
private float distanceRatio = 0; //距离比例
private Paint carPaint; //画小车的画笔
public CarTrackView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public CarTrackView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
public CarTrackView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
init();
}
private void init(){
carBitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(), R.mipmap.icon_car);
contourPaint = new Paint();
contourPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
contourPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
contourPaint.setStrokeWidth(5);
carPaint = new Paint(Paint.ANTI_ALIAS_FLAG);
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
canvas.drawColor(Color.WHITE);
int width = canvas.getWidth();
int height = canvas.getHeight();
canvas.translate(width / 2, height / 2); //移动canvas坐标系
Path path = new Path(); //第一段为直线,第二段为曲线,第三段为直线
path.moveTo(- width / 2, 0);
path.lineTo(0, 0);
path.cubicTo(0, 0, 0, -width / 2 / 2, width / 2 / 2, -width / 2 / 2); //画条三阶贝塞尔曲线
path.lineTo(width / 2, -width / 2 / 2);
distanceRatio += SPEED_RATIO;
if(distanceRatio >=1){
distanceRatio = 0;
}
PathMeasure pathMeasure = new PathMeasure(path, false);
float distance = pathMeasure.getLength() * distanceRatio;
Matrix carMatrix = new Matrix();
pathMeasure.getMatrix(distance, carMatrix, PathMeasure.TANGENT_MATRIX_FLAG | PathMeasure.POSITION_MATRIX_FLAG); //获取距离的坐标和旋转角度
carMatrix.preTranslate(-carBitmap.getWidth() / 2, -carBitmap.getHeight() / 2);//这里要将设置到小车的中心点
canvas.drawPath(path, contourPaint); //先画轨迹
canvas.drawBitmap(carBitmap, carMatrix, carPaint);
invalidate();
}
}Demo地址:https://github.com/samlss/PathMeasure
个人github总结:https://github.com/samlss/AsAndroidDevelop