C# 特性的基本用法
目录
前言
一.预定义的保留特性
1.Obsolete特性
2.Conditional特性
3.CallerFilePath、CallerLineNumber、CallerMemberName
4.DebuggerStepThough
4.其它预定义特性
二.自定义特性
三.访问特性
前言
特性是一种允许我们向程序的程序集增加元数据的语言结构,它用于保存程序结构信息的某种特殊类型的类。简单的说,特性主要是结合反射来获得程序的某些信息,在一般情况下其实没什么卵用。
特性的使用形式如下:
[Serializable] //特性
public class Myclass
{
...
}
[MyAttribute("Simple class","Version 3.57")] //带有参数的特性
public class MyOtherClass
{
...
}一.预定义的保留特性
1.Obsolete特性
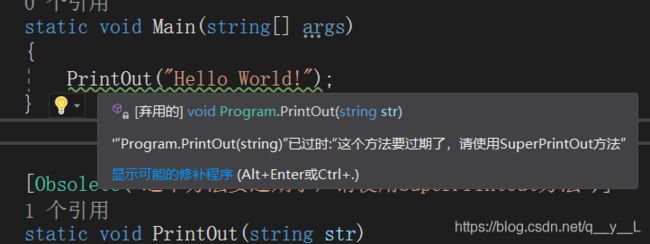
Obsolete特性将程序结构标注为过期的,但是标注的程序依然可以使用,只是用于警告用户尽量使用新的方法。
using System;
namespace AttributeTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
PrintOut("Hello World!");
}
[Obsolete("这个方法要过期了,请使用SuperPrintOut方法")]
static void PrintOut(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
static void SuperPrintOut(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str ?? "这是一个空字符串!");
}
}
}
在Vs中 被[Obsolete]修饰的方法还会给出提示:
在编译的时候也会给出类似的警告。
2.Conditional特性
Conditional特性类似于条件调用,如果熟悉#if、#endif的话,应该还是很好理解的。不同的是Conditional是对方法本省的修饰,而#if、#endif则是对调用的修饰。看下面的例子:
#define SABER
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace AttributeTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
#if TEST
PrintOut("Hello World!");
#endif
SuperPrintOut(null);
}
[Obsolete("这个方法要过期了,请使用SuperPrintOut方法")]
static void PrintOut(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str);
}
[Conditional("SABER")]
static void SuperPrintOut(string str)
{
Console.WriteLine(str ?? "这是一个空字符串!");
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
由于我没有预先定义TEST 字符串,因此PrintOut函数不会执行,并且在VS编辑器中
PrintOut("Hello World!"); //实际显示为灰色显示为灰色,很明显的告诉我们这一行不执行。而我定义了SABER,因此会执行SuperPrintOut函数。
加入你把SABER的定义去掉,在Main函数中不会有任何变化,但是运行结果不会再出现上面的那行字符串。
因为[Conditional]主要对方法进行修饰,因此要对方法进行条件调用的时候,建议用[Conditional]修饰而不是#if。且Conditional只能修饰返回值为Void类型的方法。
3.CallerFilePath、CallerLineNumber、CallerMemberName
这三个特性只能用于方法中的可选参数,分别提醒文件路径、代码所在行数、调用成员名称信息。具体的使用方法请参见我之前的博客:C# CallerMemberName特性介绍以及简化InotifyPropertyChanged的实现。
4.DebuggerStepThough
如果你很确定你的某段代码是正确的,在调试是,对其反复单步调试只会徒增时间,那么你可以使用这个特性。该特性是的在单步调试时,不要进入某些方法。
class SimpleA
{
int _x = 1;
int X
{
get => _x;
[DebuggerStepThrough] //不进入set访问器
set
{
_x = _x * 2;
_x += value;
}
}
public int Y { get; set; }
[DebuggerStepThrough] //不进入这个方法
void IncrementFields()
{
X++;
Y++;
}
}4.其它预定义特性
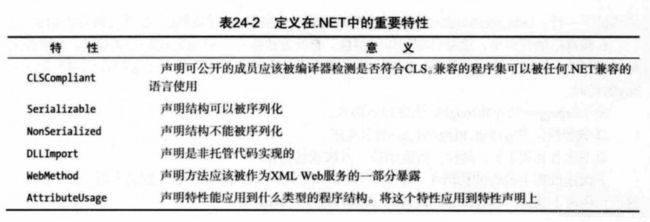
.Net框架预定义了很多编译器和CLR能理解和解释的特性,下面给出了一些重要的特性:
一直字段也可以同事被应用多个特性,下面这两种特性使用时等价的:
二.自定义特性
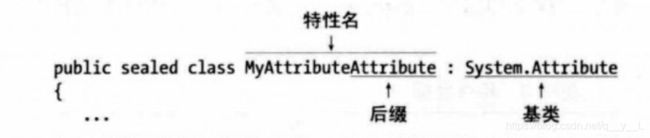
其实特性只是某个特殊类型的类。要申明一个自定义特性需要:
-
声明一个派生自System.Attribute的类
-
给它取一个以后缀Attribute结尾的名字
下面时一个特性的声明和使用:
[MyAttribyte("An simple class",reviewe:"QYL",ver:"2.0")]
class SimpleA
{
int _x = 1;
int X
{
get => _x;
[DebuggerStepThrough] //不进入set访问器
set
{
_x = _x * 2;
_x += value;
}
}
public int Y { get; set; }
[DebuggerStepThrough] //不进入这个方法
void IncrementFields()
{
X++;
Y++;
}
}
public sealed class MyAttribyteAttribute:System.Attribute
{
public string Description;
public string Version;
public string Reviewer;
public MyAttribyteAttribute(string desc)
{
Description = desc;
}
public MyAttribyteAttribute(string desc,string ver,string reviewe)
{
Description = desc;
Reviewer = reviewe;
Version = ver;
}
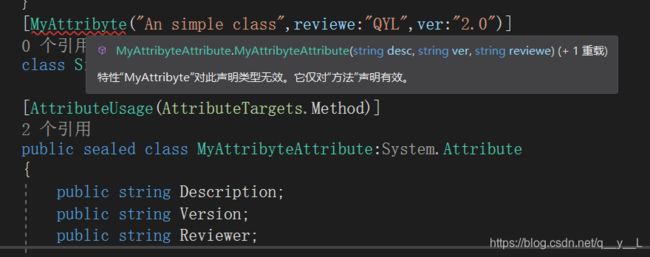
}可以使用AttributeUsage特性来限制自定义特性只能使用在某些目标上,例如一旦限制特性使用在方法上,就不能像上面那样修饰类:
AttributeUsage有三个重要的公共属性:
下面这个特性表示:MyAttribute只能用于类上、MyAttribute不会应用到它的派生类上、不能有MyAttibute的多个实例应用到同一个目标上。
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class, //必须的,位置参数
Inherited =false, //可选的,命名参数)]
AllowMultiple =false)] //可选的,命名参数三.访问特性
我们可以使用Type对象来获取类型信息,对于特性,Type也有2个重要的方法:IsDefined和GetCustomeAttributes。
IsDefined方法用来检测某个特性是否应用到了某个类上。
#define SABER
using System;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace AttributeTest
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
SimpleA simpleA = new SimpleA();
Type t = simpleA.GetType(); //从实例中获取类型对象
bool isDefined = t.IsDefined(typeof(MyAttribyteAttribute), false);
if (isDefined)
Console.WriteLine($"MyAttribute is applied to type {t.Name}");
#if TEST
PrintOut("Hello World!");
#endif
SuperPrintOut(null);
}
}
class SimpleA
{
int _x = 1;
int X
{
get => _x;
[DebuggerStepThrough] //不进入set访问器
set
{
_x = _x * 2;
_x += value;
}
}
public int Y { get; set; }
[DebuggerStepThrough] //不进入这个方法
void IncrementFields()
{
X++;
Y++;
}
}
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Class, //必须的,位置参数
Inherited =false, //可选的,命名参数)]
AllowMultiple =false)] //可选的,命名参数
public sealed class MyAttribyteAttribute:System.Attribute
{
public string Description;
public string Version;
public string Reviewer;
public MyAttribyteAttribute(string desc)
{
Description = desc;
}
public MyAttribyteAttribute(string desc,string ver,string reviewe)
{
Description = desc;
Reviewer = reviewe;
Version = ver;
}
}
}输出:MyAttribute is applied to type SimpleA
GetCustomeAttributes方法返回应用到结构的数组。实际返回的对象是object的数组,因此我们必须将他强制转换为相应的特性类型。布尔参数指定是否继续搜索继承树来查找特性。调用该方法后,每一个与目标相关联的特性的实例都会被创建
object[] attrs=t.GetCustomedAttributes(false)对Main函数作修改,使用GetCustomedAttributes函数的示例:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
SimpleA simpleA = new SimpleA();
Type t = simpleA.GetType(); //从实例中获取类型对象
bool isDefined = t.IsDefined(typeof(MyAttributeAttribute), false);
//if (isDefined)
// Console.WriteLine($"MyAttribute is applied to type {t.Name}");
object[] attrs = t.GetCustomAttributes(false);
foreach(var a in attrs)
{
if (a is MyAttributeAttribute myAttribyteAttribute)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Description: {myAttribyteAttribute.Description}");
Console.WriteLine($"Version number: {myAttribyteAttribute.Version}");
Console.WriteLine($"Reviewer ID: {myAttribyteAttribute.Reviewer}");
}
}
#if TEST
PrintOut("Hello World!");
#endif
SuperPrintOut(null);
}运行结果:
Description: An simple class
Version number: 2.0
Reviewer ID: QYL
这是一个空字符串!