Picasso源码分析
Picasso源码分析
1.使用方法
Picasso的主要使用方法如下
//加载一张图片
Picasso.with(this).load("url").placeholder(R.mipmap.ic_default).into(imageView);
//加载一张图片并设置一个回调接口
Picasso.with(this).load("url").placeholder(R.mipmap.ic_default).into(imageView, new Callback() {
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
}
@Override
public void onError() {
}
});当然,你还可以对加载的图片进行简单处理,如旋转、缩放、圆角等等
//加载一张图片并按照指定尺寸以centerCrop()的形式缩放.
Picasso.with(this).load("url").resize(200,200).centerCrop().into(imageView);
//加载一张图片旋转并且添加一个Transformation,可以对图片进行各种变化处理,例如圆形头像.
Picasso.with(this).load("url").rotate(10).transform(new Transformation() {
@Override
public Bitmap transform(Bitmap source) {
//处理Bitmap
return null;
}
@Override
public String key() {
return null;
}
}).into(imageView);3.类图关系
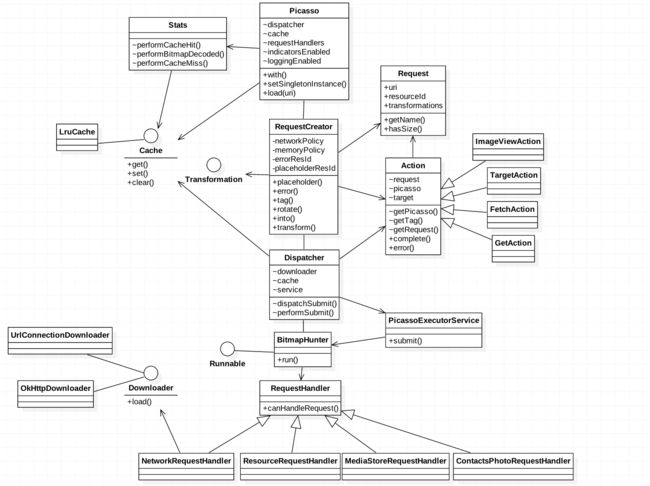
这里借用上网找的一张图片
可以看出,其核心类包括有
Picasso、
Dispatcher、
BitmapHunter、
RequestHandler、
Request、
Action、
Cache等等。
其中Picasso类是一个负责图片下载、处理、缓存的管理器,当我们给它一个图片下载请求的时候,它就会创建一个Request并提交给Dispatcher,Dispatcher会寻找对应的处理器RequestHandler,并将请求与该处理器一起提交给线程池执行,图片下载成功后,最终会交给PicassoDrawable显示在imageView上。
它将一张图片的加载过程分为八步,依次为:
创建->入队->执行->解码->变换->批处理->完成->分发->显示。
4.源码分析
4.1初始化Picasso类
Picasso是整个图片加载器的入口,负责初始化各个模块和相关参数,
Picasso.with()方法用于创建全局唯一的Picasso实例,使用了单例模式,源码如下:
public static Picasso with(Context context) {
if (singleton == null) {
synchronized (Picasso.class) {
if (singleton == null) {
singleton = new Builder(context).build();
}
}
}
return singleton;
}
Picasso#Builder#builder():
public Picasso build() {
Context context = this.context;
//初始化下载器
if (downloader == null) {
downloader = Utils.createDefaultDownloader(context);
}
//初始化缓存类
if (cache == null) {
cache = new LruCache(context);
}
//初始化服务类
if (service == null) {
service = new PicassoExecutorService();
}
//初始化转换处理类
if (transformer == null) {
transformer = RequestTransformer.IDENTITY;
}
//创建Stats,用于统计各类信息,如缓存命中率,下载数量等等
Stats stats = new Stats(cache);
//创建Dispatcher对象,用于调度任务
Dispatcher dispatcher = new Dispatcher(context, service, HANDLER, downloader, cache, stats);
return new Picasso(context, dispatcher, cache, listener, transformer, requestHandlers, stats,
defaultBitmapConfig, indicatorsEnabled, loggingEnabled);
}在Picasso()中,还做了一件非常重要的初始化工作,那就是初始化requestHandlers,部分代码如下:
List allRequestHandlers =
new ArrayList(builtInHandlers + extraCount);
// ResourceRequestHandler needs to be the first in the list to avoid
// forcing other RequestHandlers to perform null checks on request.uri
// to cover the (request.resourceId != 0) case.
allRequestHandlers.add(new ResourceRequestHandler(context));
if (extraRequestHandlers != null) {
allRequestHandlers.addAll(extraRequestHandlers);
}
allRequestHandlers.add(new ContactsPhotoRequestHandler(context));
allRequestHandlers.add(new MediaStoreRequestHandler(context));
allRequestHandlers.add(new ContentStreamRequestHandler(context));
allRequestHandlers.add(new AssetRequestHandler(context));
allRequestHandlers.add(new FileRequestHandler(context));
allRequestHandlers.add(new NetworkRequestHandler(dispatcher.downloader, stats));
requestHandlers = Collections.unmodifiableList(allRequestHandlers); 这里创建了8个用于处理不同加载来源的requestHandler,并且全部放在同一个ArrayList中,使用了 责任链模式,这部分等下面用到再说。
4.2 传入图片地址
Picasso#load():该方法返回一个RequestCreator
public RequestCreator load(Uri uri) {
return new RequestCreator(this, uri, 0);
}RequestCreator(Picasso picasso, Uri uri, int resourceId) {
if (picasso.shutdown) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Picasso instance already shut down. Cannot submit new requests.");
}
this.picasso = picasso;
this.data = new Request.Builder(uri, resourceId, picasso.defaultBitmapConfig);
}先是持有一个picasso对象,
再是构建一个Request的Builder对象,将我们先前配置的信息picasso.defaultBitmapConfig一同传进去,保存在data中。也就是说我们使用.resize()和.centerCrop()等方法的时候,实际上是在改变data的对应变量标识,在真正的处理阶段再根据这些变量标识再进行相应的处理。真正的处理操作都是由.into()方法引起的。
4.3 真正的下载操作:
RequestCreator#into():
public void into(ImageView target) {
into(target, null);
}
public void into(ImageView target, Callback callback) {
long started = System.nanoTime();
checkMain();
if (target == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Target must not be null.");
}
if (!data.hasImage()) {
picasso.cancelRequest(target);
if (setPlaceholder) {
setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
return;
}
if (deferred) {
if (data.hasSize()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Fit cannot be used with resize.");
}
int width = target.getWidth();
int height = target.getHeight();
if (width == 0 || height == 0) {
if (setPlaceholder) {
setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
picasso.defer(target, new DeferredRequestCreator(this, target, callback));
return;
}
data.resize(width, height);
}
Request request = createRequest(started);
String requestKey = createKey(request);
if (shouldReadFromMemoryCache(memoryPolicy)) {
Bitmap bitmap = picasso.quickMemoryCacheCheck(requestKey);
if (bitmap != null) {
picasso.cancelRequest(target);
setBitmap(target, picasso.context, bitmap, MEMORY, noFade, picasso.indicatorsEnabled);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_MAIN, VERB_COMPLETED, request.plainId(), "from " + MEMORY);
}
if (callback != null) {
callback.onSuccess();
}
return;
}
}
if (setPlaceholder) {
setPlaceholder(target, getPlaceholderDrawable());
}
Action action =
new ImageViewAction(picasso, target, request, memoryPolicy, networkPolicy, errorResId,
errorDrawable, requestKey, tag, callback, noFade);
picasso.enqueueAndSubmit(action);
}在开始的时候,先判断能否直接在缓存中读取,如果可以,
则取消target的request
picasso.cancelRequest(target);
设置位图后执行回调 callback.onSuccess()
如果没在缓存中读到,就构建一个Action对象,这里构建一个ImageViewAction对象,并且通过picasso将Action对象提交入列。
我们再进一步查看picasso.enqueueAndSubmit(action) 方法:
void enqueueAndSubmit(Action action) {
Object target = action.getTarget();
if (target != null && targetToAction.get(target) != action) {
// This will also check we are on the main thread.
cancelExistingRequest(target);
targetToAction.put(target, action);
}
submit(action);
}
void submit(Action action) {
dispatcher.dispatchSubmit(action);
}void dispatchSubmit(Action action) {
handler.sendMessage(handler.obtainMessage(REQUEST_SUBMIT, action));
}dispatcher.performSubmit(action);void performSubmit(Action action) {
performSubmit(action, true);
}
void performSubmit(Action action, boolean dismissFailed) {
if (pausedTags.contains(action.getTag())) {//检查该tag的请求是否被暂停
pausedActions.put(action.getTarget(), action);
if (action.getPicasso().loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_DISPATCHER, VERB_PAUSED, action.request.logId(),
"because tag '" + action.getTag() + "' is paused");
}
return;
}
BitmapHunter hunter = hunterMap.get(action.getKey());//通过action的key查询hunterMap中是否用相同的hunter
if (hunter != null) {
hunter.attach(action);//如果有就将这些action合并到一个BitmapHunter中
return;
}
if (service.isShutdown()) {
if (action.getPicasso().loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_DISPATCHER, VERB_IGNORED, action.request.logId(), "because shut down");
}
return;
}
hunter = forRequest(action.getPicasso(), this, cache, stats, action);//创建BitmapHunter对象
hunter.future = service.submit(hunter);//通过service执行hunter并返回一个future对象
hunterMap.put(action.getKey(), hunter);//将hunter添加到hunterMap中
if (dismissFailed) {
failedActions.remove(action.getTarget());
}
if (action.getPicasso().loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_DISPATCHER, VERB_ENQUEUED, action.request.logId());
}
}其中forRequest()值得注意的是这里体现了责任链模式,先看看源码:
static BitmapHunter forRequest(Picasso picasso, Dispatcher dispatcher, Cache cache, Stats stats,
Action action) {
Request request = action.getRequest();
List requestHandlers = picasso.getRequestHandlers();
// Index-based loop to avoid allocating an iterator.
//noinspection ForLoopReplaceableByForEach
for (int i = 0, count = requestHandlers.size(); i < count; i++) {
RequestHandler requestHandler = requestHandlers.get(i);
if (requestHandler.canHandleRequest(request)) {
return new BitmapHunter(picasso, dispatcher, cache, stats, action, requestHandler);
}
}
return new BitmapHunter(picasso, dispatcher, cache, stats, action, ERRORING_HANDLER);
} 这里依次调用requestHandlers里requestHandler的canHandler()方法,直至找到能执行request的requestHandler,然后就创建BitmapHunter对象并返回hunter。再通过service.submit(hunter)执行hunter,因为hunter实现了Runnable接口,所以run()方法会被执行。
继续看BitmapHunter里的run()方法。
BitmapHunter#run():
@Override public void run() {
try {
updateThreadName(data);//更新当前线程的名字
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_EXECUTING, getLogIdsForHunter(this));
}
//调用hunt()方法并返回Bitmap类型的result对象
result = hunt();
if (result == null) {
dispatcher.dispatchFailed(this);//调用dispatcher发送失败的消息
} else {
dispatcher.dispatchComplete(this);//调用dispatcher发送完成的消息
}
} catch (Downloader.ResponseException e) {//各类异常的处理
if (!e.localCacheOnly || e.responseCode != 504) {
exception = e;
}
dispatcher.dispatchFailed(this);
} catch (NetworkRequestHandler.ContentLengthException e) {
exception = e;
dispatcher.dispatchRetry(this);
} catch (IOException e) {
exception = e;
dispatcher.dispatchRetry(this);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
stats.createSnapshot().dump(new PrintWriter(writer));
exception = new RuntimeException(writer.toString(), e);
dispatcher.dispatchFailed(this);
} catch (Exception e) {
exception = e;
dispatcher.dispatchFailed(this);
} finally {
Thread.currentThread().setName(Utils.THREAD_IDLE_NAME);
}
}
Bitmap hunt() throws IOException {//读取图片
Bitmap bitmap = null;
if (shouldReadFromMemoryCache(memoryPolicy)) {//从内存中读取
bitmap = cache.get(key);
if (bitmap != null) {
stats.dispatchCacheHit();//统计缓存命中率
loadedFrom = MEMORY;
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_DECODED, data.logId(), "from cache");
}
return bitmap;
}
}
data.networkPolicy = retryCount == 0 ? NetworkPolicy.OFFLINE.index : networkPolicy; //通过对应的RequestHandler来获取result
RequestHandler.Result result = requestHandler.load(data, networkPolicy);//使用网络加载策略
if (result != null) {
loadedFrom = result.getLoadedFrom();
exifRotation = result.getExifOrientation();
bitmap = result.getBitmap();
// If there was no Bitmap then we need to decode it from the stream.
if (bitmap == null) {
InputStream is = result.getStream();
try {
bitmap = decodeStream(is, data);
} finally {
Utils.closeQuietly(is);
}
}
}
if (bitmap != null) {
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_DECODED, data.logId());
}
stats.dispatchBitmapDecoded(bitmap);//对bitmap进行解码
if (data.needsTransformation() || exifRotation != 0) {//检查图片是否需要transformation
synchronized (DECODE_LOCK) {//全局锁,保证同一时刻仅有一个图片正在处理
if (data.needsMatrixTransform() || exifRotation != 0) {
bitmap = transformResult(data, bitmap, exifRotation);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_TRANSFORMED, data.logId());
}
}
if (data.hasCustomTransformations()) {
bitmap = applyCustomTransformations(data.transformations, bitmap);
if (picasso.loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_HUNTER, VERB_TRANSFORMED, data.logId(), "from custom transformations");
}
}
}
if (bitmap != null) {
stats.dispatchBitmapTransformed(bitmap);
}
}
}
return bitmap;
}在run()方法中通过hunt()方法获取result,再通过dispatcher处理结果和相应的异常。
在hunt()方法中先判断能否从内存中获取,可以则记录缓存命中率并直接返回bitmap;否则就通过对应的RequestHandler获取相应的result,这里是从网络加载图片,自然使用网络加载策略 networkPolicy 来加载,获取result后再取出result中的bitmap,然后检测是否需要transform等操作,这里使用了一个全局锁 DECODE_LOCKM,以保证同一时间只有一个图片被处理,最后返回bitmap。
正确返回后,会调用 dispatcher.dispatchComplete(this) 方法,最后通过 handler 调用dispatcher.performComplete() 方法:
void performComplete(BitmapHunter hunter) {
if (shouldWriteToMemoryCache(hunter.getMemoryPolicy())) {
cache.set(hunter.getKey(), hunter.getResult());//写入缓存
}
hunterMap.remove(hunter.getKey());//从hunterMap中移除
batch(hunter);
if (hunter.getPicasso().loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_DISPATCHER, VERB_BATCHED, getLogIdsForHunter(hunter), "for completion");
}
}这里先判断是否写入内存缓存,再将hunter从hunterMap中移除,最后执行 batch(hunter) ,发出一个 HUNTER_DELAY_NEXT_BATCH的消息
private void batch(BitmapHunter hunter) {
if (hunter.isCancelled()) {
return;
}
batch.add(hunter);
if (!handler.hasMessages(HUNTER_DELAY_NEXT_BATCH)) {
handler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(HUNTER_DELAY_NEXT_BATCH, BATCH_DELAY);
}
}HUNTER_DELAY_NEXT_BATCH的消息触发 performBatchComplete() 方法:
void performBatchComplete() {
List copy = new ArrayList(batch);
batch.clear();
mainThreadHandler.sendMessage(mainThreadHandler.obtainMessage(HUNTER_BATCH_COMPLETE, copy));
logBatch(copy);
}
看看mainThreadHandler中的内容:
static final Handler HANDLER = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()) {
@Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
switch (msg.what) {
case HUNTER_BATCH_COMPLETE: {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked") List batch = (List) msg.obj;
//noinspection ForLoopReplaceableByForEach
for (int i = 0, n = batch.size(); i < n; i++) {
BitmapHunter hunter = batch.get(i);
hunter.picasso.complete(hunter);//依次调用 picasso.complete(hunter) 方法
}
break;
default:
throw new AssertionError("Unknown handler message received: " + msg.what);
}
}
}; Picasso#complete()&deliverAction():
void complete(BitmapHunter hunter) {
Action single = hunter.getAction();
List joined = hunter.getActions();
boolean hasMultiple = joined != null && !joined.isEmpty();
boolean shouldDeliver = single != null || hasMultiple;
if (!shouldDeliver) {
return;
}
Uri uri = hunter.getData().uri;
Exception exception = hunter.getException();
Bitmap result = hunter.getResult();
LoadedFrom from = hunter.getLoadedFrom();
if (single != null) {
deliverAction(result, from, single);
}
if (hasMultiple) {
//noinspection ForLoopReplaceableByForEach
for (int i = 0, n = joined.size(); i < n; i++) {
Action join = joined.get(i);
deliverAction(result, from, join);
}
}
if (listener != null && exception != null) {
listener.onImageLoadFailed(this, uri, exception);
}
}
private void deliverAction(Bitmap result, LoadedFrom from, Action action) {
if (action.isCancelled()) {
return;
}
if (!action.willReplay()) {
targetToAction.remove(action.getTarget());
}
if (result != null) {
if (from == null) {
throw new AssertionError("LoadedFrom cannot be null.");
}
action.complete(result, from);
if (loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_MAIN, VERB_COMPLETED, action.request.logId(), "from " + from);
}
} else {
action.error();
if (loggingEnabled) {
log(OWNER_MAIN, VERB_ERRORED, action.request.logId());
}
}
}
如果处理正确,则进入deliverAction中调用action.complete()方法,因为在最初的时候我们的Action为ImageViewAction,看看ImageViewAction的complete()实现:
@Override public void complete(Bitmap result, Picasso.LoadedFrom from) {
if (result == null) {
throw new AssertionError(
String.format("Attempted to complete action with no result!\n%s", this));
}
ImageView target = this.target.get();
if (target == null) {
return;
}
Context context = picasso.context;
boolean indicatorsEnabled = picasso.indicatorsEnabled;
PicassoDrawable.setBitmap(target, context, result, from, noFade, indicatorsEnabled);
if (callback != null) {
callback.onSuccess();
}
}
至此,Picasso的调用流程的源码分析就结束了,耶✌️✌️~~