(两百三十三)android Q Stack源码学习
前言:leetcode stack相关的简单题刷了第一遍,感觉还是挺简单的,学习一下stack 的jdk源码,加深下理解。
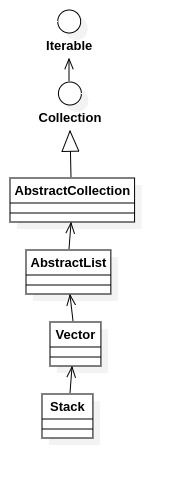
1.继承关系
class Stack extends Vector {
public class Vector
extends AbstractList
implements List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
public abstract class AbstractList extends AbstractCollection implements List {
public abstract class AbstractCollection implements Collection {
public interface Collection extends Iterable {
public interface Iterable {
画了个示意图
2.构造函数
/**
* Creates an empty Stack.
*/
public Stack() {
}构造函数啥都没有
3.push
/**
* Pushes an item onto the top of this stack. This has exactly
* the same effect as:
*
* addElement(item)
*
* @param item the item to be pushed onto this stack.
* @return the item argument.
* @see java.util.Vector#addElement
*/
public E push(E item) {
addElement(item);
return item;
}addElement是继承的vector的方法
/**
* Adds the specified component to the end of this vector,
* increasing its size by one. The capacity of this vector is
* increased if its size becomes greater than its capacity.
*
* This method is identical in functionality to the
* {@link #add(Object) add(E)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface).
*
* @param obj the component to be added
*/
public synchronized void addElement(E obj) {
modCount++;
ensureCapacityHelper(elementCount + 1);
elementData[elementCount++] = obj;
}
然后看下扩容函数
/**
* This implements the unsynchronized semantics of ensureCapacity.
* Synchronized methods in this class can internally call this
* method for ensuring capacity without incurring the cost of an
* extra synchronization.
*
* @see #ensureCapacity(int)
*/
private void ensureCapacityHelper(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?
capacityIncrement : oldCapacity);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}都是翻倍长的
4.peek
/**
* Looks at the object at the top of this stack without removing it
* from the stack.
*
* @return the object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the Vector object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E peek() {
int len = size();
if (len == 0)
throw new EmptyStackException();
return elementAt(len - 1);
}
/**
* Returns the component at the specified index.
*
* This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #get(int)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface).
*
* @param index an index into this vector
* @return the component at the specified index
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized E elementAt(int index) {
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " + elementCount);
}
return elementData(index);
}
其实就是获取列表最后一个元素并返回
5. pop
/**
* Removes the object at the top of this stack and returns that
* object as the value of this function.
*
* @return The object at the top of this stack (the last item
* of the Vector object).
* @throws EmptyStackException if this stack is empty.
*/
public synchronized E pop() {
E obj;
int len = size();
obj = peek();
removeElementAt(len - 1);
return obj;
}看下如何将数组最后一个元素移除的
/**
* Deletes the component at the specified index. Each component in
* this vector with an index greater or equal to the specified
* {@code index} is shifted downward to have an index one
* smaller than the value it had previously. The size of this vector
* is decreased by {@code 1}.
*
* The index must be a value greater than or equal to {@code 0}
* and less than the current size of the vector.
*
*
This method is identical in functionality to the {@link #remove(int)}
* method (which is part of the {@link List} interface). Note that the
* {@code remove} method returns the old value that was stored at the
* specified position.
*
* @param index the index of the object to remove
* @throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException if the index is out of range
* ({@code index < 0 || index >= size()})
*/
public synchronized void removeElementAt(int index) {
modCount++;
if (index >= elementCount) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index + " >= " +
elementCount);
}
else if (index < 0) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
int j = elementCount - index - 1;
if (j > 0) {
System.arraycopy(elementData, index + 1, elementData, index, j);
}
elementCount--;
elementData[elementCount] = null; /* to let gc do its work */
}
如果是移除最后一个,其实就是成员数量减1,末尾置空
6.empty
/**
* Tests if this stack is empty.
*
* @return true if and only if this stack contains
* no items; false otherwise.
*/
public boolean empty() {
return size() == 0;
}
/**
* Returns the number of components in this vector.
*
* @return the number of components in this vector
*/
public synchronized int size() {
return elementCount;
}
7.总结
其实数据结构很简单,我一直以为是个链表呢,其实还是个数组,只是push的时候加在尾巴上,移除的时候末尾置空而已。
使用场合就是需要后进先出的数据结构时可以使用