mybatis json字段处理
前言
最近遇到了使用mysql的json类型字段的解析问题,之前的开发的时候,刚开始用的就是mybatis,为了解决json字段的问题,有的同事是把json字段映射成Java里的String,手动在业务代码里转化,也有同事尝试用typeHandler自动解析,可惜没成功,最近我接受这部分代码,花了一天的时间才完成自动解析的配置。
目的
最终的目的是希望json字段能自动映射成java对象。
基本情况说明
Java表对应的java实体
TeacherDO {
private Student student;
get(); // 省略
set(); // 省略
}
表:
create table teacher (
student json // 省略
)
tracher.xml:
insert into teacher (student)
values(#{student)
只写了关键的内容,其它都忽略。
问题
如果在上述情况下使用,使用会报错
org.mybatis.spring.MyBatisSystemException: nested exception is org.apache.ibatis.reflection.ReflectionException: Could not set property 'student' of 'class com.xxx.Student' with value 'xxxx' Cause: java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: argument type mismatch
at org.mybatis.spring.MyBatisExceptionTranslator.translateExceptionIfPossible(MyBatisExceptionTranslator.java:78)
at org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate$SqlSessionInterceptor.invoke(SqlSessionTemplate.java:440)
at com.sun.proxy.$Proxy175.selectList(Unknown Source)
at org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate.selectList(SqlSessionTemplate.java:223)
at org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperMethod.executeForMany(MapperMethod.java:147)
at org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperMethod.execute(MapperMethod.java:80)
at org.apache.ibatis.binding.MapperProxy.invoke(MapperProxy.java:57)
at com.sun.proxy.$Proxy176.findBy(Unknown Source)
这个错误信息非常清晰,student字段的类型错误,无法匹配,原因也很明确,表中是json 字段,接收对象中student是对象Student。
开始解决
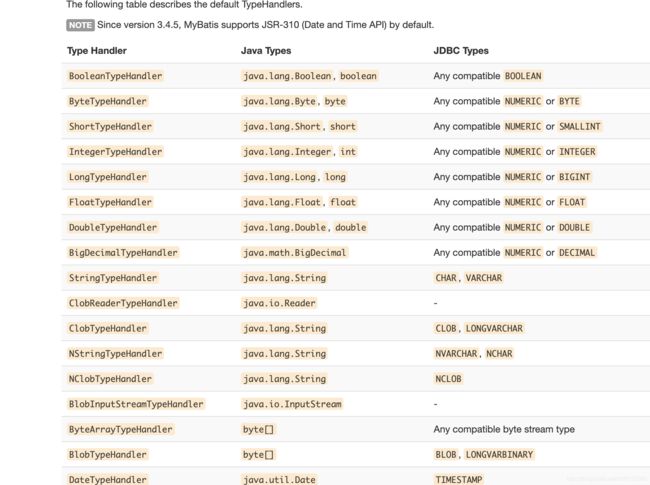
基于以上错误信息,我的第一想法是mybatis是不是还不支持json字段自动转对象,我知道了官网的typeHandler的说明(官网地址),
从官网说明来看,实际是不支持自动转化。
因此,开始考虑实现一个自定义的typeHandler来解决。
现在我需要决定需要创建几个JSONTypeHandler,因为自定义typeHandler一般都是继承下面这个类:
public abstract class BaseTypeHandler extends TypeReference implements TypeHandler {
/**
* @deprecated Since 3.5.0 - See https://github.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/issues/1203. This field will remove future.
*/
@Deprecated
protected Configuration configuration;
// 省略
}
自定义实现的时候需要决定自己的typeHandler要解决的类型是什么,也就是泛型T。
有两种实现方式:
第一种、指定具体的java类型:
public class StudentTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler {
// 省略
}
第二种、不指定具体的T,仍然使用泛型,通过配置javaType指定java类型
public class JsonTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler {
// 省略
}
考虑到未来可能有更多的json字段,因此决定使用第二种,完整的JsonTypeHandler :
package com.xxx.mybatis.handler;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.ibatis.exceptions.PersistenceException;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.MappedJdbcTypes;
/**
* Jackson 实现 JSON 字段类型处理器
*
* @author xinfeng
* @date 2019/11/7 12:29
*/
@Slf4j
@MappedJdbcTypes(JdbcType.VARCHAR)
public class JacksonTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler {
private static ObjectMapper objectMapper;
private Class type;
static {
objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
objectMapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);
}
public CommonJacksonTypeHandler(Class type) {
if (log.isTraceEnabled()) {
log.trace("JacksonTypeHandler(" + type + ")");
}
if (null == type) {
throw new PersistenceException("Type argument cannot be null");
}
this.type = type;
}
private T parse(String json) {
try {
if (json == null || json.length() == 0) {
return null;
}
return objectMapper.readValue(json, type);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
private String toJsonString(T obj) {
try {
return objectMapper.writeValueAsString(obj);
} catch (JsonProcessingException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
@Override
public T getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
return parse(rs.getString(columnName));
}
@Override
public T getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
return parse(rs.getString(columnIndex));
}
@Override
public T getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
return parse(cs.getString(columnIndex));
}
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int columnIndex, T parameter, JdbcType jdbcType)
throws SQLException {
ps.setString(columnIndex, toJsonString(parameter));
}
}
这样就实现了一个JsonTypeHandler,把对象转化为字符串(VARCHAR),用于解析json字段。
开始使用
基于以上分析决策,已经实现了typeHandler,现在开始使用。
因为自定义的typeHandler指定的是java类型是泛型T,所以无法使用下面的配置:
// 省略
// 省略
为什么无法使用?
public TypeHandler getInstance(Class javaTypeClass, Class typeHandlerClass) {
if (javaTypeClass != null) {
try {
Constructor c = typeHandlerClass.getConstructor(Class.class);
return (TypeHandler) c.newInstance(javaTypeClass);
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ignored) {
// ignored
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TypeException("Failed invoking constructor for handler " + typeHandlerClass, e);
}
}
try {
// 这一步会报错
Constructor c = typeHandlerClass.getConstructor();
return (TypeHandler) c.newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TypeException("Unable to find a usable constructor for " + typeHandlerClass, e);
}
}
因为使用的是泛型,所以mybatis反射通过构造方法实例化时会报错,报错原因是没有具体的类型。
既然这种无法使用,只能在mapper.xml中使用。
insert into teacher (student)
values(#{student ,javaType=com.xxx.Student, typeHandler = com.xxx.JacksonTypeHandler)
)
javaType用于指定,typeHandler的泛型T的具体类型,这样查询和插入就都能自动解析了。
优化
每个typeHandler的写的时候名字都太长,能不能像alias对象一样使用昵称?
经过验证,不行。
按照上述思路解决,还是无法解决问题,如何定位自己的问题
找到mybatis的DefaultResultSetHandler的 applyPropertyMappings 方法,这个方法用来遍历解析查询到的数据
private boolean applyPropertyMappings(ResultSetWrapper rsw, ResultMap resultMap, MetaObject metaObject, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix)
throws SQLException {
final List mappedColumnNames = rsw.getMappedColumnNames(resultMap, columnPrefix);
boolean foundValues = false;
final List propertyMappings = resultMap.getPropertyResultMappings();
for (ResultMapping propertyMapping : propertyMappings) {
String column = prependPrefix(propertyMapping.getColumn(), columnPrefix);
if (propertyMapping.getNestedResultMapId() != null) {
// the user added a column attribute to a nested result map, ignore it
column = null;
}
if (propertyMapping.isCompositeResult()
|| (column != null && mappedColumnNames.contains(column.toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH)))
|| propertyMapping.getResultSet() != null) {
// TODO 这一行是解析数据
Object value = getPropertyMappingValue(rsw.getResultSet(), metaObject, propertyMapping, lazyLoader, columnPrefix);
// issue #541 make property optional
final String property = propertyMapping.getProperty();
if (property == null) {
continue;
} else if (value == DEFERRED) {
foundValues = true;
continue;
}
if (value != null) {
foundValues = true;
}
if (value != null || (configuration.isCallSettersOnNulls() && !metaObject.getSetterType(property).isPrimitive())) {
// gcode issue #377, call setter on nulls (value is not 'found')
metaObject.setValue(property, value);
}
}
}
return foundValues;
}
getPropertyMappingValue方法:
private Object getPropertyMappingValue(ResultSet rs, MetaObject metaResultObject, ResultMapping propertyMapping, ResultLoaderMap lazyLoader, String columnPrefix)
throws SQLException {
if (propertyMapping.getNestedQueryId() != null) {
return getNestedQueryMappingValue(rs, metaResultObject, propertyMapping, lazyLoader, columnPrefix);
} else if (propertyMapping.getResultSet() != null) {
addPendingChildRelation(rs, metaResultObject, propertyMapping); // TODO is that OK?
return DEFERRED;
} else {
// TODO 这一步可以确认自定义的typeHandler是不是正确的
final TypeHandler typeHandler = propertyMapping.getTypeHandler();
final String column = prependPrefix(propertyMapping.getColumn(), columnPrefix);
// TODO 这一步用来调自定义的typeHandler的数据解析方法
return typeHandler.getResult(rs, column);
}
}
经过这两步判断一般都能判断出自己的typeHandler为什么不能正常起作用。
总结
问题溯本归源,总能定位具体的原因的,分析一下过程有助于解决同类问题。