Hash和Hash表总结
Hash和Hash表总结
Hash基础内容Hash函数设计- 重写
hashCode()和equals()方法 - 使用数组+红黑树实现
HashMap - 使用数组+链表实现
HashMap - 相关时间复杂度分析以及更多处理冲突的方法
- 用
HashMap实现一个小栗子(统计单词出现的次数) - 使用
LeetCode-350. Intersection of Two Arrays II测试我们实现的Map
Hash基础内容
- 哈希表,也称散列表,是实现字典操作的一种有效的数据结构。尽管在最坏的情况下,散列表查找一个元素的时间复杂度与链表中查找的时间相同,达到了O(n),然而实际应用中,散列表查找的性能是极好的,在一些合理的假设下,在散列表中可以查找一个元素的平均时间复杂度是O(1)。
Hash函数设计
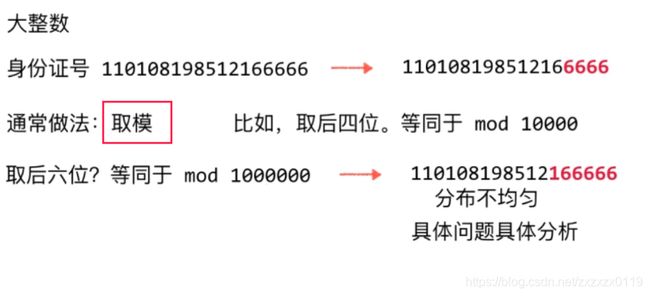
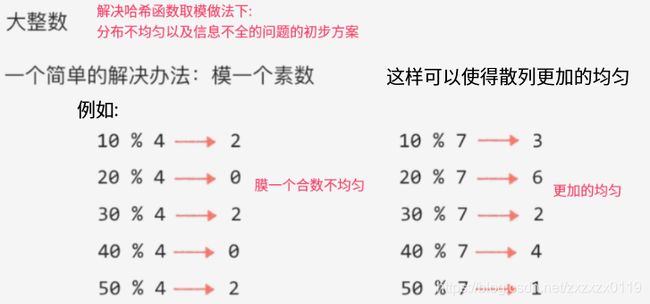
- 但是如果随便模一个数的话容易导致分布不均匀,所以可以使用摸一个素数的方法来使得散列更加的均匀(数学证明)
于是不管是浮点型数还是字符串数都可以转换成字符串处理:
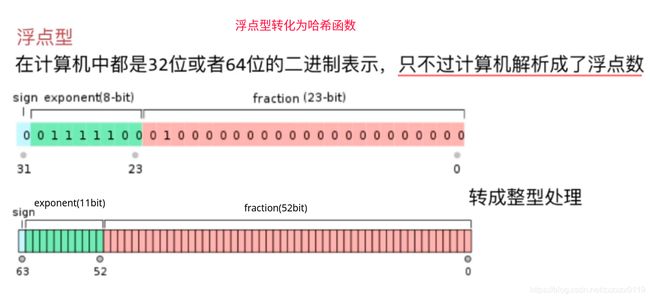
注意字符串处理的时候:
- 可以把字符串看作是
26进制的数,然后来计算它的hash值; - 在运算的过程中,为了防止高次方的运算,可以利用多项式的拆解来处理提高运算效率;
- 为了防止大整数的溢出,取模的时候我们每次运算一次就进行取模,和最后取模的效果是一样的;

如果是一个复合的类,也可以进行类似的处理:

综上: hash函数设计的原则:

重写hashCode()和equals()方法
按照上面的方式,使用java中的hashCode()重写,来计算我们的hash值,例如下面的Student类,我们计算hash的值的方法如下:
public class Student {
private int grade;//年级
private int cls; //班级
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public Student(int grade, int cls, String firstName, String lastName) {
this.grade = grade;
this.cls = cls;
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
}
//复合类型重写 Object类中的hashCode()方法
// Object类中已经写了,是通过地址比较的
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int hash = 0;
int B = 31; //这个就是那个进制
hash = hash*B + grade;
hash = hash*B + cls;
hash = hash*B + firstName.toLowerCase().hashCode();
hash = hash*B + lastName.toLowerCase().hashCode();
return hash;
}
/**
由于hashCode中如果自己重写了hashCode方法,那么有可能导致 不是同一个引用地址的对象是相同的
所以要使用equals方法来真的比较对象是否相同
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
if(obj == null){
return false;
}
if(getClass() != obj.getClass()){
return false;
}
Student another = (Student)obj;
return this.grade == another.grade &&
this.cls == another.cls &&
this.firstName.toLowerCase().equals(another.firstName.toLowerCase()) &&
this.lastName.toLowerCase().equals(another.lastName.toLowerCase());
}
}
为什么要重写equals()?
-
由于
hashCode中如果自己重写了hashCode方法,那么有可能导致 不是同一个引用地址的对象是相同的(冲突); -
所以要使用
equals方法来真的比较对象是否相同;
相关测试:
public class HashCodeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/**
* 测试各个类型的hashCode() 都是使用一个整数映射
*/
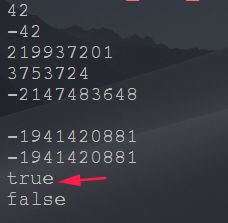
int a = 42;
System.out.println(((Integer)a).hashCode());
int b = -42;
System.out.println(((Integer)b).hashCode());
double c = 3.1415926;
System.out.println(((Double)c).hashCode());
String d = "zxzx";
System.out.println(d.hashCode());
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE + 1);
System.out.println();
/**
(1)如果没有重写 Object中的hashCode,那么下面的student和student2是不同的,hashCode按照地址比较
(2)如果按照自己重写的 hashCode,那么下面的student和student2是相同的
由于不能仅仅只按照hashCode来比较两个对象是否相同,所以就有重写equals方法
自己写的hashCode只是计算hash函数的值,但是产生hash冲突的时候(虽然hash函数值相等),还是要比较是否相等
*/
Student student = new Student(3, 2, "xinxin", "zheng");
System.out.println(student.hashCode());
Student student2 = new Student(3, 2, "xinxin", "zheng");
System.out.println(student2.hashCode());
System.out.println(student.hashCode() == student2.hashCode()); //true
System.out.println(student == student2); //false
}
}
使用数组+红黑树实现HashMap
- 数组的里面是红黑树实现,红黑树的可以看一下这篇博客解释。
- 因为JDK中的红黑树使用的
TreeMap实现,所以这里直接使用TreeMap当做红黑树使用;
public class MyHashMap<K extends Comparable<K>,V> {
/**为什么要这样的扩容,原因就是这些数都是素数,可以让哈希函数分布均匀,而且都是大致成两倍的关系 */
private final int[] capacity = {
53, 97, 193, 389, 769, 1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433, 1572869, 3145739, 6291469,
12582917, 25165843, 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457, 1610612741
};
private static final int upperTol = 10; /**每一个TreeMap内部超过这个就要扩容 --> size >= upperTol * M */
private static final int lowerTol = 2; /** 每一个TreeMap内部小于这个就要缩容 --> size < lowerTol * M */
private int capacityIndex = 0; /**这个是容量数组的下标,一开始是capacity[0]的容量*/
private TreeMap<K,V>[] hashtable;/** hash数组,每一个数组对应的都是一棵红黑树 */
private int size; /**总的元素个数*/
private int M; /**数组大小*/
public MyHashMap(){
this.M = capacity[capacityIndex];//一开始大小为53
size = 0;
hashtable = new TreeMap[M];
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) hashtable[i] = new TreeMap<>();
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
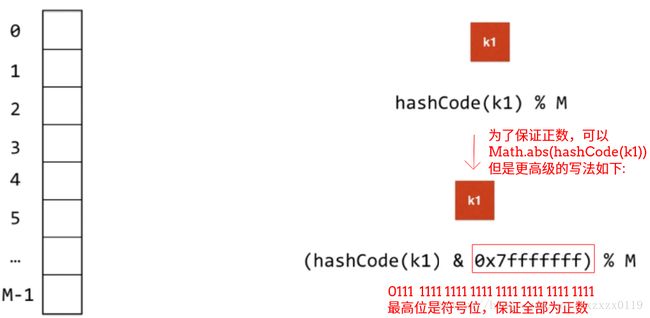
/** 计算hash值(也就是对应数组的索引) 使用hashCode % M 的方法 注意hashCode()要取绝对值*/
private int hash(K key){
return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;
}
/** add */
public void put(K key,V value){
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[hash(key)]; //找到对应的数组index
if(map.containsKey(key)){
map.put(key,value);
}else {
map.put(key,value);
size++;
/**判断是否要扩容 */
if(size >= upperTol * M && capacityIndex + 1 < capacity.length) {//需要扩容且可以扩容
capacityIndex++;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]); //扩容到容量数组的下一个值
}
}
}
public V remove(K key){
V ret = null;
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[hash(key)];
if(map.containsKey(key)){
ret = map.remove(key);
size--;
if(size < lowerTol * M && capacityIndex - 1 >= 0){
capacityIndex--;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]);
}
}
return ret;
}
private void resize(int newM) {
TreeMap<K,V>[] newHashtable = new TreeMap[newM];
for(int i = 0; i < newM; i++)
newHashtable[i] = new TreeMap<>();
int oldM = this.M;
this.M = newM;
for(int i = 0; i < oldM; i++){
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[i];
for(K key : map.keySet()){
newHashtable[hash(key)].put(key,map.get(key));
}
}
this.hashtable = newHashtable;
}
public void set(K key,V value){
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[hash(key)];
if(!map.containsKey(key))
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + "doesn't exist!");
map.put(key,value);
}
public boolean contains(K key){
return hashtable[hash(key)].containsKey(key);
}
public V get(K key){
return hashtable[hash(key)].get(key);
}
}
上述代码有几点要注意的:
- 第一:
capacity数组是用来resize(扩容,缩容)的时候使用的数组,因为我们上面说过,M要设计成素数会更好的均匀分布; - 第二:
upperTol和lowerTol表示平均TreeMap数组内的容量达到这两个容量的时候就进行扩容或者缩容; - 第三:
(key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M; 其实就是Math.abs(key.hashCode()) % M; - 第四:
resize()函数中的int oldM = this.M; this.M = newM;使用oldM来保存之前的M的做法是为了在下面求hash(key)求的是新的hash函数的值,不是旧的hash的值,这点很容易忽视;
使用数组+链表实现HashMap
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* 自定义map的升级版,查询效率较高
* map底层实现 : 数组+链表
*/
public class LinkHashMap<K,V> {
private class Node{
public K key;
public V value;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
private final int[] capacity
= {53, 97, 193, 389, 769, 1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433, 1572869, 3145739, 6291469,
12582917, 25165843, 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457, 1610612741};
private static final int upperTol = 10;
private static final int lowerTol = 2;
private int capacityIndex = 0;
private LinkedList<Node>[] linkedLists;
private int size;
private int M;
public int size() {
return size;
}
public LinkHashMap() {
this.M = capacity[capacityIndex];
size = 0;
linkedLists = new LinkedList[M];
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
linkedLists[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
private int hash(K key){
return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
Node node = new Node(key, value);
int hash = hash(key);
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[hash];
if (list == null) {
list = new LinkedList<>();
linkedLists[hash] = list;
list.add(node);
} else {
Node node2 = null;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
node2 = list.get(i);
if (node2.key.equals(key)) {
node2.value = value;
return;
}
}
linkedLists[hash].add(node);
}
size++;
if(size >= upperTol * M && capacityIndex + 1 < capacity.length){
capacityIndex ++;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]);
}
}
public V remove(K key) {
int hash = hash(key);
V ret = null;
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[hash];
if(list != null){
Node node2 = null;
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
node2 = list.get(i);
if(node2.key.equals(key)){
ret = node2.value;
list.remove(i);// list.remove(node2);
size--;
//resize
if(size < lowerTol * M && capacityIndex - 1 >= 0){
capacityIndex --;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]);
}
return ret;
}
}
}
return null;
}
private void resize(int newM) {
LinkedList<Node>[]newLinkedLists = new LinkedList[newM];
for(int i = 0; i < newM; i++)
newLinkedLists[i] = new LinkedList<>();
int oldM = this.M;
this.M = newM;
Node node = null;
for(int i = 0; i < oldM; i++){
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[i];
for(int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++){
node = list.get(j);
newLinkedLists[hash(node.key)].add(node);
}
}
this.linkedLists = newLinkedLists;
}
public boolean contains(K key){
int hash = hash(key);
for(int i = 0; i < linkedLists[hash].size(); i++){
if(linkedLists[hash].get(i).key.equals(key))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public V get(K key){
int hash = hash(key);
Node node = null;
for(int i = 0; i < linkedLists[hash].size(); i++){
node = linkedLists[hash].get(i);
if(node.key.equals(key))
return node.value;
}
return null;
}
public void set(K key,V value){
int hash = hash(key);
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[hash];
if(list == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + " doesn't exist!");
Node node = null;
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
node = list.get(i);
if(node.key.equals(key)){
node.value = value;
return;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + " doesn't exist!");
}
}
相关时间复杂度分析
如果我们没有使用resize()动态扩容的话: 时间复杂度不是O(1),于是我们进行了扩容,可以达到平均时间复杂度为O(1)(是均摊复杂度分析):

不过HashMap达到了O(1),但是相比搜索树牺牲了有序性:
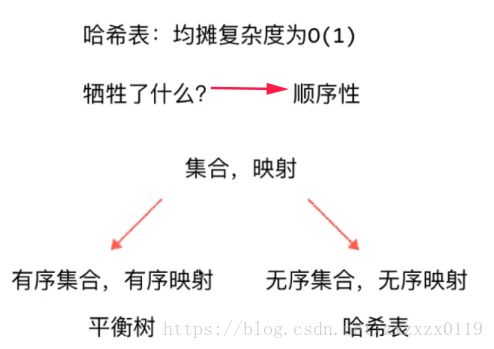
更多处理冲突的方法
开放地址法:
- 线性探测: 遇到哈希冲突
+1; - 平方探测:
+ 1,+ 4,+9,+16; - 二次
hash:hash2(key);
使用LeetCode-350. Intersection of Two Arrays II测试我们实现的Map
最后使用LeetCode-350测试我们实现的Map:
题目链接
题目
解析
题目很简单,使用HashMap和TreeMap来记录nums1中的数字的个数,然后对nums2进行操作,这里测试我们的Map; LinkHashMap:
class Solution {
private class LinkHashMap<K,V> {
private class Node{
public K key;
public V value;
public Node(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
private final int[] capacity
= {53, 97, 193, 389, 769, 1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433, 1572869, 3145739, 6291469,
12582917, 25165843, 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457, 1610612741};
private static final int upperTol = 10;
private static final int lowerTol = 2;
private int capacityIndex = 0;
private LinkedList<Node>[] linkedLists;
private int size;
private int M;
public int size() {
return size;
}
public LinkHashMap() {
this.M = capacity[capacityIndex];
size = 0;
linkedLists = new LinkedList[M];
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
linkedLists[i] = new LinkedList<>();
}
private int hash(K key){
return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
Node node = new Node(key, value);
int hash = hash(key);
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[hash];
if (list == null) {
list = new LinkedList<>();
linkedLists[hash] = list;
list.add(node);
} else {
Node node2 = null;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
node2 = list.get(i);
if (node2.key.equals(key)) {
node2.value = value;
return;
}
}
linkedLists[hash].add(node);
}
size++;
if(size >= upperTol * M && capacityIndex + 1 < capacity.length){
capacityIndex ++;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]);
}
}
public V remove(K key) {
int hash = hash(key);
V ret = null;
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[hash];
if(list != null){
Node node2 = null;
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
node2 = list.get(i);
if(node2.key.equals(key)){
ret = node2.value;
list.remove(i);// list.remove(node2);
size--;
//resize
if(size < lowerTol * M && capacityIndex - 1 >= 0){
capacityIndex --;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]);
}
return ret;
}
}
}
return null;
}
private void resize(int newM) {
LinkedList<Node>[]newLinkedLists = new LinkedList[newM];
for(int i = 0; i < newM; i++)
newLinkedLists[i] = new LinkedList<>();
int oldM = this.M;
this.M = newM;
Node node = null;
for(int i = 0; i < oldM; i++){
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[i];
for(int j = 0; j < list.size(); j++){
node = list.get(j);
newLinkedLists[hash(node.key)].add(node);
}
}
this.linkedLists = newLinkedLists;
}
public boolean contains(K key){
int hash = hash(key);
for(int i = 0; i < linkedLists[hash].size(); i++){
if(linkedLists[hash].get(i).key.equals(key))
return true;
}
return false;
}
public V get(K key){
int hash = hash(key);
Node node = null;
for(int i = 0; i < linkedLists[hash].size(); i++){
node = linkedLists[hash].get(i);
if(node.key.equals(key))
return node.value;
}
return null;
}
public void set(K key,V value){
int hash = hash(key);
LinkedList<Node>list = linkedLists[hash];
if(list == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + " doesn't exist!");
Node node = null;
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){
node = list.get(i);
if(node.key.equals(key)){
node.value = value;
return;
}
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + " doesn't exist!");
}
}
public int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
LinkHashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new LinkHashMap<>();
for(int num: nums1){
if(!map.contains(num))
map.put(num, 1);
else
map.set(num, map.get(num) + 1);
}
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int num: nums2){
if(map.contains(num)){
res.add(num);
map.set(num, map.get(num) - 1);
if(map.get(num) == 0)
map.remove(num);
}
}
int[] ret = new int[res.size()];
for(int i = 0 ; i < res.size() ; i ++)
ret[i] = res.get(i);
return ret;
}
}
MyHashMap:
class Solution {
private class MyHashMap<K extends Comparable<K>,V> {
/**为什么要这样的扩容,原因就是这些数都是素数,可以让哈希函数分布均匀,而且都是大致成两倍的关系 */
private final int[] capacity = {
53, 97, 193, 389, 769, 1543, 3079, 6151, 12289, 24593,
49157, 98317, 196613, 393241, 786433, 1572869, 3145739, 6291469,
12582917, 25165843, 50331653, 100663319, 201326611, 402653189, 805306457, 1610612741
};
private static final int upperTol = 10; /**每一个TreeMap内部超过这个就要扩容 --> size >= upperTol * M */
private static final int lowerTol = 2; /** 每一个TreeMap内部小于这个就要缩容 --> size < lowerTol * M */
private int capacityIndex = 0; /**这个是容量数组的下标,一开始是capacity[0]的容量*/
private TreeMap<K,V>[] hashtable;/** hash数组,每一个数组对应的都是一棵红黑树 */
private int size; /**总的元素个数*/
private int M; /**数组大小*/
public MyHashMap(){
this.M = capacity[capacityIndex];//一开始大小为53
size = 0;
hashtable = new TreeMap[M];
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) hashtable[i] = new TreeMap<>();
}
public int size(){
return size;
}
/** 计算hash值(也就是对应数组的索引) 使用hashCode % M 的方法 注意hashCode()要取绝对值*/
private int hash(K key){
return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;
}
/** add */
public void put(K key,V value){
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[hash(key)]; //找到对应的数组index
if(map.containsKey(key)){
map.put(key,value);
}else {
map.put(key,value);
size++;
/**判断是否要扩容 */
if(size >= upperTol * M && capacityIndex + 1 < capacity.length) {//需要扩容且可以扩容
capacityIndex++;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]); //扩容到容量数组的下一个值
}
}
}
public V remove(K key){
V ret = null;
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[hash(key)];
if(map.containsKey(key)){
ret = map.remove(key);
size--;
if(size < lowerTol * M && capacityIndex - 1 >= 0){
capacityIndex--;
resize(capacity[capacityIndex]);
}
}
return ret;
}
private void resize(int newM) {
TreeMap<K,V>[] newHashtable = new TreeMap[newM];
for(int i = 0; i < newM; i++)
newHashtable[i] = new TreeMap<>();
int oldM = this.M;
this.M = newM;
for(int i = 0; i < oldM; i++){
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[i];
for(K key : map.keySet()){
newHashtable[hash(key)].put(key,map.get(key));
}
}
this.hashtable = newHashtable;
}
public void set(K key,V value){
TreeMap<K,V>map = hashtable[hash(key)];
if(!map.containsKey(key))
throw new IllegalArgumentException(key + "doesn't exist!");
map.put(key,value);
}
public boolean contains(K key){
return hashtable[hash(key)].containsKey(key);
}
public V get(K key){
return hashtable[hash(key)].get(key);
}
}
public int[] intersect(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
MyHashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new MyHashMap<>();
for(int num: nums1){
if(!map.contains(num))
map.put(num, 1);
else
map.set(num, map.get(num) + 1);
}
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
for(int num: nums2){
if(map.contains(num)){
res.add(num);
map.set(num, map.get(num) - 1);
if(map.get(num) == 0)
map.remove(num);
}
}
int[] ret = new int[res.size()];
for(int i = 0 ; i < res.size() ; i ++)
ret[i] = res.get(i);
return ret;
}
}