EL-第四次比赛
EL第四次比赛终于结束啦~
和自己的队友共同作战了一个月 虽然最后一场队长因为赶论文忘记了。。。 但整体大家还是用尽全力去做吧,但显然策略上有问题,习惯性一个题死磕,有时候甚至很简单的问题最后也没有接打出来。而且会有那种划水的现象,就是自己已经做完了一道题好像已经万事大吉,这是万不可取得。
C

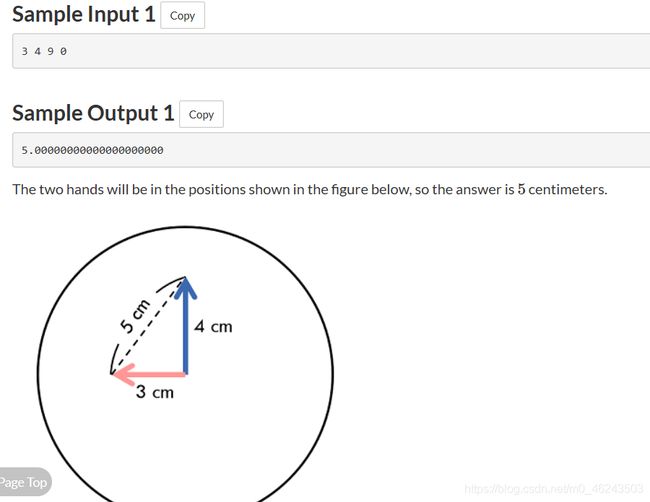

这道题 就是纯粹数学题,但难点在于求角度和如何保证精确度。
这就牵扯到牛顿迭代法与时钟问题求加角(自己感觉是小学数学但差点没想起来
import java.util.Scanner;
public class vendingMachine {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int short_hand=in.nextInt();
int long_hand=in.nextInt();
int hour=in.nextInt();
int minutes=in.nextInt();
double pai=Math.PI;
double x=Math.abs(hour*pai/6+minutes*pai/360-minutes*pai/30); //计算其中度数
double cos_x=Math.cos(x); //得到余弦值
double result_pow2= short_hand*short_hand+long_hand*long_hand-2*short_hand*long_hand*cos_x;
double result=1.0;
while(Math.abs(result-result_pow2/result)>1e-10)
{
result=(result+result_pow2/result)/2;
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}感觉自己代码风格写的蛮好看的 (●’◡’●)
D


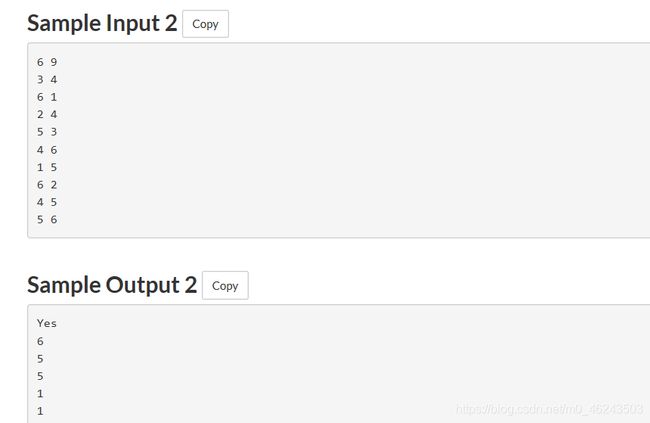
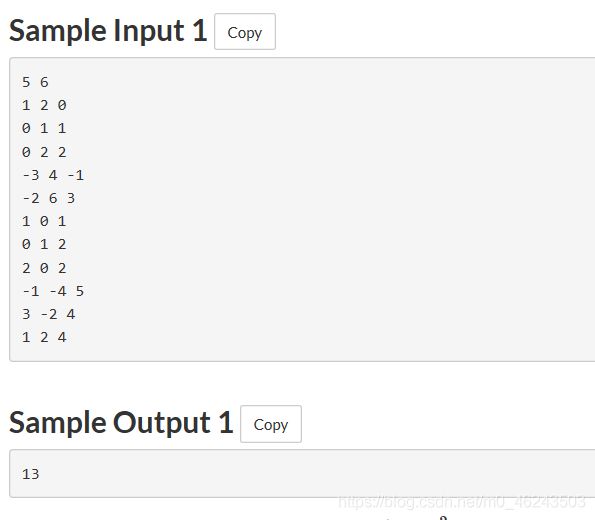
这个问题又是两个通道有道路,然后走路回到终点问题,但是,自己并没有看懂用例二,为什么最小是6呢?请在评论区告诉小编吧!
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
List<Integer>[] edge = new ArrayList[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
edge[i] = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a = sc.nextInt()-1;
int b = sc.nextInt()-1;
edge[a].add(b);
edge[b].add(a);
}
int[] ans = new int[N];
Queue<Integer> s = new ArrayDeque<>();
s.offer(0);
while(s.size() > 0) {
int x = s.poll();
for(int i : edge[x]) {
if(ans[i] == 0) {
ans[i] = x+1;
s.add(i);
}
}
}
System.out.println("Yes");
for(int i = 1; i < N; i++)
System.out.println(ans[i]);
}
}我惊讶于这个人是最短的(滑稽
这是正常版本
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var sc = new Scanner(System.in);
var n = sc.nextInt();
var m = sc.nextInt();
var set = new HashSet[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
set[i] = new HashSet<Integer>();
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
var a = sc.nextInt();
var b = sc.nextInt();
set[a - 1].add(b);
set[b - 1].add(a);
}
sc.close();
var count = 0;
var r = new int[n];
var list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
while (count < n -1) {
var list2 = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(var n2 : list) {
for (var x : set[n2 - 1]) {
if ((int)x != 1 && r[(int) x - 1] == 0) {
r[(int) x - 1] = n2;
list2.add((int)x);
}
}
}
list.clear();
list.addAll(list2);
count += list2.size();
}
System.out.println("Yes");
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println(r[i]);
}
}
}E
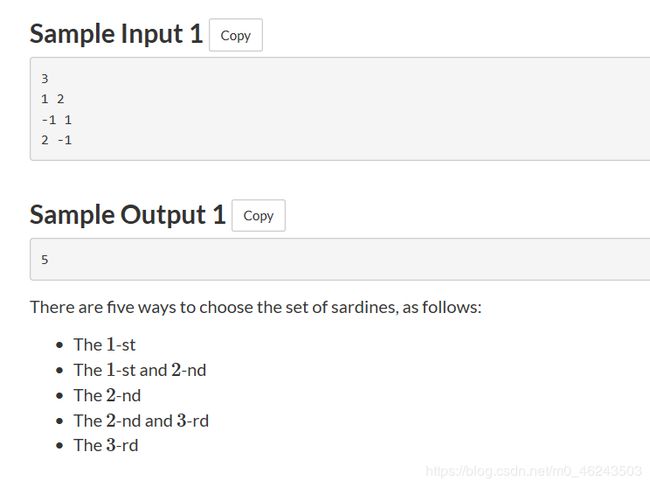
意思就是给定一个限定条件,如某两个不能组合在一起,求在这n个物品中,有多少种挑选方式
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static long gcd(long a, long b) {
return b == 0 ? a: gcd(b, a % b);
}
static String rev(String S) {
if(S.equals("1,0"))
return "0,1";
else if(S.equals("0,1"))
return "1,0";
String[] s = S.split(",");
if(s[0].charAt(0) == '-')
return s[1] + "," + s[0].substring(1);
else
return "-" + s[1] + "," + s[0];
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int MOD = 1000000007;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int N = sc.nextInt();
String C;
Map<String, Integer> m1 = new HashMap<>();
Map<String, Integer> m2 = new HashMap<>();
int zero = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
long A = sc.nextLong();
long B = sc.nextLong();
if(A == 0 && B == 0) {
zero++;
continue;
}
long gcd = gcd(A, B);
A /= gcd;
B /= gcd;
if(B < 0) {
A = -A;
B = -B;
}
if(B == 0)
C = "1,0";
else if(A == 0)
C = "0,1";
else
C = A + "," + B;
if(A >= 0 && B != 0)
m1.put(C, m1.getOrDefault(C, 0)+1);
else
m2.put(C, m2.getOrDefault(C, 0)+1);
}
long ans = 1;
long[] pow2 = new long[N+1];
pow2[0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++)
pow2[i] = pow2[i-1] * 2 % MOD;
for(String s : m1.keySet()) {
int a = m1.get(s), b = m2.getOrDefault(rev(s), 0);
ans = ans * (pow2[a] + pow2[b] - 1) % MOD;
}
for(String s : m2.keySet())
if(!m1.containsKey(rev(s)))
ans = ans * pow2[m2.get(s)] % MOD;
System.out.println((ans + zero - 1 + MOD) % MOD);
}
}
F
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n];
int[] b = new int[n];
int[] c = new int[n];
int[] d = new int[m];
int[] e = new int[m];
int[] f = new int[m];
Set<Integer> xs = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> ys = new HashSet<>();
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
b[i] = sc.nextInt();
c[i] = sc.nextInt();
xs.add(a[i]);
xs.add(b[i]);
ys.add(c[i]);
}
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
d[i] = sc.nextInt();
e[i] = sc.nextInt();
f[i] = sc.nextInt();
xs.add(d[i]);
ys.add(e[i]);
ys.add(f[i]);
}
int xn = xs.size();
int[] xl = new int[xs.size()];
int ii=0;
for(int num : xs) {
xl[ii++] = num;
}
Arrays.sort(xl);
int[] yl = new int[ys.size()];
int yn = ys.size();
ii=0;
for(int num : ys) {
yl[ii++] = num;
}
Arrays.sort(yl);
Map<Integer, Integer> mapx = new HashMap<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> mapy = new HashMap<>();
int zx = xn;
int zy = yn;
long[] dx = new long[xn];
long[] dy = new long[yn];
for(int i=0; i<xn; i++) {
if(i>0) {
dx[i] = xl[i]-xl[i-1];
}
mapx.put(xl[i], i);
if(zx == xn && xl[i]>0) {
zx = i;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<yn; i++) {
if(i>0) {
dy[i] = yl[i]-yl[i-1];
}
mapy.put(yl[i], i);
if(zy == yn && yl[i]>0) {
zy = i;
}
}
if(zx == xn || zy == yn || zx == 0 || zy == 0) {
System.out.println("INF");
return;
}
boolean[][] yw = new boolean[xn][yn];
boolean[][] xw = new boolean[xn][yn];
for(int i=0; i<n; i++) {
int x1 = mapx.get(a[i]);
int x2 = mapx.get(b[i]);
int y1 = mapy.get(c[i]);
for(int j=x1+1; j<=x2; j++) {
yw[j][y1] = true;
}
}
for(int i=0; i<m; i++) {
int x1 = mapx.get(d[i]);
int y1 = mapy.get(e[i]);
int y2 = mapy.get(f[i]);
for(int j=y1+1; j<=y2; j++) {
xw[x1][j] = true;
}
}
Queue<P> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(new P(zx, zy));
boolean[][] v = new boolean[xn][yn];
v[zx][zy] = true;
long res = dx[zx] * dy[zy];
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
P p = q.poll();
int nx;
int ny;
if (!xw[p.x - 1][p.y]) {
nx = p.x - 1;
ny = p.y;
if (nx == 0) {
System.out.println("INF");
return;
}
if(!v[nx][ny]) {
q.add(new P(nx, ny));
res += dx[nx] * dy[ny];
v[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
if (!xw[p.x][p.y]) {
nx = p.x + 1;
ny = p.y;
if (nx == xn) {
System.out.println("INF");
return;
}
if(!v[nx][ny]) {
q.add(new P(nx, ny));
res += dx[nx] * dy[ny];
v[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
if (!yw[p.x][p.y-1]) {
nx = p.x;
ny = p.y - 1;
if (ny == 0) {
System.out.println("INF");
return;
}
if(!v[nx][ny]) {
q.add(new P(nx, ny));
res += dx[nx] * dy[ny];
v[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
if (!yw[p.x][p.y]) {
nx = p.x;
ny = p.y + 1;
if (ny == yn) {
System.out.println("INF");
return;
}
if(!v[nx][ny]) {
q.add(new P(nx, ny));
res += dx[nx] * dy[ny];
v[nx][ny] = true;
}
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
static class P {
public int x;
public int y;
P(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
}
}回顾这几场 自己是有提高 但和某些奆佬做五个题目差距还不小
每天坚持连题目 不在于多 而在于掌握每一道题的 真正解法 还有属于自己的 !!
奥里给
都看到这里了,给个赞吧 (●’◡’●)
比赛链接请点击这里