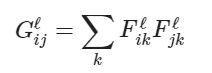2020 cs231n 作业3 笔记 StyleTransfer-PyTorch
目录
StyleTransfer-PyTorc
Content loss
Style loss
Total-variation regularization
Style Transfer
StyleTransfer-PyTorc
论文地址,风格迁移是取两张图片,把一张图片的风格和另一张图片的内容合成为一张新的图片。
Content loss
content loss用来计算原图片和生成的图片之间像素的差距,这里用的是卷积层获取的feature map之间的差距。
关于feature map:
通过卷积层,有多少个卷积核就会生成多少个feature map。
def content_loss(content_weight, content_current, content_original):
"""
Compute the content loss for style transfer.
Inputs:
- content_weight: Scalar giving the weighting for the content loss.
- content_current: features of the current image; this is a PyTorch Tensor of shape
(1, C_l, H_l, W_l).
- content_target: features of the content image, Tensor with shape (1, C_l, H_l, W_l).
Returns:
- scalar content loss
"""
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
N,C,H,W = content_current.shape
Fc = content_current.view(C,H*W)
Pc = content_original.view(C,H*W)
Lc = content_weight * (Fc - Pc).pow(2).sum()
return Lc
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****Style loss
这里我们使用格拉姆矩阵(Gram matrix G)来表示feature map每个通道(channel)之间的联系(也就是风格)。
输入F的维度为(N,C,H,W),转换为(N,C,M),M=H*W,则输出的G维度为(N,C,C)
则风格的loss就是原图片和生成的图片之间格拉姆矩阵的差距:
def gram_matrix(features, normalize=True):
"""
Compute the Gram matrix from features.
Inputs:
- features: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N, C, H, W) giving features for
a batch of N images.
- normalize: optional, whether to normalize the Gram matrix
If True, divide the Gram matrix by the number of neurons (H * W * C)
Returns:
- gram: PyTorch Tensor of shape (N, C, C) giving the
(optionally normalized) Gram matrices for the N input images.
"""
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
N,C,H,W = features.shape
F = features.view(N,C,H*W) # N*C*M
F_t = F.permute(0,2,1) # N*M*C
gram = torch.matmul(F,F_t) # N*C*C
if normalize:
gram = gram / (C*H*W)
return gram
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****def style_loss(feats, style_layers, style_targets, style_weights):
"""
Computes the style loss at a set of layers.
Inputs:
- feats: list of the features at every layer of the current image, as produced by
the extract_features function.
- style_layers: List of layer indices into feats giving the layers to include in the
style loss.
- style_targets: List of the same length as style_layers, where style_targets[i] is
a PyTorch Tensor giving the Gram matrix of the source style image computed at
layer style_layers[i].
- style_weights: List of the same length as style_layers, where style_weights[i]
is a scalar giving the weight for the style loss at layer style_layers[i].
Returns:
- style_loss: A PyTorch Tensor holding a scalar giving the style loss.
"""
# Hint: you can do this with one for loop over the style layers, and should
# not be very much code (~5 lines). You will need to use your gram_matrix function.
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
style_current = []
#style_loss = torch.zeros([1],dtype=float)
style_loss = 0
for i,idx in enumerate(style_layers):
style_current.append(gram_matrix(feats[idx].clone()))
style_loss += (style_current[i] - style_targets[i]).pow(2).sum() * style_weights[i]
return style_loss
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****Total-variation regularization
total variation loss可以使图像变得平滑。信号处理中,总变差去噪,也称为总变差正则化,是最常用于数字图像处理的过程,其在噪声去除中具有应用。
def tv_loss(img, tv_weight):
"""
Compute total variation loss.
Inputs:
- img: PyTorch Variable of shape (1, 3, H, W) holding an input image.
- tv_weight: Scalar giving the weight w_t to use for the TV loss.
Returns:
- loss: PyTorch Variable holding a scalar giving the total variation loss
for img weighted by tv_weight.
"""
# Your implementation should be vectorized and not require any loops!
# *****START OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****
N,C,H,W = img.shape
x1 = img[:,:,0:H-1,:]
x2 = img[:,:,1:H,:]
y1 = img[:,:,:,0:W-1]
y2 = img[:,:,:,1:W]
loss = ((x2-x1).pow(2).sum() + (y2-y1).pow(2).sum()) * tv_weight
return loss
# *****END OF YOUR CODE (DO NOT DELETE/MODIFY THIS LINE)*****Style Transfer
接下来就是进行完整的风格迁移过程:
初始化img图片(可以初始化为随机噪声或从另一张图片复制)
for t in (迭代次数)
使用cnn获取feature map
计算img的总loss(content loss+style loss+tv loss)
反向传播计算img的梯度
更新img
输出结果:
Iteration 0
Iteration 100
Iteration 199