算法4第5章霍夫曼/LZW压缩算法讲解
双位编码压缩
对于DNA编码ATAGATGCATAGCGCATAGCTAGATGTGCTAGC,如果按ACSII码来存储,需要8*35=280位,而DNA编码只有ACGT这4个字母,所以可以用两位00代表A,01代表C,10代表G,11代表T,只需要2*35=70位
代码实现如下:
public class Genome {
// Do not instantiate.
private Genome() { }
public static void compress() {
Alphabet DNA = Alphabet.DNA;
String s = BinaryStdIn.readString();
int n = s.length();
BinaryStdOut.write(n);
// Write two-bit code for char.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
int d = DNA.toIndex(s.charAt(i));
BinaryStdOut.write(d, 2);
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
public static void expand() {
Alphabet DNA = Alphabet.DNA;
int n = BinaryStdIn.readInt();
// Read two bits; write char.
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
char c = BinaryStdIn.readChar(2);
BinaryStdOut.write(DNA.toChar(c), 8);
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
游程编码
对于40位比特流字符串0000000000000001111111000000011111111111,含有大量重复字符,并且只有0和1两种字符,字符串中含有15个0,7个1,7个0,11个1,可以用1个16位长的字符串来表示1111011101111011(15=1111,7=0111,11=1011),压缩率16/40=40%
常见的位图就属于这种类型,示意图如下:
我们规定游程编码以0开头,游程的长度为8位在0到255之间,如果超过255,存一个长度为0的游程,代码如下:
public class RunLength {
private static final int R = 256;
private static final int LG_R = 8;
// Do not instantiate.
private RunLength() { }
public static void expand() {
boolean b = false;
while (!BinaryStdIn.isEmpty()) {
int run = BinaryStdIn.readInt(LG_R);
for (int i = 0; i < run; i++)
BinaryStdOut.write(b);
b = !b;
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
public static void compress() {
char run = 0;
boolean old = false;
while (!BinaryStdIn.isEmpty()) {
boolean b = BinaryStdIn.readBoolean();
if (b != old) {
BinaryStdOut.write(run, LG_R);
run = 1;
old = !old;
}
else {
if (run == R-1) {
BinaryStdOut.write(run, LG_R);
run = 0;
BinaryStdOut.write(run, LG_R);
}
run++;
}
}
BinaryStdOut.write(run, LG_R);
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
霍夫曼压缩
霍夫曼压缩使用较少的比特数表示出现频率高的字符,用较多的比特数表示出现频率低的字符,
例如字符串ABRACADABRA!,用0表示A,1表示B,00表示R,01表示C,D为10,!为11,这样字符串就是0 1 00 0 01 0 10 0 1 00 0 11
这样需要空格来分割,加上空格也节省不到多少空间,如果所有字符的编码都不会是其他字符编码的前缀就不需要空格了。
例如将A编码成0,B编码成1111,C编码成110,D编码成100,R编码成1110,!编码成101,这种编码被称为前缀码。
一个字符可以有不同的编码只要所有字符的编码都不会是其他字符编码的前缀就可以了,怎样编码才能使占用的空间最小呢
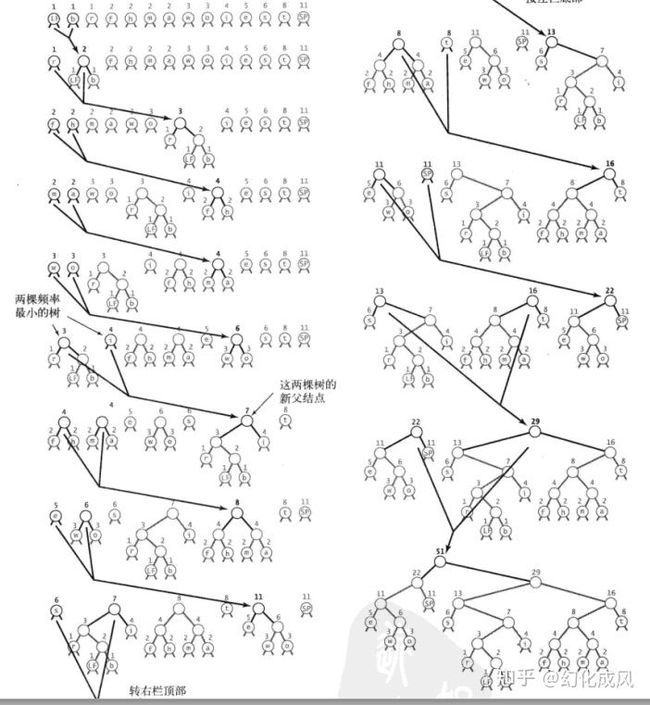
霍夫曼使用单词查找树来表示每个字符和它对应的编码,被称为霍夫曼编码,霍夫曼编码可以构造出最优的前缀码,示意图如下:
霍夫曼压缩解压缩代码如下:
public class Huffman {
// alphabet size of extended ASCII
private static final int R = 256;
// Do not instantiate.
private Huffman() { }
// Huffman trie node
private static class Node implements Comparable
private final char ch; //该节点表示的字符
private final int freq;//该节点表示的字符出现的频率,或它的子节点表示的字符总数
private final Node left, right;//左右链接,左链接表示0,右链接表示1
Node(char ch, int freq, Node left, Node right) {
this.ch = ch;
this.freq = freq;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
// is the node a leaf node?
private boolean isLeaf() {
assert ((left == null) && (right == null)) || ((left != null) && (right != null));
return (left == null) && (right == null);
}
// compare, based on frequency
public int compareTo(Node that) {
return this.freq - that.freq;
}
}
/**
* Reads a sequence of 8-bit bytes from standard input; compresses them
* using Huffman codes with an 8-bit alphabet; and writes the results
* to standard output.
*/
//压缩的流程如下
public static void compress() {
// read the input
String s = BinaryStdIn.readString();
char[] input = s.toCharArray();
//计算每个字符出现的频率
int[] freq = new int[R];
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++)
freq[input[i]]++;
//根据每个字符的频率构造霍夫曼树
Node root = buildTrie(freq);
//前序遍历霍夫曼树,找到每个字符对应的编码存在st中,如st['A']=110
String[] st = new String[R];
buildCode(st, root, "");
// 保存霍夫曼树用于解码
writeTrie(root);
// 保存原始未压缩字符总数
BinaryStdOut.write(input.length);
//根据霍夫曼编码压缩保存输入中的每个字符
for (int i = 0; i < input.length; i++) {
String code = st[input[i]];
for (int j = 0; j < code.length(); j++) {
if (code.charAt(j) == '0') {
BinaryStdOut.write(false);
}
else if (code.charAt(j) == '1') {
BinaryStdOut.write(true);
}
else throw new IllegalStateException("Illegal state");
}
}
// close output stream
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
//根据每个字符的频率构造霍夫曼树,首先把每个字符按频率大小存入优先队列,组成森林
//然后逐步把两个频率最小的子树合成一个子树,直到最后只剩下一颗树,这颗树构造的编码就是最优的,示意图如下:
private static Node buildTrie(int[] freq) {
// initialze priority queue with singleton trees
MinPQ
for (char i = 0; i < R; i++)
if (freq[i] > 0)
pq.insert(new Node(i, freq[i], null, null));
// special case in case there is only one character with a nonzero frequency
if (pq.size() == 1) {
if (freq['\0'] == 0) pq.insert(new Node('\0', 0, null, null));
else pq.insert(new Node('\1', 0, null, null));
}
// merge two smallest trees
while (pq.size() > 1) {
Node left = pq.delMin();
Node right = pq.delMin();
Node parent = new Node('\0', left.freq + right.freq, left, right);
pq.insert(parent);
}
return pq.delMin();
}
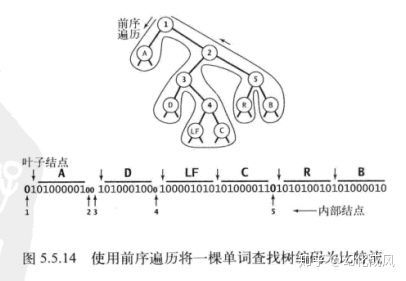
// 保存霍夫曼树用于解码,示意图如下
private static void writeTrie(Node x) {
if (x.isLeaf()) {
BinaryStdOut.write(true);
BinaryStdOut.write(x.ch, 8);
return;
}
BinaryStdOut.write(false);
writeTrie(x.left);
writeTrie(x.right);
}
// make a lookup table from symbols and their encodings
private static void buildCode(String[] st, Node x, String s) {
if (!x.isLeaf()) {
buildCode(st, x.left, s + '0');
buildCode(st, x.right, s + '1');
}
else {
st[x.ch] = s;
}
}
//解码流程
public static void expand() {
// read in Huffman trie from input stream
Node root = readTrie();
// number of bytes to write
int length = BinaryStdIn.readInt();
// decode using the Huffman trie
//根据霍夫曼树解码
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
Node x = root;
while (!x.isLeaf()) {
boolean bit = BinaryStdIn.readBoolean();
if (bit) x = x.right;
else x = x.left;
}
BinaryStdOut.write(x.ch, 8);
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
private static Node readTrie() {
boolean isLeaf = BinaryStdIn.readBoolean();
if (isLeaf) {
return new Node(BinaryStdIn.readChar(), -1, null, null);
}
else {
return new Node('\0', -1, readTrie(), readTrie());
}
}
LZW算法
霍夫曼编码是把每个字符按不同的长度进行编码,组成编译表
LZW算法是把待压缩的字符串中取不同长度的字符串编码成相同长度的编码,组成编译表而且不需要在输出中存编译表
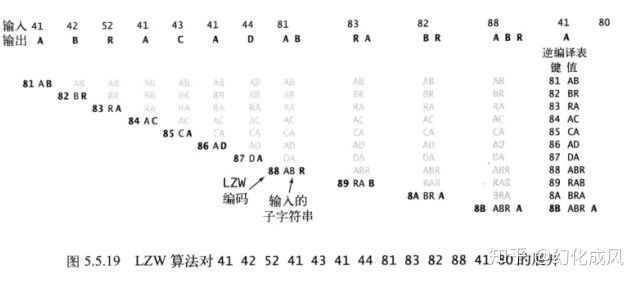
例如字符串ABRACADABRABRABRA, 把A编码成41,B编码成42,AB编码成81
代码如下
public class LZW {
private static final int R = 256; // number of input chars
private static final int L = 4096; // number of codewords = 2^W
private static final int W = 12; // codeword width
// Do not instantiate.
private LZW() { }
/**
* Reads a sequence of 8-bit bytes from standard input; compresses
* them using LZW compression with 12-bit codewords; and writes the results
* to standard output.
*/
//压缩流程如下
public static void compress() {
String input = BinaryStdIn.readString();
//构造编译表,存放每个字符串对应的编码,如st[A]=41,st[AB]=81,过程中逐渐构造出编译表
TST
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++)
st.put("" + (char) i, i);
int code = R+1; // 用于标记组合字符串的开始,开始code=81
//例如待压缩的字符串是input=ABRACADABRABRABRA,压缩流程如下
//从st中找出input的最长前缀A写入编码41,把A和下一个字母B组成AB编码成81存在符号表st中,input长度减1变成BRACADABRABRABRA
//从st中找出input的最长前缀B写入编码42,把B和下一个字母R组成BR编码成82存在符号表st中,input长度减1变成RACADABRABRABRA
//继续下去依次把RA,AC,CA,AD,DA加入st,input变成ABRABRABRA
//从st中找出input的最长前缀AB写入编码81,把AB和下一个字母R组成ABR编码成88存在符号表st中,input长度减2变成RABRABRA
//以此继续直到input的每个字符写完,最终编码成41,42,52,41,43,41,44,81,83,82,88,41,示意图如下:
while (input.length() > 0) {
String s = st.longestPrefixOf(input); // Find max prefix match s.
BinaryStdOut.write(st.get(s), W); // Print s's encoding.
int t = s.length();
if (t < input.length() && code < L) // Add s to symbol table.
st.put(input.substring(0, t + 1), code++);
input = input.substring(t); // Scan past s in input.
}
BinaryStdOut.write(R, W); //存R标记字符串的结束
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
//解压缩流程代码如下
//例如字符串ABRACADABRABRABRA的编码41,42,52,41,43,41,44,81,83,82,88,41的解码流程
//示意图如下
public static void expand() {
//逆编译表存放编码对应的字符串,如st[41]=A,st[81]=AB,过程中不断构造出逆编译表
String[] st = new String[L];
int i; // next available codeword value
// initialize symbol table with all 1-character strings
for (i = 0; i < R; i++)
st[i] = "" + (char) i;
st[i++] = ""; // (unused) lookahead for EOF
int codeword = BinaryStdIn.readInt(W); //首先读取41
if (codeword == R) return; // 已到文件结尾
//读取一个字符串
String val = st[codeword];
//i开始为R+1, while循环里先输出val=A,读取42,s=B, 设置st[81]=AB, val = B
//输出B,读取52,s=R, 设置st[82]=BR, val = R
//输出R,读取41,s=A, 设置st[83]=RA, val = A
//依次输出A,C,A,D,把AC,CA,AD,DA,加入st中,val=D
//读取81,s=AB, 设置st[83]=DA, val = AB
//输出AB,读取83,s=RA, 设置st[88]=ABR, val = RA
//直到所有字符读完
while (true) {
BinaryStdOut.write(val);
codeword = BinaryStdIn.readInt(W);
if (codeword == R) break;
String s = st[codeword];
if (i == codeword) s = val + val.charAt(0); // special case hack,当i == codeword时说明codeword还不在st中,通过设置s = val + val.charAt(0),正好可以修正s的值
if (i < L) st[i++] = val + s.charAt(0);
val = s;
}
BinaryStdOut.close();
}
}