css3新特性总览
css3新特性
css3选择器
| 选择器 | 示例 | 示例说明 |
|---|---|---|
| .class | .intro | 选择所有class="intro"的元素 |
| #id | #firstname | 选择所有id="firstname"的元素 |
| * | * | 选择所有元素 |
| element | p | 选择所有< p>元素 |
| element,element | div,p | 选择所有< div>元素和 < p>元素 |
| element element | div p | 选择< div>元素内的所有< p>元素 |
| element>element | div>p | 选择所有父级是 < div> 元素的 < p> 元素 |
| element+element | div+p | 选择所有紧接着< div>元素之后的< p>元素 |
| [attribute] | [target] | 选择所有带有target属性元素 |
| [attribute=value] | [target=-blank] | 选择所有使用target="-blank"的元素 |
| [attribute~=value] | [title~=flower] | 选择标题属性包含单词"flower"的所有元素 |
[attribute|=language] |
[lang | =en] |
选择一个lang属性的起始值="EN"的所有元素 |
| :link | a:link | 选择所有未访问链接 |
| :visited | a:visited | 选择所有访问过的链接 |
| :active | a:active | 选择活动链接 |
| :hover | a:hover | 选择鼠标在链接上面时 |
| :focus | input:focus | 选择具有焦点的输入元素 |
| :first-letter | p:first-letter | 选择每一个< P>元素的第一个字母 |
| :first-line | p:first-line | 选择每一个< P>元素的第一行 |
| :first-child | p:first-child | 指定只有当< p>元素是其父级的第一个子级的样式。 |
| :before | p:before | 在每个< p>元素之前插入内容 |
| :after | p:after | 在每个< p>元素之后插入内容 |
| :lang(language) | p:lang(it) | 选择一个lang属性的起始值="it"的所有< p>元素 |
| element1~element2 | p~ul | 选择p元素之后的每一个ul元素 |
| [attribute^=value] | a[src^=“https”] | 选择每一个src属性的值以"https"开头的元素 |
| [attribute$=value] | a[src$=".pdf"] | 选择每一个src属性的值以".pdf"结尾的元素 |
| [attribute*=value] | a[src*=“44lan”] | 选择每一个src属性的值包含子字符串"44lan"的元素 |
| :first-of-type | p:first-of-type | 选择每个p元素是其父级的第一个p元素 |
| :last-of-type | p:last-of-type | 选择每个p元素是其父级的最后一个p元素 |
| :only-of-type | p:only-of-type | 选择每个p元素是其父级的唯一p元素 |
| :only-child | p:only-child | 选择每个p元素是其父级的唯一子元素 |
| :nth-child(n) | p:nth-child(2) | 选择每个p元素是其父级的第二个子元素 |
| :nth-last-child(n) | p:nth-last-child(2) | 选择每个p元素的是其父级的第二个子元素,从最后一个子项计数 |
| :nth-of-type(n) | p:nth-of-type(2) | 选择每个p元素是其父级的第二个p元素 |
| :nth-last-of-type(n) | p:nth-last-of-type(2) | 选择每个p元素的是其父级的第二个p元素,从最后一个子项计数 |
| :last-child | p:last-child | 选择每个p元素是其父级的最后一个子级 |
| :root | :root | 选择文档的根元素 |
| :empty | p:empty | 选择每个没有任何子级的p元素(包括文本节点) |
| :target | #news:target | 选择当前活动的#news元素(包含该锚名称的点击的URL) |
| :enabled | input:enabled | 选择每一个已启用的输入元素 |
| :disabled | input:disabled | 选择每一个禁用的输入元素 |
| :checked | input:checked | 选择每个选中的输入元素 |
| :not(selector) | :not§ | 选择每个并非p元素的元素 |
| ::selection | ::selection | 匹配元素中被用户选中或处于高亮状态的部分 |
| :out-of-range | :out-of-range | 匹配值在指定区间之外的input元素 |
| :in-range | :in-range | 匹配值在指定区间之内的input元素 |
| :read-write | :read-write | 用于匹配可读及可写的元素 |
| :read-only | :read-only | 用于匹配设置 “readonly”(只读) 属性的元素 |
| :optional | :optional | 用于匹配可选的输入元素 |
| :required | :required | 用于匹配设置了 “required” 属性的元素 |
| :valid | :valid | 用于匹配输入值为合法的元素 |
| :invalid | :invalid | 用于匹配输入值为非法的元素 |
CSS3 边框(Borders)
用CSS3,可以创建圆角边框,添加阴影框,并作为边界的形象而不使用设计程序
| 属性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| border-image | 设置所有边框图像的速记属性 |
| border-radius | 一个用于设置所有四个边框- *-半径属性的速记属性 |
| box-shadow | 附加一个或多个下拉框的阴影 |
div{
width:60px;
color:greenyellow;
border:10px solid;
border-radius:25px;
box-shadow: 10px 10px 5px #888888;
}
CSS3 背景
CSS3中包含几个新的背景属性,提供更大背景元素控制。
| 顺序 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| background-clip | 规定背景的绘制区域 |
| background-origin | 规定背景图片的定位区域 |
| background-size | 规定背景图片的尺寸 |
div
{
height:300px;
width:400px;
background:url(2.jpg);
background-repeat:no-repeat;
background-size:100% 100%;
background-origin:content-box;
}
多背景
div
{
height:300px;
width:400px;
background-color: aqua;
background:url(1.jpg),url(2.jpg);
//当第一张背景图片可以找到就显示第一张背景图片,如果实现则会显示第二张背景图片
background-repeat:no-repeat;
background-size:100% 100%;
background-origin:content-box;
}
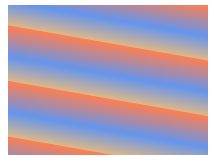
CSS3 渐变
CSS3 定义了两种类型的渐变(gradients):
线性渐变(Linear Gradients)- 向下/向上/向左/向右/对角方向
background: linear-gradient(direction, color-stop1, color-stop2, ...);
示例:
div
{
height: 150px;
width:200px;
background-color: coral ;/* 不支持线性的时候显示 */
background-image: linear-gradient(to bottom right, coral, greenyellow);
}
如果想要在渐变的方向上做更多的控制,可以定义一个角度,而不用预定义方向(to bottom、to top、to right、to left、to bottom right,等等)。
语法
background-image: linear-gradient(angle, color-stop1, color-stop2);
使用透明度(transparent)
CSS3 渐变也支持透明度(transparent),可用于创建减弱变淡的效果。
为了添加透明度,我们使用 rgba() 函数来定义颜色结点。rgba() 函数中的最后一个参数可以是从 0 到 1 的值,它定义了颜色的透明度:0 表示完全透明,1 表示完全不透明。
div
{
height: 150px;
width:200px;
background-image: linear-gradient(to right, rgba(255,0,0,0), rgba(255,0,0,1));
}
repeating-linear-gradient() 函数用于重复线性渐变:
div
{
height: 150px;
width:200px;
background-color: burlywood; /* 浏览器不支持的时候显示 */
background-image: repeating-linear-gradient(190deg,coral ,cornflowerblue 17%,burlywood 30%);
}
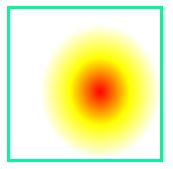
径向渐变(Radial Gradients)- 由它们的中心定义
background: radial-gradient(center, shape size, start-color, ..., last-color);
设置形状
shape 参数定义了形状。它可以是值 circle 或 ellipse。其中,circle 表示圆形,ellipse 表示椭圆形。默认值是 ellipse。
div
{
height: 150px;
width:200px;
background-image: radial-gradient(circle, mediumspringgreen, powderblue, greenyellow);
}
size 参数定义了渐变的大小。它可以是以下四个值:
- closest-side
- farthest-side
- closest-corner
- farthest-corner
div
{
height: 150px;
width: 150px;
color:mediumspringgreen;
border:3px solid;
background-color: red; /* 浏览器不支持的时候显示 */
background-image: radial-gradient(closest-side at 60% 55%, red, yellow, white);
}
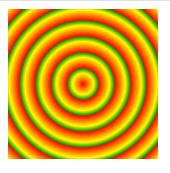
repeating-radial-gradient() 函数用于重复径向渐变:
div
{
height: 150px;
width: 150px;
background-image: repeating-radial-gradient(red, yellow 10%, green 15%);
}
CSS3 文本效果
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| hanging-punctuation | 规定标点字符是否位于线框之外 |
| punctuation-trim | 规定是否对标点字符进行修剪 |
| text-align-last | 设置如何对齐最后一行或紧挨着强制换行符之前的行 |
| text-emphasis | 向元素的文本应用重点标记以及重点标记的前景色 |
| text-justify | 规定当 text-align 设置为 “justify” 时所使用的对齐方法 |
| text-outline | 规定文本的轮廓 |
| text-overflow | 规定当文本溢出包含元素时发生的事情 |
| text-shadow | 向文本添加阴影 |
| text-wrap | 规定文本的换行规则 |
| word-break | 规定非中日韩文本的换行规则 |
| word-wrap | 允许对长的不可分割的单词进行分割并换行到下一行 |
CSS3 字体
以前CSS3的版本,网页设计师不得不使用用户计算机上已经安装的字体。使用CSS3,网页设计师可以使用他/她喜欢的任何字体。当你发现您要使用的字体文件时,只需简单的将字体文件包含在网站中,它会自动下载给需要的用户。所选择的字体在新的CSS3版本有关于@font-face规则描述。"自己的"的字体是在 CSS3 @font-face 规则中定义的。
<style>
@font-face{
font-family: Cx;
src: url(../Font/Cx/Cx.ttf);
}
div
{
font-family:Cx;
}
</style>
css3动画
要创建CSS3动画,你需要了解@keyframes规则。@keyframes规则是创建动画。 @keyframes规则内指定一个CSS样式和动画将逐步从目前的样式更改为新的样式。
@keyframes 规则和所有动画属性:
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @keyframes | 规定动画 |
| animation | 所有动画属性的简写属性,除了 animation-play-state 属性 |
| animation-name | 规定 @keyframes 动画的名称 |
| animation-duration | 规定动画完成一个周期所花费的秒或毫秒。默认是 0 |
| animation-timing-function | 规定动画的速度曲线。默认是 “ease” |
| animation-fill-mode | 规定当动画不播放时(当动画完成时,或当动画有一个延迟未开始播放时),要应用到元素的样式 |
| animation-delay | 规定动画何时开始。默认是 0 |
| animation-iteration-count | 规定动画被播放的次数。默认是 1 |
| animation-direction | 规定动画是否在下一周期逆向地播放。默认是 “normal” |
| animation-play-state | 规定动画是否正在运行或暂停。默认是 “running” |
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>动画实例</title>
<style>
div
{
width:100px;
height:100px;
background:red;
position:relative;
//方法一
animation-name: myfirst;
animation-duration: 5s;
animation-timing-function: linear;
animation-delay: 2s;
animation-iteration-count: infinite;
animation-direction: alternate;
animation-play-state: running;
/* Safari 与 Chrome: */
-webkit-animation-name: myfirst;
-webkit-animation-duration: 5s;
-webkit-animation-timing-function: linear;
-webkit-animation-delay: 2s;
-webkit-animation-iteration-count: infinite;
-webkit-animation-direction: alternate;
-webkit-animation-play-state: running;
//方法二
animation:myfirst 5s linear 2s infinite alternate;
/* Firefox: */
-moz-animation:myfirst 5s linear 2s infinite alternate;
/* Safari and Chrome: */
-webkit-animation:myfirst 5s linear 2s infinite alternate;
/* Opera: */
-o-animation:myfirst 5s linear 2s infinite alternate;
}
@keyframes myfirst
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
@-moz-keyframes myfirst /* Firefox */
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
@-webkit-keyframes myfirst /* Safari and Chrome */
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
@-o-keyframes myfirst /* Opera */
{
0% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
25% {background:yellow; left:200px; top:0px;}
50% {background:blue; left:200px; top:200px;}
75% {background:green; left:0px; top:200px;}
100% {background:red; left:0px; top:0px;}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
CSS3 多列
CSS3 多列属性:
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| column-count | 指定元素应该被分割的列数 |
| column-fill | 指定如何填充列 |
| column-gap | 指定列与列之间的间隙 |
| column-rule-color | 指定两列间边框的颜色 |
| column-rule-style | 指定两列间边框的样式 |
| column-rule-width | 指定两列间边框的厚度 |
| column-span | 指定元素要跨越多少列 |
| column-width | 指定列的宽度 |
| columns | 设置 column-width 和 column-count 的简写 |
| column-rule | 所有 column-rule-* 属性的简写 |
CSS3 盒模型
在 CSS3 中, 增加了一些新的用户界面特性来调整元素尺寸,框尺寸和外边框,主要包括以下用户界面属性:
- resize:none | both | horizontal | vertical | inherit
- box-sizing: content-box | border-box | inherit
- outline:outline-color outline-style outline-width outine-offset
resize属性指定一个元素是否应该由用户去调整大小。
box-sizing 属性允许以确切的方式定义适应某个区域的具体内容。
outline-offset 属性对轮廓进行偏移,并在超出边框边缘的位置绘制轮廓。
CSS3伸缩布局盒模型(弹性盒)
CSS3 弹性盒( Flexible Box 或 flexbox),是一种当页面需要适应不同的屏幕大小以及设备类型时确保元素拥有恰当的行为的布局方式。
引入弹性盒布局模型的目的是提供一种更加有效的方式来对一个容器中的子元素进行排列、对齐和分配空白空间。
下表列出了在弹性盒子中常用到的属性:
| 属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| display | 指定 HTML 元素盒子类型 |
| flex-direction | 指定了弹性容器中子元素的排列方式 |
| justify-content | 设置弹性盒子元素在主轴(横轴)方向上的对齐方式 |
| align-items | 设置弹性盒子元素在侧轴(纵轴)方向上的对齐方式 |
| flex-wrap | 设置弹性盒子的子元素超出父容器时是否换行 |
| align-content | 修改 flex-wrap 属性的行为,类似 align-items, 但不是设置子元素对齐,而是设置行对齐 |
| flex-flow | flex-direction 和 flex-wrap 的简写 |
| order | 设置弹性盒子的子元素排列顺序 |
| align-self | 在弹性子元素上使用。覆盖容器的 align-items 属性 |
| flex | 设置弹性盒子的子元素如何分配空间 |
CSS3 多媒体查询
从 CSS 版本 2 开始,就可以通过媒体类型在 CSS 中获得媒体支持。如果您曾经使用过打印样式表,那么您可能已经使用过媒体类型。清单 1 展示了一个示例。
使用媒体类型
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="site.css" media="screen" />
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="print.css" media="print" />
媒体查询规则
@media all and (min-width: 800px) { ... }
@media all 是媒体类型,也就是说,将此 CSS 应用于所有媒体类型。
(min-width:800px) 是包含媒体查询的表达式,如果浏览器的最小宽度为 800 像素,则会告诉浏览器只运用下列 CSS。
and 条件
@media (min-width:800px) and (max-width:1200px) and (orientation:portrait) { ... }
or 关键词
@media (min-width:800px) or (orientation:portrait) { ... }
使用 not
@media (not min-width:800px) { ... }
CSS 多媒体查询,适配各种设备尺寸
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title>CSS 多媒体查询,适配各种设备尺寸</title>
<style>
.example {
padding: 20px;
color: white;
}
/* Extra small devices (phones, 600px and down) */
@media only screen and (max-width: 600px) {
.example {background: red;}
}
/* Small devices (portrait tablets and large phones, 600px and up) */
@media only screen and (min-width: 600px) {
.example {background: green;}
}
/* Medium devices (landscape tablets, 768px and up) */
@media only screen and (min-width: 768px) {
.example {background: blue;}
}
/* Large devices (laptops/desktops, 992px and up) */
@media only screen and (min-width: 992px) {
.example {background: orange;}
}
/* Extra large devices (large laptops and desktops, 1200px and up) */
@media only screen and (min-width: 1200px) {
.example {background: pink;}
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<h2>响应式判断</h2>
<p class="example">操作浏览器窗口,查看效果。</p>
</body>
</html>
参考原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/star91/p/5659134.html