C# 普通字典、并发字典(ConCurrent)和HashTable读写性能比较
C# 普通字典、并发字典(ConCurrent)和HashTable读写性能比较
最近在做程序效率改进,加快检查程序检查时间,所以有时候不得不考虑改用效率更高的容器,以减少程序运行时间。参考了一篇文章(点击可查看原文),在此基础上,我进行了修改,添加了对类的读取和写入以及HashTable。
程序有时候需要并发多线程操作,多线程读取同一个容器内的东西是可以的,但是如果需要修改及写入到同一容器内,会有索引失败的问题,即两个进程同时向同一个位置写入内容,这种情况下需要通过lock(var),将容器锁定,也可以直接使用可并发读写的容器,如ConCurrentDictionary。
于是,测试分2部分,一次是写入操作,包含带锁写入和不带锁写入,其中每个里面又细分为写入字符串和写入一个类,还有一次是遍历操作,同样包含带锁读和不带锁读,其中也分为读取字符串和读取类。
测试结果:
比较普通字典、并发字典和HashTable效率,用10000000数据做测试,时间单位为毫秒。
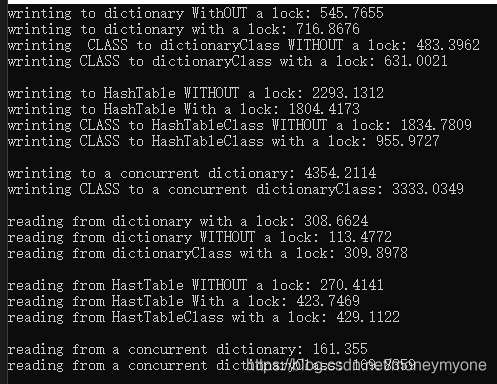
- 对于写入操作速度:普通词典 > HashTable > 并发词典
- 对于读操作速度:并发字典 > 带锁字典 > HashTable
- 无论普通字典还是HashTable,带锁花费的时间都要比不带锁慢,为了线程安全,肯定要牺牲时间的。
所以如果需要自己写入的话,推荐带锁普通字典,读写速度都很均衡。
原文作者解释:
concurrentDictionary采用细粒度锁定[fine-grained locking]
普通带锁dictionary采用粗粒度锁定[coarse-grained locking]
在多核多线程的情况下concurrentDictionary将有更好的性能表现
实验代码如下:
class Program
{
public class student
{
public string name;
public int age;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var concurrentDictionary = new ConcurrentDictionary<int, string>();
var concurrentDictionaryClass = new ConcurrentDictionary<int, student>();
var dictionary = new Dictionary<int, string>();
var dictionaryClass = new Dictionary<int, student>();
Hashtable ht = new Hashtable();
Hashtable htClass = new Hashtable();
string CurrentItem = "";
student stu = new student { name = Item, age = 333 };
var sw = new Stopwatch();
//写入字典 无锁
sw.Start();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
dictionary[i] = Item;
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("wrinting to dictionary WithOUT a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//写入字典 带锁
dictionary = new Dictionary<int, string>();
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
lock (dictionary)
{
dictionary[i] = Item;
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("wrinting to dictionary with a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//类写入字典 无锁
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
dictionaryClass[i] = stu;
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("wrinting CLASS to dictionaryClass WITHOUT a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//类写入字典 带锁
dictionaryClass = new Dictionary<int, student>();
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
lock (dictionaryClass)
{
dictionaryClass[i] = stu;
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("wrinting CLASS to dictionaryClass with a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
Console.WriteLine("");
// 字符串写入HashTable 无锁
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
ht[i] = Item;
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("wrinting to HashTable WITHOUT a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//字符串写入HashTable 有锁
ht = new Hashtable();
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
lock (ht)
{
ht[i] = Item;
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("wrinting to HashTable With a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//类写入HashTable 无锁
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
htClass[i] = stu;
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("wrinting CLASS to HashTableClass WITHOUT a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//类写入HashTable 有锁
htClass.Clear();
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
lock (htClass)
{
htClass[i] = stu;
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("wrinting CLASS to HashTableClass with a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
Console.WriteLine("");
//字符串写入ConcurrentDictionary
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
concurrentDictionary[i] = Item;
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("wrinting to a concurrent dictionary: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//类写入ConcurrentDictionary
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
concurrentDictionaryClass[i] = stu;
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("wrinting CLASS to a concurrent dictionaryClass: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
Console.WriteLine("");
//对于写入操作并发词典要比普通带锁词典要慢
//遍历普通字典 有锁
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
lock (dictionary)
{
CurrentItem = dictionary[i];
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("reading from dictionary with a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//遍历普通字典 无锁
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
CurrentItem = dictionary[i];
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("reading from dictionary WITHOUT a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
student CurrentStu = new student();
//遍历普通字典(类) 有锁
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
lock (dictionaryClass)
{
CurrentStu = dictionaryClass[i];
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("reading from dictionaryClass with a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
Console.WriteLine("");
//遍历HashTable 无锁
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
CurrentItem = ht[i].ToString();
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("reading from HastTable WITHOUT a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//遍历HashTable 有锁
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
lock (ht)
{
CurrentItem = ht[i].ToString();
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("reading from HastTable With a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//遍历HashTable(类) 有锁
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
lock (htClass)
{
CurrentStu = (student)htClass[i];
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("reading from HastTableClass with a lock: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
Console.WriteLine("");
//遍历ConCurrent字典
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
CurrentItem = concurrentDictionary[i];
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("reading from a concurrent dictionary: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//遍历ConCurrent字典(类)
sw.Restart();
for (int i = 0; i < 10000000; i++)
{
CurrentStu = concurrentDictionaryClass[i];
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("reading from a concurrent dictionaryClass: {0}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds);
//reading from a concurrent dictionary: 00:00:00.0196372
//对于读取操作并发词典要比普通带锁词典要快
//concurrentDictionary采用细粒度锁定[fine-grained locking]
//普通带锁dictionary采用粗粒度锁定[coarse-grained locking]
//在多核多线程的情况下concurrentDictionary将有更好的性能表现
sw.Restart();
Console.ReadKey();
}
const string Item = "Dictionary item";
}
以上。



