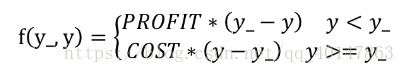TensorFlow笔记-06-神经网络优化-损失函数,自定义损失函数,交叉熵
TensorFlow笔记-06-神经网络优化-损失函数,自定义损失函数,交叉熵
- 神经元模型:用数学公式比表示为:f(Σi xi*wi + b), f为激活函数
- 神经网络 是以神经元为基本单位构成的
- 激活函数:引入非线性激活因素,提高模型的表达能力
常用的激活函数有relu、sigmoid、tanh等 - (1)激活函数relu:在Tensorflow中,用tf.nn.relu()表示

- (2)激活函数sigmoid:在Tensorflow中,用tf.nn.sigmoid()表示

- (3)激活函数tanh:在Tensorflow中,用tf.nn.tanh()表示

- 神经网络的复杂度:可用神经网络的的层数和神经网络中待优化参数个数表示
- 神经网络的层数:一般不计入输入层,层数 = n个隐藏层 + 1个输入层
- 神经网络待优化的参数:神经网络中所有参数w的个数 + 所有参数b的个数
- 例如:

在该神经网络中,包含1个输入层,1个隐藏层和1个输出层,该神经网络的参数为2层
在该神经网络中,参数的个数是所有参数w的个数加上所有参数b的总数,第一层参数用三行四列的二阶张量表示(即12个线上的权重w)再加上4个偏置b;第二层参数是四行二列的二阶张量(即8个线上的权重w)再加上2个偏置b
总参数 = 34+4 + 42+2 = 26
损失函数
- 损失函数(loss):用来表示预测(y)与已知答案(y_)的差距。在训练神经网络时,通过不断改变神经网络中所有参数,使损失函数不断减小,从而训练出更高准确率的神经网络模型
- 常用的损失函数有均方误差,自定义和交叉熵等
- 均方误差mse:n个样本的预测值(y)与(y_)的差距。在训练神经网络时,通过不断的改变神经网络中的所有参数,使损失函数不断减小,从而训练出更高准确率的神经网络模型
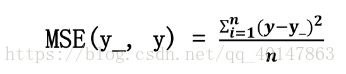
- 在Tensorflow中用loss_mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_-y))
- 例如:
- 预测酸奶日销量y,x1和x2是两个影响日销量的因素
- 应提前采集的数据有:一段时间内,每日的x1因素、x2因素和销量y_。且数据尽量多
- 在本例子中用销量预测产量,最优的产量应该等于销量,由于目前没有数据集,所以拟造了一套数据集。利用Tensorflow中函数随机生成x1、x2,制造标准答案y_ = x1 + x2,为了真实,求和后还加了正负0.05的随机噪声
- 我们把这套自制的数据集喂入神经网络,构建一个一层的神经网络,拟合预测酸奶日销量的函数
- 代码tf07sale文件:https://xpwi.github.io/py/TensorFlow/tf07sale.py
# coding:utf-8
# 预测多或者预测少的影响一样
# 导入模块,生成数据集
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 一次喂入神经网络8组数据,数值不可以过大
BATCH_SIZE = 8
SEED = 23455
# 基于seed产生随机数
rdm = np.random.RandomState(SEED)
# 随机数返回32行2列的矩阵 表示32组 体积和重量 作为输入数据集
X = rdm.rand(32, 2)
Y_ = [[x1+x2+(rdm.rand()/10.0-0.05)] for (x1, x2) in X]
print("X:\n", X)
print("Y:\n", Y_)
# 定义神经网络的输入,参数和输出,定义前向传播过程
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 2))
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 1))
# w1为2行1列
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 1], stddev=1, seed=1))
y = tf.matmul(x, w1)
# 定义损失函数及反向传播方法
# 定义损失函数为MSE,反向传播方法为梯度下降
loss_mse = tf.reduce_mean(tf.square(y_-y))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss_mse)
# 其他优化方法
# train_step = tf.train.GMomentumOptimizer(0.001, 0.9).minimize(loss_mse)
# train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss_mse)
# 生成会话,训练STEPS轮
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
# 训练模型20000轮
STEPS = 20000
for i in range(STEPS):
start = (i*BATCH_SIZE) % 32
end = start + BATCH_SIZE
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: X[start:end], y_: Y_[start:end]})
# 没500轮打印一次loss值
if i % 1000 == 0:
total_loss = sess.run(loss_mse, feed_dict={x: X, y_: Y_})
print("After %d training step(s), loss on all data is %g" %(i, total_loss))
print(sess.run(w1),"\n")
print("Final w1 is: \n", sess.run(w1))
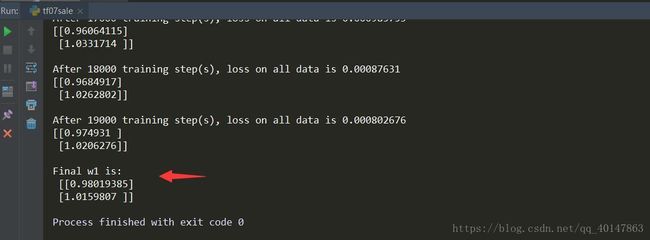
运行结果
结果分析
有上述代码可知,本例中神经网络预测模型为y = w1x1 + w2x2,损失函数采用均方误差。通过使损失函数值(loss)不断降低,神经网络模型得到最终参数w1 = 0.98,w2 = 1.02,销量预测结果为y = 0.98x1 + 1.02x2。由于在生成数据集时,标准答案为y = x1 + x2,因此,销量预测结果和标准答案已经非常接近,说明该神经网络预测酸奶日销量正确
自定义损失函数
- 自定义损失函数:根据问题的实际情况,定制合理的损失函数
- 例如:
用Tensorflow函数表示为:
- loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.where(tf.greater(y, y_), COST*(y-y_), PROFIT*(y_-y)))
(1)第1种情况:若酸奶成本为1元,酸奶销售利润为9元,则制造成本小于酸奶利润,因此希望预测结果y多一些。采用上述的自定义损失函数,训练神经网络模型
- 代码tf07sale2文件:https://xpwi.github.io/py/TensorFlow/tf07sale2.py
# 第一种情况:酸奶成本1元,酸奶利润9元
# 预测少了损失大,故不要预测少,故生成的模型会多预测一些
# 导入模块,生成数据集
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 一次喂入神经网络8组数据,数值不可以过大
BATCH_SIZE = 8
SEED = 23455
COST = 1
PROFIT = 9
# 基于seed产生随机数
rdm = np.random.RandomState(SEED)
# 随机数返回32行2列的矩阵 表示32组 体积和重量 作为输入数据集
X = rdm.rand(32, 2)
Y_ = [[x1+x2+(rdm.rand()/10.0-0.05)] for (x1, x2) in X]
# 定义神经网络的输入,参数和输出,定义前向传播过程
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 2))
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 1))
# w1为2行1列
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 1], stddev=1, seed=1))
y = tf.matmul(x, w1)
# 定义损失函数及反向传播方法
# 定义损失函数使得预测少了的损失大,于是模型应该偏向多的放心预测
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.where(tf.greater(y, y_), COST*(y-y_), PROFIT*(y_-y)))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss)
# 其他优化方法
# train_step = tf.train.GMomentumOptimizer(0.001, 0.9).minimize(loss)
# train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss)
# 生成会话,训练STEPS轮
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
# 训练模型20000轮
STEPS = 20000
for i in range(STEPS):
start = (i*BATCH_SIZE) % 32
end = start + BATCH_SIZE
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: X[start:end], y_: Y_[start:end]})
# 没500轮打印一次loss值
if i % 1000 == 0:
total_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x: X, y_: Y_})
print("After %d training step(s), loss on all data is %g" %(i, total_loss))
print(sess.run(w1),"\n")
print("Final w1 is: \n", sess.run(w1))
运行结果
运行结果分析
由代码执行结果可知,神经网络最终参数为w1=1.03,w2=1.05,销量预测结果为y = 1.03x1 + 1.05x2。由此可见,采用自定义损失函数预测的结果大于采用均方误差的结果,更符合实际需求
(2)第2种情况:若酸奶成本为9元,酸奶销售利润为1元,则制造利润小于酸奶成本,因此希望预测结果y小一些。采用上述的自定义损失函数,训练神经网络模型
- 代码tf07sale3文件:https://xpwi.github.io/py/TensorFlow/tf07sale3.py
# 第二种情况:酸奶成本9元,酸奶利润1元
# 预测多了损失大,故不要预测多,故生成的模型会少预测一些
# 导入模块,生成数据集
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 一次喂入神经网络8组数据,数值不可以过大
BATCH_SIZE = 8
SEED = 23455
COST = 9
PROFIT = 1
# 基于seed产生随机数
rdm = np.random.RandomState(SEED)
# 随机数返回32行2列的矩阵 表示32组 体积和重量 作为输入数据集
X = rdm.rand(32, 2)
Y_ = [[x1+x2+(rdm.rand()/10.0-0.05)] for (x1, x2) in X]
# 定义神经网络的输入,参数和输出,定义前向传播过程
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 2))
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None, 1))
# w1为2行1列
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, 1], stddev=1, seed=1))
y = tf.matmul(x, w1)
# 定义损失函数及反向传播方法
# 重新定义损失函数使得预测多了的损失大,于是模型应该偏向少的方向预测
loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.where(tf.greater(y, y_), COST*(y-y_), PROFIT*(y_-y)))
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss)
# 其他优化方法
# train_step = tf.train.GMomentumOptimizer(0.001, 0.9).minimize(loss)
# train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(0.001).minimize(loss)
# 生成会话,训练STEPS轮
with tf.Session() as sess:
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
# 训练模型20000轮
STEPS = 20000
for i in range(STEPS):
start = (i*BATCH_SIZE) % 32
end = start + BATCH_SIZE
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: X[start:end], y_: Y_[start:end]})
# 没500轮打印一次loss值
if i % 1000 == 0:
total_loss = sess.run(loss, feed_dict={x: X, y_: Y_})
print("After %d training step(s), loss on all data is %g" %(i, total_loss))
print(sess.run(w1),"\n")
print("Final w1 is: \n", sess.run(w1))
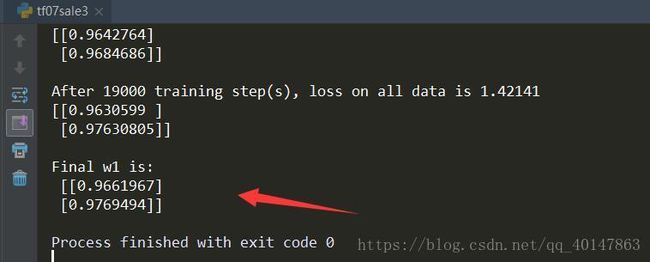
运行结果
运行结果分析
由执行结果可知,神经网络最终参数为w1 = 0.96,w2 = 0.97,销量预测结果为y = 0.96+x1 + 0.7*x2。
因此,采用自定义损失函数预测的结果小于采用均方误差预测得结果,更符合实际需求
交叉熵
- 交叉熵(Cross Entropy):表示两个概率分布之间的距离,交叉熵越大,两个概率分布距离越远,两个概率分布越相异;交叉熵越小,两个概率分布距离越近,两个概率分布越相似
- 交叉熵计算公式:H(y_, y) = -Σy_ * log y
- 用 Tensorflow 函数表示
ce = -tf.reduce_mean(y_*tf.clip_by_value(y, le-12, 1.0)))
- 例如:
两个神经网络模型解决二分类问题中,已知标准答案为 y_ = (1, 0),第一个神经网络模型预测结果为 y1 = (0.6, 0.4),第二个神经网络模型预测结果为 y2 = (0.8, 0.2),判断哪个神经网络模型预测得结果更接近标准答案 - 根据交叉熵的计算公式得:
H(1, 0), (0.6, 0.4) = -(1 * log0.6 + 0log0.4) ≈ -(-0.222 + 0) = 0.222
H(1, 0), (0.8, 0.2) = -(1 * log0.8 + 0log0.2) ≈ -(-0.097 + 0) = 0.097
softmax 函数
- **softmax 函数:将 n 分类中的 n 个输出(y1, y2…yn)变为满足以下概率分布要求的函数: **
∀x = P(X = x) ∈ [0, 1] - softmax 函数表示为:

- softmax 函数应用:在 n 分类中,模型会有 n 个输出,即 y1,y2 … n, 其中yi表示第 i 中情况出现的可能性大小。将 n 个输出经过 softmax 函数,可得到符合概率分布的分类结果
- 在 Tensorflow 中,一般让模型的输出经过 softmax 函数,以获得输出分类的概率分布再与标准答案对比,求出交叉熵,得到损失函数,用如下函数实现:
ce = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = y, labels = tf.argmax(y_, 1))
cem = tf.reduce_mean(ce)
更多文章链接:Tensorflow 笔记
- 本笔记不允许任何个人和组织转载