Android 标题背景渐变
有些应用上面的标题的背景色默认的是全透明的,也就是以背景图片来作为背景色。然后随着ListView的滑动标题的背景色会有全透明慢慢的变为和背景图一样的颜色。以图为证:
上面的效果图想必大家并不陌生,我们手机上面的一些应用就有。那么这个效果是怎么实现的呢?其实这个效果就是一个自定义的ScrollView,其中要重写里面的onScrollChanged这个方法,
protected void onScrollChanged(int l, int t, int oldl, int oldt) {
throw new RuntimeException("Stub!");
}int l, int t, int oldl, int oldt分别是left、top、oldLeft、oldTop。也就是左,上,上次的左,上次的上。怎么说呢,就是屏幕的原点也就是ScrollVIew的原点为(left,top)默认的初始值为(0,0)这点应该很好懂吧。为什么要重写这个方法呢?看到onScrollChanged这个方法名我们应该就能知道这是一个监听关于ScrollVIew滑动时发生变化的方法。 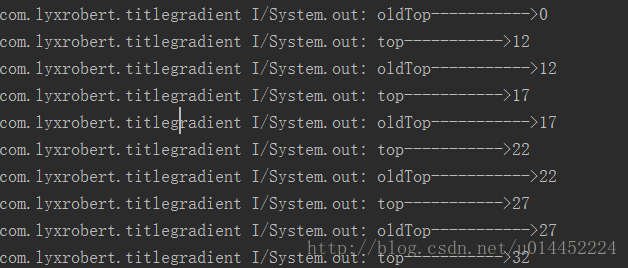
看到打印出来的日志也许你就会知道这些参数的意义了。left为什么不打印,是因为我们实现的是ScrollVIew的上下滑动而不是左右滑动,所以就没有必要打印left了。
要想实现上面的标题渐变的效果,我们需要测量出标题背景图的高度,当ScrollVIew未滑动的时候,标题的背景色是全透明的,也就是alpha值为0。当我们开始滑动的时候,我们的alpha的值=top/背景图的高度,当我们向上滑动的ScrollVIew的距离大于标题的背景图的高度时,此时的标题背景色是普通的背景色也就是我们背景图的颜色。
@Override
public void onScrollChanged(CustomScrollView scrollView, int left, int top, int oldLeft, int oldTop) {
if (top <= 0) {
ll_title.setBackgroundColor(Color.argb(0, 74,204,185));
} else if (top > 0 && top <= bgHeight) {
float scale = (float) top / bgHeight;
float alpha = (255 * scale);
ll_title.setBackgroundColor(Color.argb((int) alpha, 74,204,185));
} else {
ll_title.setBackgroundColor(Color.argb(255, 74,204,185));
}
}我们都知道在onCreate()里面获取控件的高度是0,这是为什么呢?
12-08 14:43:25.691 29095-29095/com.lyxrobert.titlegradient I/System.out: onCreate----->
12-08 14:43:34.791 29095-29095/com.lyxrobert.titlegradient I/System.out: onMeasure----->
12-08 14:43:34.801 29095-29095/com.lyxrobert.titlegradient I/System.out: onMeasure----->对比一下时间你就会发现,原来onCreate的执行的要比onMeasure要早。就是控件还没有测量具体的宽高的时候onCreate就已经执行了。这也是为什么我们在onCreate方法里面获取不到控件宽高度的原因。那么我们既然在onCreate里面获取不到控件的宽高怎么办呢?所以现在需要使用getViewTreeObserver().addOnGlobalLayoutListener()来获得宽度或者高度。这是获得一个view的宽度和高度的方法之一。
OnGlobalLayoutListener 是ViewTreeObserver的内部类,当一个视图树的布局发生改变时,可以被ViewTreeObserver监听到,这是一个注册监听视图树的观察者(observer),在视图树的全局事件改变时得到通知。ViewTreeObserver不能直接实例化,而是通过getViewTreeObserver()获得。
ViewTreeObserver vto = rel_title_bg.getViewTreeObserver();
vto.addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
ll_title.getViewTreeObserver().removeGlobalOnLayoutListener(
this);
bgHeight = rel_title_bg.getHeight();
}
});还有就是ScrollView嵌套ListView的时候会产生ListView只显示一条的效果,这个问题怎么解决呢?有两种办法。一种是测量ListView的Item的高度,根据ListView的实际高度=Item的高度*Item的总条数+Item之间的空间得到ListView的高度。
TestAdp adp = new TestAdp(this,list);
lv_title.setAdapter(adp);
adp.notifyDataSetChanged();
int totalHeight = 0;
int size = 0;
size = adp.getCount();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
View listItem = adp
.getView(i, null, lv_title);
listItem.measure(0, 0);
totalHeight += listItem.getMeasuredHeight();
}
ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = lv_title
.getLayoutParams();
params.height = totalHeight
+ (lv_title.getDividerHeight() * (lv_title
.getCount()));
lv_title.setLayoutParams(params);另外一种就是自定义一个ListView,然后重写里面的onMeasure方法
@Override
public void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int expandSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(Integer.MAX_VALUE >> 2,
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, expandSpec);
}至于为什么要设置为Integer.MAX_VALUE >> 2,为什么要右移两位,因为Integer.MAX_VALUE 的前两位是mode,向右移两位得到的就是高度或宽度值了。MeasureSpec.AT_MOST当模式为MeasureSpec.AT_MOST时则意味着控件大小一般随着控件的子空间或内容进行变化,此时控件尺寸只要不超过父控件允许的最大尺寸即可,我们经常使用的wrap_content就是这种模式。如果还不明白请点击前往自定义控件
还有一点就是,如果ScrollView里面嵌套ListView很容易产生ListView因获取焦点而导致打开页面的时候ListView的第一条显示在屏幕的原点,也就是说ScrollView的原点默认的不是屏幕原点,也就是下图的情况 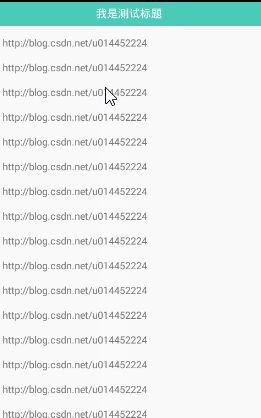
这是为什么呢?CustomScrollView 继承ScrollView继承FrameLayout 继承ViewGroup,而CustomListView 继承ListView继承AbsListView继承AdapterView继承ViewGroup。我们都知道子控件抢占父控件的焦点,而我们自定义的ListView又包含在自定义的ScrollView里面,这也就说明了这个问题。如何解决呢?很简单,就是让子空间默认不获取焦点即可。也就是设置为setFocusable(false);
不多说了看代码
MainActivity.class
package com.lyxrobert.titlegradient;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.ViewTreeObserver;
import android.widget.LinearLayout;
import android.widget.RelativeLayout;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MainActivity extends Activity implements CustomScrollView.ScrollChangedListener{
private CustomScrollView tsv_title;
private CustomListView lv_title;
private LinearLayout ll_title;
private RelativeLayout rel_title_bg;
private int bgHeight;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
initView();
initEvent();
initData();
}
private void initView() {
tsv_title = (CustomScrollView) findViewById(R.id.tsv_title);
lv_title = (CustomListView) findViewById(R.id.lv_title);
lv_title.setFocusable(false);
ll_title = (LinearLayout) findViewById(R.id.ll_title);
rel_title_bg = (RelativeLayout) findViewById(R.id.rel_title_bg);
}
private void initEvent() {
ViewTreeObserver vto = rel_title_bg.getViewTreeObserver();
vto.addOnGlobalLayoutListener(new ViewTreeObserver.OnGlobalLayoutListener() {
@Override
public void onGlobalLayout() {
ll_title.getViewTreeObserver().removeGlobalOnLayoutListener(
this);
bgHeight = rel_title_bg.getHeight();
}
});
tsv_title.setOnScrollChanged(this);
}
private void initData() {
List list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i =0;i<30;i++){
list.add("http://blog.csdn.net/u014452224");
}
TestAdp adp = new TestAdp(this,list);
lv_title.setAdapter(adp);
adp.notifyDataSetChanged();
}
@Override
public void onScrollChanged(CustomScrollView scrollView, int left, int top, int oldLeft, int oldTop) {
if (top <= 0) {
ll_title.setBackgroundColor(Color.argb(0, 74,204,185));
} else if (top > 0 && top <= bgHeight) {
float scale = (float) top / bgHeight;
float alpha = (255 * scale);
ll_title.setBackgroundColor(Color.argb((int) alpha, 74,204,185));
} else {
ll_title.setBackgroundColor(Color.argb(255, 74,204,185));
}
}
} 自定义ScrollView
package com.lyxrobert.titlegradient;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.ScrollView;
public class CustomScrollView extends ScrollView {
public interface ScrollChangedListener {
void onScrollChanged(CustomScrollView scrollView, int left, int top, int oldLeft, int oldTop);
}
private ScrollChangedListener scrollChangedListener = null;
public CustomScrollView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public CustomScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs,
int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
public CustomScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public void setOnScrollChanged(ScrollChangedListener scrollChangedListener) {
this.scrollChangedListener = scrollChangedListener;
}
@Override
protected void onScrollChanged(int left, int top, int oldLeft, int oldTop) {
super.onScrollChanged(left, top, oldLeft, oldTop);
if (scrollChangedListener != null) {
scrollChangedListener.onScrollChanged(this, left, top, oldLeft, oldTop);
}
}
}自定义ListView
package com.lyxrobert.titlegradient;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.widget.ListView;
public class CustomListView extends ListView {
public CustomListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public CustomListView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public CustomListView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
}
@Override
public void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int expandSpec = MeasureSpec.makeMeasureSpec(Integer.MAX_VALUE >> 2,
MeasureSpec.AT_MOST);
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, expandSpec);
}
}
Adapter类
package com.lyxrobert.titlegradient;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.TextView;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Created by ytx on 2016/12/8.
*/
public class TestAdp extends BaseAdapter {
private Context mContext;
private List mList;
public TestAdp(Context context, List list) {
this.mContext = context;
this.mList = list;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
return mList!=null?mList.size():0;
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
return mList.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
return position;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup viewGroup) {
ViewHolder viewHolder;
if (convertView ==null){
convertView = LayoutInflater.from(mContext).inflate(R.layout.item_test,null);
viewHolder = new ViewHolder();
viewHolder.tv_test = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.tv_test);
convertView.setTag(viewHolder);
}else {
viewHolder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
viewHolder.tv_test.setText(mList.get(position));
return convertView;
}
class ViewHolder{
TextView tv_test;
}
}
布局
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
>
<com.lyxrobert.titlegradient.CustomScrollView
android:id="@+id/tsv_title"
android:scrollbars="none"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<RelativeLayout
android:id="@+id/rel_title_bg"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@drawable/icon_title_bg">
RelativeLayout>
<com.lyxrobert.titlegradient.CustomListView
android:id="@+id/lv_title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
com.lyxrobert.titlegradient.CustomListView>
LinearLayout>
com.lyxrobert.titlegradient.CustomScrollView>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/ll_title"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<TextView
android:text="我是测试标题"
android:textSize="20dp"
android:padding="10dp"
android:textColor="#FFF"
android:gravity="center"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
LinearLayout>
RelativeLayout>
