JAVA学习之GUI(上篇)
一、基础
GUI:Graphics User Interface 图形用户界面
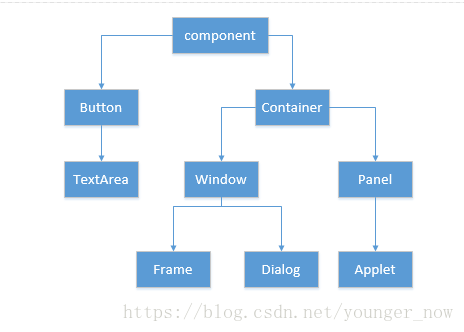
(1)Component:例如按钮,下拉框
(2)Component必须放在Container中才能显现出来
(3)Container是Component的子类,可以容纳别的Component对象
(4)Container可以使用add()添加其他Component对象
(5)Container可以容纳Container
(6)两种常用Container
Window:自由停泊的顶级窗口
Panel:可以容纳其他Component,不能独立存在,必须添加在其他Container中(如Window,Applet)
Frame:有一些方法可以设置窗口
GUI:Graphics User Interface 图形用户界面
(1)Component:例如按钮,下拉框
(2)Component必须放在Container中才能显现出来
(3)Container是Component的子类,可以容纳别的Component对象
(4)Container可以使用add()添加其他Component对象
(5)Container可以容纳Container
(6)两种常用Container
Window:自由停泊的顶级窗口
Panel:可以容纳其他Component,不能独立存在,必须添加在其他Container中(如Window,Applet)
Frame:有一些方法可以设置窗口
Panel:可以添加到Frame
结构图:
简单示例:
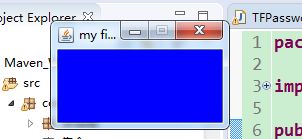
Frame1:
public class TestFrame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame f = new Frame("my first title");
f.setBackground(Color.blue);
f.setVisible(true);
f.setSize(170, 100);
f.setLocation(100, 100);
f.setResizable(false);
}
}运行结果:
Frame2:
public class TestMultiFrame {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyFrame myFrame1 = new MyFrame(100, 100, 200, 200, Color.blue);
MyFrame myFrame2 = new MyFrame(300, 100, 200, 200, Color.yellow);
MyFrame myFrame3 = new MyFrame(100, 300, 200, 200, Color.GREEN);
MyFrame myFrame4 = new MyFrame(300, 300, 200, 200, Color.magenta);
}
}
class MyFrame extends Frame{
static int id = 0;
public MyFrame(int x,int y,int w,int h,Color color) {
super("MyFrame"+(++id));
setVisible(true);
setLayout(null);
setBounds(x, y, w, h);
setBackground(color);
}
}运行结果:
Panel1:
public class TestPanel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame f = new Frame("java with panel");
Panel p = new Panel(null);
f.setLayout(null);
f.setBounds(300, 300, 500, 500);
f.setBackground(new Color(0, 0, 102));
p.setBounds(50, 50, 400, 400);
p.setBackground(new Color(204, 204, 255));
f.add(p);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}运行结果:
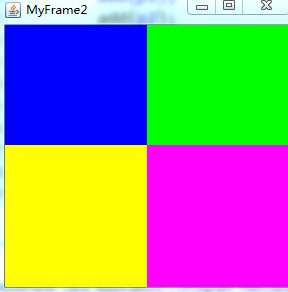
Panel2:
public class TestMultiPanel {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new MyFrame2("MyFrame2", 300, 300, 300, 300);
}
}
class MyFrame2 extends Frame{
private Panel p1,p2,p3,p4;
MyFrame2(String s,int x,int y,int w,int h){
super(s);
setLayout(null);
p1 = new Panel(null);
p2 = new Panel(null);
p3 = new Panel(null);
p4 = new Panel(null);
p1.setBounds(0, 0, w/2, h/2);
p2.setBounds(0, h/2, w/2, h/2);
p3.setBounds(w/2, 0, w/2, h/2);
p4.setBounds(w/2, h/2, w/2, h/2);
p1.setBackground(Color.blue);
p2.setBackground(Color.YELLOW);
p3.setBackground(Color.green);
p4.setBackground(Color.magenta);
add(p1);
add(p2);
add(p3);
add(p4);
setBounds(x, y, w, h);
setVisible(true);
}
}运行结果:
二、布局管理器
管理Component在Container的布局,不必直接设置Component的大小和位置
窗口的大小改变,组件会自动调整位置
Awt提供5种布局管理器类:FlowLayout、BorderLayout、GridLayout、CardLayout、GridBagLayout
(1)FlowLayout:一行一行的,像流水一样,默认对齐是居中
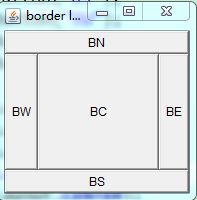
(2)BorderLayout:布局分为东西南北中,每个区域只能加一个组件,如加多个,之前的会被替换掉
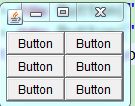
(3)GridLayout:可以分成一个个小格,可以指定行列数
示例:
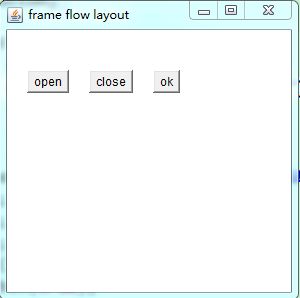
FlowLayout:
public class TestFlowLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame f = new Frame("frame flow layout");
Button b1 = new Button("open");
Button b2 = new Button("close");
Button b3 = new Button("ok");
f.setLayout(new FlowLayout(FlowLayout.LEFT,20,40));
f.add(b1);
f.add(b2);
f.add(b3);
f.setSize(300, 300);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}运行结果:
BorderLayout:
public class TestBorderLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame f = new Frame("border layout");
Button bn = new Button("BN");
Button bs = new Button("BS");
Button bw = new Button("BW");
Button be = new Button("BE");
Button bc = new Button("BC");
f.add(bn, BorderLayout.NORTH);
f.add(bs, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
f.add(bw, BorderLayout.WEST);
f.add(be, BorderLayout.EAST);
f.add(bc, BorderLayout.CENTER);
f.setSize(200, 200);
f.setVisible(true);
}
}运行结果:
GridLayout:
public class TestGridLayout {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame f = new Frame("GridLayout example");
Button b1 = new Button("Button");
Button b2 = new Button("Button");
Button b3 = new Button("Button");
Button b4 = new Button("Button");
Button b5 = new Button("Button");
Button b6 = new Button("Button");
f.setLayout(new GridLayout(3, 2));
f.add(b1);
f.add(b2);
f.add(b3);
f.add(b4);
f.add(b5);
f.add(b6);
f.pack();
f.setVisible(true);
}
}运行结果:
三、事件模型
事件监听:
事件源对象:如按钮,下拉框。。。。
实现监听接口的类:监听到后,会执行方法
过程:当某种事件发生时,向监听器传送某种事件对象,接到事件对象后进行某种处理(实现监听接口的类),
事件源对象需要注册(实现监听接口的类)
public class TestActionEvent2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Frame f = new Frame("test");
Button b1 = new Button("start");
Button b2 = new Button("stop");
Monitor2 m = new Monitor2();
b1.addActionListener(m);
b2.addActionListener(m);
b2.setActionCommand("game over");
f.add(b1, "North");
f.add(b2, "Center");
f.pack();
f.setVisible(true);
}
}
class Monitor2 implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
System.out.println("进来了"+e.getActionCommand());
}
}运行结果:点击start按钮控台输出start,点击stop按钮,控台输出game over
四、TextField类
用来创建文本框对象,敲回车触发事件
示例1:普通输入文本
public class TFActionEvent {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TFFrame();
}
}
class TFFrame extends Frame{
TFFrame(){
TextField tf = new TextField();
add(tf);
tf.addActionListener(new TFActionListener());
pack();
setVisible(true);
}
}
class TFActionListener implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
TextField tf =(TextField) e.getSource();
System.out.println(tf.getText());
tf.setText("");
}
}运行结果:回车后触发事件,文本框输入什么,控台显示什么
示例2:输入密码
public class TFPassword {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new TFFrame2();
}
}
class TFFrame2 extends Frame{
TFFrame2(){
TextField tf = new TextField();
add(tf);
tf.setEchoChar('*');//密码不显示
tf.addActionListener(new TFActionListener2());
pack();
setVisible(true);
}
}
class TFActionListener2 implements ActionListener{
@Override
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
TextField tf =(TextField) e.getSource();
System.out.println(tf.getText());
tf.setText("");
}
}运行结果:输入文本框显示为****