二叉树——根据先序(后序)和中序遍历建树
假设有棵树,长下面这个样子,它的前序遍历,中序遍历,后续遍历都很容易知道。
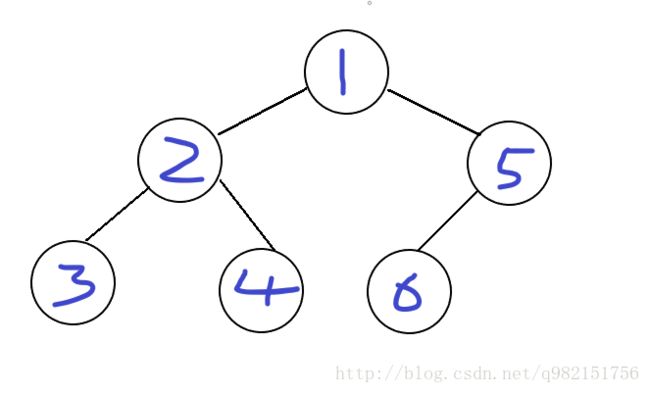
PreOrder: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
InOrder: 3, 2, 4, 1, 6, 5
PostOrder: 3, 4, 2, 6, 5, 1
现在,假设仅仅知道前序和中序遍历,如何求后序遍历呢?或者只知道后序和中序遍历,如何求前序遍历呢?(因为这两种情况的差别不大,所以只讲一种)
第一步,root最简单,前序遍历的第一节点“1”就是root。
第二步,继续观察前序遍历“1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6”,除了知道“1”是root,剩下的节点必然是root的左右子树之外,没法找到更多信息了。
第三步,那就观察中序遍历“ 3, 2, 4, 1, 6, 5”。其中root节点“1”左侧的“3, 2, 4”必然是root的左子树,“1”右侧的“6, 5”必然是root的右子树。
第四步,观察左子树“3, 2, 4”,左子树的中的根节点必然是大树的root的leftchild。在前序遍历中,大树的root的leftchild位于root之后,所以左子树的根节点为“2”。
第五步,同样的道理,root的右子树节点“6,5”中的根节点也可以通过前序遍历求得。在前序遍历中,一定是先把root和root的所有左子树节点遍历完之后才会遍历右子树,并且遍历的右子树的第一个节点就是右子树的根节点。
如何知道哪里是前序遍历中的左子树和右子树的分界线呢?通过中序遍历去数节点的个数。
在上一次中序遍历中,root左侧是“3,2,4”,所以有3个节点位于root左侧。那么在前序遍历中,必然是第1个是“1”,第2到第4个由“2,3,4”构成,第5个就是root的右子树的根节点了,是“5”。
第六步,观察发现,上面的过程是递归的。先找到当前树的根节点,然后划分为左子树,右子树,然后进入左子树重复上面的过程,然后进入右子树重复上面的过程。最后就可以还原一棵树了。
代码:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Node {
int value;
Node left = null;
Node right = null;
}
public class CreatTree {
static int pre[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
static int post[] = {3, 4, 2, 6, 5, 1};
static int in[] = {3, 2, 4, 1, 6, 5};
static int cnt1 = 0, cnt2 = post.length - 1;
public static Node creatTreeByPreAndIn(int start, int end) {
if(start > end) return null;
int root = pre[cnt1];
cnt1++;
int rootindex = findIndex(in, root);
Node t = new Node();
t.value = root;
if(start == end) {
t.left = t.right = null;
}
else {
t.left = creatTreeByPreAndIn(start, rootindex - 1);
t.right = creatTreeByPreAndIn(rootindex + 1, end);
}
return t;
}
public static Node creatTreeByPostAndIn(int start, int end) {
if(start > end) return null;
int root = post[cnt2];
cnt2--;
int rootindex = findIndex(in, root);
Node t = new Node();
t.value = root;
if(start == end) {
t.left = t.right = null;
}
else {
t.right = creatTreeByPostAndIn(rootindex + 1, end);
t.left = creatTreeByPostAndIn(start, rootindex - 1);
}
return t;
}
public static int findIndex(int[] a, int b) {
int i = 0;
for(i=0;iif(a[i] == b) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void Show(Node root) {
Queue q = new LinkedList<>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()) {
Node temp = q.poll();
System.out.printf("%d ",temp.value);
if(temp.left != null) {
q.offer(temp.left);
}
if(temp.right != null) {
q.offer(temp.right);
}
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int start = 0;
int end = in.length - 1;
Node head = creatTreeByPreAndIn(start, end);
Show(head);
Node head2 = creatTreeByPostAndIn(start, end);
Show(head2);
}
}