(一百零八)omnipeek 抓包尝试与简单分析
omnipeek抓包可参考:https://blog.csdn.net/flyingcys/article/details/82534737
dhcp分析参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_24421591/article/details/50936469
1.omnipeek抓包
我是设置了过滤只抓了路由器和手机的mac地址,如下截图:
上面截图是设置了ip的过滤条件后在wireshark看到的样子。
2.dhcp协议
摘录自https://www.rfc-editor.org/rfc/pdfrfc/rfc1531.txt.pdf
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) provides configuration
parameters to Internet hosts. DHCP consists of two components: a
protocol for delivering host-specific configuration parameters from a
DHCP server to a host and a mechanism for allocation of network
addresses to hosts.
DHCP is built on a client-server model, where designated DHCP server
hosts allocate network addresses and deliver configuration parameters
to dynamically configured hosts. Throughout the remainder of this
document, the term "server" refers to a host providing initialization
parameters through DHCP, and the term "client" refers to a host
requesting initialization parameters from a DHCP server.
Droms [Page 2]
RFC 1531 Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol October 1993
A host should not act as a DHCP server unless explicitly configured
to do so by a system administrator. The diversity of hardware and
protocol implementations in the Internet would preclude reliable
operation if random hosts were allowed to respond to DHCP requests.
For example, IP requires the setting of many parameters within the
protocol implementation software. Because IP can be used on many
dissimilar kinds of network hardware, values for those parameters
cannot be guessed or assumed to have correct defaults. Also,
distributed address allocation schemes depend on a polling/defense
mechanism for discovery of addresses that are already in use. IP
hosts may not always be able to defend their network addresses, so
that such a distributed address allocation scheme cannot be
guaranteed to avoid allocation of duplicate network addresses.
DHCP supports three mechanisms for IP address allocation. In
"automatic allocation", DHCP assigns a permanent IP address to a
host. In "dynamic allocation", DHCP assigns an IP address to a host
for a limited period of time (or until the host explicitly
relinquishes the address). In "manual allocation", a host’s IP
address is assigned by the network administrator, and DHCP is used
simply to convey the assigned address to the host. A particular
network will use one or more of these mechanisms, depending on the
policies of the network administrator.
Dynamic allocation is the only one of the three mechanisms that
allows automatic reuse of an address that is no longer needed by the
host to which it was assigned. Thus, dynamic allocation is
particularly useful for assigning an address to a host that will be
connected to the network only temporarily or for sharing a limited
pool of IP addresses among a group of hosts that do not need
permanent IP addresses. Dynamic allocation may also be a good choice
for assigning an IP address to a new host being permanently connected
to a network where IP addresses are sufficiently scarce that it is
important to reclaim them when old hosts are retired. Manual
allocation allows DHCP to be used to eliminate the error-prone
process of manually configuring hosts with IP addresses in
environments where (for whatever reasons) it is desirable to manage
IP address assignment outside of the DHCP mechanisms.
The format of DHCP messages is based on the format of BOOTP messages,
to capture the BOOTP relay agent behavior described as part of the
BOOTP specification [7, 23] and to allow interoperability of existing
BOOTP clients with DHCP servers. Using BOOTP relaying agents
eliminates the necessity of having a DHCP server on each physical
network segment.
3.dhcp包分析
参照了参考文章https://blog.csdn.net/qq_24421591/article/details/50936469发现dhcp虽然不可以用dhcp进行过滤,但是可以用bootp进行过滤,也许是因为DHCP的前身是BOOTP协议(Bootstrap Protocol)?
3.1 DHCP Discover
When a server receives a DHCPDISCOVER message from a client, the
server chooses a network address for the requesting client. If no
address is available, the server may choose to report the problem to
the system administrator and may choose to reply to the client with a
DHCPNAK message. If the server chooses to respond to the client, it
may include an error message in the ’message’ option. If an address
is available, the new address should be chosen as follows:
o The client’s previous address as recorded in the client’s binding,
if that address is in the server’s pool of available addresses and
not already allocated, else
o The address requested in the ’Requested IP Address’ option, if that
address is valid and not already allocated, else
o A new address allocated from the server’s pool of available
addresses.
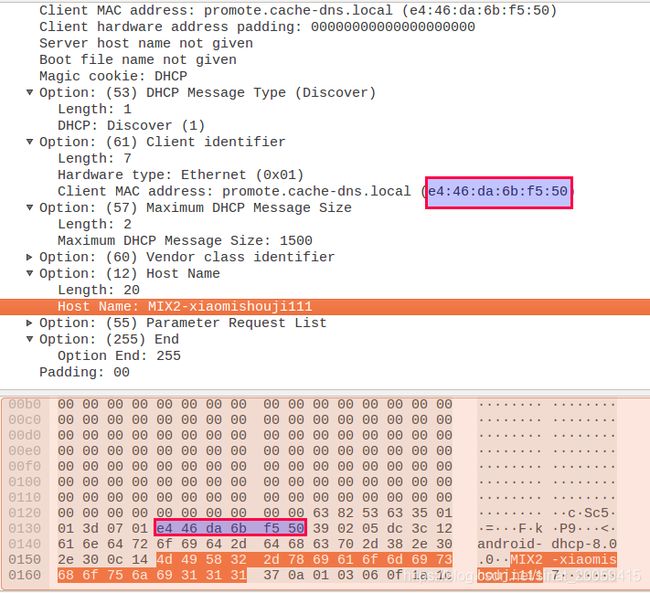
简单的过了一遍DHCP discover的包,中间白框的信息应该都是从最下发的红框中解析出来的,比如mac地址,比如手机名字
3.2 DHCP Offer
我连的路由器band是40MHz的,但这边显示的是20MHz,应该指的不是一回事。
dhcp服务器分配了一个如下的ip地址
3.3 DHCP Request
手机向192.168.0.1申请192.168.0.101这个ip
3.4 DHCP Ack
在数据包中包含以下信息,表示将这些资源信息分配给Client.
Your(client) IP address:分配给Client的可用IP。
后面有许多项option信息,前两项是DHCP服务器发送的消息类型(ACK)和服务器的身份标识,后面几项是:
Subnet Mask:Client端分配到的IP的子网掩码;
Router:路由器
Domain Name Server:DNS,域名服务器
Domain Name:域名
IP Address Lease Time:IP租用期。
4.总结
如果用Wireshark看dhcp包的话,由于Wireshark都将包解析好了,我们可以直接看到参数的含义,不用对照协议慢慢看了,还挺方便的。协议一大段英文看了真头疼。。。