Android Input流程
一.input 系统初始化
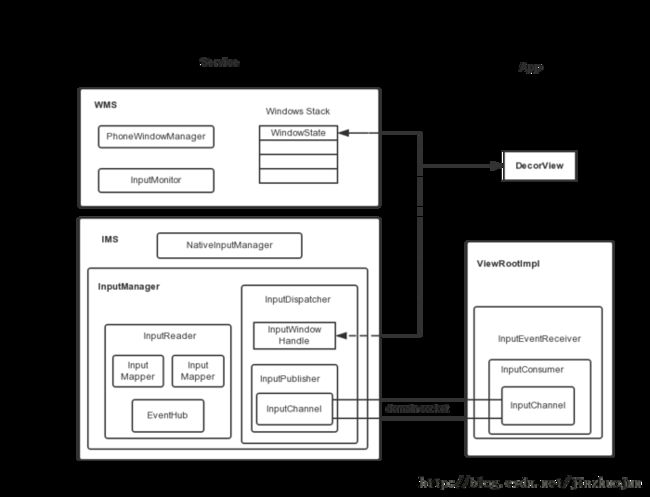
安卓系统启动时,会开启SystemServer进程,SystemServer执行main函数,调用startOtherService()初始化windowManagerService和InputManagerService等
InputManagerService的构造函数如下,mPtr是一个指向nativeInputManager对象的指针.
mPtr = nativeInit(this, mContext, mHandler.getLooper().getQueue());
LocalServices.addService(InputManagerInternal.class, new LocalService());
这里的nativeInit方法调用到com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp中NativeInputManager的构造函数
这里会构造一个EventHub对象并将它传入InputManager的构造函数中,
321 sp eventHub = new EventHub();
322 mInputManager = new InputManager(eventHub, this, this);
27InputManager::InputManager(
28 const sp& eventHub,
29 const sp& readerPolicy,
30 const sp& dispatcherPolicy) {
31 mDispatcher = new InputDispatcher(dispatcherPolicy);
32 mReader = new InputReader(eventHub, readerPolicy, mDispatcher);
33 initialize();
34}
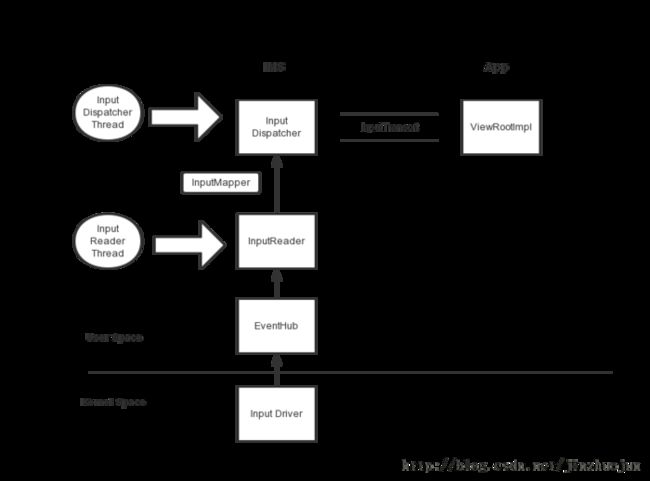
initialize函数中会设置两个线程来运行InputReader和InputDispatcher
49 mReaderThread = new InputReaderThread(mReader);
50 mDispatcherThread = new InputDispatcherThread(mDispatcher);
inputManagerService会设置一个回调,供windowManager调用,之后会调用inputManager的start()方法
wm = WindowManagerService.main(context, inputManager,
mFactoryTestMode != FactoryTest.FACTORY_TEST_LOW_LEVEL,
!mFirstBoot, mOnlyCore);
inputManager.setWindowManagerCallbacks(wm.getInputMonitor());
inputManager.start();
start方法会最终调用到InputManager.cpp 文件中的 status_t InputManager::start()函数
主要步骤如下,运行dispatcherThread的run()方法和mReaderThread的run()方法.
54 status_t result = mDispatcherThread->run("InputDispatcher", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
55 if (result) {
56 ALOGE("Could not start InputDispatcher thread due to error %d.", result);
57 return result;
58 }
59
60 result = mReaderThread->run("InputReader", PRIORITY_URGENT_DISPLAY);
61 if (result) {
62 ALOGE("Could not start InputReader thread due to error %d.", result);
63
64 mDispatcherThread->requestExit();
65 return result;
66 }
67
68 return OK;
二.读取input events
mReaderThread->run()方法会调用自身的 threadLoop()方法,进而调用mReader的loopOnce()方法,
loopOnce()方法主要分为三个主要的步骤.
步骤一:
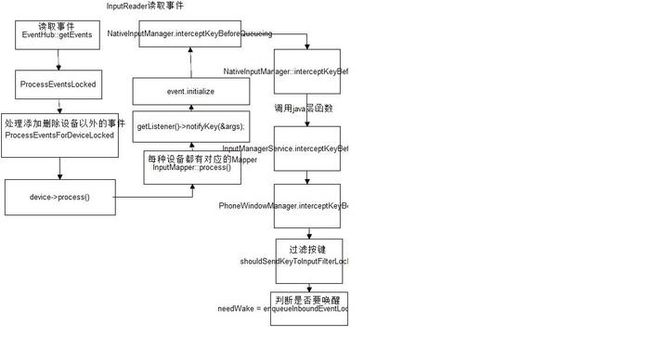
在该方法中会通过EventHub来获取input事件,计算缓冲区大小,判断是否有新的事件产生,然后用processEventsLocked()方法来处理events
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);
314 if (count) {
315 processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
316 }
步骤二:
在processEventsLocked()方法中会调用processEventsForDeviceLocked(deviceId, rawEvent, batchSize)函数,该函数会确定设备编号并调用
531 device->process(rawEvents, count);
安卓系统中每种输入设备都对应了一种Mapper,比如SwitchInputMapper, VibratorInputMapper,KeyBoardInputMapper
在process()函数中会调用对应mapper的processKey()函数,在该函数中具体处理不同的input事件
在processKey()函数中会调用 getListener()->notifyKey(), 也就是调用mQueuedListener.notifyKey();
而这个listener的notifyKey()方法只有一行代码,将notifyKeyArgs对象放入到mArgsQueue队列中.
mArgsQueue.push(**new** NotifyKeyArgs(*args));
步骤三:
最后一步会将mQueuedListener队列中的所有内容全部清空.
mQueuedListener->flush();
flush()函数中将所有的NotifyArgs对象取出,依次执行args->notify()
171void QueuedInputListener::flush() {
172 size_t count = mArgsQueue.size();
173 for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
174 NotifyArgs* args = mArgsQueue[i];
175 args->notify(mInnerListener);
176 delete args;
177 }
178 mArgsQueue.clear();
179}
而notify()函数会调用innnerListener的notifyKey()函数,innerListener实际上就是构造InputReader时传入的InputDispatcher,所以调用的就是InputDispatcher的notifyKey()函数
62void NotifyKeyArgs::notify(const sp& listener) const {
63 listener->notifyKey(this);
64}
在notifyKey()函数中会新建一个KeyEvent对象并进行初始化,然后调用mPolicy的interceptKeyBeforeQueueing__(mPolicy就是NativeInputManagers)
2548 KeyEvent event;
2549 event.initialize(args->deviceId, args->source, args->action,
2550 flags, keyCode, args->scanCode, metaState, 0,
2551 args->downTime, args->eventTime);
2552
2553 mPolicy->interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(&event, /*byref*/ policyFlags);
这里会在c++代码中调用java层的代码,会先把keyEvent转换为jobject对象,然后调用java层对应的interceptBeforeQueueing函数
894 jobject keyEventObj = android_view_KeyEvent_fromNative(env, keyEvent);
896 if (keyEventObj) {
897 wmActions = env->CallIntMethod(mServiceObj,
898 gServiceClassInfo.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing,
899 keyEventObj, policyFlags);
这里调用了native的interceptKeyBeforeQueueing函数,用到了在初始化时设定的一个windowManager持有的回调.
// Native callback.
private int interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(KeyEvent event, int policyFlags) {
return mWindowManagerCallbacks.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(event, policyFlags);
}
通过这个windowManager持有的回调,最终会调用到WindowPhoneManager的interceptKeyBeforeQueueing函数(mpolicy就是windowPhoneManager),这样以来对input的管理最终集中到了windowManager中.
/* Provides an opportunity for the window manager policy to intercept early key
* processing as soon as the key has been read from the device. */
@Override
public int interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(KeyEvent event, int policyFlags) {
return mService.mPolicy.interceptKeyBeforeQueueing(event, policyFlags);
}
input events从java层的windowManagerService的拦截函数返回后,会继续在notify()函数中运行,这里会继续判断是否打开了过滤器开关,如果打开了就对event进行过滤,并返回
2559 if (shouldSendKeyToInputFilterLocked(args)) {
2560 mLock.unlock();
2561
2562 policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_FILTERED;
2563 if (!mPolicy->filterInputEvent(&event, policyFlags)) {
2564 return; // event was consumed by the filter
2565 }
2566
2567 mLock.lock();
2568 }
将event信息存储在一个KeyEntry对象中,调用enqueueInboundEventLocked函数并判断是否需要唤醒
2571 KeyEntry* newEntry = new KeyEntry(args->eventTime,
2572 args->deviceId, args->source, policyFlags,
2573 args->action, flags, keyCode, args->scanCode,
2574 metaState, repeatCount, args->downTime);
2575
2576 needWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(newEntry);
之后如果需要唤醒,就会调用mLooper.wake()唤醒分发线程进行事件分发.
三.分发events到UI窗口
回到InputDispatcher中分析:
mDispatcherThread::threadLoop()方法中会调用dispatchOnce()函数,该函数中主要调用两个方法一个是
DispatchOnceInnerLocked()函数.
319 if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {
320 dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);
321 }
主要会调用到pokeUserActivityLocked()函数
394 // Poke user activity for this event.
395 if (mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {
396 pokeUserActivityLocked(mPendingEvent);
397 }
在 pokeUserActivityLocked()函数中会将key事件封装成系统需要处理的key事件.
1902 CommandEntry* commandEntry = postCommandLocked(
1903 & InputDispatcher::doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible);
1904 commandEntry->eventTime = eventEntry->eventTime;
1905 commandEntry->userActivityEventType = eventType;
在这里会调用 doPokeUserActivityLockedInterruptible函数,函数中会调用NativeInputManager的pokeUserActivity函数
mPolicy->pokeUserActivity(commandEntry->eventTime, commandEntry->userActivityEventType);
通过JNI调用到java层PowerManagerService中的 userActivityFromNative函数,
106 env->CallVoidMethod(gPowerManagerServiceObj,
107 gPowerManagerServiceClassInfo.userActivityFromNative,
108 nanoseconds_to_milliseconds(eventTime), eventType, 0);
private void userActivityInternal(long eventTime, int event, int flags, int uid) {
synchronized (mLock) {
if (userActivityNoUpdateLocked(eventTime, event, flags, uid)) {
updatePowerStateLocked();
}
}
}
回到dispatchOnceInnerLocked函数之后会对event的类型进行判断,按照event的类型进行不同的操作.
首先会调用 findFocusedWindowTargetLocked函数得到要对应的UI窗口
875 int32_t injectionResult = findFocusedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime,
876 entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime);
如果是按键事件,会调用dispatchKeyLocked()函数,又会调用dispatchEventLocked()函数:
确定对应输出的UI窗口,并得到它们之间的connection.
1029 const InputTarget& inputTarget = inputTargets.itemAt(i);
1030
1031 ssize_t connectionIndex = getConnectionIndexLocked(inputTarget.inputChannel);
之后会调用prepareDispatchCycleLocked函数
之后会进入到enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked函数中.
1945 enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(currentTime, connection,
1946 splitMotionEntry, inputTarget);
1947 splitMotionEntry->release();
connection中维护一个outboundQueue队列,这个队列中存储input与该window之间的事件.
如果队列为空,就开始循环分发.
1974 // If the outbound queue was previously empty, start the dispatch cycle going.
1975 if (wasEmpty && !connection->outboundQueue.isEmpty()) {
1976 startDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection);
1977 }
在startDisplayCycleLocked函数中:
会不断地取出事件进行分发,具体的分发过程利用到了linux的epoll机制,后面有具体分析.
status = connection->inputPublisher.publishMotionEvent
操作完成后会释放掉pendingEvent
478 if (done) {
479 if (dropReason != DROP_REASON_NOT_DROPPED) {
480 dropInboundEventLocked(mPendingEvent, dropReason);
481 }
482 mLastDropReason = dropReason;
483
484 releasePendingEventLocked();
485 *nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; // force next poll to wake up immediately
486 }
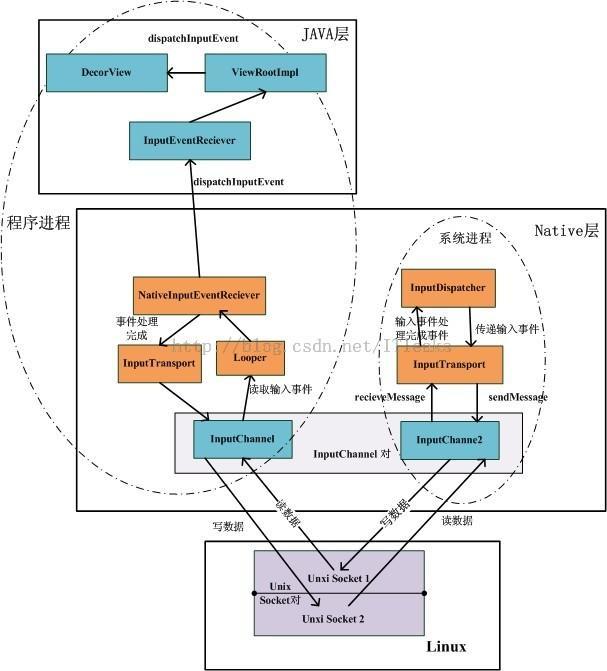
Looper利用epoll机制接收events,并调用callback回调的handleEvent方法.也就是NativeInputEventReceiver的handleEvent() 方法
361 // Invoke the callback. Note that the file descriptor may be closed by
362 // the callback (and potentially even reused) before the function returns so
363 // we need to be a little careful when removing the file descriptor afterwards.
364 int callbackResult = response.request.callback->handleEvent(fd, events, data);
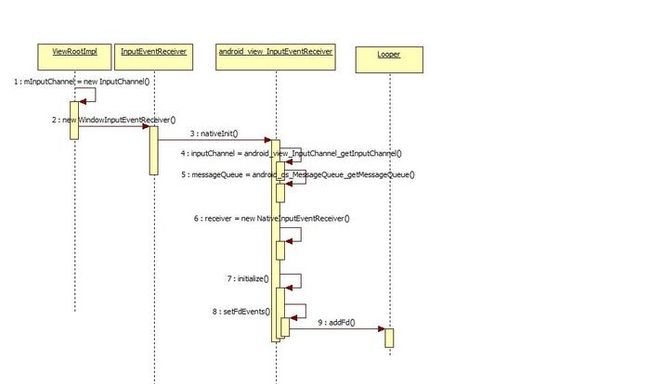
而为什么会调用到这个InputEventReciever呢,InputEventReceiver是在ViewRootImpl中的setView()方法中被声明的,它的构造函数中有两个变量: mInputChannel和 Looper.myLooper()
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(mInputChannel, Looper.myLooper());
而在InputEventReceiver的构造函数中,会先取得主线程的looper对象和client端的java层inputChannel对象,然后调用NativeInit()方法进行初始化.
mInputChannel = inputChannel;
mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue();
mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference(this),
inputChannel, mMessageQueue);
在JNI层,首先获得了inputChannel和messageQueue的指针,并构造一个NativeInputEventReceiver对象.
352 sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,
353 inputChannelObj);
359 sp<MessageQueue> messageQueue = android_os_MessageQueue_getMessageQueue(env, messageQueueObj);
365 sp<NativeInputEventReceiver> receiver = new NativeInputEventReceiver(env,
366 receiverWeak, inputChannel, messageQueue);
之后会调用receiver的initialize()方法.
122status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::initialize() {
123 setFdEvents(ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT);
124 return OK;
125}
setFdEvents函数中,会将client端的inputChannel的socket文件描述符加入到Looper的监控中.
162void NativeInputEventReceiver::setFdEvents(int events) {
163 if (mFdEvents != events) {
164 mFdEvents = events;
165 int fd = mInputConsumer.getChannel()->getFd();
166 if (events) {
167 mMessageQueue->getLooper()->addFd(fd, 0, events, this, NULL);
168 } else {
169 mMessageQueue->getLooper()->removeFd(fd);
170 }
171 }
172}
173
当有消息到来的时候,会调用inputChannel对应的NativeInputEventReceiver回调函数.
它的handleEvent()函数中会调用consumeEvents函数,
status_t status = consumeEvents(env, false /*consumeBatches*/, -1, NULL);
在 consumeEvents()函数中会调用到InputChannel的receiveMessage方法.
493 // Receive a fresh message.
494 status_t result = mChannel->receiveMessage(&mMsg);
然后通过JNI调用到java层InputEventReceiver的dispatchInputEvent()回调函数.
330 env->CallVoidMethod(receiverObj.get(),331 gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.dispatchInputEvent, seq, inputEventObj);
private void dispatchInputEvent(int seq, InputEvent event) {
mSeqMap.put(event.getSequenceNumber(), seq);
onInputEvent(event);
}
然后调用到ViewRoot的OnInputEvent()方法,继而调用了enqueuInputEvent()方法,
if (processImmediately) {
doProcessInputEvents();
} else {
scheduleProcessInputEvents();
}
之后进入到delieverInputEvent()方法中,对stage进行判断,如果为空则结束分发,否则
if (stage != null) {
stage.deliver(q);
} else {
finishInputEvent(q);
}
deliver()函数中会执行stage的onPorcess()方法.
apply(q, onProcess(q));
这里的stage时这样取值的
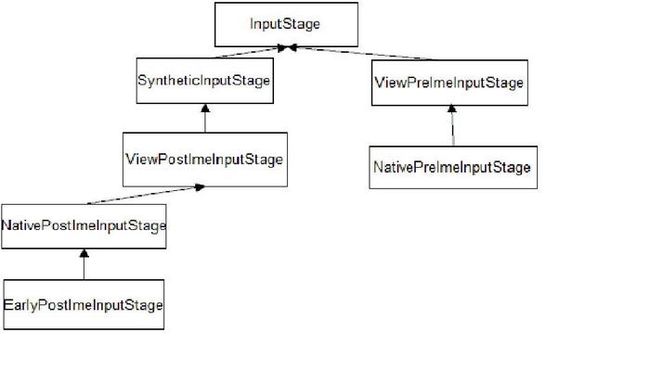
if (q.shouldSendToSynthesizer()) {
stage = mSyntheticInputStage;
} else {
stage = q.shouldSkipIme() ? mFirstPostImeInputStage : mFirstInputStage;
}
这里InputStage的设计用到了流水线或者叫
责任链的模式
InputStage有很多子类,所有InputStage类的构造方法都会传入一个InputStage类的变量,这样最终会形成流水线线式的处理结构,每经过一个InputStage对象的处理都会进行判断,看是否还需要将 events继续向前传输,如果需要就调用forward()函数让该变量中存储的下一个InputStage对象处理该events,如果不需要就调用finish()函数结束events的传输.
只需知道最终会调用到ViewRootImpl的enqueueInputEvent()方法.
该方法中会立即或者延迟处理events.
if (processImmediately) {
doProcessInputEvents();
} else {
scheduleProcessInputEvents();
}
在 doProcessInputEvent()方法中会判断是否要经过IME输入法框架处理.
stage = q.shouldSkipIme() ? mFirstPostImeInputStage : mFirstInputStage;
最后经过判断后会层层处理,最终进入到view.dispatchKeyEvent()方法中.
四.
最后返回到dispatchOnceLocked()函数中,执行runCommandsLockedInterruptible()函数.
323 // Run all pending commands if there are any.
324 // If any commands were run then force the next poll to wake up immediately.
325 if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {
326 nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;
327 }
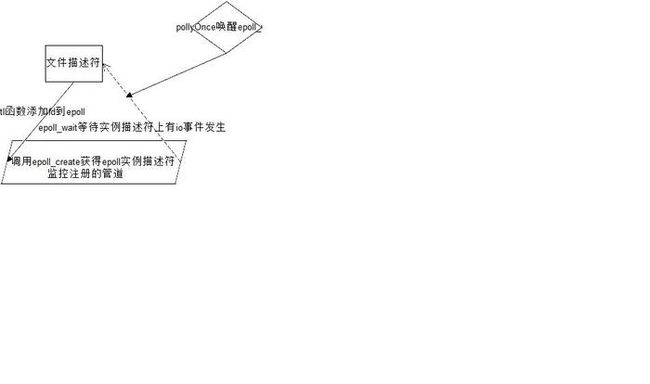
五.Epoll机制
Looper->wake()函数利用了linux中的epoll机制。
首先,注册一个epoll的实例描述符,将所有的管道对象的fd都注册到该epoll实例上,利用epoll_wait函数来睡眠等待管道上IO事件的发生;
调用PollOnce()函数来启动epoll_wait的睡眠等待,而wake()函数则是向epoll中的管道写入一个字符来唤醒epoll_wait.
六.InputChannel分析
首先是server端的inputChannel注册
- 首先打开一对InputChannelPair,调用到JNI中的
android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair方法,最终会调用到linux中的socketPair()函数打开一对socket管道,而inputChannel就是由socket管道来构建的.
184 outServerChannel = **new** InputChannel(serverChannelName, sockets[0]);
- inputChannel在WMS中注册,保存在一个WindowState的类中,WMS使用这对inputChannel的第一个
- 然后会调用registerInputChannel方法进行注册.
mInputManager.registerInputChannel(win.mInputChannel, win.mInputWindowHandle);
- 最终会调用Native层的方法
nativeRegisterInputChannel(mPtr, inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, false);
将inputChannel和connection保存在映射表中,mLooper加入对该fd的监听,当有数据到来的时候会唤醒等待的线程.
3511 sp connection = new Connection(inputChannel, inputWindowHandle, monitor);
3512
3513 int fd = inputChannel->getFd();
3514 mConnectionsByFd.add(fd, connection);
3516 if (monitor) {
3517 mMonitoringChannels.push(inputChannel);
3518 }
3519
3520 mLooper->addFd(fd, 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT, handleReceiveCallback, this);
- 而当InputDispatcher分发消息时,会调用InputChannel::sendMessage()方法,该方法调用了linux socket中的send函数,向socket管道中写入数据.
client端inputChannel的注册
WMS中创建的inputChannel跨进程传输到cilent端,转换为client端的inputChannel使用.
讲解java JNI的注册:http://my.oschina.net/u/157503/blog