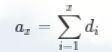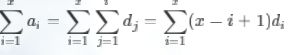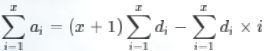poj 3468 A Simple Problem with Integers(线段树+树状数组区间更新区间查询)
A Simple Problem with Integers
Time Limit: 5000MS Memory Limit: 131072K
Total Submissions: 122283 Accepted: 37929
Case Time Limit: 2000MS
Description
You have N integers, A1, A2, … , AN. You need to deal with two kinds of operations. One type of operation is to add some given number to each number in a given interval. The other is to ask for the sum of numbers in a given interval.
Input
The first line contains two numbers N and Q. 1 ≤ N,Q ≤ 100000.
The second line contains N numbers, the initial values of A1, A2, … , AN. -1000000000 ≤ Ai ≤ 1000000000.
Each of the next Q lines represents an operation.
“C a b c” means adding c to each of Aa, Aa+1, … , Ab. -10000 ≤ c ≤ 10000.
“Q a b” means querying the sum of Aa, Aa+1, … , Ab.
Output
You need to answer all Q commands in order. One answer in a line.
Sample Input
10 5
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Q 4 4
Q 1 10
Q 2 4
C 3 6 3
Q 2 4
Sample Output
4
55
9
15
Hint
The sums may exceed the range of 32-bit integers.
树状数组
分析:
首先不考虑原始的情况,我们只考虑区间更新过后带来的影响的话,首先对于询问一个区间当中的元素和的话,肯定就是这个区间的原始的元素和,加上区间更新后所带来的影响,所以我们用a[]数组来保存前i个元素的和。
然后考虑区间更新所带来的影响,采用差分的思想,
设原数组第i位的值为ai,di=ai−a[i−1],则有(这里认为a0=0,此时的a表示的是数组中的原始值,与代码中的a不一样):
于是我们把原数组差分后维护两个树状数组,一个维护di,一个维护di×i。
这样区间求和时可以在两个树状数组中查询得到前缀和,区间修改时就是差分数组的修改,每次修改两个点即可。
其中c[i]维护的是d[i],c1[i]维护的是d[i]×i。
但是这里的c[]和c1[]都是差分数组,保存的也就只是更新所带来的值的变化,但因为这里要求的是在原来的基础上更新后的区间和,所以最终还要加上最原始的区间和。
#includescanf("%c",&ch);
if(ch=='Q')
{
scanf("%lld%lld",&s,&r);
printf("%lld\n",sum(r)-sum(s-1));
}
else
{
scanf("%lld%lld%lld",&s,&r,&va);
update(s,va);
update(r+1,-va);
}
}
}
return 0;
}
线段树:
#include1,rr,t<<1|1);
pu(t);
}
int main()
{
int n,q,a,b;
long long int c;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&q);
build(1,n,1);
char s[3];
while(q--)
{
scanf("%s",s);
if(s[0]=='Q')
{
cin>>a>>b;
cout<1,n,1)<else if(s[0]=='C')
{
cin>>a>>b>>c;
up(a,b,c,1,n,1);
}
}
return 0;
}